APHG Midterm Review (Units #1, #2. #3, and #4)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What must a territory have to be considered a state?
It must have a territory, with a permanent population, subject to the control of a government, and the capacity to conduct international relations (sovereignty).
State
An area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government with control over its internal and foreign affairs. (country)
Example: Mexico
nation-state
A state whose territory corresponds to that occupied by a particular ethnicity that has been transformed into a nationality
Example: Japan (they are typically isolated countries)
nation
a group of people with a common culture living in a territory and having a strong sense of unity
Example: The American people
multistate nation
nation that stretches across borders and across states
Example: The Kurds that spread around the region of the Middle East
multinational state
State that contains two or more ethnic groups with traditions of self-determination that agree to coexist peacefully by recognizing each other as distinct nationalities.
Example: The Untied States of America
stateless nation
A nationality that is not represented by a state.
Example: The Kurdish people
autonomous region
a political unit with limited self-government
Example: Greenland
semi-autonomous region
an area that can govern itself in certain areas, but does not have complete power to govern
Example: Scotland
Sovereignty
Ability of a state to govern its territory free from control of its internal affairs by other states.
Self Determination
Concept that ethnicities have the right to govern themselves
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.
Colonialism
Attempt by one country to establish settlements and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles in another territory.
How do colonialism/imperialism shape political borders today?
They shape boundaries because they have formed territories and countries over pre-existing nations. The Berlin Conference is an example of this.
The Berlin Conference
A meeting from 1884-1885 at which representatives of European nations agreed on rules colonization of Africa. It effects Africa today because they imposed boundaries on conflicting ethnic groups with not take social differences into account.
Neocolonialism
Economic dominance of a weaker country by a more powerful one, while maintaining the legal independence of the weaker state. In the late nineteenth century, this new form of economic imperialism characterized the relations between the Latin American republics. It is different that traditional colonialism because leaders are not actually setting up colonies in affected area but instead highly influencing them.
Chokepoint
A narrow, strategically significant area where trade could be easily blocked or controlled
Shatterbelts
regions that are politically fragmented and are often areas of competition between two ideological or two religious realms
Territoriality
Defense of a space against encroachment by other individuals.
How do states express their power/control over the land?
States express their power and control over land can be expressed through physical means like stone, fences, flags, symbols, and national identification.
Relic Boundaries
former state boundaries that still have political or cultural meaning
Example: The Berlin Wall
Antecedent Boundaries
A boundary line established before an area is populated
Example: many parts of Africa
Superimposed Boundaries
Boundary line drawn in an area ignoring the existing cultural pattern.
Example: The Berlin Conference
Geometric Boundaries
Political boundaries that are defined and delimited by straight lines.
Example: Canada and USA border
Subsequent Boundaries
Boundary line established after an area has been settled that considers the social and cultural characteristics of the area
Example: Borders of former British colonies in Africa
consequent boundaries
boundary that coincides with a particular cultural divide (such as religion, language, or ethnicity); a.k.a. cultural boundaries
Example: Pakistan and India Boundaries
Defined boundaries
established by a legal document such as a treaty that divides one entity from another (invisible line)
delimited boundaries
Process of drawing political boundaries. Often controversial and changing.
demarcated boundaries
A border that is physically marked off with a wall, fence, or other structure
Administrated boundaries
a limit or border of a geographic area under the jurisdiction of some governmental or managerial entity
How can borders influence national/regional identity and encourage/discourage international interactions?
Borders can influence national identities and encourage or discourage international interactions by making their borders harder to cross and access the country.
UNCLOS
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea: a code of maritime law approved by the UN in 1982 that authorizes, among other provisions, territorial waters extending 12 nautical miles from shore and 200 nautical mile wide exclusive economic zones.
Territorial Zone
12 mile zone belonging to a nation that no one may enter without permission
Contiguous Zone
Between 12 and 24 nautical miles from shore, a state may enforce laws concerning pollution, taxation, customs, and immigration
Exclusive Economic Zone
area in which resources found up to 200 nautical miles offshore belong exclusively to the geographically bordering country
Median-line principle
lines made to distribute water ways when states are within 200 miles of each other
Gerrymandering
Process of redrawing legislative boundaries for the purpose of benefiting the party in power.
Gerrymandering consequences
- It protects incumbents and discourages challengers.
- It strengthens the majority party while weakening the opposition party.
- It increases or decreasing minority representation.
Redistricing
The drawing of new electoral district boundary lines in response to population changes.
Voting Districts
House members represent a particular district of voters, southern states had to be forced to choose a district. (ex of spatial organization)
How are states organized on a sub-national level?
Provinces, states, territories, etc.
Unitary State
An internal organization of a state that places most power in the hands of central government officials
Federal State
An internal organization of a state that allocates most powers to units of local government.
Unitary state advantages
-Easier to communicate and control in a unitary state
-More Unity
Unitary state disadvantages
-Tyrannical governments
-Detachment for local needs
Federal state advantages
Federalism promotes political participation.
Federalism encourages economic equality across the country.
Federalism provides for multiple levels of government action.
Federalism accommodates a diversity of opinion.
Federal state disadvantages
1) Tough to achieve nationwide standards in education, health care, etc.
2) InconsistentL citizens get systematically different treatments
3) Unitary governments in better position to redistribute wealth/resources from richer to poorer regions
Unitary State Characteristics
n a unitary system, most political power and responsibility belongs to the central government while the smaller, local government units have very little power and are reliant on the central government.
Federal State Characteristics
A centralized administration and powerful centripetal forces are considered typical features of federal states. Because of the centralization of authority in this system of governance, high-level governmental objectives can be effectively pursued. Internal forces from a state keep it together and preserve the nation.
Devolution
The process whereby regions within a state demand and gain political strength and growing autonomy at the expense of the central government.
Ethnic Seperatism
When a ethnic group desires to separate from the larger group. Ex. The Basques in Spain, Quebec, and Belgium
Ethnic Cleansing
the mass expulsion or killing of members of an unwanted ethnic or religious group in a society.
Devolution: Physical Geography
▪ Regions that are separated from the central state due to physical features such as mountain ranges, deserts, or bodies of water.
▪ Fragmented states like Indonesia or the Philippines
Devolution: Ethnic Separatism
▪ People of a particular ethnicity in a multinational state identify more strongly with their ethnic group than as citizens of the state.
▪ Many times a result of mistreatment or disparity between dominant ethnic group and minority ethnic group within a state.
Devolution: Ethnic Cleansing
▪ State governments attack an ethnic group in an attempt to try to eliminate them through expulsion, imprisonment, or mass murder.
▪ Similar to genocide -> The Holocaust
Devolution: Terrorism
Used by separatists groups to achieve their goals
Irredentism
a policy of cultural extension and potential political expansion by a country aimed at a group of its nationals living in a neighboring country
Devolution- Economic and social problems
Economic devolutionary forces can occur when regions seek control of natural resources. Social issues due to different languages, cultures, or religions can lead to devolution
Supranational Organizations
A venture involving three or more nation-states involving formal political, economic, and/or cultural cooperation to promote shared objectives.
Economic Supranational Organizations
-European Union (EU)
-ASEAN
-OPEC
Political Supranational Organizations
-African Union
-Artic Council
-United Nations (UN)
Military Supranational Organizations
-NATO
-Warsaw Pact (disbanded)
How can globalization spread to ideas that can lead to devolution?
It can influence people to act upon the multiple factors that cause devolution in their state and attempt to break away from it.
Example: Arab Spring 2011
Stimulus Diffusion
an original cultural trait causes the innovation and development of a new idea

hierarchical diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places

reverse hierarchical diffusion
diffusion up a hierarchy, such as from a small town to large cities

Contagious Diffusion
The rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population.
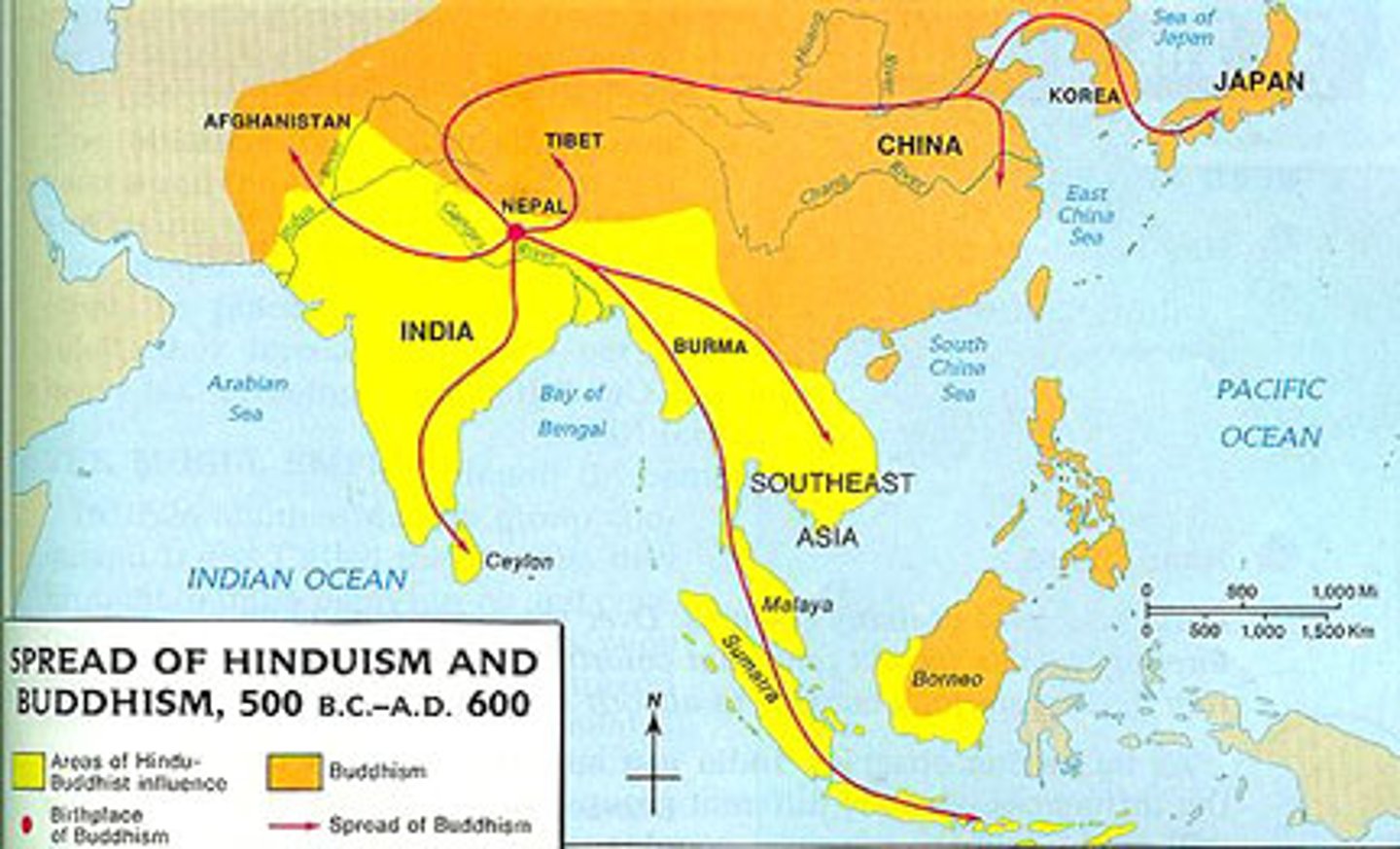
Expansion Diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend among people from one area to another in a snowballing process.
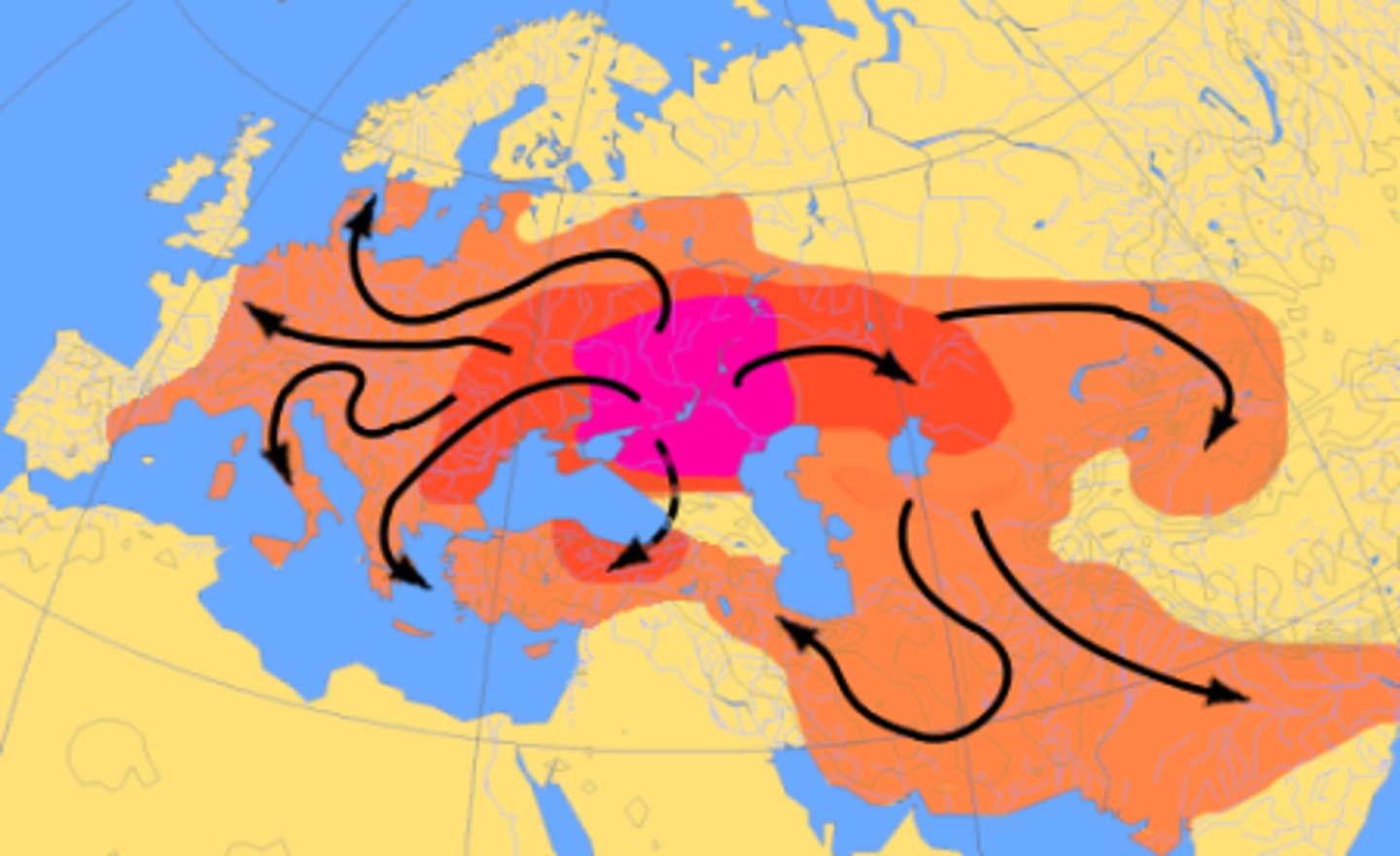
relocation diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend through bodily movement of people from one place to another.

Globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.

Urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements.

Pros of Globalization
-better access to goods and services
-potential for increased trade and competition
-increased foreign capital and technology
-cultural integration
Cons of Globalization
- strain on natural resources
- the rich get richer; the poor get poorer
- unethical issues arise
- outsourcing and the loss of jobs

cultural convergence
contact and interaction of one culture and another
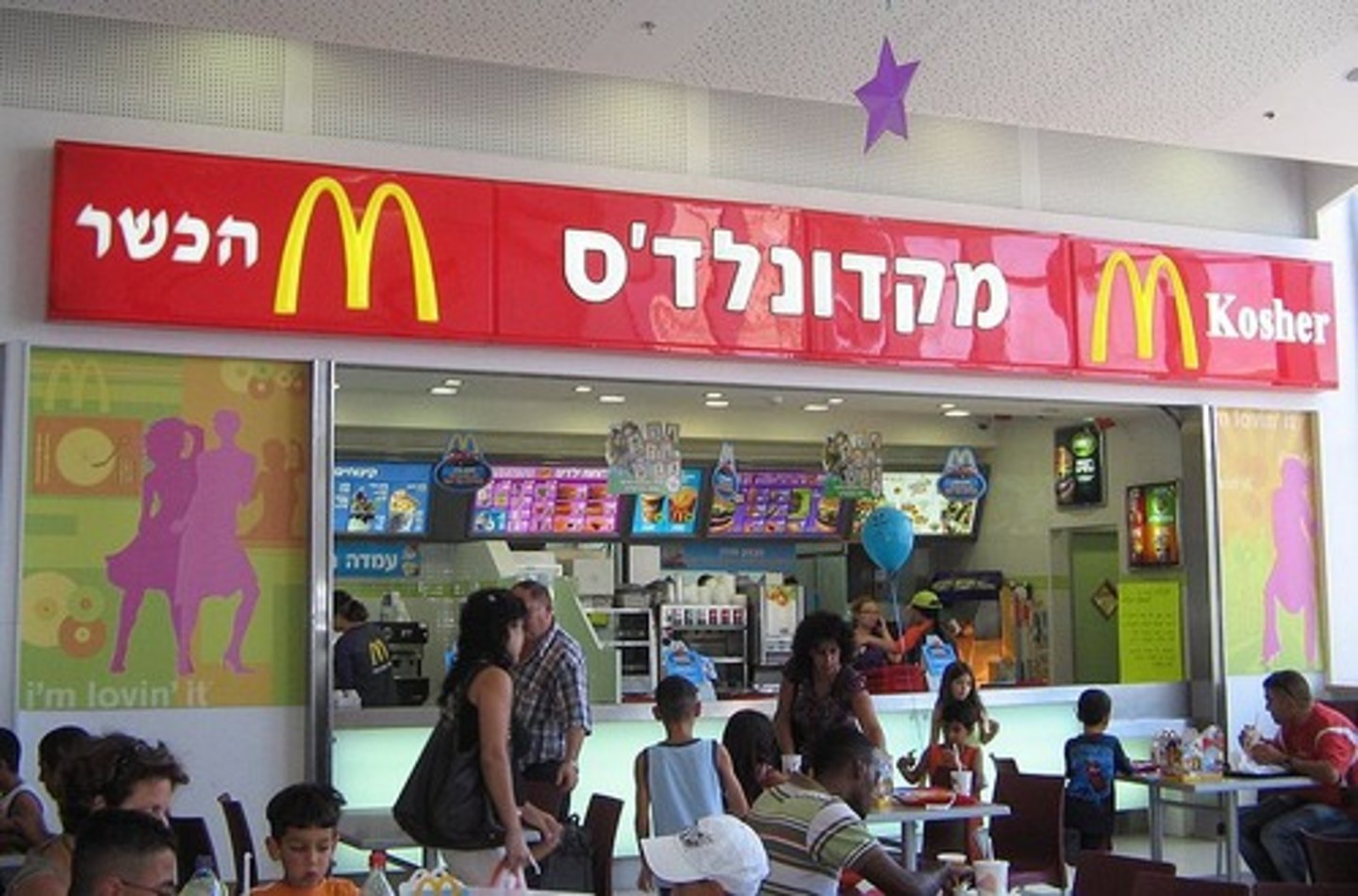

cultural convergence examples
Cuisine
Religious Syncretism
Fast food chains (Mcdonald's)
cultural divergence
the restriction of a culture from outside influences
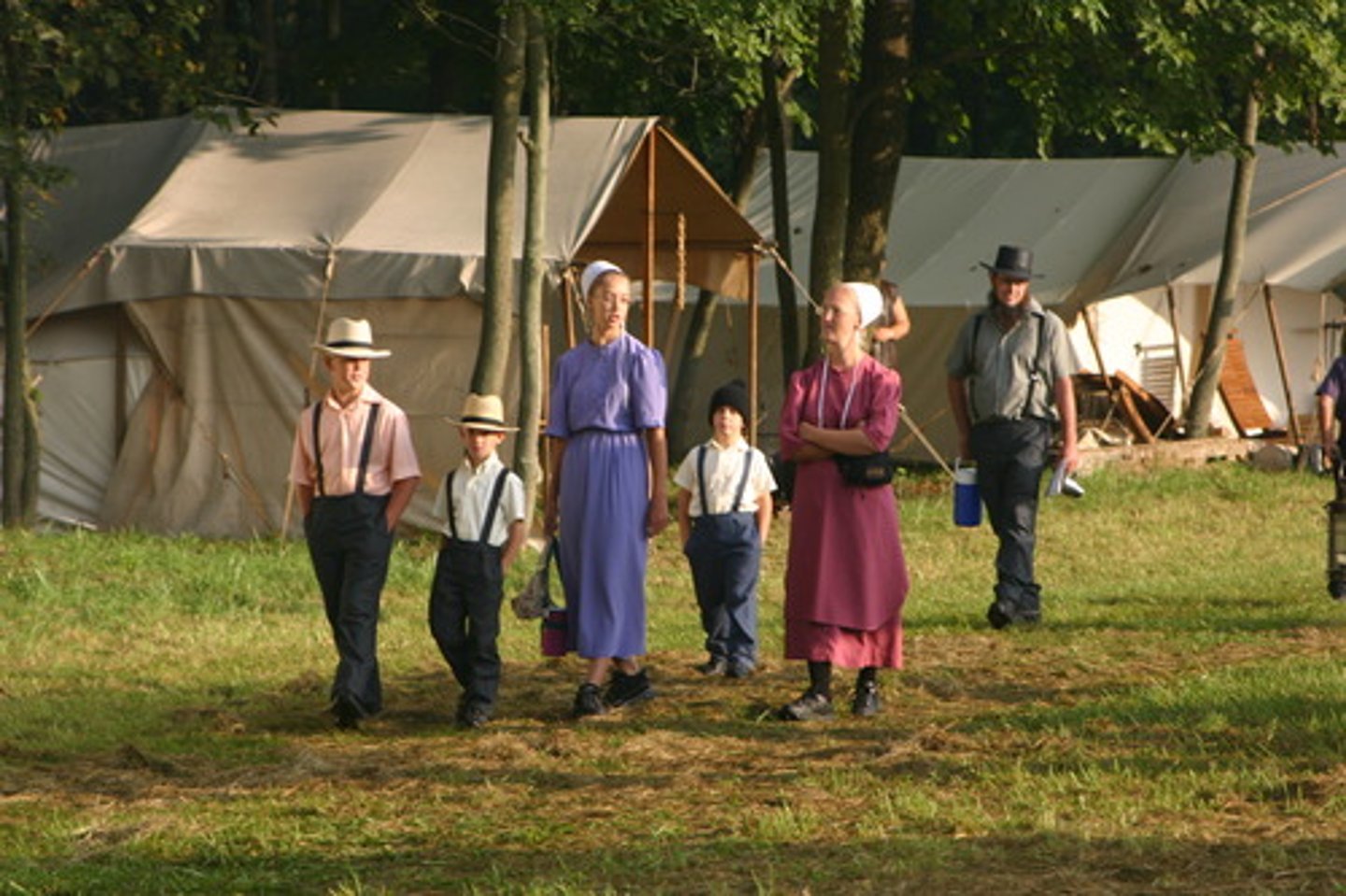

cultural divergence examples
Religion (The Amish people)
Indigenous Amazonian Tribes
North Sentinel Island
Colonialism
Attempt by one country to establish settlements and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles in another territory.
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.

examples of colonialism
Spain = South America, British = South Asia, Berlin Conference, United States
Examples of Imperialism
England in India
Soviet Russia
Roman Empire
Creolization
The process in which two or more languages converge and form a new language; occurs when foreign influences integrate with local meanings

lingua franca
A language mutually understood and commonly used in trade by people who have different native languages
sense of place
The feeling that an area has a distinct and meaningful character

placemaking
a community-driven process in which people collaborate to create a place where they can live, work, play, and learn

dialect
a particular form of a language that is peculiar to a specific region or social group.
adherent
A follower of a person or idea

sect
a subgroup of a major religious group
centripetal force
An attitude that tends to unify people and enhance support for a state

centripetal force examples
language/religion/ethnicity
effective government/institutions/infrastructure (public education, military, justice systems, transportation/communication)
healthy econmony
national holidays (July 4th, Bastille Day), flags, symbols
centrifugal force
a force that divides people and countries
centrifugal force examples
- ineffective government/institutions/infrastructure (public education, military, justice system, transportation/communication)
- language/religion/ethnicity
- separatist movements
- struggling economy
- peripheral location
- religious extremism

popular culture
cultural traits such as dress, diet, and music that identify and are part of today's changeable, urban-based, media-influenced, western societies

Ethnocentrism
Belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group.

cultural relativism
the practice of judging a culture by its own standards

what is culture?
the way of life for a group of people

cultural norms
behavior patterns that are typical of specific groups

cultural traits
a particular group's individual skills, customs, and ways of doing things

cultural landscape
the visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape

sequent occupance
the notion that successive societies leave their cultural imprints on a place, each contributing to the cumulative cultural landscape
