Environmental Engineering CIVE225
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Laws of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it simply changes form.
Systems move spontaneously from being highly organized to more random (entropy increases)
Entropy 0 at absolute temp 0 K
Acid
a substance that donates protons (H+) in a chemical reaction
Base
a compound that can accept H+ protons, produce OH-
Strong acids and bases
Acids
HCl hydrochloric
H2SO4 sulfuric
HNO3 nitric
Bases
KOH
NaOH
Ba(OH)2
Why are acid-base reactions so important in environmental engineering?
Aquatic forms of life are sensitive to small pH changes (∴waste must be neutralized)
pH can affect mobilization of pollutants in the environment
pH can be manipulated to drive contaminants out of solution (precipitate them) before effluent is released
Importance of carbonate system
most important acid-base system in environment
controls pH in natural waters
controls pH in drinking water
provides buffering system for water treatment (alkalinity)
components of carbonate system
dissolved CO2
carbonic acid (H2CO3 aq)
Bicarbonate ion (HCO3- aq)
Carbonate ion (CO3 2- aq)
chemical equations of the carbonate system
see ipad
alkalinity
measure of a waters’ capacity to neutralize acids (mol/L)
buffering capacity
ability of water to resist changes in pH when acids or alkaline material are added.
(acids: H+, H2CO3*, HCO3-)
(bases: OH, CO32-, HCO3-)
open vs closed carbonate systems
based on speed of gas/water exchange relative to speed of reactions affecting acid-base equilibrium
Open: gas/water exchanges faster than other reactions (henry’s law true)
Closed: gas/water exchanges slower than other reactions, no new C from air
sorption
any process by which one substance becomes attached, fixed or captured by another
absorption vs adsorption
absorption: captured substance buried randomly within the sorbate (density differences, capillary action) like a sponge
adsorption: captured substance adheres to the surface on specific adsorption sites (e.g. hydrophobicity)
Adsorption equilibrium: isotherms
experiments conducted at constant temperatures showing relationship between qe (concentration of adsorbate on adsorbent) and Ce (concentration of adsorbate in solution)
Two common isotherms:
langmuir - derived from theory
freundlich - derived empirically
what does the octanol-water partition coefficient Kow indicate?
correlate biological effects of organic substances
small for highly polar compounds, high for long non-polar
measure of how lipophilic (fat loving) vs hydrophilic (water loving) a compound is
helps assessing potential toxicity
more likely to stick to fat - bioaccumulates in fatty tissue and cause chronic toxicity
differences between CMFR and PFR
CMFR: completely mixed flow reactor, can be steady state or transient, conservative or non-conservative compound
PFR: plug flow reactor, only interested in steady state, rivers where upstream and downstream don’t mix
what do alpha 0, 1, and 2 represent in the carbonate cycle?
see ipad notes
three pillars of sustainability
Economy: create and maintain a prosperous society
Environment: maintain a sufficient stock of natural resources for current and future generation
Society: ensure high quality of life for population with equity between classes
through what process does active carbon remove contaminants? what contaminants does it remove?
adsorption
VOCs
Pesticides (atrazine)
Petroleum products
General: hydrophobic compounds adsorb better (stick to hydrophobic carbon surface better, prefer to be there than in water)
Non-polar compounds
1 ppm
= 1 mg / L in water
Evolution phases of micro-organisms in aerated batch culture
Lag phase
Acclimation period
Log phase
exponential increase in cell growth
Stationary phase
rate of cell division and death equal
Death phase
substrate no longer available to support bacteria growth
how to simplify charge balance?
if comparing with H+ concentration, consider pH and concentration of given chemical, is it significantly lower? can cross out
why is temperature increase bad for marine life
solubility of O2 decreases as temperature increases (faster molecules evaporate more, less O2 stays in water)
difference between collecting sample from effluent tube and inside a reactor
tubing length
small delay caused by volume moving through tube = volume / flow rate
sedimentation
Use gravity settling to remove particles from water
Need long enough retention time to let particles settle out before they leave the tank
Sedimentation tank = clarifier or settling tank
what do sedimentation tanks do to water to settle out particles?
slow water down
reduce turbulence (chaotic flow of water)
laminar flow
zones in a sedimentation basin and purposes
influent zone
decreases the velocity of incoming water, distributes flow evenly across settling zone
settling zone:
slow, calm area for suspended particles to settle out
effluent zone
transition from settling zone to effluent flow area
sludge zone
settled solids separated from other particles in the zone
overflow rate (OR) or critical velocity (Vc)
measure of how quickly water flows over the
surface of a sedimentation tank
OR = Q/A
want particle (Vs) to move downward faster than water moves upward (Vs>OR)
assumptions for calculations of sedimentation tanks
velocity vectors of particles evenly distributed
plug flow (eliminates complexities of turbulence and differing residence times)
any particle hitting bottom is removed
how would you make a settling tank more efficient?
remove greater % of particles
Adjust length of the tank (not depth) to increase area and decrease OR
Lamella tank (inclined plates for increased settling area but still greater OR)
two types of granular media filtration
slow sand filtration:
slow flow rate and big SA required
fast filtration:
can process lots of water fast
includes routine backwashing
purpose of granular media filtration
step after sedimentation tank
remove finer particles that did not get settled out
filtration: separating suspended particles by passing them through a porous medium
granular media filtration mechanisms
straining
interception: particle has affinity to surface
settling
impaction/brownian motion
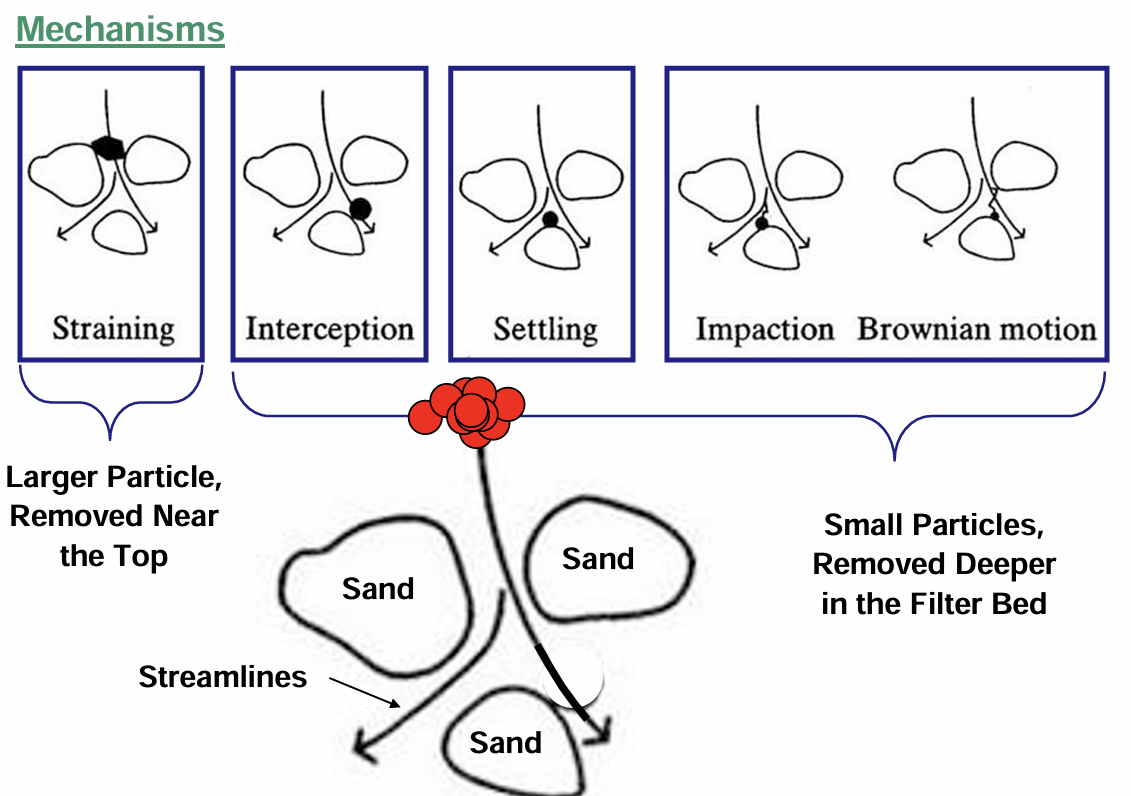
rapid sand filtration and dual media filters
backwashing: forcing water upward through filter at high velocity to remove/dislodge particles
dual media filters: anthracite (big and light) and sand (small and dense)
after backwash, gradation remains
want big particles on top and smaller on the bottom - efficient use of length

slow sand filters
good at removing biological particles
large surface area
does not require pre-treatment: coagulation/flocculation
not as effective as fast filters
impacts of air pollution
health (asthma, death)
property damage
visibility reduction
forest decline
fish death
skin cancer
severe weather
primary vs secondary air pollutants
primary
emitted directly in the atmosphere
volatile organic carbon
particles
NOx SOx CO
secondary
created by physical processes and chemical reactions in the atmosphere
e.g. Ozone
major sources of air pollutants
stationary fuel consumption (industrial boilers, electric utilities)
stationary petroleum processes (petroleum refineries)
mobile sources (vehicles, construction equipment, planes)
smog
smoke + fog = smog
general term to describe poor air quality with reduced visibility
photochemical vs industrial smog
photochemical: motor vehicles
CO, VOCs, NOx
O3 - most abundant
industrial: stationary sources
SOx, particulate matter (PM)
criteria air pollutants
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Ozone (O3)
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Particulate Matter (PM)
Sulfur Oxides (SOx)
Lead (not discussed)
criteria air pollutants: NOx
transportation sector + stationary fuel
reaction: Thermal NOx (N2 becomes reactive at high temps) + Fuel NOx
NO - no health effects
NO2
eutrophication
acid rain
respiratory diseases
criteria air pollutants: O3
no direct source - series of reactions
health: airway constriction, reduced lung function, irritation
vegetation: byproducts inhibit photosynthesis, loss of crop yield
production mechanism (write in ipad)
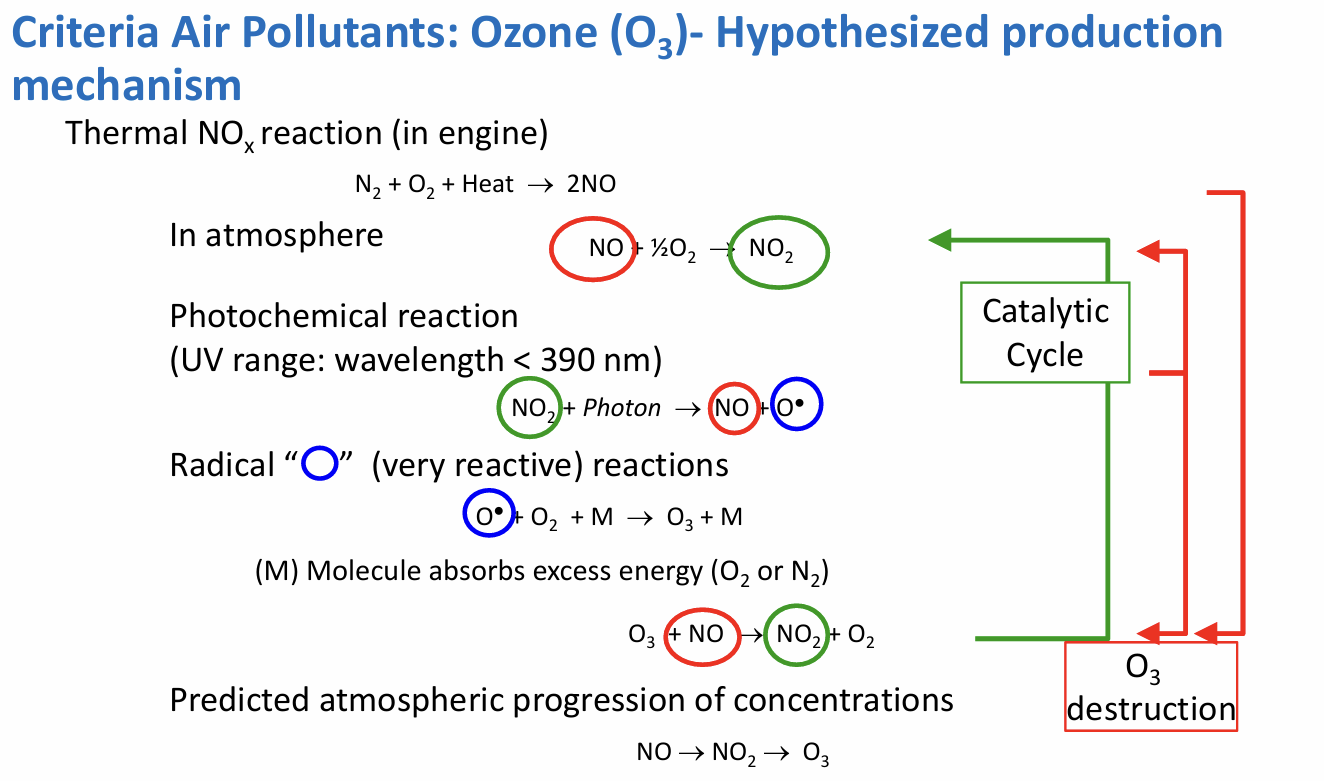
criteria air pollutants: CO
Most prevalent air pollutant
Vast majority emissions from transportation sector
Main source of CO: incomplete combustion (low temp, low O2)
health:
Greater affinity for hemoglobin—> low O2 in blood
Reduced mental clearness, headache, coma, death
criteria air pollutants: Particulate Matter (PM)
Very diverse chemical composition
Sources: fuel combustion, wildfires, dust, grinding, abrasion
Cause of winter smog in Montreal
PM10 short atmospheric life
PM2.5 very long atmospheric life
health:
anxiety
premature birth
cardiovascular disease
Particulates = Aerosols or
Solid: Dust, Soot
Liquid: Fumes, Mist, Fog
criteria air pollutants: SOx
Main source: combustion (electric power plants burning sulfur-containing coal)
forms sulfuric acids - Acid rain
health: similar to PM damages
how is air quality monitored?
air quality index (AQI) - the lower the better
5 criteria pollutants, 7 standards
worst standard becomes the index
how does air mix vertically?
difference in temperature
change of temperature with altitude
pressure decreases as you go up, so does temperature (PV=nRT)
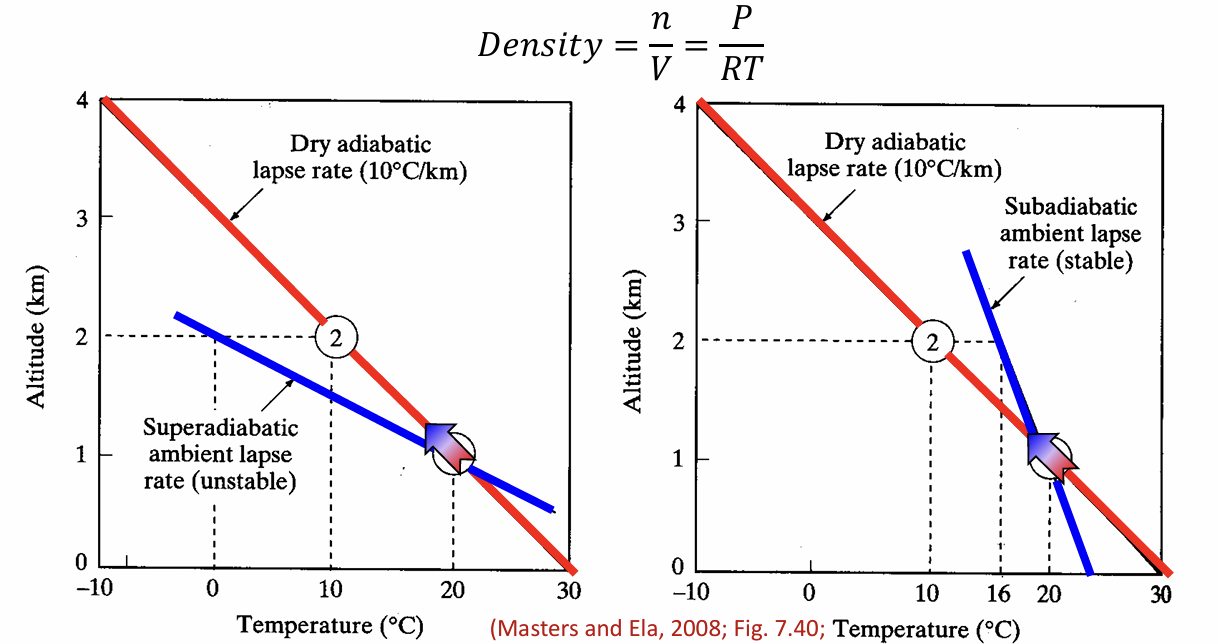
dry and saturated adiabatic lapse rates
rate at which an air parcel (dry or saturated) cools and rises in the atmosphere WITHOUT heat transfer
why does saturated air cool more slowly than dry air?
water condensates as temp decreases, releasing latent heat
latent heat moderates cooling of parcel
how to predict vertical air mixing?
graph compares ambient and adiabatic (ideal) lapse rates to determine stability of atmosphere
what is the solution to air pollution and why does it work
solution to pollution is dilution
dilute by creating taller stacks
the taller the stack, the lower the concentration of the pollutant at ground-level
assumptions and overall accuracy of Point Source Gaussian Plume Model
Rate of emissions from source =constant
Wind speed = constant
Pollutant is conservative
Accuracy: uncertain model
within ± 50%
Widely accepted
good for comparison
conservative pollutant
once it’s emitted it undergoes NO chemical reactions/degradation
only changes by dilution and physical transportation
what are Gaussian Dispersion Coefficients (σy, σz)
standard deviations
depend on downwind dist (x) and atmospheric conditions
reducing air pollution from stationary sources
pre-combustion: fuel switching, coal cleaning
improving combustion
post-combustion: emission capture, air treatment for each specific emission
average velocity vs Darcy velocity
Darcy velocity = Q/A
average velocity accounts for actual Surface Area that flow goes through
How do we describe contaminant transport with groundwater flow? (Transport mechanisms)
advection
plug flow of contaminants flowing with water at Darcy velocity
Diffusion
particles move in direction of their concentration gradient
no water movement required
Mechanical dispersion
solute spreads out from expected path and contaminant is diluted
differing velocities of particles
Retardation
slowing down of chemical relative to water movement
potable vs palatable drinking water
potable: healthy for human consumption
palatable: healthy and aesthetically acceptable to drink
physical characteristics of water: turbidity
measures ability of particles suspended in water to scatter light
water optical clarity
physical characteristics of water: particles
solids greater than molecules but generally not visible to naked eye
Total Suspended Solids (TSS) vs Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
pass water through filter and the ones that are small enough to pass are “dissolved”
water hardness and how it is classified
caused by presence of multivalence cations
Most common inorganic constituents of water that cause hardness: Mg2+, Ca2+
may be classified by cations themselves (Total Hardness) or by the associated anions
carbonate and non-carbonate (permanent) hardness
carbonate: hardness associated with carbonate anions
non-carbonate: hardness associated with other anions
why is water hardness an issue?
bad lathering of soaps
formation of hard to remove precipitates on infrastructure
good vs bad microorganisms
bad = Waterborne organisms that cause disease in humans or damage the ecosystem
good = Can be harnessed in biological treatment systems to degrade organic matter
pathogens
microorganisms capable of causing disease in humans
what are the stages/basins of a drinking water treatment plant?
Raw water
Coagulation / Flocculation Basin
Sedimentation Basin
Filtration Basin
Disinfection/oxidation Basin
Softening/reducing inorganic constituents
Adjust pH and alkalinity
Fluoridation
Finished Water Storage
what does each unit of drinking water treatment address?
Coagulation / flocculation and Filtration: turbidity, colour, particles
Disinfection: pathogens, organic material
Fluoridation and water softening: inorganics and final chemical adjustment (adjust pH and alkalinity)
coagulation / flocculation / sedimentation / filtration
coagulation: add a coagulant like alum (contains Al 3+) that neutralizes electric charges on suspended particles so they stop repelling
forms microflocs
flocculation: gently stir the water to bring the particles together to create flocs
sedimentation: now particles are ready to be settled out
filtration: any remaining particles get caught on the filter
how much alkalinity does alum consume and why does it need to be restored?
1 mol alum = 6 eq of alkalinity
1mg/L of alum will consume about 0.5mg as CaCO3/L of alkalinity
why restore:
treatment processes work best in certain pH ranges (coagulation included)
corrosion of pipes
aquatic organisms have narrow pH ranges to survive
alkalinity acts as a buffer against pH changes
what is the optimum alum dose in the jar test?
reduces turbidity the most
produces the most visible and fast settling flocs
leads to the smallest change in pH (aka lowers alkalinity the least)
what is the purpose of water softening and how is it done?
to remove Ca2+ and Mg2+ from solution
processes
ion exchange softening
lime-soda softening
in water treatment plants
Precipitate Mg and Ca by increasing pH (adding lime)
Chick-Watson Kinetics
Rate of number of microorganisms killed is proportional to number of microorganisms and concentration of disinfectant
primary vs secondary disinfection
primary: disinfection in the treatment plant
secondary: disinfection before entering distribution system to protect against intrusion and biofilm formation in pipes
major approaches to disinfection
Adding oxidative agents
free chlorine, O3
stops cell metabolism
UV radiation
stops cell capacity to reproduce
what is the log-removal concept?
Microbes present in very high cell numbers
Disinfection requires the cell removals by several orders of magnitude
useful to discuss in terms of log removal: −log(Nt/N0)
Log-removals with successive processes are additive
if process 1 has a 2-log removal and process 2 has a 3-log removal = total removal of 5-log
log-removal credit vs log-removal
credit: # of credits assigned to a specific treatment process (e.g., chlorine disinfection), expressed in log units, for the inactivation of a given pathogen
Log-Removal: a base-10 logarithmic scale used to describe the level of pathogen reduction achieved by a treatment process
log-removal = # of 9’s in a number 99.9% = 3-log removal
adsorption vs partitioning
adsorption
adhere to surface of adsorbent
hydrophobicity, to reach a lower energy state
most common adsorbent = Activated Carbon (AC)
partitioning
how much of a compound exists in each phase when multiple phases are present (air and water)
why treat wastewater?
protect source of drinking water
there’s always someone downstream!
protect aquatic ecology
what are the stages of a wastewater treatment plan?
Primary treatment / Pretreatment
Screening
Grit chamber: Removal of settleable solids (grit)
Possibly: Coagulation and settling tanks (like drinking water clarifiers)
Secondary (Biological) treatment
Aeration basin: Removal of soluble BOD
injected O2 + Return Activated Sludge (RAS) aka good bacteria: remove BOD
Removal of non-settlable solids
Advanced treatment
Removal of nutrients
No removal of dissolved BOD, nutrients, and pathogens
Disinfection: Removal of micro-pollutants (biologically resistant)
Removal of colour