Biological Molecules OCR A level Biology
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is a polar molecule? Give an example.
A combination of atoms in which the electrical charge is not distributed symmetrically. An example is H2O. Hydrogen and oxygen are bonded together by sharing electrons, but the oxygen atoms pulls the shard electrons closer to it, creating negative and positive sides of the water molecules.
What is a coenzyme?
an organic nonprotein compound that aids enzymes by carrying molecules/ions between enzymes and reactions.
Elements of carbohydrates
C, H, O
Elements of Lipids
C, H, O
Lactose is made of
Galactose and BETA glucose
Which sugars are reducing sugars
glucose, galactose, fructose, maltose, and lactose
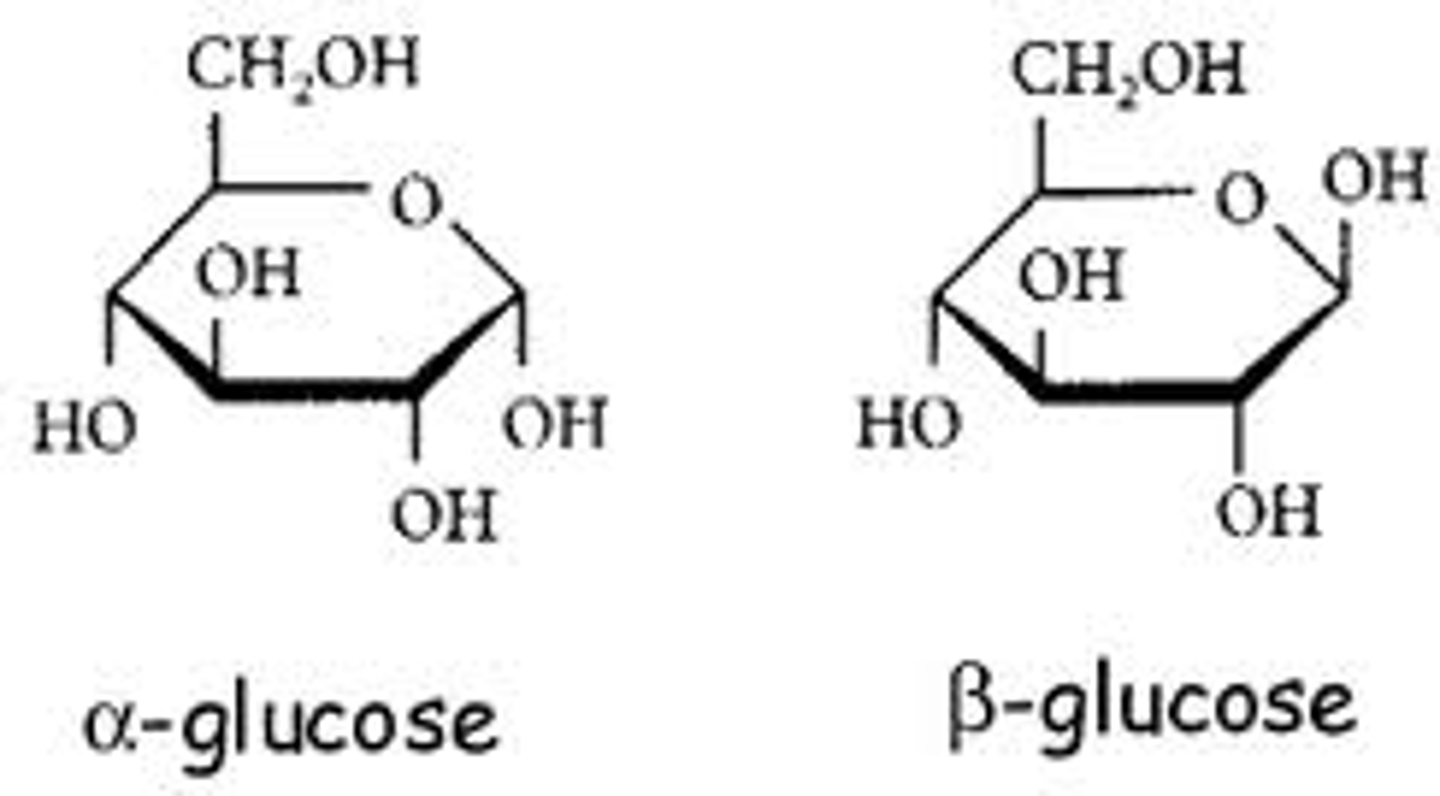
Alpha and beta glucose
Elements of amino acids
C, H, O, N, (S in cystine)
Which amino acid contains sulphur?
Cysteine
What is a polar atom group example?
OH
What is a Hydrogen bond?
the attraction between a hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge and another atom with a partial negative charge. Creating a relatively weak bond.
What do Hydrogen bonds do in water?
makes water cohesive and give it its other unique characteristics. Hydrogen bonds constantly break and reform between water molecules.
What does adhesive mean in terms of water?
The water molecules are attracted to other materials.
What does cohesive mean in terms of water?
Water moves as one mass because the polar molecules are attracted to one another- allowing for capillary action, plants can draw it up through their roots.
Why does ice float?
It is less dense than water. This is caused through the hydrogen bonds fixing the positions of the polar molecules further apart than normal. This produces a giant, open, but rigid structure with atoms at the centre of a tetrahedron of Hydrogen atoms. It is therefore less dense, and floats.
Why does water have a high boiling point?
Many hydrogen bonds take a lot of energy to increase temperature and evaporate
Why does the polarity of water allow it to sustain life?
Water acts as a solvent, the cytosol of prokaryotes and eukaryotes is mainly water. Water acts as a medium for chemical reactions.
How do cohesion and adhesion make water useful for sustaining life?
Water has Capillary action - it can rise against gravity.
Why does water's high heat capacity make it useful for sustaining life?
It provides a constant environment, when frozen ice provides an insulating layer to prevent the water below from freezing.
Difference between alpha and beta glucose?
on Carbon 1, alpha glucose has a OH group below the carbon ring and beta glucose has a OH group above the carbon ring.
Are polar molecules soluable?
Yes, hydrogen bonds between OH groups allow it to dissolve.
What happens when two glucose monomers form maltose?
A condensation reaction causes a 1,4 glyosidic bond between two glucose monomers.
Where is the monomer fructose found?
in fruit
Where is the monomer galactose found?
in milk
Why is amylase coiled?
the angle of the bonds and hydrogen bonds make it coiled - making it insoluable and compact.
What is the structure of amylopectin?
amylopectin is a long, branched chain of α glucose subunits
the subunits are joined by both 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds masking the molecule branched.
What is glycogen?
An energy storage molecule in animals, it is more branched than amylopectin - making it more compact.
How does the structure of glycogen make it useful for animals?
Branching causes the molecule to have free ends - allowing for places where glucose can be easily added or removed.
Are amylopectin and glycogen insoluable?
Yes.
What do plants use to store energy?
starch
What makes up Starch
Amylose and amylopectin
Is amalopectin coiled?
Yes, and also has free ends
Structure of cellulose
β-glucose arranged in a straight chain (each alternative β-glucose is rotated 180 degrees). They are linked through 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds.
What are the 'stages' of cellulose fibres?
Cellulose forms hydrogen bonds making microfibrils, these microfibrils join together to make macrofibrils, which condense to form cellulose fibres - which are strong and insoluble.
Chemical test for reducing sugars
Benedict's solution. Place the soluble sample in a boiling tube
then add an equal volume of Benedict's solution, then heat the mixture in a water bath. The mixture will change colour depending on how much reducing sugar is present. 100% would make it completely brick red.
How does the Benedict's test work?
Blue Cu2+ ions have electrons donated to them by the reducing sugars - causing them to become red Cu+ ions.
Why won't a Benedict's test go entirely brick red?
Some copper 2+ ions are unreacted and therefore stay blue.
Emulsion test
Test for lipids. Dissolve samples in ethanol, add an equal volume of water, shake the test tube, an emulsion will form.
How can the Benedict's test be used to test for non-reducing sugars?
Boil the solute in dilute HCL, hydrolysing the non-reducing sugars into reducing sugars.
Iodine test for starch method
- Dissolve sample in iodine/potassium iodide
- Mix with the sample
- If the test is positive, it will turn blue/black
reagent strips
most widely used technique to chemically analyze urine. Used with a colour chart.
Quantitative test using benedict's solution
- Do Benedict's test
- Place a filter on the colourimiter
- Calibrate the colourimiter using a curvette of distilled water.
- Find the absorbance of a known glucose solution
- Plot a calibration graph using the known glucose solution
What is a biosensor?
A device that uses a biological molecule, such as an enzyme to detect a chemical. A protein is imobilised on a transducer and this then binds to the sample. The transducer then changes, this change in the transducer then produces a visual change.
A biosensor detects the presence of a chemical, a transducer converts the response into a detectable signal.
How do tryglycerides form?
Condensation reactions between one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid chains react in condensation reactions forming ester bonds.
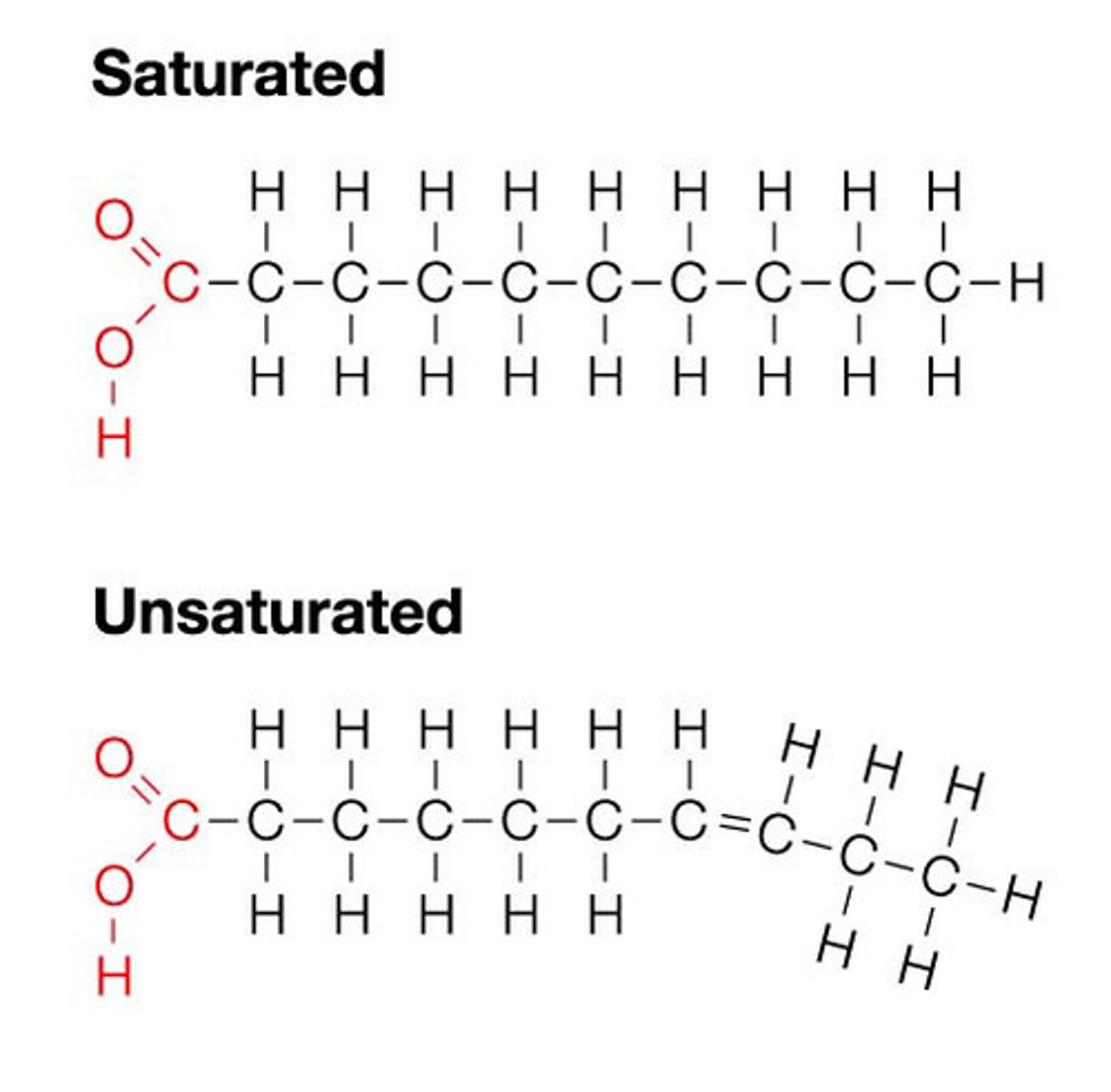
Difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
- Saturated acids contain only single bonds while unsaturated acids contain C=C double bonds.
- Saturated fatty acids have many contact points, while unsaturated fatty acids are kinked and therefore have fewer contact points.
- Saturated fatty acids have a higher melting point than unsaturated fatty acids.
- Saturated fatty acids are found in animal fats while unsaturated fatty acids are found in plant oils.
How does the structure of triglycerides relate to their functions?
- Triglycerides have a high energy to mass ratio, giving them a high calorific value.
- They have insoluble hydrocarbon chains, causing them to have no effect on the water potential of cells - forming insoluable - droplets - and also allowing them to be useful for waterproofing.
- They conduct heat slowly, allowing them to be useful for thermal insulation.
- They are less dense than water, allowing them to provide animals with buoyancy.
Triglyceride structure
glycerol + 3 fatty acid tails
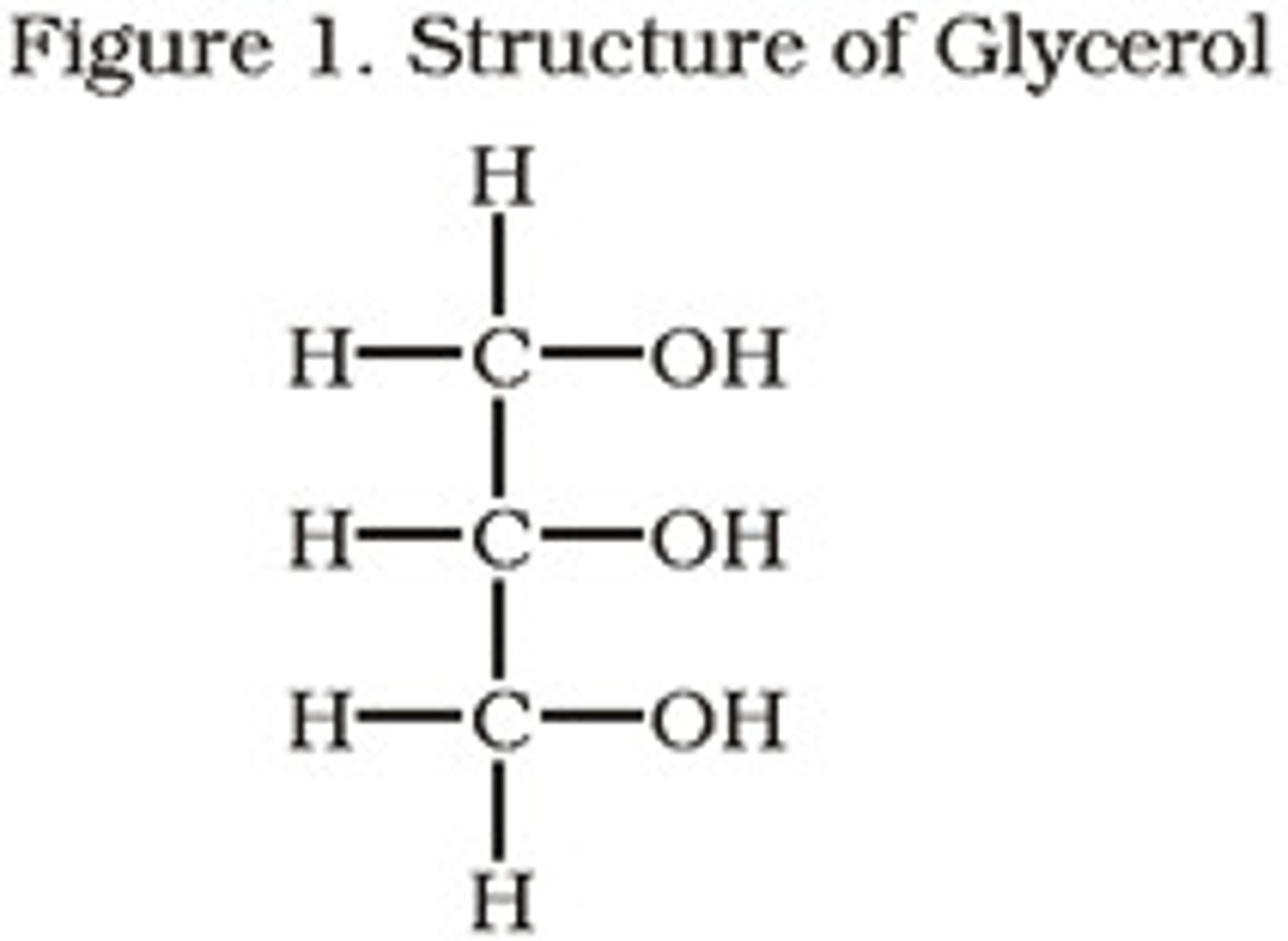
Glycerol structure
Fatty Acid Structure
Ester Bond
Condensation reaction between glycerol and fatty acids, bond includes double O, single O and Carbon.

What is the structure and function of phospholipids?
Similar to a triglyceride but with the third fatty acid tail replaced with a hydrophillic polar phosphate head. It forms a phospholipid bilayer in water, the tails can splay outwards - allowing for waterproofing.
What is the structure and function of cholesterol?
A structure of four hydrocarbon rings with a hydrocarbon tail on one side and a OH group on the other side.
It reduces the fluidity of the phospholipid bilayer, adding stability to it.
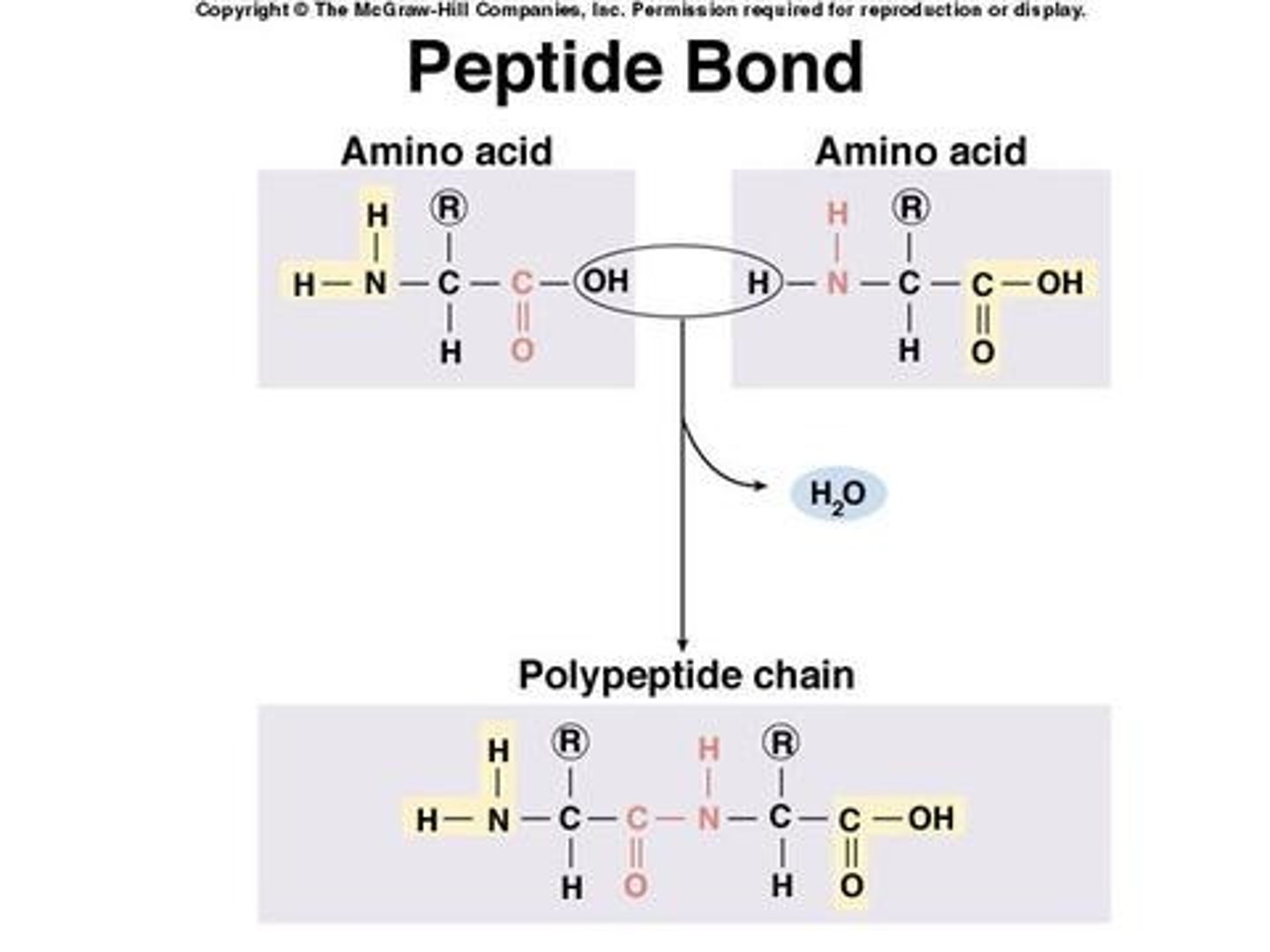
How do peptide bonds form?
Bond includes N single H, and C double O
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain, held together by peptide bonds. Created from the sequence of codons on mRNA
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
alpha helix or beta pleated sheet. Oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen atoms of the basic amino acid structure interact.
What is the tertiary structure of proteins?
The folding of the protein into its final shape. The coiling or folding in the secondary structure brings R groups closer together.
What bonds are involved in the tertiary structure?
1. Disulfide Bridges, covalent bonds caused by sulphur-containing R groups interacting. Only occurs in certain amino acids
2. H Bonds, weakest bonds formed.
3. Hydrophobic and Hydrophillic Interactions, weak interactions between polar and non-polar R groups.
4. Ionic Bonds, caused by oppositely charged R groups.
What are the tertiary structure bonds listed strongest to weakest?
Disulfide
Ionic
Hydrogen
Hydrophobic and Hydrophillic
Which bonds in the tertiary structure denature?
Ionic and Hydrogen
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
interactions between different polypeptide chains in proteins composed of more than one polypeptide (subunit interaction).
They are held together by the same bonds in the tertiary structure. Many involve the addition of prosthetic groups.
Structure and function of globular proteins.
● Spherical & compact.
● Hydrophilic R groups face outwards & hydrophobic R groups face inwards = usually water-soluble.
● Involved in metabolic processes e.g. enzymes & haemoglobin.
How does the protein's environment affect its structure?
The cytoplasm is mostly water - leading to the hydrophillic R groups facing outwards and the hydrophillic groups facing inwards.
Biuret test for proteins
1. Place the liquid sample in the solution. Make the solution alkaline by adding a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution. Then add copper (II) sulfate solution. DONT HEAT.
Mix and leave for five minutes.
2. If colour changed from pale blue to lilac then a protein is present.
This is a qualitative test. To make it quantitative you could use a colorimeter.
examples of globular proteins
Insulin, a hormone that regulates blood/glucose concentration.
It needs to be soluable to be transported in blood - it has a percise shape and is therefore taken in by receptors.
Conjugated proteins
Globular proteins with non-protein prosthetic groups
Examples of conjugated proteins
Haemoglobin and catalase
Haemoglobin
A Quaternary protein made of four polypeptides. Each subunit in haemoglobin contains the prosthetic haem group. The iron ions in haem combine with oxygen, allowing haemoglobin to be transported in blood.
Catalase
A quaternary protein that is an enzyme. It has four prosthetic haem groups. The iron II in haem breaks doen hydrogen peroxide.
fibrous proteins
Long insoluable molecules caused by more hydrophobic R groups, usually has a repetitive amino acid chain. Very organised long, strong molecules.
Examples of Fibrous proteins
keratin, elastin, collagen
Collagen
Fibrous protein that gives the skin form and strength. 3 polypeprides wound together like a rope - allowing it to be flexible. Found in connective tissue in skin, tendons, and ligaments.
Elastin
A fibrous protein in elastic fibres, elastic fibres are located in blood vessels and the lungs - giving them flexibility.
Keratin
A group of fiberous proteins found in hair, skin, and nails. Has many sulphur R groups - making it strong and inflexible.
Can lipids form polymers?
No, they form macromolecules, but not polymers.
How is Rf calculated in chromatography?
Distance travelled by solute/distance travelled by solvent.
Scale factor formula
Original Concentration/Desired Concentration
How to find solute volume from scale factor
Volume required/Scale factor
Replace rest with water
% Uncertainty Formula
(Max Value - Minimum Value)/Original Value
How to calculate the rate of reaction at a given point on a graph
- Draw tangent line
- Make right-angled triangle
- Change in y's scale divided by change in x scale
- answer
How to find the original amount of bacteria from a diluted sample
1. Find number of bacteria in undiluted sample
(multiply number of bacteria seen by dilution factor)
2. Calculate number of bacteria in total volume
((original volume/sample volume)*number in undiluted sample)