EMES 101 Exam 1 Study Guide
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Which is NOT a benefit of the strong inference approach?
Pet hypotheses are not preferred as they are counter to the process of the scientific method.
Which of the following statements is TRUE of Karl Popper's work as it relates to scientific knowledge?
C. Science must be refutable.
Which type of study allows causation between variables to be determined?
A. manipulative
Apply your understanding of the scientific method to determine kind of example the following sentence is, "If a there's a ball in the box, then it will roll when the box is tilted." The sentence is an example of a(n) _______.
A. hypothesis
Find the characteristic of a manipulative study.
C. It requires a control, multiple treatments, and replication.
Differentiate science from pseudoscience.
B. Science is always falsifiable while pseudoscience only gathers data to support itself.
Recall which is required by the strong inference approach.
C. mutually exclusive hypotheses

Determine which is the INFERENCE about the photograph below.
A. This is a volcanically active area.
Identify the type of study that allows correlation between variables to be drawn.
B. mensurative
Select the TRUE statement about Karl Popper's work as it relates to scientific knowledge.
D. Science must be refutable.
Select the TRUE statement about the scientific method and the evolution of scientific thought.
B. Facts change.
Find the FIRST and LAST steps of the scientific method as discussed in class.
A. observations, reexamination

Apply your understanding to pick the QUALITATIVE OBSERVATION about the photograph below.
D. The mountains are tall.
Infer which question can NOT be answered using the scientific method.
C. What is the nature of evil?
Apply your understanding to find the best HYPOTHESIS about our in-class practice assignment on Lake Nyos.
D. If Lake Nyos released a lot of volcanic gas, suffocating people and animals, then measured levels of volcanic gases after its release will be lower than before the release.
Which of the following are used to correlate rock units (strata) locally, regionally, and globally? Select all options that apply.
C. lithology, numeric age of rock units, fossils
Which statement is FALSE?
A. Relative age relationships and observed changes in the fossil record determined the numeric ages on the geologic time scale.
Which is NOT a factor that influences the fossil record?
A. ecosystem stabilization
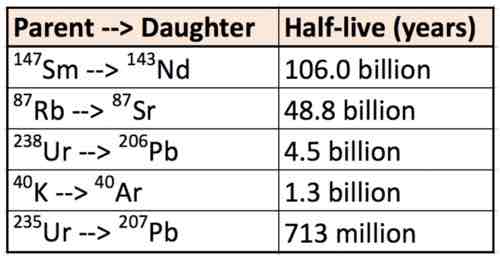
Select the correct definition of "half life".
D. The time it takes for half of the present parent material to decay to the daughter product at any given time.
How many half lives have passed if the parent:daughter ratio of an isotopic system reduces to 1:3?
B. 2
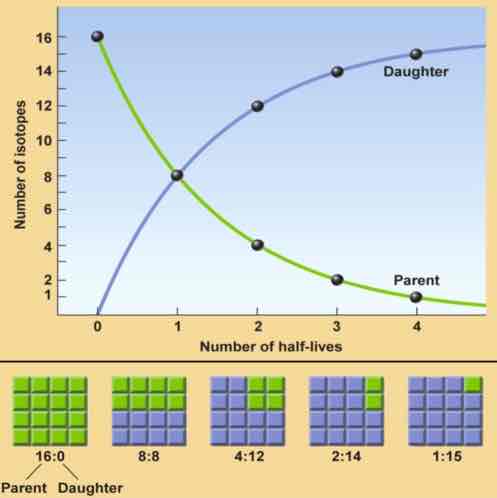
How is a mineral's absolute age determined using isotopic data?
A. Age = (the number of half lives) x (the half life of the isotopic system)
How old is a rock that has undergone 5 half lives as determined using the 40K-40Ar isotopic system?
D. 6.5 Ga
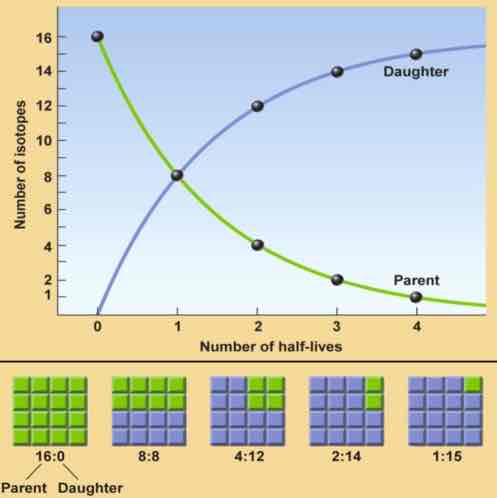
How will losing daughter isotope or adding parent isotope (i.e. having an open system) affect an absolute age?
B. The calculated age will be too young.
What are the two ways Earth's layers are classified?
D. composition and physical state
Which of Earth's layers is liquid?
A. the outer core
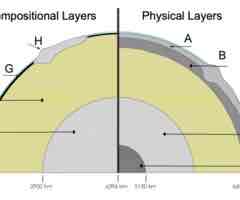
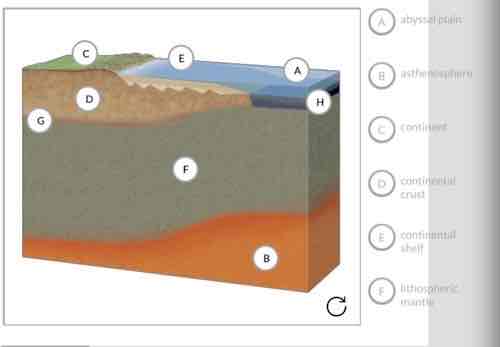
What is the name of layer G on the cross section?
D. the oceanic crust
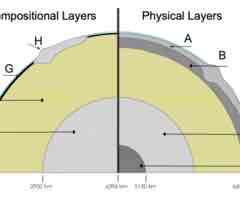
What is the name of layer B on the cross section?
D. the asthenosphere
Which statement is TRUE?
B. The lithosphere is composed of the crust and the rigidly solid uppermost portion of the mantle.
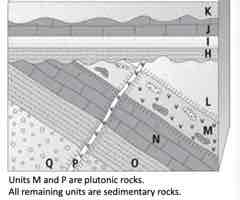
Apply relative age relationships to determine the FIRST 5 events from oldest to youngest.
A. Q, O, N, L, M
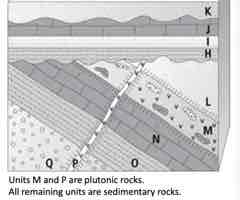
Apply relative age relationships to determine the LAST 5 events from oldest to youngest.
B. I, J, weathering & erosion, K, weathering & erosion
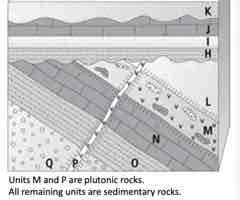
Select the relative age principle you use to determine if M or L came first.
D. cross-cutting relations
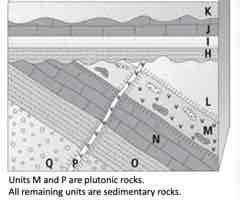
Select the relative age principle you use to determine if H or I came first.
superposition
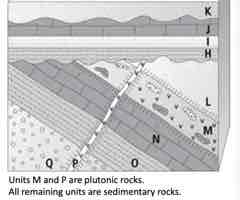
Apply your understanding to locate the YOUNGEST unconformity.
A. disconformity
Apply your understanding to identify the OLDEST unconformity. Select all answers that apply.
B. angular unconformity Correct answer: C. nonconformity
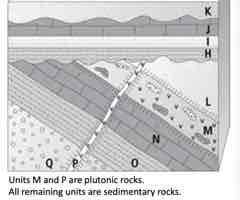
Determine which units should be baked contacts and, therefore, metamorphosed.
A. Units Q, O, N, M, L
Apply the principle of fossil succession to determine which unit listed below should have the OLDEST fossils.
D. O
Select the unit that would NOT yield a radiometric date that indicated when it formed.
B. K
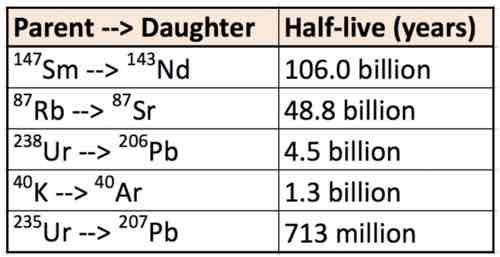
Unit M is selected for radiometric dating using the 40K-40Ar isotopic system. Analysis yields 50 K isotopes and 350 Ar isotopes. Calculate the age of M.
C. 3.9 billion years old
Based on your previous answer for the age of unit M, identify the TRUE statement.
B. Unit L could be 4 billion years old.
You take another sample of unit M to replicate your results from question 10 and the age that comes back is 1 billion years old. You know this can't be correct based on relative age relationships. Determine what likely happened.
B. K (parent isotope) was added.
Which type of plate boundary forms from the divergence of continental lithosphere?
A. continental rift
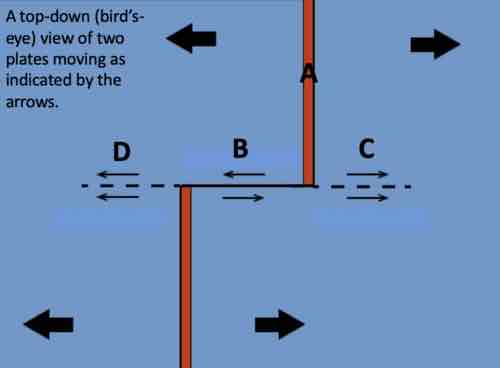
What letter on the map identifies the transform plate boundary?
B. B
Select the two plate boundaries that may occur when plates converge. Select all answers that apply.
A. subduction zone C. collisional boundary
What property largely determines which plate will subduct (oceanic or continental)?
C. density
Which location(s) is/are a subduction zone? Select all answers that apply.
D. The Pacific Northwest, U.S. (Washington State, Oregon, and Northern California)
Which are used to calculate the absolute motion of a plate? Choose all that apply.
A. hot spots B. global positioning systems
Which statement(s) about HOT SPOTS is/are FALSE? Choose all that apply.
A. They're composed of molten lava originating from the inner core. D. They are responsible for the weathering and erosion of volcanoes.

The hot spot track below has two segments. The younger segment has the active volcanoes that mark the current location of the hot spot while the older segment is composed of only seamounts. What was the plate's velocity for the older segment and then the younger segment? Recall Velocity = distance/time Ma = million years 1 km = 1000 meters, 1 meter = 100 cm
C. 2.0 cm/year and 1.0 cm/year
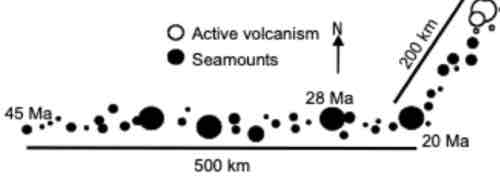
What direction was the plate moving when the OLDER segment of the hot spot was created? What direction was the plate moving when the YOUNGER segment of the hot spot track was created?
D. west then southwest
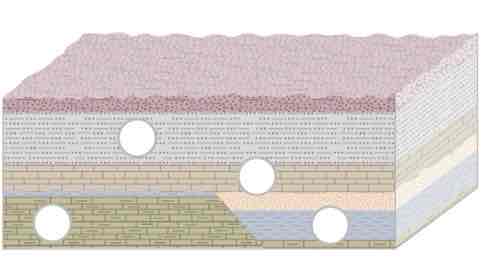
In this relative age dating interactivity, order the geologic events chronologically from oldest to youngest, with the oldest being labeled "1st" and the youngest being labeled "4th."
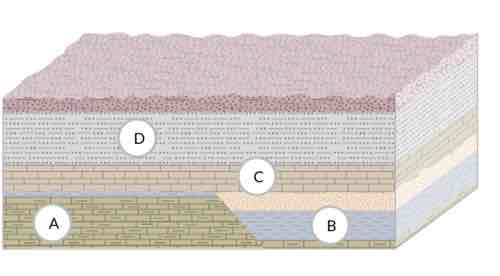
Sort youngest to oldest.
1.) Fault 2.) Mafic intrusion 3.) Conglomerate 4.) Felsic crystalline rocks
1.) Fault 2.) Conglomerate 3.) Mafic intrusion 4.) Felsic crystalline rocks
Select statements true of unconformities.
B. There are three major types of unconformities. C.Unconformities represent periods of nondeposition in the rock record. D.Unconformities represent periods of erosion in the rock record.

Which of the illustration represents a disconformity?
B
Order the steps in the formation of a disconformity.
Erosion took place.
Sediments were deposited in a marine environment.
Sea level rose, covering the erosional surface, which was buried by marine sediments.
Sea level fell, exposing marine deposits subaerially.
Sediments were deposited in a marine environment.
Sea level fell, exposing marine deposits subaerially.
Erosion took place.
Sea level rose, covering the erosional surface, which was buried by marine sediments.
Why can radioisotopic dating methods be used to determine the numerical age of igneous rocks but not of sedimentary rocks?
Numerical ages of minerals in sedimentary rocks provide the age the minerals crystallized in their original rock.
The time it takes for half of a group of radioactive isotopes to decay is called a(n)
half life
If you start with 80 radioactive atoms, how many daughter atoms exist after 2 half-lives?
60 daughter atoms
Why is the fossil record of clams more complete than that of spiders?
Clams have very hard shells, whereas spiders have soft shells that break down more easily.
Organisms are more likely to be fossilized in a low-energy deposition environment compared to a high-energy environment because __________.
hard parts are more easily broken up in high-energy environments
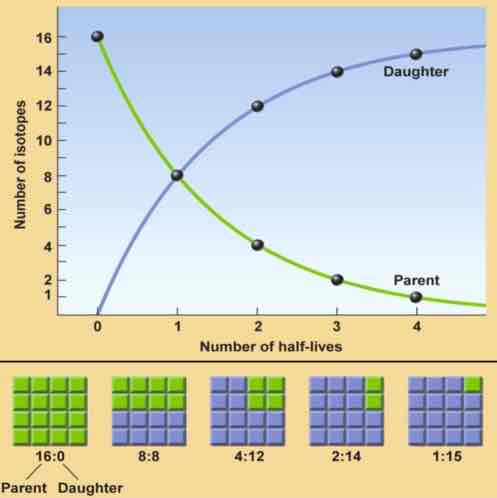
What conclusion can you make from the following diagram?
If the half-life of the parent material is 4,000 years, 3 on the horizontal axis of the graph represents 12,000 years.
According to the theory of plate tectonics, the plates are:
discrete pieces of lithosphere which move with respect to one another. moved by the creation of new crust and subduction of old crust.
Identify statements true of Pangaea.
Rates of seafloor spreading in the Atlantic Ocean are compatible with what is known about the breakup of Pangaea.
Pangaea was one of several supercontinents that have formed and broken up during Earth's history.
The regional-scale folds visible in the Appalachian Mountains are remnants of Pangaea's formation.
ALL OF THE ABOVE
Rates of seafloor spreading in the Atlantic Ocean are compatible with what is known about the breakup of Pangaea.
Pangaea was one of several supercontinents that have formed and broken up during Earth's history.
The regional-scale folds visible in the Appalachian Mountains are remnants of Pangaea's formation.
Magnetic reversals
reflect changes in the direction of the flow of molten iron in the Earth's outer core.
Which of the following variables could influence the width of marine magnetic anomalies on the floor of the ocean?
A.duration of the magnetic polarity event C.rate at which the plates are moving away from the mid-ocean ridge
The paleomagnetic record is
preserved in stripes of rock parallel to the mid-ocean ridge.
Seafloor spreading is driven by volcanic activity that occurs
along mid-ocean ridges.
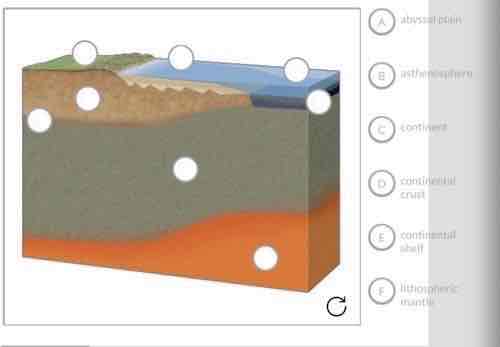
Label the image with the features of tectonic plates.
Order the steps of volcanic island arc formation.
Convergence begins
Magma, created by flux melting of the mantle, rises through the overriding plate.
A subduction trench forms where the subducting plate bends downward into the mantle.
Lava erupts onto the surface, forming volcanoes.
An accretionary prism begins to form.
A volcanic island arc forms
Convergence begins
A subduction trench forms where the subducting plate bends downward into the mantle.
An accretionary prism begins to form.
Magma, created by flux melting of the mantle, rises through the overriding plate.
Lava erupts onto the surface, forming volcanoes.
A volcanic island arc forms
Categorize processes related to transform boundaries. Sort the following processes those likely to be related to a transform boundary or those likely associated with other boundary types.
earthquakes
divergence
convergence
subduction
Transform Boundary
earthquakes
Other Boundary
divergence
convergence
subduction
Sort outcomes of continental collision versus those related to ocean-ocean (oceanic) convergence.
crustal thickening
mountain building
subduction
volcanism
Continental Collision
crustal thickening
mountain building
Oceanic Convergence
subduction
volcanism
Order the steps in continental rift formation.
Rifting Initiates
The lithospheric mantle begins to stretch horizontally and thin vertically.
Magma erupts as lava, creating volcanoes along and near the center of the rift.
The crust fractures, and faults develop.
Large fault blocks of crust slide down into the widening rift.
A Continental Rift Is Formed
Rifting Initiates
The lithospheric mantle begins to stretch horizontally and thin vertically.
The crust fractures, and faults develop.
Large fault blocks of crust slide down into the widening rift.
Magma erupts as lava, creating volcanoes along and near the center of the rift.
A Continental Rift Is Formed
Sort these mountain chains based on what caused them to form.
Alps Himalayas
Appalachian Mountains
Rocky Mountains
Continental Collision
Alps Himalayas
Appalachian Mountains
Other Causes
Rocky Mountains
Which of the following changes occurred to the crust as this collisional mountage range formed?
suturing
creation of a fold-thrust belt
regional metamorphism
During the formation of a collisional mountain range, the crust will __________ horizontally and __________ vertically.
shorten; thicken
In what geologic settings do mountain ranges form?
continental collisions like the Himalayas
subduction zones like the Andes Mountains
rift-related settings like in Nevada