A&P Exam 4 (Ch 29 pt 2)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Parturition
process by which a baby is born, blood levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease dramatically due to the removal of the placenta, precise trigger of parturition is unknown
Gestation Period
length of pregnancy calculated by physicians, 280 days (40 weeks) from last menstrual period to date of delivery of infant
Changes Near End of Pregnancy
uterus becomes more excitable and usually exhibits occasional contraction
cervix gradually dilates
strong uterine contractions help expel the fetus from the uterus through the vagina
Labor
period during which uterine contractions occur to eventually expel the fetus and placenta
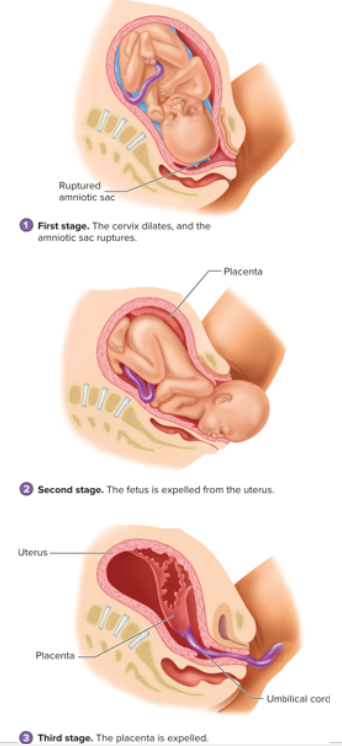
3 Stages of Labor
dilation
expulsion
placental
Dilation Stage
first stage of labor, begins with onset of regular uterine contractions, extends until the cervix is dilated, amniotic sac ruptures, usually lasts 8-24 hours, head of fetus is positioned inferior to force cervix and vagina to open during contractions
Expulsion Stage
second stage of labor, lasts from the time of maximum cervical dilation until the fetus exit the vagina, lasts from a minute to an hour or more
Contractions During Expulsion Stage of Labor
contractions of the abdominal muscles assist the uterine contractions
contractions generate enough pressure to compress blood vessels in the placenta so blood flow to fetus stops, blood flow is restored during relaxation
Placental Stage
third stage of labor, occurs after birth, placenta is expelled from the uterus, uterine contractions cause the placenta to tear away from the uterine wall, some bleeding from uterine wall occurs, contraction compresses blood vessels to placenta to limit bleeding
4-5 Weeks After Parturition
uterus becomes smaller, cells of uterine lining become smaller and many degenerate, vaginal discharge is composed of small amounts of blood and degenerating endometrium for 1 week or more
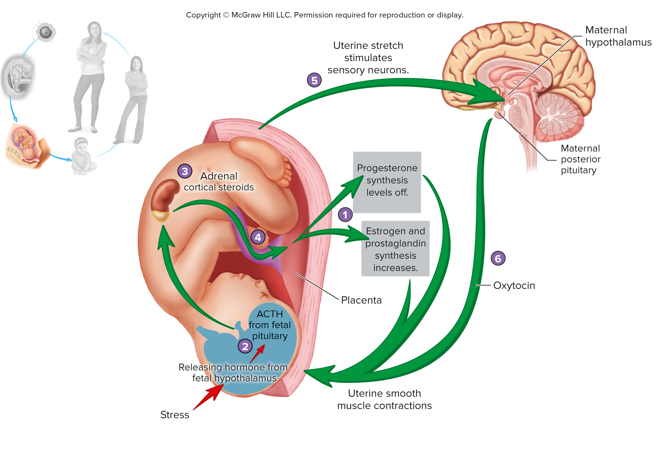
Maternal Hormones Before Parturition
progesterone concentration in maternal blood is at its highest level and inhibits uterine smooth muscle cells
Hormones Near End of Pregnancy
estrogen levels rapidly increase in maternal blood and have excitatory influence overcomes progesterone’s inhibition
Fetal Hormones Before Parturition
adrenal glands of fetus are greatly enlarged, acth secretion (anterior pituitary) increases due to stress of confined space and limited oxygen supply
ACTH Effect on Fetus
causes fetal adrenal cortex to produce glucocorticoids, alters hormone secretion from the placenta
Glucocorticoids Effect on Fetus
decrease the rate of progesterone secretion and increase rate of estrogen synthesis, stimulates prostaglandin synthesis to stimulate uterine contractions
Hormones During Parturition
stretching of uterine cervix stimulates the release of oxytocin from maternal posterior pituitary
Oxytocin
stimulates uterine contraction, moves fetus farther into cervix causing stretching (positive feedback), after delivery cervix is not stretching and oxytocin secretion decreases
Hormones of Parturition Diagram
Stages of Labor Diagram