Adrenocorticosteroids (Glucocorticoids and Mineralocorticoids)
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary-style flashcards covering key terms, pathways, actions, clinical uses, and pharmacologic modifiers of adrenocorticosteroids.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Adrenal cortex
Outer layer of the adrenal gland with three zones (glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis) that secrete mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens.
Zona glomerulosa
Adrenal zone that secretes aldosterone; activity regulated by the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS).
Zona fasciculata
Adrenal zone that secretes glucocorticoids (chiefly cortisol) and corticosterone.
Zona reticularis
Adrenal zone that secretes androgens (sex steroids) such as DHEA and androstenedione.
Adrenal medulla
Inner part of the adrenal gland; secretes predominantly epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Glucocorticoids
Cortisol or Hydrocortisone by HPA
Glucocorticoids and aldosterone are essential for life
Glucocorticoid Metabolic Actions
Carb Metabolism - anti-insulin effect, Hyperglycemia
Protein Metabolism - inhibits protein synthesis in muscles, connective tissues, skin
Fat Metabolism - Increase glucocorticoid levels increase fat deposition, centripetal obesity, cutaneous striae
Glucocorticoid Antiinflammatory Actions
Inhibits phosphlipase A2 via lipocortin production and lowers prostaglandins
Blocks synthesis and release of cytokines (IL 1, IL 4, IL 6, TNF)
Suppress fibroblast proliferation and proinflammatory transcription factors
Mast cell and basophils decrease IgE dependent release of histamine and LTC4 respectively
Glucocorticoids Immunosuppressive Actions
Suppress the cell mediated immunity
Suppress humoral immunity
Controls graft rejection by reducing antigen expression, delay revascularization, decrease cytotoxic lymphocytes
Glucocorticoid Other Actions
Ca metabolism - Antagonize vit D3, osteoporosis on long term
Central Nervous System - Euphoria, anxiety, insomnia, depression
Cardiovascular - hypertension, coronary artery disease
Skeletal Muscles - muscle wasting and weakness in cortisol excess
Plays vital role in fetal lung development (pulm surfactant), depress growth hormone secretion, associated w development of peptic ulcers
Aldosterone Effects
Promotes Na reabsorption
Enhance excretion of K and H
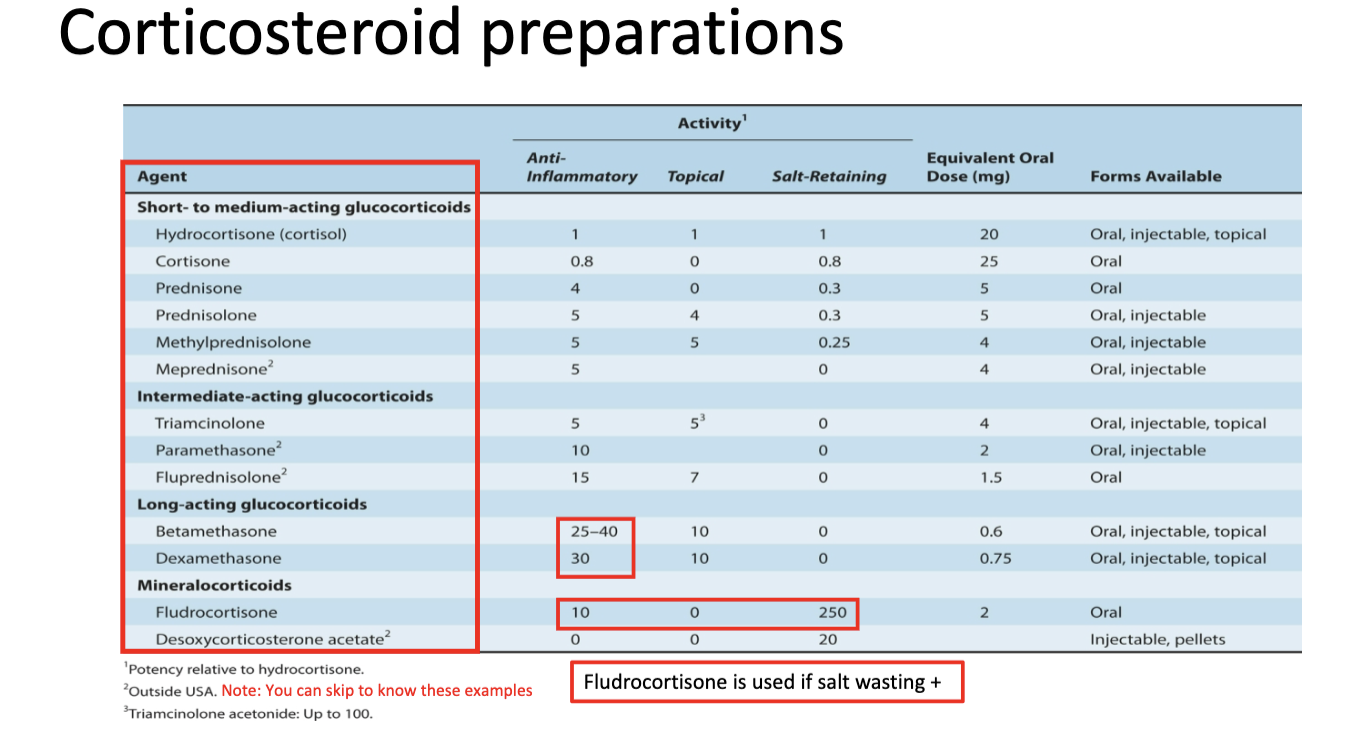
Corticosteroid preparations
Corticosteroid preparations
Cinical Uses Endocrinal Replacement Therapy
Acute Adrenal Insufficiency, Chronic Adrenal Insufficiency
Clinical Uses - Endocrine Maintenance Therapy
Cushings Syndrom, Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Dexamethasone suppression test
Clinical Uses Antiinflammatory Therapy
Osteoarthritis, Rheumatic fever, Gout, Rh Arthritis, IBD, Allergic conjunctivitis, iridocyclitis, iritis
Clinical Uses Immunosuppressive Therapy
Collagen Vascular Disease, Organ Transplant/skin graft, Nephrotic syndrome, AI disease (AI hemolytic anemia, Immune thrombocytopenia purpura, myastenia gravis), MS, Guillain Barre Syn.
Clinical Uses NonEdocrinal
Bronchial Asthma - systemic steroid for acute sever, Inhaled for long term (beclomethasone, budesonide, fluticasone, flunisolide)
Severe allergic rxn, stimulation of fetal lung maturation, malignancies, skin disease
Glucocorticoids A/E
Altered fat distiribution, Edema from Na retention, Osteoporosins, Hyperglycemia, susceptible to infections, delayed healing, peptic ulcer, acne, ocular effects, CNS effects, fragile skin, anovulation, gynecomastia, suppression of HPA axis, myopathy, growth retardation, cutaneous atrophy

Glucocorticoids C/I
Diabetes, Osteoporosis, TB and bacteria infection, Herpes Keratitis, Epilepsy, Renal failure, Peptic ulcer, Pregnancy, psychosis, fungal and viral infections, CHF and hypertension
Adrenocorticoids: Pharmacologic Actions
Mineralocorticoid actions - mediated by aldosterone, regulates Na, K and fluid homeostasis
Gluococorticoid actions - mediated by cortisol, governs protein, fat, and carb metabolism, antiinflammatory, immunosuppressant
Principles in Steroid Therapy
Risk of iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome (most common cause of Cushings), use local therapy, single high dose, less than 1 weeks, short courses
Long term Rx - hazardous due to A/E profile, alternate day dosing to minimize HPA axis suppression, slow tapering, increase dose in stressful events
Ketoconazole
17 alpha hydroxylase inhibitor - antifungal, cushing’s syndrome
Mifepristone
Antagonist at progesterone and glucocorticoid receptors
Mineralocorticoid antagonist
Spironolactone, eplerenone
HPA axis
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis; regulates cortisol production via CRH, ACTH, and negative feedback.
Dexamethasone suppression test (DST)
Diagnostic test to determine source of cortisol excess (adrenal vs ectopic/pituitary) by dexamethasone suppression.
Primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s disease)
Deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone due to adrenal destruction; requires glucocorticoids ± mineralocorticoids.
Secondary adrenal insufficiency
Cortisol deficiency due to HPA axis suppression; aldosterone usually preserved.