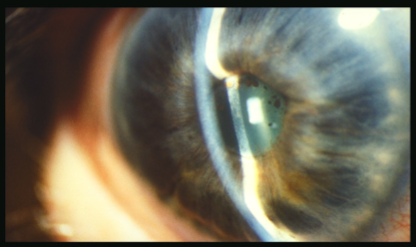
Angle Closure Spectrum
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
FHx of angle closure
older age
female
Chinese, Vietnamese, Pakistani, Inuit descent
what are the demographic risk factors for ACG?
hyperopia
shallow peripheral AC depth
shallow central anterior chamber depth
steep corneal curvature
thick crystalline lens
short axial length
anterior position of CB (plateau iris)
anterior lens position
what are the ocular risk factors for ACG?
primary angle-closure suspect
180deg or more of iridotrabecular contact (occludable angle), normal IOP, & no optic nerve damage, normal VF
primary angle closure
180 deg or more of iridotrabecular contact (occludable angle) w/ peripheral anterior synechiae or elevated IOP but no optic neuropathy, normal VF
primary angle closure glaucoma
180 deg or more iridotrabecular contact w/ PAS, elevated IOP, & optic neuropathy, VF abnormalities
acute angle closure crisis
occluded angle w/ symptomatic high IOP
plateau iris configuration
narrow angle due to an anteriorly positioned CB, w/ deep central AC
plateau iris syndrome
narrow angle due to an anteriorly positioned CB, w/ deep central anterior chamber, & any iridotrabecular contact persisting after patent peripheral iridotomy
peripheral iris prevents aqueous from reaching the TM
why does IOP become elevated in angle closure?
pupillary block
impedance to aqueous flow from the posterior to the anterior chamber through the pupil, causes pressure in the posterior chamber to become higher than that in the anterior chamber, pushing the peripheral iris forward & narrowing the angle (angle closure)
pupillary block
plateau iris
retrolenticular mechanisms
what are the mechanism classifications of angle closure?
pupillary block
what is the most common form of angle closure?
plateau iris
anteriorly positioned ciliary processes push the iris forward
ciliary block, posterior aqueous diversion, aqueous misdirection, malignant glaucoma
what are the retrolenticular mechanisms?
pupillary block
without pupillary block
anterior mechanisms
what are the angle closure configuration classifications?
lens related mechanisms
phakic IOLs
uveitis
what are some “pupillary block” causes of angle closure?
plateau iris configuration/syndrome
aqueous misdirection syndrome, ciliary block
uveal edema
tumors
cysts
what are some “without pupillary block” causes of angle closure?
ICE
PPMD
NVG
uveitis
what are some “anterior mechanism "causes of angle closure?
plateau iris
due to a large or anteriorly positioned CB
iris root is short & inserted anteriorly on ciliary face, so that the angle is shallow & narrow, w/ a sharp drop-off of the peripheral iris at the inner aspect of the angle
iris surface appears flat & the AC is of relatively normal depth
double hump sign on gonioscopy
most common in younger women
tx: peripheral iridoplasty/cataract surgery
plateau iris syndrome
refers to the development of angle closure, either spontaneously or after pupillary dilation in eye w/ plateau iris configuration despite the presence of patent LPI
plateau iris configuration
deep axial anterior chamber
flat iris plane
steeply rising peripheral iris
anterior positioned ciliary process
narrow ciliary sulcus
latent/suspect
no symptoms
narrow Van Herick angle, shallow AC depth, iris bombe
occludable angle w/ no pigmented TM visible on gonio
clinical course:
IOP may remain normal
acute or subacute angle closure may develop
chronic angle closure
tx:
consider LPI
subacute angle closure
symptoms:
halos
smoking vision
frontal HAs by 1-2hrs then resolution
occludable angles on gonioscopy
clinical course:
acute attack or chronic angle closure
tx:
LPI ASAP
acute angle closure
sight threatening emergency
symptoms:
severe pain
HA
halos
nausea
vomiting
sweating
blurry vision
signs:
ciliary flush
corneal edema
shallow angle
cells & flare
vertical oval fixed mid-dilated pupil
convex iris
iris blood vessels congested
IOP elevated (50-100mmHg)
disc edema
chronic angle closure
often no symptoms
varying degrees of angle closure w/ creeping PAS that starts superiorly
PAS from subacute attacks
signs of POAG
tx:
LPI
medical
trabeculectomy?
postcongestive angle closure
postsurgical LPI - normal IOP, elevated IOP w/ trabecular damage or PAS > 180; medical or surgical management
signs:
iris atrophy & spiraling
glaukomfleckin lens opacities
IOPs normal or still elevated
malignant or aqueous misdirection glaucoma
occurs in phakic eye after intraocular surgery w/o lens extraction or narrow angles w/ cataract surgery
occurs in eyes which were partially closed preoperatively
shallow or flat AC w/ increased IOP after surgery
malignant glaucoma in aphakia
occurs w/ aphakia w/ intact vitreous face
aqueous misdirected behind vitreous
vitreous pushes forward, narrowing the AC
decreasing IOP
decrease inflammation
rapid breaking of the attack
clear cornea
protect optic nerve
open the angle
prevent PAS
what are the goals for managing acute angle closure?
miotics
beta blockers
alpha adrenergic agonists
topical steroids
CAIs
oral/IV hyperosmotic agents
corneal indentation
LPI (laser peripheral gonioplasty/iridoplasty, surgical iredectomy, parecentesis, cataract surgery, trabeculectomy, goniosynechialysis)
what are the tx options for acute angle closure?
laser peripheral iridotomy
reestablishes communication b/t the posterior & anterior chamber
indications: AAC, prophylactic in fellow eye, intermittent & chronic AC, possibly occludable angles
Yag
is argon or Yag preferred for LPI?
T
T/F: LPI is contraindicated if there is corneal edema & severe iris congestion
we were overdoing it on the prophylactic LPIs
what did the ZAP trial tell us?
more severe cataracts, higher IOP
the ZAP trial found that LPI eyes had a _________
higher IOP
shallower limbal anterior chamber depth
greater central anterior chamber depth
what did the ZAP trial find were risk factors for greater likelihood of reaching endpoint in the control group?
higher IOP
shallower limbal anterior chamber depth
less IOP elevation after being in a dark room
what risk factors did the ZAP trial find for post LPI eyes having PAC?
examined the effectiveness of early lens extraction for the tx of primary angle closure glaucoma
what was the goal of the EAGLE study?
10
___% of acute angle closure attacks present w/ bilateral disease
50
__% of acute angle closure pts have an acute attack in the contralateral eye if untreated over a 5y period
days
contralateral involvement in an acute angle closure can occur within ____
LPI
miotic agents
peripheral gonioplasty
argon laser peripheral iridoplasty
clear lens extraction/cataract surgery
what are the tx options for plateau iris syndrome?
LPI
cataract surgery
goniosynechialysis
trabeculectomy
what are the options for PACG management?
cycloplegic
topical/systemic steroids
aqueous humor suppressants
NO MIOTICS
what are the tx options for a systemic topamax AAC attack?
T
T/F: if cornea is too edematous, perform gonio on uninvolved eye, if the angle is not occludable then this is prob not AACG
F (must r/o plateau iris)
T/F: the presence of patent LPI means the patient is always safe to be dilated
narrow angle, no structures evident

PAS

pupillary block
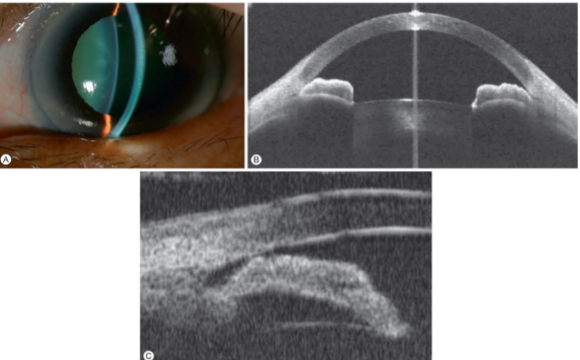
double hump
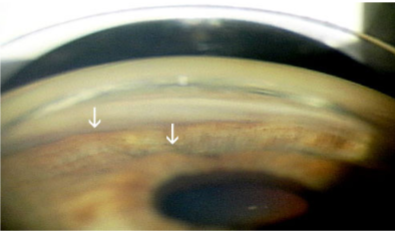
acute angle closure glaucoma
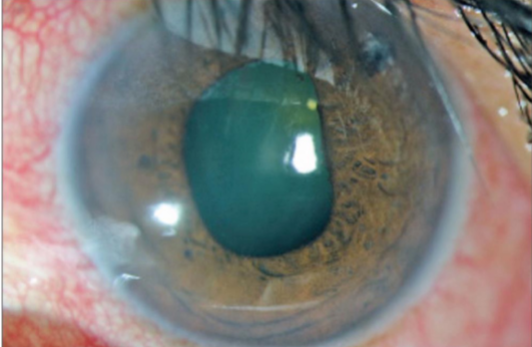
glaukomflecken
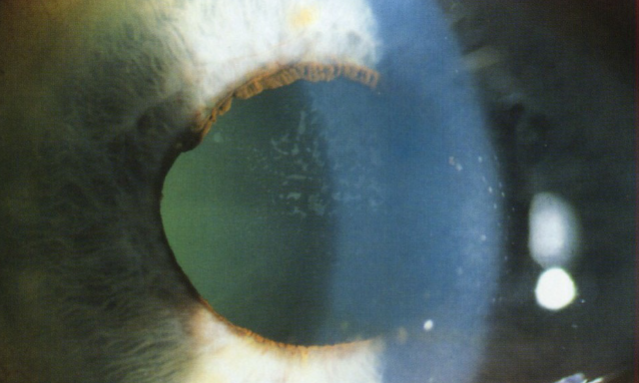
pupil block