Decision Making Lecture Flashcards
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about Decision Making 1 Lecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Dual Process Theory
This theory helps explain how people make decisions and judgments in different contexts.
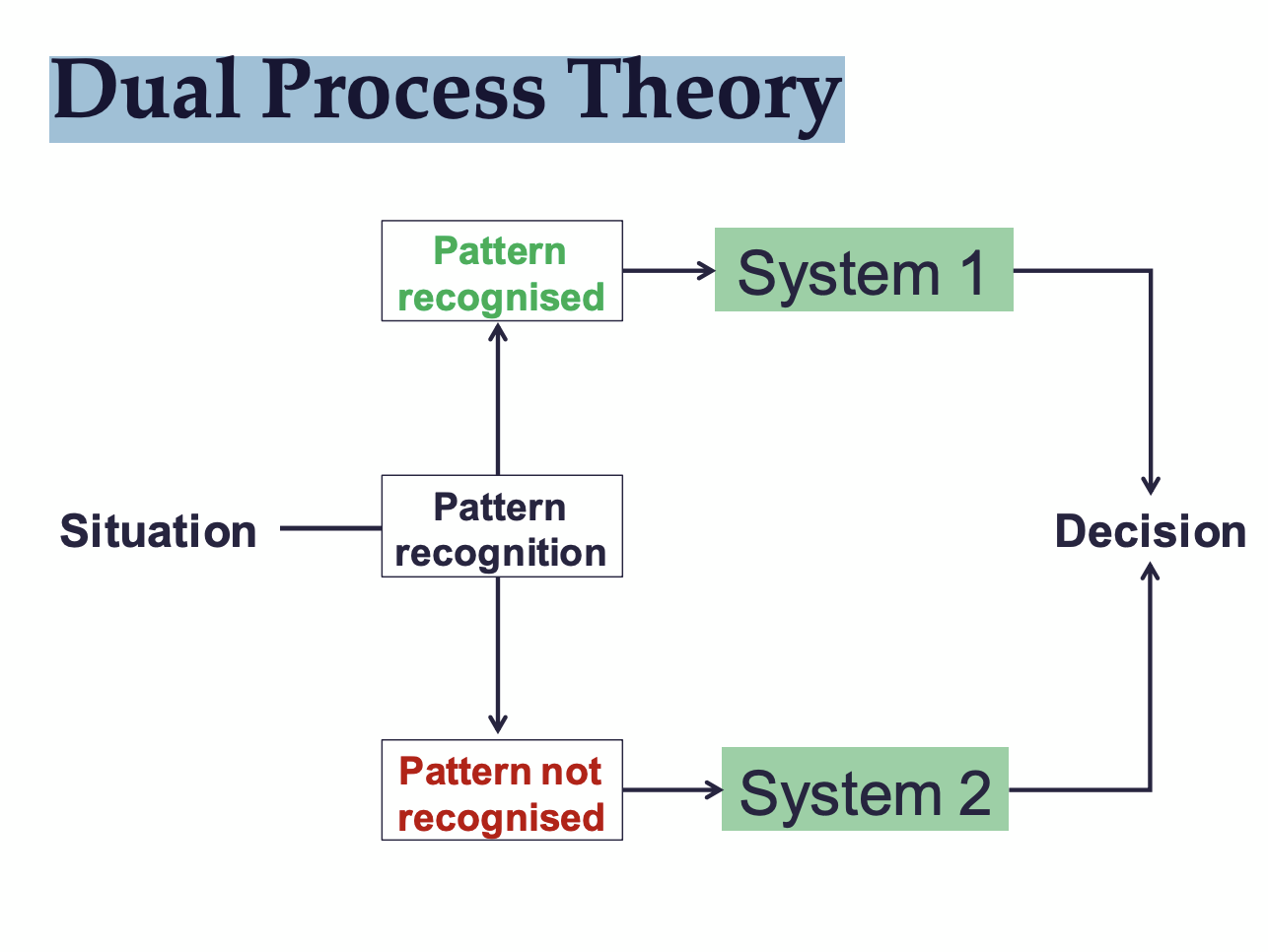
What are the key characteristics of System 1 decision making?
Fast, unconscious, automatic, used for everyday decisions.
What are the key characteristics of System 2 decision making?
Slow, conscious, requires effort, used for unfamiliar decisions.
According to the lecture, what happens when a pattern isn't recognised?
System 2 is activated.
What does "Cognitive Miser" mean according to Daniel Kahneman?
Humans try to avoid thinking.
What is the advice when facing a complex decision after System 1 activation?
STOP AND THINK: Consider alternatives and look for inconsistencies.
What factors influence whether a situation is processed by System 1 or System 2?
task difficulty, task ambiguity
What elements are needed for effective practice?
Repetition, instruction, demonstration, practice, and feedback.
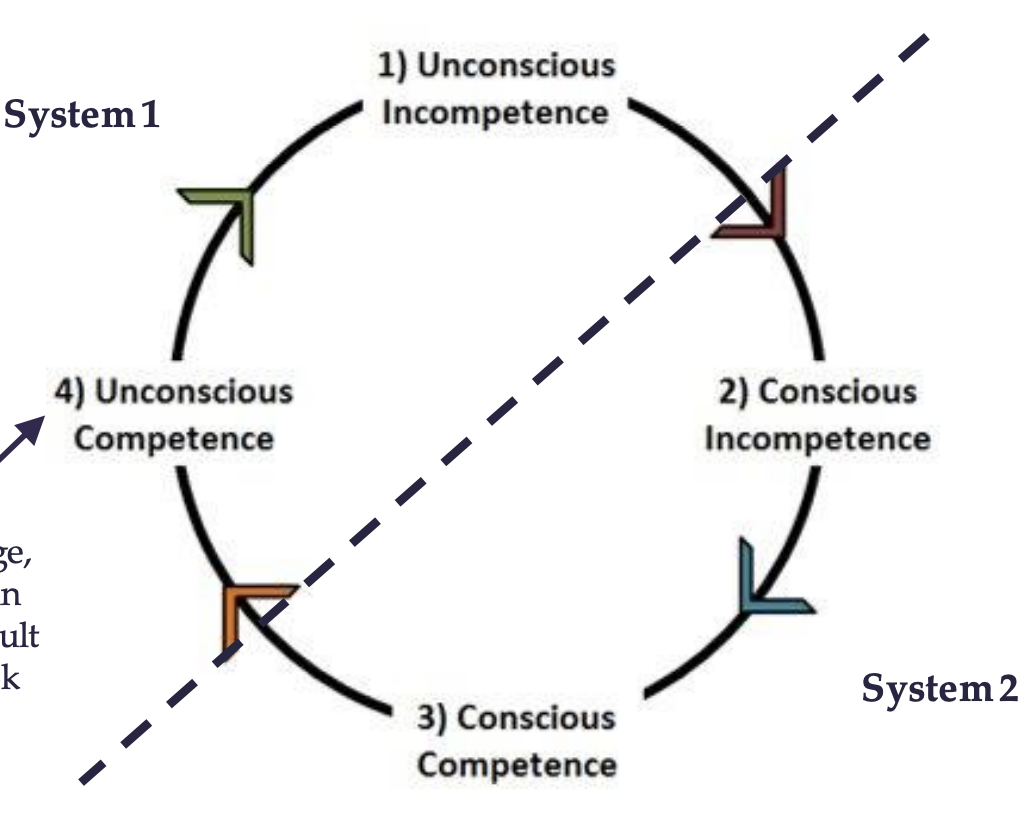
What are the four stages of competence?
Unconscious incompetence, conscious incompetence, conscious competence, and unconscious competence.
What is a cognitive bias?
A systematic distortion in how we represent objective reality.
Give an example of Ascertainment Bias.
Thinking shaped by prior expectation
Thinking a stumbling person on a Saturday night is drunk instead of having a stroke.
What are examples of affective biases?
HALT plus positive moods
Hungry, angry, late, or tired moods influencing decisions.
How can bias affect equality?
Analgesia - some medical students hold incorrect beliefs about the difference in pain between ethnic groups (Hoffman 2016)
A patient's race can affect whether or not they receive pain relief (Singhal 2016)
Boys are more likely to receive pain relief than girls (Earp 2019)
Pulse Oximetry Differences in readings from pulse oximeters between races (Sjoding 2020)
Name a few ways to deal with biases.
Be aware of biases, take breaks, invite other viewpoints, and use scoring systems/checklists cautiously(judgement needed).
Describe bounded rationality-Herbert Simon (1916 - 2001)
Decision-making is limited by our ability to gather and process information.
Humans gather a sufficient amount of information to make a satisfactory decision.
What is 'satisficing' in the context of decision making?-Herbert Simon (1916 - 2001)
Gathering just enough information to make a satisfactory decision.
What is the impact of multi-tasking?
Switching between tasks has a 'switching-cost', reducing productive time by up to 40%.
In dual process theory which system is better?
Neither system is good or bad
Which system can we not turn off?
system 1 – we’re always trying to pattern recognise
Name 3 cognitive biases?
Ascertainment bias
Bandwagon effect – “We do it like this here”
Vertical line failure – routine tasks lead to thinking in silos