Surgery Midterm (Instruments, anesthesia, dental, PE, behavior)
1/230
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
231 Terms
what are the directional terms for teeth?
Mesial - towards midline
distal - away from midline
labial - lips
lingual - tongue
buccal - cheek
occlusal - chewing surface
where does the crown meet the cementum?
cementoenamel junction
what pathology occurs at the CEJ
periodontal disease, FORLs
Job for incisors
cutting, nibbling
job for canines
holding, tearing
job for the premolars
cutting, shearing, holding
job for the molars
grinding
canine dental formula
3142, 3143
feline dental formula
3131, 3121
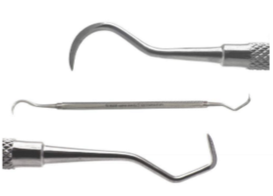
sickle scaler
purpose of sickle scaler
curved or straight, triangular head tapers to a sharp point, removes calculus above gumline and in between teeth, always pull away from the gumline
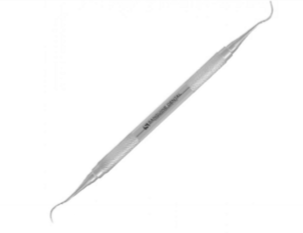
curette
purpose of the curette
U shaped, removes calculus under the gumline
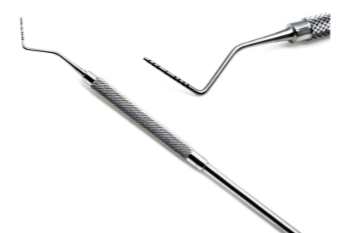
periodontal probe
purpose of the periodontal probe
used to measure pockets, tiny little ruler

explorer
purpose of the explorer
used to detect subgingival calculus, tooth mobility, FORLs, enamel defects

dental elevator
purpose of the dental elevator
use to break down periodontal ligament, regular and winged, need to be sharp

periosteal elevator
purpose of the periosteal elevator
used to make gingival flaps, must be sharp
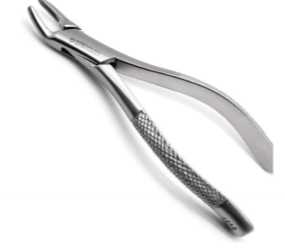
extraction forceps
purpose of the extraction forceps
used for extractions

tartar removal forceps
purpose of tartar removal forceps
used for removal of heavy calculus

mechanical scalers
COHAT
comprehensive oral health assessment and treatment
what does COHAT include
PE and work up
general anesthesia
complete sedated oral exam
record all findings before proceeding
remove supragingival calculus with scaler
remove subgingival calculus with a curette
dental radiography
extractions
dental rads of extraction sites
polish and fluoride
how is safety and infection controlled
sterile instruments
appropriate sized mouth gags
appropriate sized cuffed ET tube
gauze in back of throat
keep patient head tipped
cover eyes and catheter
PPE
comfortable position
light
support hands while working
be careful not to injure yourself
dental radiography reading
top/bottom
left or right
find landmark tooth
label teeth
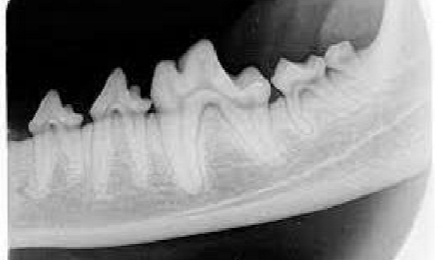
bottom - air on both sides of jaw bone
left - lower 300s
landmark - big fat tooth (308)
label teeth - 306, 307, 308, 309, 310
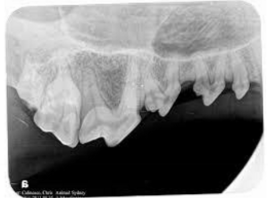
top - sinuses
right - 100s
landmark - big fat tooth - 108
label teeth - 110, 109, 108, 107, 106, 105
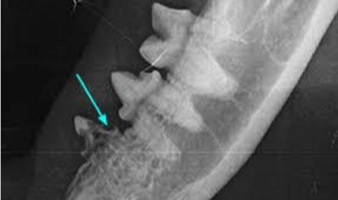
what type of tooth is the arrow pointing at
FORL
what is required for a diagnostic radiograph
entire root
surrounding alveolar bone
landmark teeth
be able to fix bad shot
what are the two dental radiograph techniques
parallel
bisecting

mayo scissors - dense tissue dissection

metzenbaum - delicate tissue dissection

iris scissors
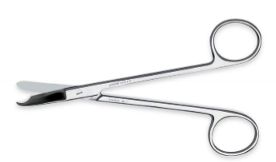
suture removal scissors
lister bandage scissors

rat tooth - 3 giant teeth

adson - 3 tiny teeth

brown-adson - sideways teeth

dressing - transverse grooves, no teeth
Allis tissue forceps

sponge forceps - holds gauze and lap sponges
Doyen Forceps - has a gap to hold intestines, GENTLE
Ferguson Angiotribe - gigantic and terrifying, CRUSHES and DESTROYS
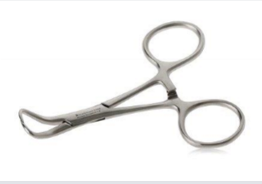
Backhaus Towel Clamp - sterility breaker
purpose of hemostats
stop bleeding

halstead mosquito - so tiny
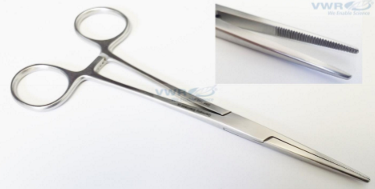
Kelly - regular size, transverse grooves at tips
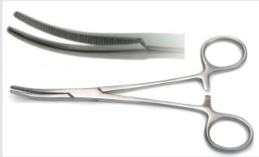
Crile - regular size, transverse grooves all the way up
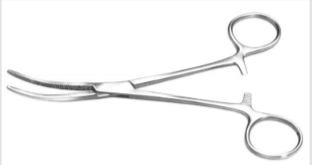
Rochester-Pean - Larger
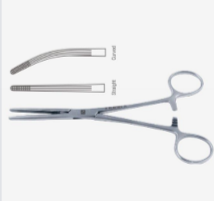
Rochester-Carmalt - double grooved at tip

Olsen-hager needle holders - scissors

mayo-hager needle holders

surgical needle rack

Spay hook

Groove director

Gallipot
What are tips for a good PE
consistent - same procedure for every pt
thorough
efficient - should be quick and easy
appropriate documentation - legal, SOAP
first step in PE
history
what is included in the history
reason for exam
vaccines
previous dx
current meds
diet
relevant medical hx
what is the second step in a PE
physical examination
what are the vitals during a PE
HR/pulse
RR
temp
hydration
perfusion
mentation
BCS
FAS
what should the eye be examined for?
d/c
chemosis
hyperemia
blepharedema
ulcer
neovascularization
corneal opacity
lens opacity
what should the ear be examined for
d/c
stenosis
pain/pruritis
erythema
what should the nares be examined for
d/c
stenosis
how should the cardiovascular system be examined
murmur - grade and location
arrhythmia - abnormal beats
how should the resp system be examined
effort
auscultation - sound
how is the GI examined?
mouth - periodontal dz
abdomen - palpation, distention, pain
anus - appearance
how should the integument be examined?
coat condition
ectoparasites
pruritis
alopecia
lesions
peripheral lymphnodes
how should the urogenital system be examined?
male - testicles, prepuce, penis
female - vulva, mammary glands
how should the musculoskeletal system be examined
gait - lameness
posture
range of motion - normal, reduced, limited
how is the neurological system examined
cranial nerves - pupillary light reflex, vision, hearing
peripheral nerves - conscious proprioception
how should the behavior be examined
in kennel/cage - cage aggressive, difficult to leash
on exam - difficult to restrain, reactive to treatments
what is the third step in performing a PE
list all problems found on physical exam; DO NOT DIAGNOSE
what is the fourth step in PE
exam presentation
what is the flow of the heart
superior vena cave —> rigth atrium —>tricupsid valve —> right ventricle —> pulmonary valve —> pulmonary artery —> pulmonary veins —>left atrium —> mitral valve —> left ventricle —> aortic valve —> aorta
how does the electricity flow through the heart
SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, R/L bundle branches, Purkinje Fibers
Where should the electrodes be placed for ecg?
LA - black
RA - white
LL - red
RL - green
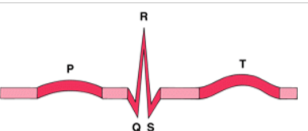
What does each part of the wave mean
P - Atria
QRS - ventricles
T - repolarization
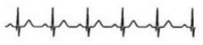
Regular sinus rhythm
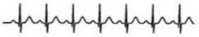
sinus tachycardia

Sinus bradycardia

sinus arrhythmia
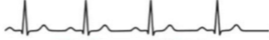
1st degree AV block - PQ interval elongated

2nd degree AV block - occasional P wave w/o QRS, can occur due to high vagal tone

3rd degree AV block - P waves and QRS waves are no longer coordinated; MUST be treated due to low cardiac output
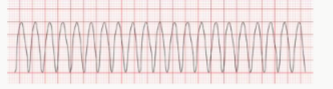
ventricular tachycardia - must be treated
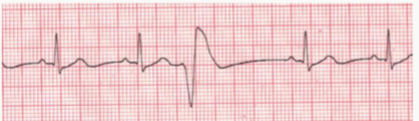
Ventricular Premature Contractions - ventricles create QRS complex before the next p wave
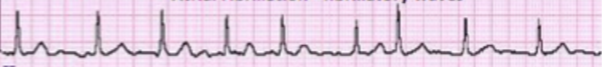
atrial fibrillation
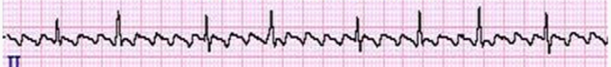
atrial flutter
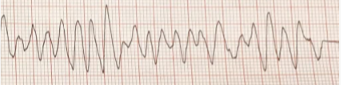
ventricular fibrillation
What are the expectations of the anesthetist
know patient, know your protocol, know your team
how should you know your patient
signalment, PE and diagnostic workup
how should you know your protocol
drugs being used (class/mechanism, timing and expected effects, route, side effects), machine and equipment setup
what and why are the pre-op analgesics given to cat/dog before a procedure
prevent central sensitization, start night before procedure
canine - rimadyl/meloxicam
feline - onsior
why are premedications given
sedation, relax the patient