nucleic acids
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
what are nucleic acids?
large long polymer molecules contained in the nucleus of the cell important in the storage and transfer of genetic information used to make proteins
what are the two types of nucleic acids?
DNA - deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA - ribonucleic acid
what are nucleic acids made of?
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
phosphorus
what is the difference between DNA and RNA?
dna contains deoxyribose sugar whereas rna contains ribose sugar containing an extra oxygen on the second carbon
what is the phosphate group?
negatively charged inorganic chemical
what do the nitrogen bases do?
make up the five different nucleotides
how are nucleotides formed?
a phosphate group, sugar and base are joined together by a condensation reaction
how are polynucleotides formed?
nucleotides are joined together through condensation reaction creating a phosphodiester bond and a sugar phosphate backbone
purine bases :
adenine
guanine
double ring structure
pyrimidine bases :
thymine
cytosine
uracil
single ring structure
how do bases bond together to create DNA molecule?
two hydrogen bonds between a and t
three hydrogen bonds between c and g
what bonds the sugar and phosphate group together?
covalent bond
structure of DNA :
many nitrogenous bases bonded by hydrogen bonds
double helix
antiparallel
sugar phosphate back bone
how to break polynucleotides down?
break the phosphodiester bonds by hydrolysis
PUAG
purine a g
t for 2
thymine has two hydrogen bonds
reasons for DNA replication :
cell division (mitosis)
reproduction (meiosis)
semi conservative DNA replication :
hydrogen bonds between bases are broken by dna helicase
double helix structure unwinds
free activated nucleotides join unpaired bases
hydrogen bonds form
dna polymerase cause phosphodiester bonds to form between nucleotides
DNA helicase :
breaks hydrogen bonds between bases and unwinds the molecule
DNA polymerase :
form covalent bonds between phosphates and sugars catalysing formation of new polynucleotide chain
DNA ligase :
joins together short sections of the lagging and leading strand of polynucleotides
single strand binding protein :
keeps dna strands separated during replication
what is the genetic code?
sequence of bases along dna coding for amino acids to form a specific polypeptide
what does it mean the genetic code is universal?
the same sequence of bases codes for the asame amino acids in all organisms
the triplet code :
three bases code for one amino acid
non overlapping :
base code is read in groups of three
degnerate :
more than one triplet can code for each amino acid
what are the three types of dna replication?
conservative
semi conservative
dispersive
which way does DNA polymerase read the polynucleotide chain?
5’ to 3’
when is mRNA created?
when a polypeptide is required the triplet code is converted into a molecule of mRNA
difference between DNA and mRNA?
mRNA single stranded
contains ribose instead of deoxyribose
contains uracil
mRNA is non overlapping :
each base is only part of one codon coding for one amino acid
protein synthesis - transcription :
dna helicase breaks hydrogen bonds
rna polymerase matches complementary rna nucleotides
c-g and a-u
mRNA is formed
dna behind rna rejoins double helix
when rna polymerase reaches stop codon the chain is terminated
pre mRNA detaches leaving through nuclear pore
mRNA :
used to transfer the dna code to the cytoplasm
complementary to dna code
in cytoplasm associates with ribosomes
determines sequence of amino acids
protein synthesis - translation :
mRNA attaches to ribosome
tRNA attaches with complementary anticodon
tRNA is attached to amino acid
ribosome moves along mRNA
enzymes and ATP are used to form peptide bond between amino acids
repeated until a stop codon
features of tRNA :
amino acid attachment site
hydrogen bonds
anticodon
nucleotides
each amino acid has a different anticodon
clover shaped
what is synthesis?
the building of large complex molecules from smaller ones e.g. protein synthesis
what is transport?
pumping molecules or ions across membranes by active transport
adenosine triphosphate :
universal energy currency cells
store of potential chemical energy
hydrolysed to release chemical energy
structure of ATP :
adenine - nitrogenous base
ribose - pentose sugar
three phosphate groups
how does ATP release energy?
energy is released when bonds are formed (exothermic)
small amount of energy required to break the last phosphate groups bond
more energy released when new bonds are formed
overall net energy is released
properties of ATP :
small - easily transportable
water soluble
immediate energy source
small quantities so energy is not wasted
easily regenerated
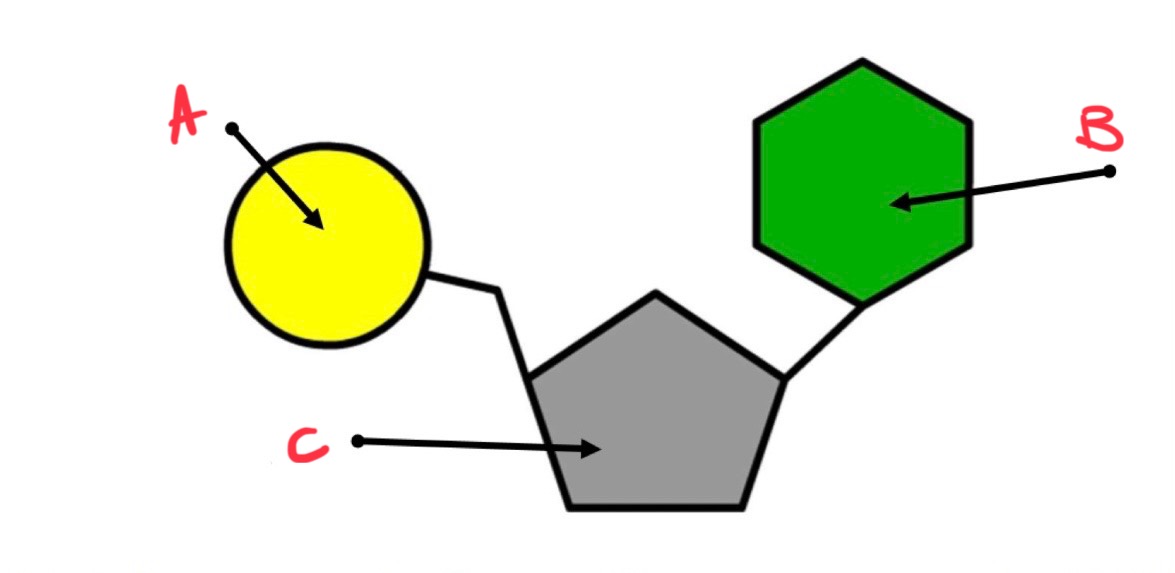
what is a?
phosphate group
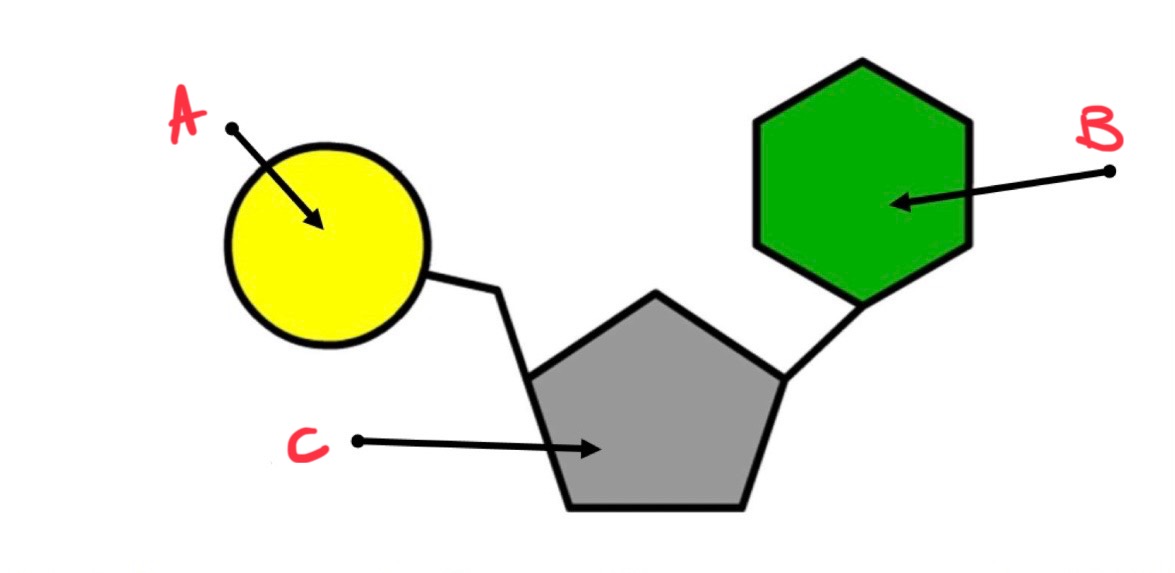
what is b?
nitrogen containing base
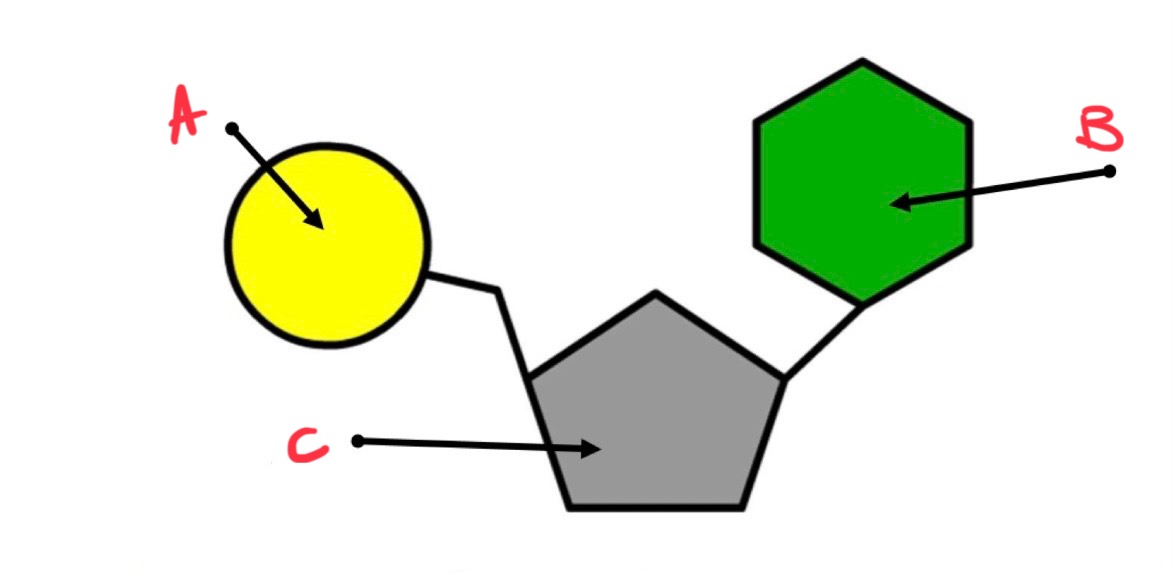
what is c?
pentose sugar