Tissue Types and Characteristics in Anatomy
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Epithelial
Covers and lines the body, passageways, and forms glands.
Connective
Found throughout the body and helps connect tissues.
Muscle
Found in skeletal muscles, walls of hollow organs, in the heart, and other locations.
Nervous
Primary component of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
Cellularity
Tightly packed cells; minimal ECM between cells.
Polarity
Apical and basal surface.
Attachment to a basement membrane
Thin layer but composed substances that act like 'glue.'
Avascularity
Lacks blood vessels.
Extensive innervation
Contains nerves to detect changes in the environment.
High regeneration capacity
Frequent cell division from deepest epithelial cells (stem cells).
One layer epithelium
We say it is simple.
Two or more layers epithelium
We say it is stratified.
Flat cell shape
We call it squamous, and its nucleus is also flat.
Cube-like cell shape
We then call it cuboidal, and its nucleus is round.
Column-like cell shape
We then call it columnar, and its nucleus is elongated.
Column-like appearance with multiple layers
We call those pseudostratified.
Simple squamous epithelium
Thin barrier, rapid filtration and diffusion; air sacs in lungs.
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Absorption and secretion; lining of kidney tubules.
Ciliated simple columnar epithelium
Secretion of mucus and movement by cilia; lining of uterine tubes.
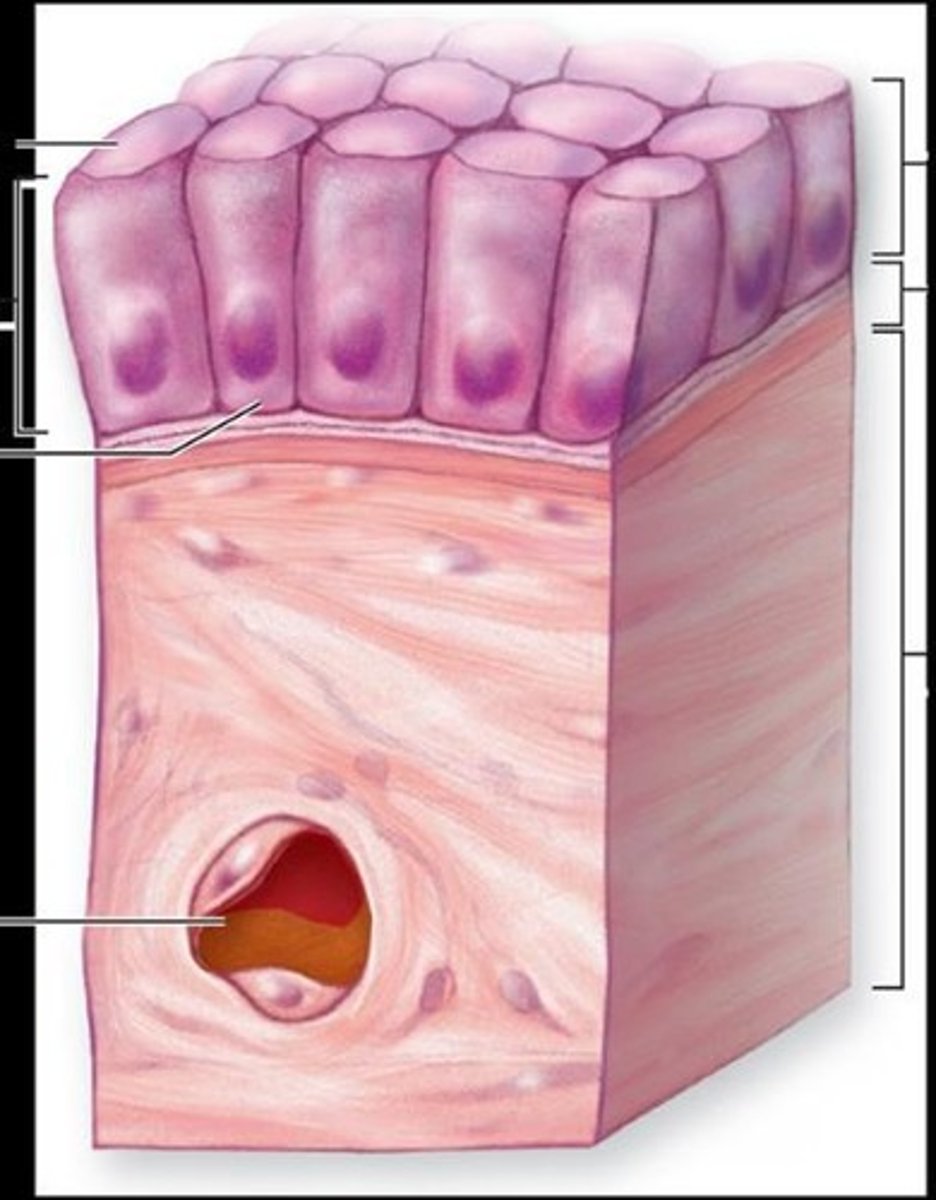
Nonciliated simple columnar epithelium
Absorption and secretion; lining of most digestive organs.
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Secretion of mucus and movement by cilia; lining of airways.
Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
Protection of underlying tissue; epidermis of skin.
Stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium
Protection of underlying tissue; lining of MAVE.
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Protection and secretion; ducts of most exocrine glands.
Stratified columnar epithelium
Protection; rare - lining of part of male urethra.
Transitional epithelium
Accommodates volume change; lining of urinary bladder.
Glands
Can be either individual or multicellular; their goal is to secrete substances.
Label A
The part that secretes substances.

Label B
The area where secreted substances travel.
Exocrine glands classification
Can be classified anatomically and physiologically.
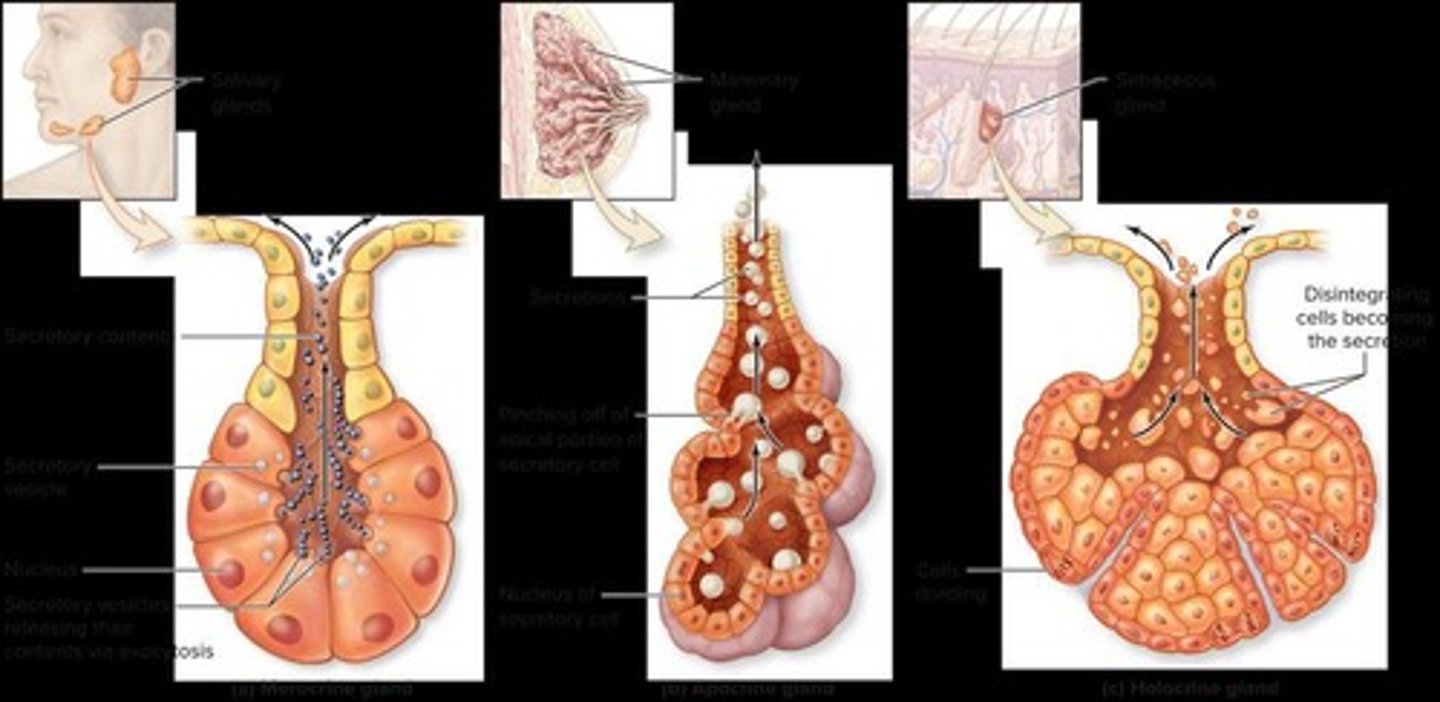
Anatomical classification
Based on whether the glands have branches.
Unbranched glands
Are referred to as simple.
Branched glands
Are referred to as compound.
Physiological classification
Based on how their substances are secreted.
Molecular material
Produced by connective tissue cells.
Types of connective tissue
Include loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, and specialized connective tissue.
Protein fibers
Found in connective tissue.
Loose connective tissue types
Include areolar, adipose, and reticular connective tissue.
Areolar connective tissue
Binds skin and some epithelial to deeper tissue.
Adipose connective tissue
Stores lipids, an energy fuel source.
Reticular connective tissue
Creates a meshwork of 'nets' to filter.
Dense connective tissue types
Include regular, irregular, and elastic connective tissue.
Regular dense connective tissue
Resists stress in one direction.
Irregular dense connective tissue
Resists stresses in all directions.
Elastic dense connective tissue
Can stretch, but more importantly, it also recoils.
Types of cartilage
Include hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage.
Hyaline cartilage
Provides a nearly frictionless surface for bones.
Fibrocartilage
Weight-bearing and resists compression.
Elastic cartilage
Maintains shape of structure; stretches and recoils.
Superficial fascia
Also called the subcutaneous layer.
Superficial fascia composition
Composed of both loose and dense connective tissue.
Dermis
Deep to the epidermis, composed of two layers.
Papillary layer
Immediately deep to the stratum corneum and made of loose connective tissue.
Functions of the skin
The 8 functions of the skin include protection, sensation, temperature regulation, excretion, secretion, vitamin D synthesis, immune defense, and water resistance.
Nail plate
The hard, visible part of the nail.
Nail bed
The skin beneath the nail plate.
Nail matrix
The tissue under the base of the nail that produces cells that become the nail plate.
Zones of hair
The three zones along the length of hair are the bulb, shaft, and root.
Sudoriferous glands
Sweat glands that can be divided into eccrine glands and apocrine glands.
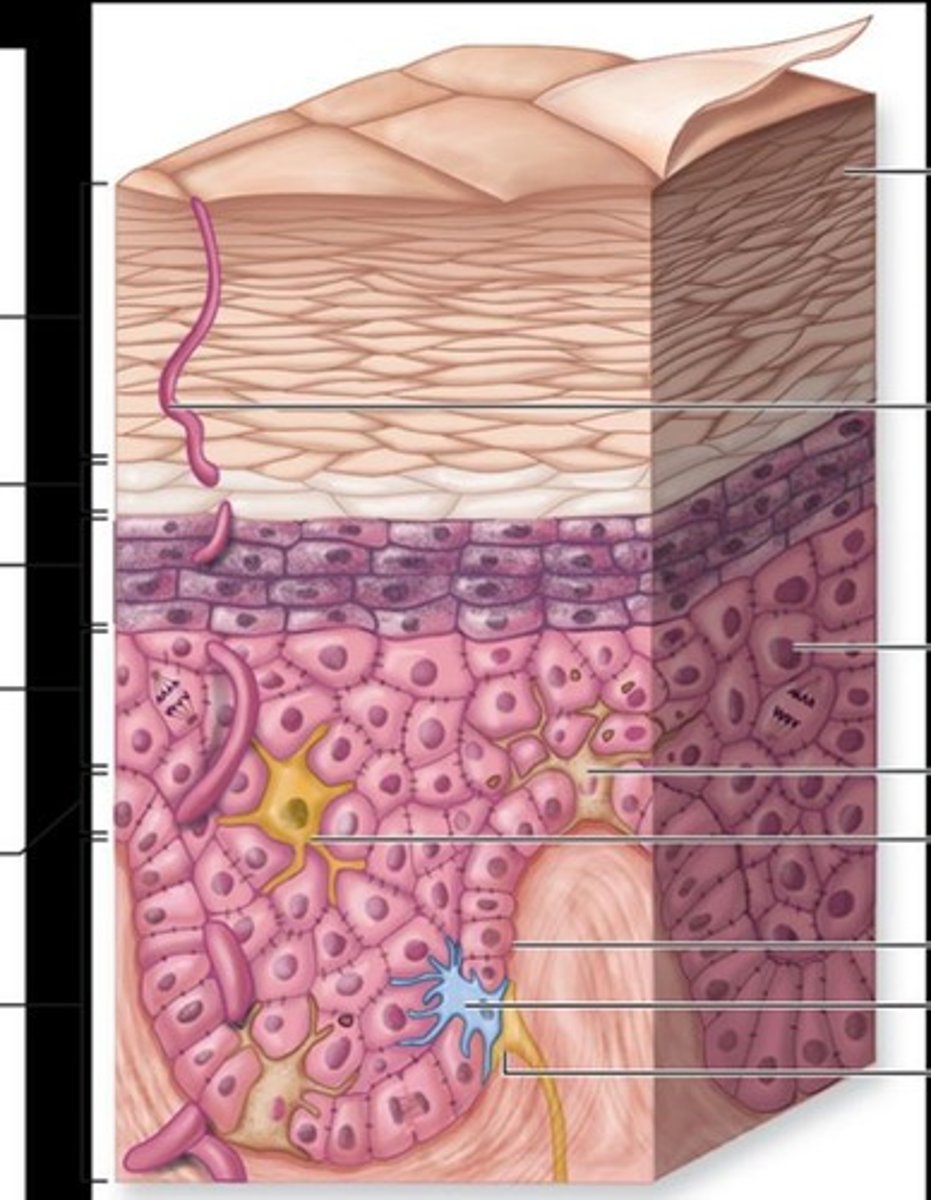
Repetitive stress
Can stimulate cell division in the stratum basale.
Sebaceous glands
Oil glands that can be classified as holocrine glands.
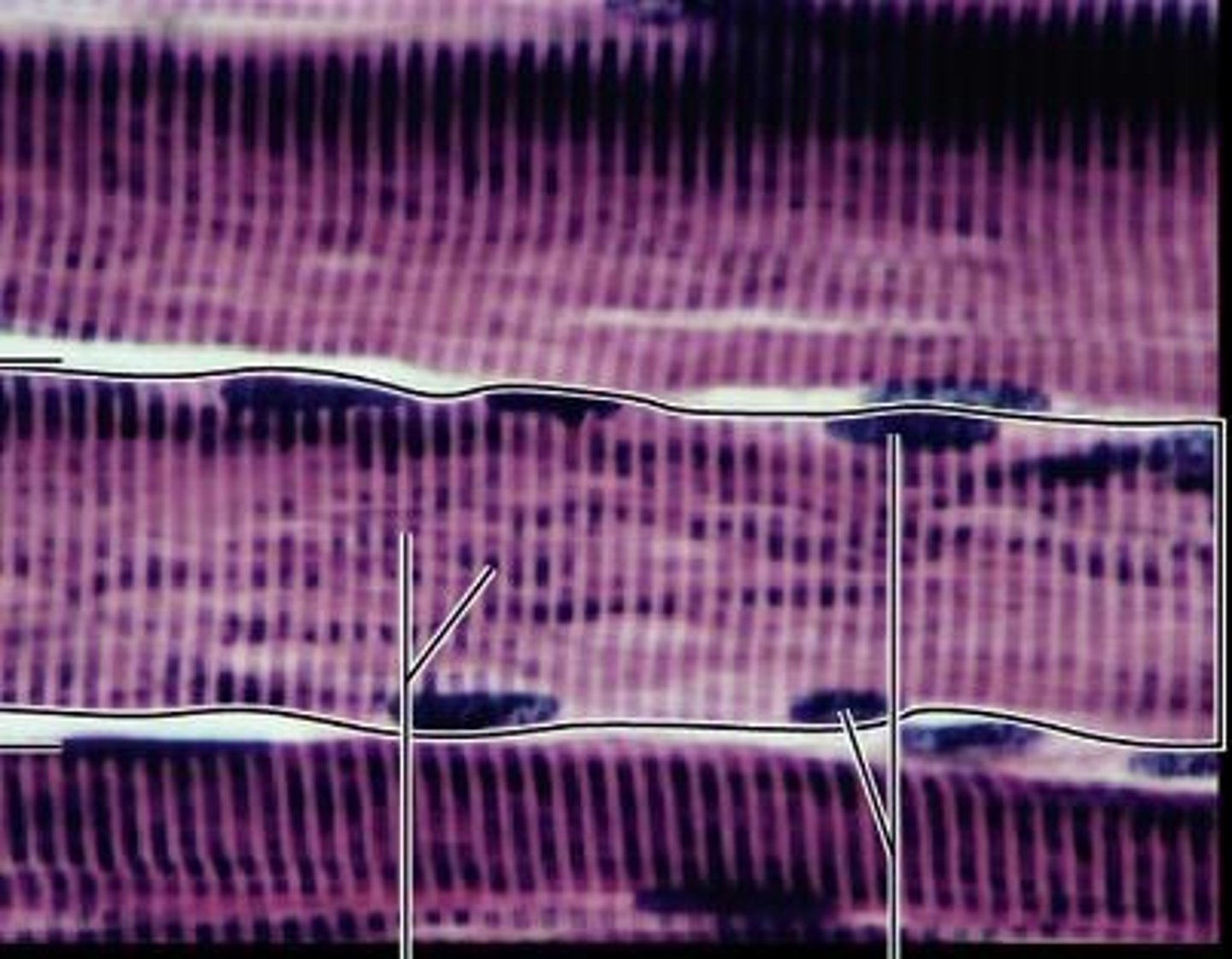
Skeletal muscle unit
The smallest functional unit of skeletal muscle is the sarcomere, composed of repeating myofibril structures.

Cell repair methods
Cells can be repaired through regeneration (replacement of damaged/dead cells) or fibrosis (filling a gap with scar tissue).
Somatic neurons
Nerve cells that transmit nerve signals from the brain or spinal cord to control skeletal muscle activity.
Neuromuscular junction
The connection point where the neuron meets the muscle fiber.
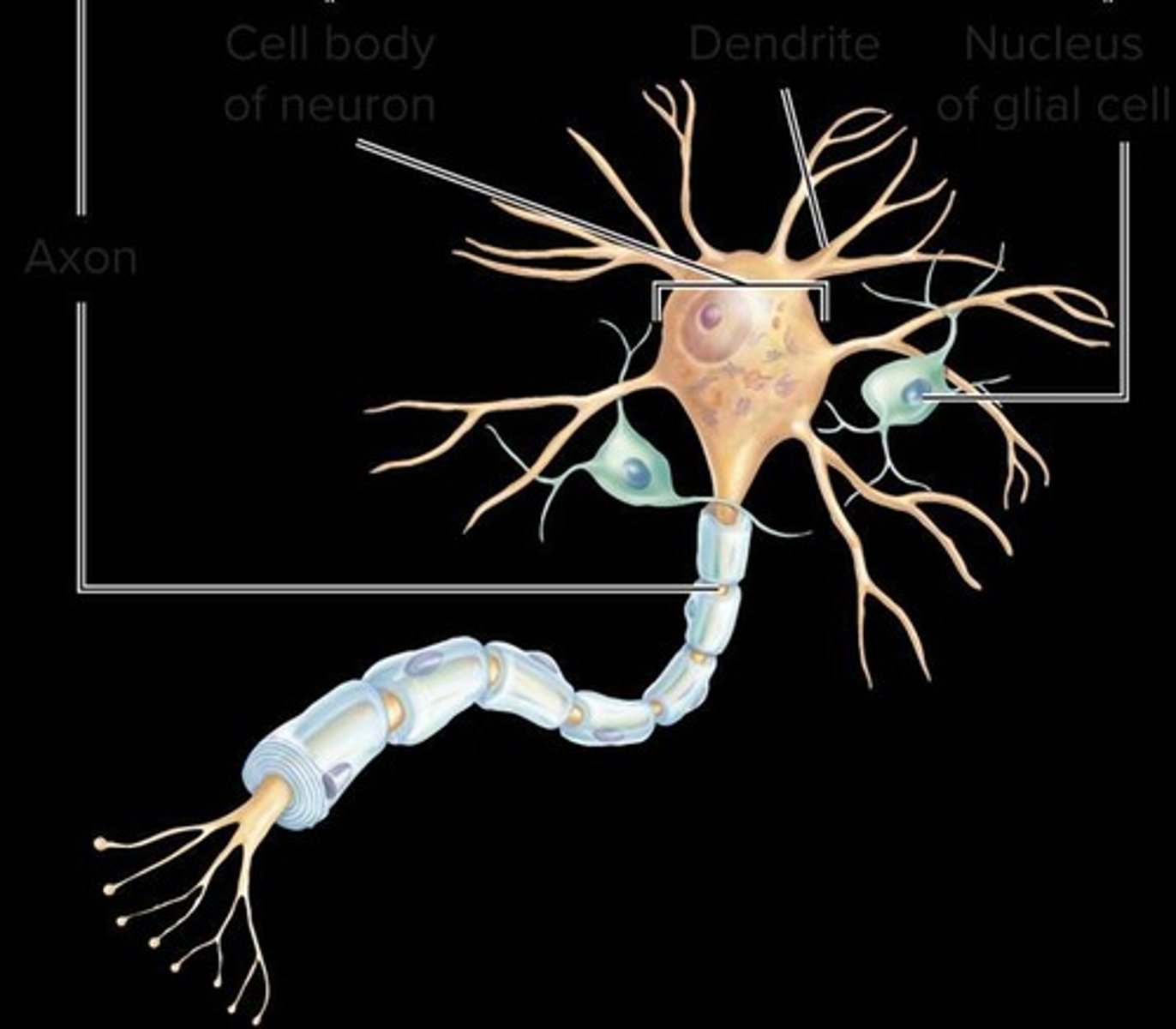
Characteristics of neurons
The 5 characteristics of neurons include excitability, conductivity, secretion, longevity, and amitotic nature.
Nervous tissue cells
Neurons are nervous tissue cells that collect information, process it, and initiate responses.
Glial cells of the central nervous system
The 4 glial cells include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells.
Glial cells of the peripheral nervous system
The 2 glial cells include Schwann cells and satellite cells.
Myelination process
The process by which part of an axon is wrapped in myelin is called myelination.
Myelin composition
Myelin is an insulating cover made of mostly lipids and some proteins.
Myelinating cells in CNS
In the central nervous system, the cells that myelinate axons are called oligodendrocytes.
Myelinating cells in PNS
In the peripheral nervous system, the cells that myelinate axons are called Schwann cells.