Math 150 trig memorization
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
complementary angle
An angle that, when added to another angle, equals 90 degrees. Complementary angles can be adjacent or separate.
supplementary angle
An angle that, when added to another angle, equals 180 degrees. Supplementary angles can also be adjacent or separate.
co-terminal angle
An angle that shares the same terminal side as another angle but differs by a full rotation of 360 degrees.
degrees to radians
radians = degrees × (π/180).
radians to degrees
degrees = radians × (180/π).
average velocity
v(bar) = displacement/time or r*(theta/t)
omega
w, average change in angle thetaover time, usually measured in radians per second.
angular velocity
v = wr
sin
opp/hyp
cos
adj/hyp
Pythagorean theorem
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides, expressed as a² + b² = c².
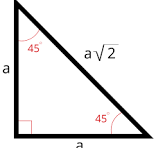
45-45-90 triangle
In a 45-45-90 triangle, the legs are of equal length, and the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the length of a leg multiplied by the square root of 2. 45 degrees = pi/4
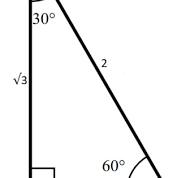
30-60-90 triangle
In a 30-60-90 triangle, the lengths of the sides are in the ratio 1:√3:2. The side opposite the 30-degree angle is the shortest, and the hypotenuse is twice that length. 30 degrees = pi/6, 60 degrees = pi/3 The side opposite the 60-degree angle is 1 times the length of the shortest side.
sin(pi/3)
In trigonometry, sin(pi/3) is equal to √3/2.
cos(pi/3)
In trigonometry, cos(pi/3) is equal to 1/2.
sin(pi/6)
In trigonometry, sin(pi/6) is equal to 1/2.
cos(pi/6)
In trigonometry, cos(pi/6) is equal to √3/2.
cos(0)
In trigonometry, cos(0) is equal to 1.
cos(pi/4)
In trigonometry, cos(pi/4) is equal to √2/2.
cos(pi/2)
In trigonometry, cos(pi/2) is equal to 0.
sin(0)
In trigonometry, sin(0) is equal to 0.
sin(pi/4)
In trigonometry, sin(pi/4) is equal to √2/2.
sin(pi/2)
In trigonometry, sin(pi/2) is equal to 1.
Period of sin
is 2π, meaning it repeats every 2π units along the x-axis.
period of cos
The period of the cosine function is 2π, meaning it repeats every 2π units along the x-axis.
sin domain and range
The domain of the sine function is all real numbers, while its range is from -1 to 1. is an odd function
cos domain and range
The domain of the cosine function is all real numbers, while its range is from -1 to 1. is an even function
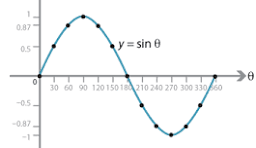
the graph of sin
is a wave that oscillates between -1 and 1, starting at the origin and moving in a smooth manner with a period of 2π.
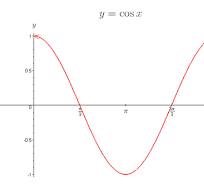
the graph of cos
is a wave-like curve that oscillates between -1 and 1, starting at 1 when x = 0. It is periodic with a period of 2π.
frequency
B
period T
2pi/b
amplitude
IAI
phase shift
bt+c
vertical shift
d
tan
opp/adj
csc
hyp/opp, opposite of sin
sec
hyp/adj, opposite of cos
cot
adj/opp, opposite of tan
sec
1/cos
csc
1/sin
tan
sin/cos
cot
cos/sin
sec(0)
1
sec(pi/6)
2/√3 or 2√3/3
sec(pi/4)
√2
sec(pi/3)
2
sec(pi/2)
undefined
csc(0)
undefined
csc(pi/6)
2
csc(pi/4)
√2.
csc(pi/3)
2√3/3
csc(pi/2)
1
tan(0)
0
tan(pi/6)
1/√3 or √3/3
tan(pi/4)
1
tan(pi/3)
√3
tan(pi/2)
undefined
cot(0)
undefined
cot(pi/6)
√3
cot(pi/4)
1
cot(pi/3)
1/√3 or √3/3
cot(pi/2)
0
graph of sec
is a curve that represents the secant function, showing vertical asymptotes at odd multiples of π/2 where the cosine is zero.
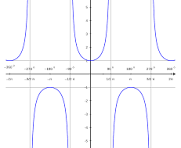
graph of csc
is a curve that represents the cosecant function, showing vertical asymptotes at integer multiples of π where the sine is zero.
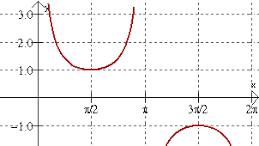
graph of tan
is a curve that represents the tangent function, featuring vertical asymptotes at odd multiples of π/2 where the cosine is zero.
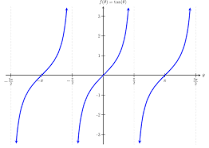
graph of cot
is a curve that represents the cotangent function, exhibiting vertical asymptotes at integer multiples of π where the sine is zero.
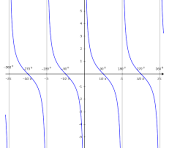
sec period
is the length of one complete cycle of the secant function, which is equal to 2π.
csc period
is the length of one complete cycle of the cosecant function, which is equal to 2π.
sec domain and range
The domain of the secant function is all real numbers except where the cosine is zero, specifically at odd multiples of π/2. The range of the secant function is all real numbers less than or equal to -1 or greater than or equal to 1. is even
csc domain and range
The domain of the cosecant function is all real numbers except where the sine is zero, specifically at integer multiples of π. The range of the cosecant function is all real numbers less than or equal to -1 or greater than or equal to 1. is odd
tan domain and range
The domain of the tangent function is all real numbers except where the cosine is zero, specifically at odd multiples of π/2. The range of the tangent function is all real numbers, as it can take any value. is odd
tan period
The period of the tangent function is π, meaning it repeats its values every π units along the x-axis.
cot domain and range
The domain of the cotangent function is all real numbers except where the sine is zero, specifically at integer multiples of π. The range of the cotangent function is all real numbers, similar to tangent. is even
cot period
The period of the cotangent function is π, indicating it repeats its values every π units along the x-axis.