7- Transport in plants (incomplete)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
dicotyledonous plants (dicots)
have broad bladed leaves and petioles (stalks)
have a network of veins
have seeds that contain 2 cotyledons (seed leaves)
have a taproot system
xylem vs phloem in electron micrographs
xylem usually larger, darkly staining and more defined vessels
phloem darker than cambium, lots of small cells, may be able to see dark spots of companion cells
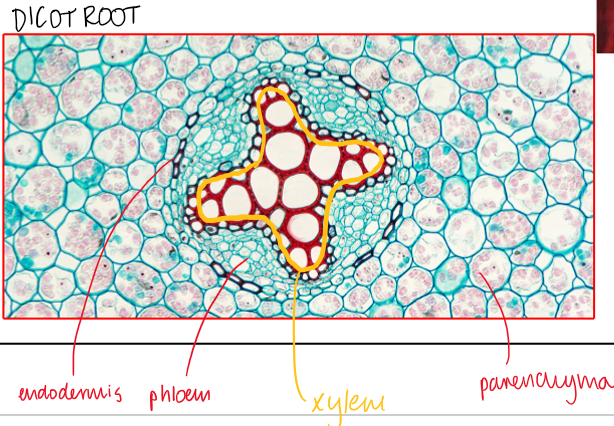
distribution of xylem and phloem in dicot root
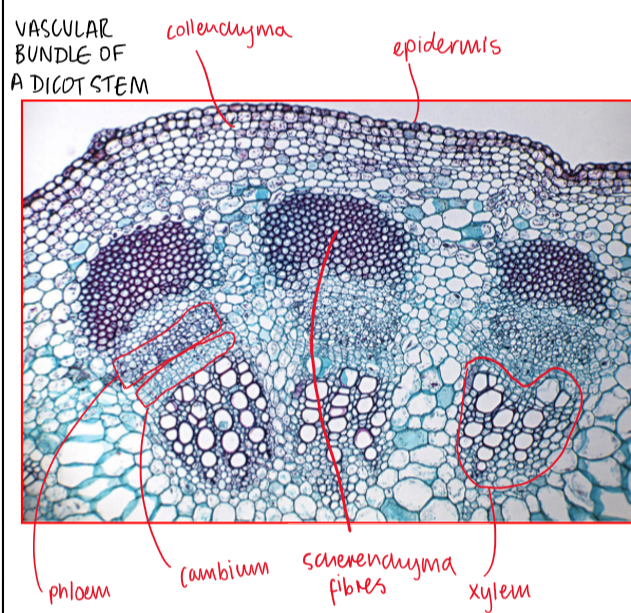
distribution of xylem and phloem in dicot stem
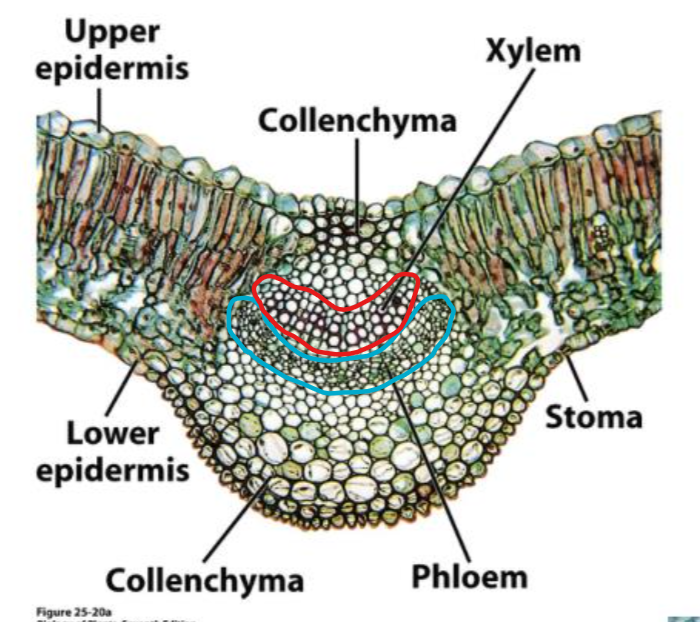
distribution of xylem and phloem in dicot leaf vein
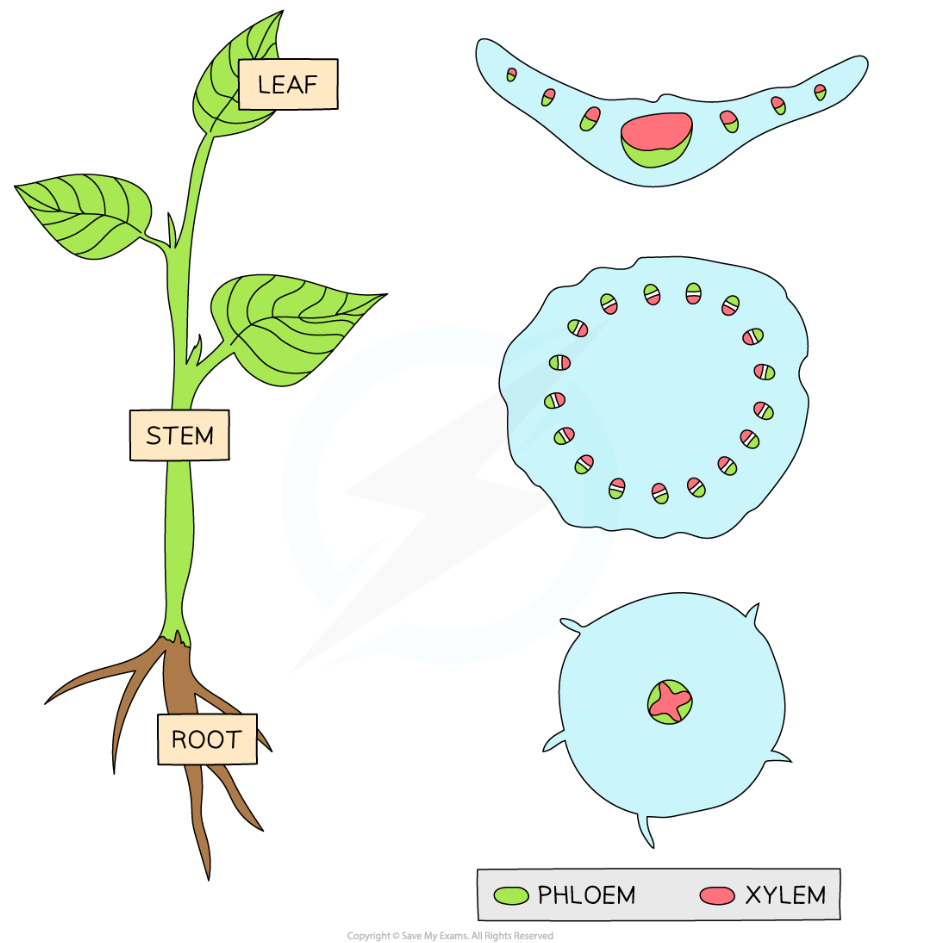
general distribution of xylem and phloem vessels
xylem usually on the inside (roots and stem), in the leaf the xylem is on the top (closes to upper epidermis)
functions of xylem vessel
vascular tissue that carries dissolved minerals and water up the plant
structural support
food storage
functions of phloem
transport organic compounds, particularly sucrose, from source to sink