STM 008 M1-M12
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
alleles
pairs of genes are called?
Trait
any characteristic that can be passed from
parent to offspring
Heredity
passing of traits from parent to offspring
Genetics
study of heredity
Genes
a hereditary unit consisting of DNA that
occupies a spot on a chromosome and determines a
characteristic in an organism.
Monohybrid cross
- cross involving a single trait
e.g. flower color
Dihybrid cross
- cross involving two traits
e.g. flower color & plant height
Alleles
two forms of a gene (dominant & recessive)
Dominant
stronger of two genes expressed in the
hybrid; represented by a capital letter (R)
Recessive
gene that shows up less often in a cross;
represented by a lowercase letter (r)
Genotype
gene combination for a trait (ex. RR, Rr, rr)
Homozygous genotype
gene combination involving 2
dominant or 2 recessive genes (ex. RR or rr); also called
pure
Heterozygous genotype
gene combination of one dominant
& one recessive allele (ex. Rr); also called hybrid
Gregor mendel
a humble monk and part time scientist
law of dominance
in a cross of parents that are pure for contrastic traits, online one form of the traid will appear in the next generation.
when two alleles are present, only one dominant and will be expressed
LAW OF SEGREGATION
During the formation of
gametes (eggs or sperm),
the two alleles
responsible for a trait
separate from each other.
Alleles for a trait are then
"recombined" at
fertilization, producing
the genotype for the
traits of the offspring.
two alleles are each gene are placed in different gametes.
LAW OF INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT
states that the alleles of two (or
more) different genes get sorted
into gametes independently of
one another. In other words, the
allele a gamete receives for one
gene does not influence the
allele received for another gene.
DIHYBRID CROSS
the inheritance of one gene doesn't affect the inheritance of any other gene.
Dominance or Recessiveness.
Mendelian Genetics describes inheritance patterns based on
NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS
•CODOMINANCE
•INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE
•MULTIPLE ALLELES
CO-DOMINANCE
•Both traits are dominant, and show up in the phenotype together. Co means "together"
•both alleles are expressed equally in the phenotype of the heterozygote.
like spotted cow
INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE
The hybrid (heterozygous) offspring displays a THIRD Phenotype!! Neither trait is completely dominant, as a result, there appears to be a blending phenotype.
example red and white flower created a pink flower.
MULTIPLE ALLELES
•When more than two different form of given gene exist in a species they are called as multiple allele"
•Multiple alleles always influence the same character.
•more than 2 alleles for that trait must exist in the population.
•Examples of Multiple Alleles
•a) Blood group (ABO) in human.
•b) Coat color in mice.
•c) Coat color in rabbit.
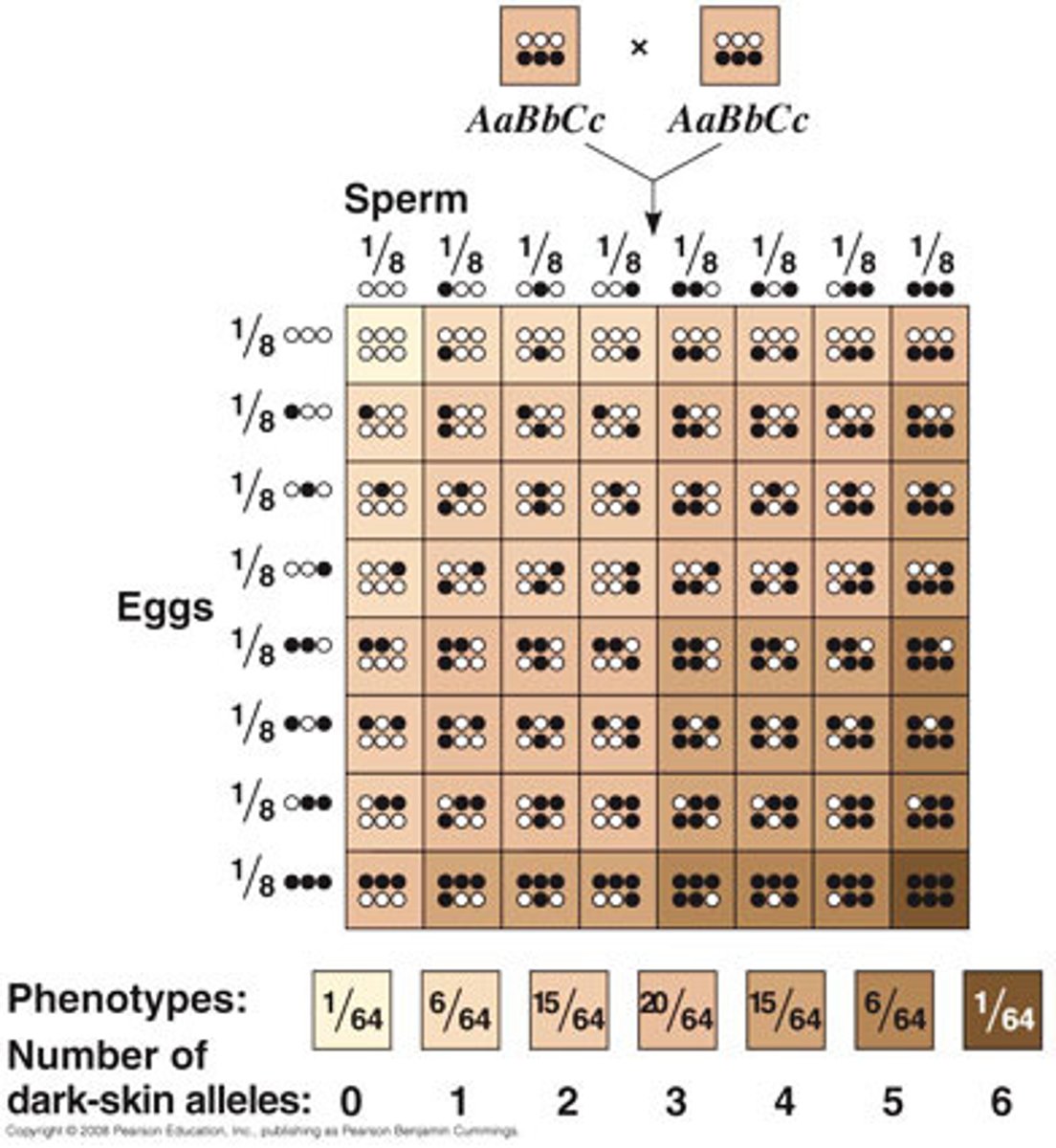
POLYGENIC TRAIT
Require more than one gene (allele) to determine trait.
Skin tone is determined by 4-6 genes—that means that there may be six different chromosomes involved!
Recombination
referes to the exchange of alleles
In meiosis results to variation in the genome of gametes; rhe sperm cells and egg cells.
The result is sex linked trait.
recombinants
recombination results in new combinations of parent characteristics in the off spring they are called?
X and Y chromosomes
What do you call the sex chromosome?
X linked trait
Is a sex linked trait where the gene or allele for the trait is found on the X chromosome.
Y linked trait
Is a sex linked trait where the gene or allele or found in the Y chromosome
Color blindness and Hemophilia
Effects of X linked recessive trait
Females and only carriers? Male is the most affected one.
Remember
Hypertrichoeis Pinnae Auris
Effects of Y linked
1,098 human X linked genes
Most of them code for something other than female anatomica traits.
Queen victoria of Englang
Was a carrier of the gene for hemophilia.
Sex linked inheritance
some traits are located on the sex chromosomes, so the inheritance of these traits depends on the sex of the parent carrying the trait
Sex determination
is determined by the sex chromosomes contributed to the zygote by the sperm and the egg
an egg can donate an x, a sperm can donate X or Y
Sex linked
carried on the x chromosome. this is probably because of the X chromosome is much larger than Y chromosome.
Male pattern baldness,
red-green color blindness
(people with
deuteranomaly and protanomaly),
myopia,
night blindness
hemophilia
EXAMPLES OF SEX-LINKED TRAITS and DISORDERS
MEN! Genes for certain traits are on the X
chromosome only...
Who is usually affected by Sex-Linked Disorders?
Pisium sativum
Mendel's experimental material was?
Variation
tendency of offspring to differ from parents is called?
Phenotype
refers to the actual appearance of an individual
Color
allele
one of several forms of gene
•a form of a gene which codes for one possible outcome of a phenotype
punnett square
use to predict the genotype of alleic combinationg
law of dominance
law of segregation
law of independent assortment
three laws of gregor mendel
dominant trait
law of dominance
one of the traits will always suppress the other, thereby expressing itself
recessive trait
it is the suppressed trait
law of segregation
two alleles to form a gamete, which is mother and father
Homozygous dominant
two capital letters
Homozygous recessive
two small letters
DIHYBRID CROSS
a cross between two parents that differ by two pairs of alleles (AABB x aabb)
Dihybrid
An individual that is heterozygous for two pairs of alleles
Central dogma (1958)
Is the process by which the instructions in DNa are converted into a functional product.
What year too?
Francis Crick
Who discovered the structure of DNA?
Transcription and Translation
Gene expression has two stages
Gene expression
Process which DNA instructions are converted into the functional product is called?
Two allele
An individual inherits two allele
Multiple alleles
Have multiple (more than two) alleles, an example is ABO blood type in humans
Polygenic Characteristics
Are controlled by more than one gene.
Reconv
Cellular structure
Heredity
Homeostasis
Movement
Adaptation
Growth
Reproduction
Respond to stimuli
what does chhomagrr stands for?
Apoptasis
Lysosome Suicide bomb
Heredity
Traits that are passed down through a family.
traits, disease, gene
Homeostasis
sweat perspiration
Glucagon
What balances low sugar
Insulin
when blood sugars are high, the pancreas releases insulin. Insulin helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, lowering blood sugar levels.
movement
releases toxin like urine and weat
helps with locomotion
to reproduce
Adaptation
irritability - response to environmental change in order to adapt
growth
maturity goes thru various stages in order to mature
Reproduction
asexual -
sexual
Fragmentation (Starfish)
An organism breaks into pieces, and each piece grows into a new organism.
Regeneration
The process of regrowing lost or damaged body parts.
Planarians can regenerate their entire body from a small fragment.
starfish also experience this, it regenerates too
Budding (hydra)
A new organism grows from a bud on the parent organism.
Binary Fission (Bacteria)
single organism divides into two identical organisms.
Respond to stimuli
It refers to the ability to detect and react to changes in the environment
sphorophyte
organism that produces spores
gametophyte
sperm or egg cell or known as gametes
Parthenogenesis
is a form of asexual reproduction where an egg develops into an organism without being fertilized by a sperm.
exmaple is wasps, ants, bees
autotrophic
organisms that can produce their own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals.
Example:
Plants: They use photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy, producing their own food. glucise and oxygen
Algae: Similar to plants, algae also perform photosynthesis to create their own food.
Photoautotrophs Plants
are organisms that can produce their own food using light energy through the process of photosynthesis. T=
Villi
absorb nutrients from digested food as it passes through the small intestine. The nutrients then enter the bloodstream and are transported to various parts of the body for use.
Thermophiles
are microorganisms that thrive in extremely hot environments
Chemoautotrophs
e organisms that obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic substances, such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, or iron, and use this energy to fix carbon dioxide into organic compounds. They do not rely on sunlight for energy, unlike photoautotrophs.
Extremophiles
re organisms that thrive in extreme environmental conditions that are typically hostile to most life forms. These conditions can include extreme temperatures, acidity, salinity, or pressure.
small intestine
absorbs nutrients
Xerophytes (cactus)
plants IN DESERT
saprophytic fungi
organisms obtain nutrients by decomposing dead and decaying organic matter.
Holozoic
organisms ingest solid food, which is then digested internally. This mode of nutrition involves several stages: ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion.
parasitic
refers to a relationship where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, and benefits at the host's expense.
plants absorbs nutrients thru roots
did you know
xylem
Transports water and minerals from roots to leaves. Moves in one direction (upwards).
Phloem
Transports sugars and nutrients throughout the plant. Moves in both directions (up and down).
plant stem
negative tropism
plant roots
postive tropism
atom
molecule
organelle
cell
tissues
organs
organ system
organism
population
community
ecosystem
biosphere
levels of organization
Aerotaxis
follows aroma thru air
Phototaxis
moth, night insects for navigation