BICH 410: Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sivaram 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Carbs can be divided into _ and _ isomers
D and L
Epimers are:
a type of diastereomer that differ at only one specific carbon atom. They are a subtype of stereoisomers related to carbohydrates.
Cyclization occurs when
A linear sugar molecule forms a ring structure. -OH of C5 attacks the aldehyde or ketone group at carbon 1 to form a hemiacetal or carbon 2 to form a hemiketal.
Carbohydrates can go through _____ reactions
Oxidation
Reduction
Esterification
Amination
Cyclization
Polysaccharides
Multiple monosaccharides linked together by glycosidic bonds.
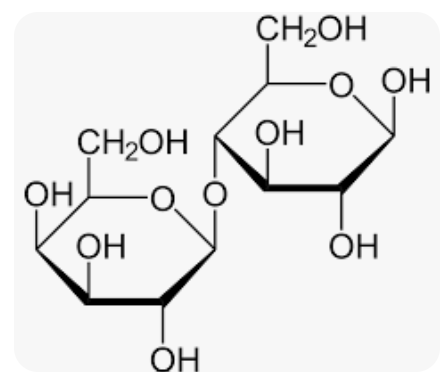
Lactose’s Glycosidic Linkage:
B(1—>4)
Reducing sugar
Bond between Galactose and Glucose
Lactase
Enzyme that breaks up the B(1—>4) glycosidic bond
Hydrolase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of lactose into glucose and galactose.
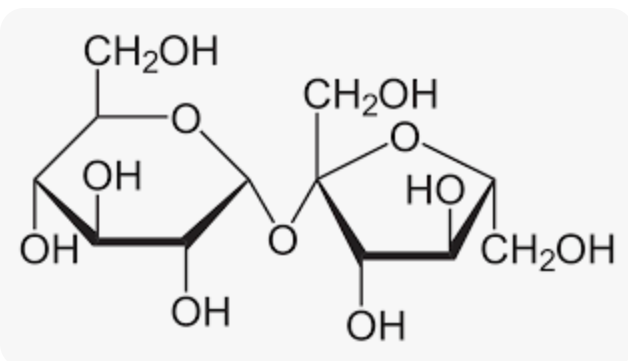
Sucrose’s Glycosidic Linkage:
a(1—>2)
Non-reducing sugar
Bond between Glucose and Fructose
Homopolysaccharides:
Polysaccharides made up of only one type of monosaccharide unit.
Heteropolysaccharides:
Polysaccharides composed of two or more different types of monosaccharide units.
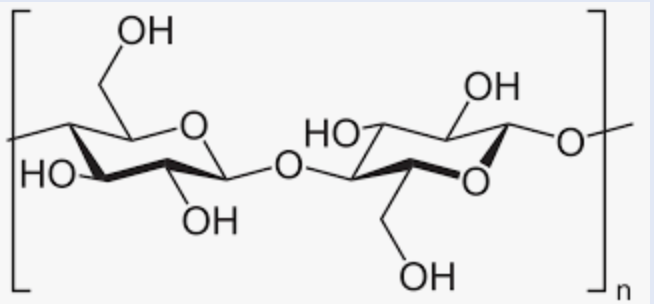
Cellulose’s Linkage:
b(1—>4) glycosidic bonds
Homopolysaccharide (Composed of glucose units)
Cellulase
An enzyme that breaks down cellulose into glucose units by hydrolyzing the beta(1—>4) glycosidic bonds.
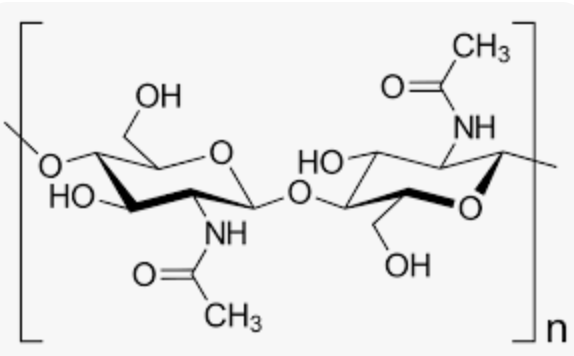
Chitin’s Linkage:
B(1—>4)
Homopolysaccharide composed of N-acetylglucosamine units.
Starch’s Linkage:
a(1—>4) mainly and can form a(1—>6) glycosidic bonds
Homopolysaccharide composed of glucose units.
3D, which stores glucose efficiently
Glycogen Linkage:
a(1—>4) and a(1—>6) linkage
Present in animal cells for energy storage.
a-amylose’s Linkage:
a(1—>4) linkage
Homopolysaccharide composed of glucose units, a component of starch.
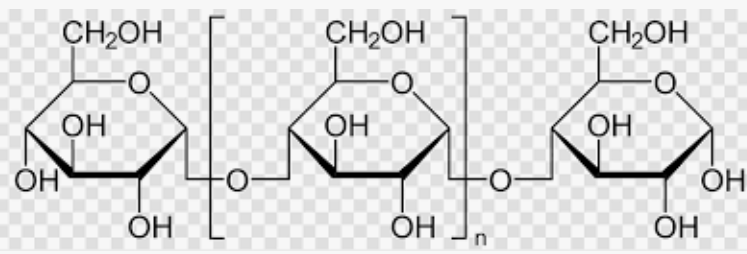
Amylopectin Linkage:
a(1—>4) and a(1—>6) linkageIt differs from amylose due to its branched structure, which allows for more efficient glucose storage.
A branched homopolysaccharide made of glucose units, also a component of starch.
How is starch broken down?
Amylase hydrolyzes the a(1—>4) glycosidic bond
a-glucosidase hydrolyzes on glucose residue at time
Debranching enzyme hydrolyzes both a(1—>4) and a(1—>6) glycosidic bonds
Glycogen Breakdown:
Glycogen phosphorylase breaks down the a(1—>4) glycosidic bonds from NON-REDUCING ENDS
Glycogen debranching enzyme will cleave a(1—>6) bonds
Glycosaminoglycans
Important components of connective tissue and synovial fluid
Component of cell surface structure and extracellular substance in blood vessel walls and brain
Wound healing
Development
Examples of Glycosaminoglycans
Heparin, Hyaluronate, Chondroitin sulfate, and Keratan sulfate
Joint Supplements
Glucosamine and chondroitin are part of normal cartilage
Cartilage acts as a cushion between bones in a joint
Dasuquin:
Two drugs that work together to cause a great effect for joint health and mobility by combining glucosamine hydrochloride and low MW chondroitin sulfate.
Glycoproteins:
Proteins with carbohydrate components
Can be O-glycosidic or N-glycosidic bonds
Fatty Acids:
Simple fats
Made up of a carboxylic acid and long hydrocarbon tail
Amphipathic
Structurally ordered aggregates
Saturated Chains:
Can pack tightly together and form rigid, organized aggregates
Unsaturated Chains:
Bend (because of double bonds) and pack in a less ordered way
Misshaped, forming kinks and changes in shape
Flexible
Cis configuration
Stearic Acid
Saturated
18 hydrocarbon chain
Oleic Acid:
Unsaturated
18 hydrocarbon chain with 1 double bond at carbon 9
Linoleic Acid:
Unsaturated
18 carbon chain with 2 double bonds at carbons 9 and 12
a-Linolenic Acid:
Unsaturated
18 carbon chain with 3 double bonds at carbon’s 9, 12, and 15
Why are trans-fats bad?
Trans fats are bad because these fats will get stuck in adipose fat tissues and can lead to higher levels of LDL cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
We don’t have the machinery to break it down
Palmitic Acid:
Saturated
16 carbon chain with no double bonds
Myristic Acid:
Saturated
14 carbon chain with 0 double bonds
Melting Point Rules:
More carbons = Higher the melting temp
More double bonds = Lower the melting temp
Triacylglycerols
Nonpolar
Water insoluble
Glycerol backbone with three fatty acid chains.
Energy reservoirs
Phospholipids —> Glycerophospholipids
Amphiphilic
Can contain a head group after phosphate
Major component of biological membranes
Phospholipids —> Sphingolipids
Composed of a sphingosine backbone with one fatty acid and a phosphate and a choline head group