biochem exam 1
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
201 Terms
amino acids
protein monomer
glucose
carbohydrate monomer (most common)
fatty acids
lipid monomer
nucleotide
- nucleic acid monomer
- nitrogenous base + 5C sugar (ribose) + phosphate
nucleoside
nitrogenous base + 5C sugar (ribose)
purines
- bicyclic structure
- adenine and guanine
pyrimidines
- unicyclic structure
- uracil, thymine, and cytosine
phosphate or phosphoryl group
a functional group common to both lipids and nucleic acids
thymine
pyrimidine that pairs with adenine in DNA
uracil
pyrimidine that pairs with adenine in RNA
cytosine
pyrimidine that pairs with guanine in DNA and RNA
guanine
purine that pairs with cytosine in DNA and RNA
adenine
purine that pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA
nitrogenous bases
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, uracil
rotation around a single bond
> double bond > triple bond
bulk elements
gram quantities
trace elements
milligram or micrograms
carbonyl (aldehyde and ketone)
carbohydrate functional groups
imidazole
histidine functional group
carboxylate
fatty acid functional group
disulfide
cystine functional group
sulfhydryl
cysteine functional group
thioester
acetyl CoA functional group
thioether
methionine functional group
phosphoanhydride
ATP functional group
stereoisomers
have different physical properties
geometric isomers
- have different physical and chemical properties
- cis vs trans
cis isomers
similar substituents or functional groups on the same side of the double bonded carbon atoms
ex: maleic acid
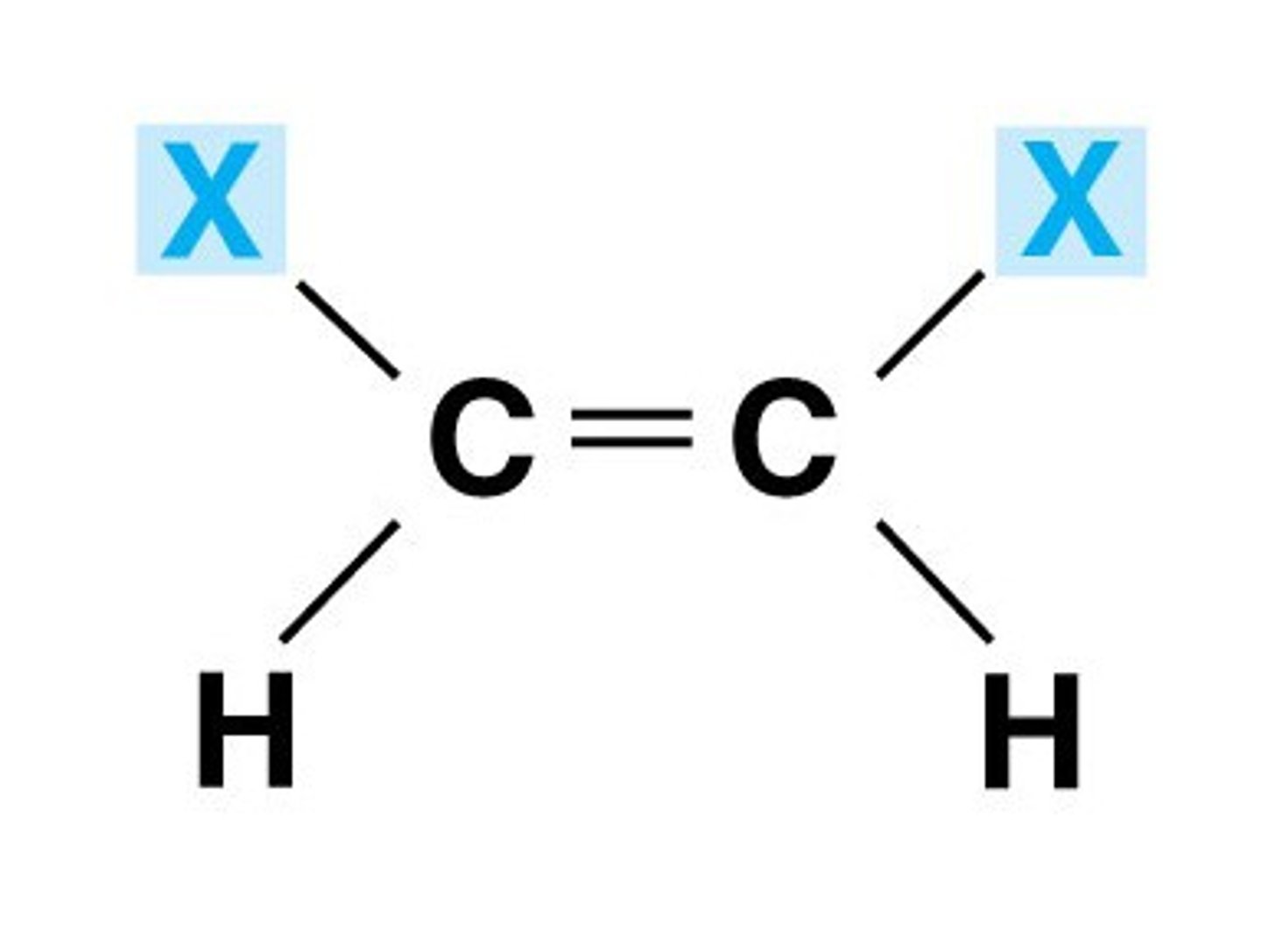
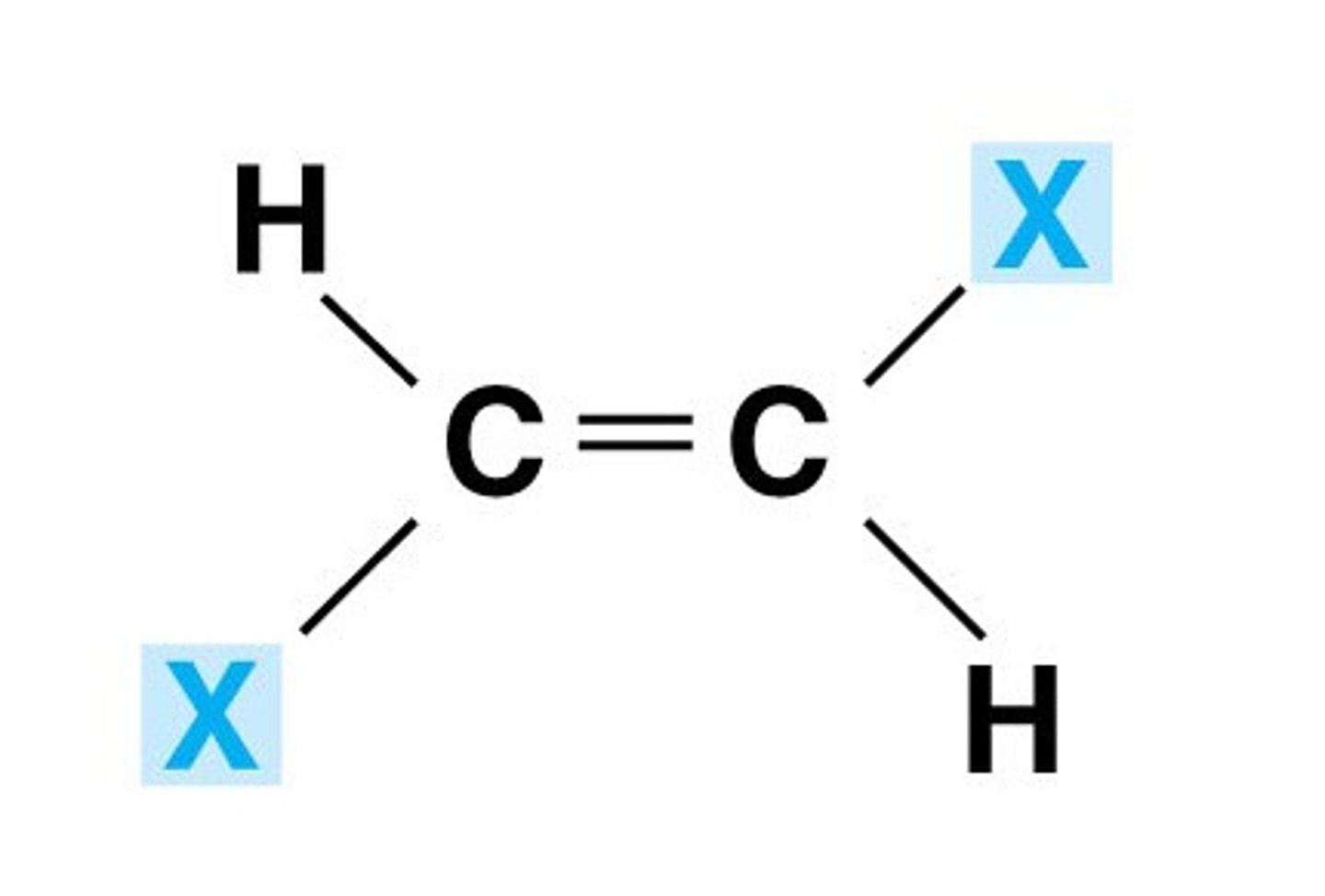
trans isomers
substituents diagonally opposite to the double bonded carbon atoms
ex: fumaric acid
enantiomers
- mirror images
- have identical physical properties (except w regard to polarized light) and react identically with achiral molecules
diastereomers
- isomers that are not mirror images
- have different physical and chemical properties
chiral center
asymmetric carbon with 4 different substituents
stereospecific
binding of chiral biomolecules
second law of thermodynamics
- entropy of the universe always increases
- ultimate driving force of cell chemical and physical processes is the tendency for entropy of universe to be maximized
entropy
disorder/randomness in a system
free energy (G)
energy capable of doing work under conditions of constant temperature and pressure
actual free energy changes
depend on reactant and product concentrations (supply and demand)
additive
standard free energy changes
application of free energy
allows the prediction of the direction and the equilibrium position of chemical reactions
endergonic
input of energy
exergonic
generation (release) of energy
endothermic
absorbs heat
exothermic reaction
releases heat
more entropic
disorder of system increases
less entropic
disorder of system decreases
ΔG
free energy change
+ΔG
endergonic
unfavorable/non-spontaneous
-ΔG
exergonic
favorable/spontaneous
ΔH
heat change
+ = endothermic
- = exothermic
ΔS
entropy change
+ = more entropic
- = less entropic
ΔG =
ΔH - TΔS
ΔG'°
- standard free energy change
- a constant
- is the difference between the free energy content of the products and reactants under standard condition
[products]/[reactants]
K'eq =
reaction proceeds forward (spontaneuous, more products)
K'eq is > 1 and ΔG'° is negative
reaction is at equilibrium
K'eq = 1 and ΔG'° is zero
reaction proceeds in reverse (not spontaneous, more reactants)
K'eq is < 1 and ΔG'° is positive
chemical coupling
- (of exergonic and endergonic reactions) allows otherwise unfavorable reactions to be favorable
- ΔG'° is additive
high energy phosphorylated biomolecules
- phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
- phosphocreatine
- 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG)
phosphate groups donated to ADP to make ATP
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
nitrogenous base
- adenine : purine
sugar
- pentose (5C): ribose
3 phosphate groups
- 2 high energy phosphoanhydride linkages
classified as a nucleotide
catabolic pathways
- breaking down
- exergonic
- generate ATP
anabolic pathways
- building up
- endergonic
- consume ATP
hydrolysis
breaking bonds by adding water
high energy of hydrolysis
- charge repulsion
- resonance stabilization
- ionization
oxidation
losing electrons (hydrogen)
reduction
gaining electrons (hydrogen)
oxidation is losing, reduction is gaining (electrons)
OIL RIG
glucose (sugars)
- oxidized by all human cells to generate energy
- partially oxidized (in the absence of O2) of completely oxidized (with O2)
palmitate (fats)
- complete oxidation generates more energy
- more energy, more reduced
how to speed reactions up (used by living organisms)
- change the reaction by coupling to a fast one
- lower activation barrier by catalysts
catalysts
- increases the rate of a chemical reaction
- lowers the activation free energy
- does not alter free energy
metabolic pathway
produces energy or useful byproducts
signal transduction pathway
- transmits information
- hormones
feedback/end product inhibition
pathways are controlled in order to regulate levels of metabolites
ex: product of enzyme 5 inhibits enzyme 1
complementarity of DNA
allows for replication with near-perfect fidelity
central dogma of biochemistry
DNA → RNA → protein
transcription
DNA to RNA
translation
RNA to protein
ribozymes
catalytic RNA molecules that function as enzymes and can splice RNA (reverse transcription)
water molecule structure
- 4 electron pairs around an oxygen
- two pairs covalently link two H to a central O2
- remaining two pairs nonbonding (lone)
- distorted tetrahedron
- net dipole movement
- H donor and acceptor due to dipole nature
- high BP
- high MP
- large surface tension
up to 4 H-bonds per water molecule gives water its...
H donor
H acceptor
water can serve as both
covalent bonds
strong bonds found in biomolecules
non-covalent bonds
weaker bonds, contribute to structure, stability, and functions of biomolecules
directionality of H bonds
linear = strong
bent = weak
entropy of water
increases as ordered crystal lattice is dissolved
high dielectric constant of water
reduces attraction between oppositely charged ions in a salt crystal
ionic (coloumbic) interactions
electrostatic interactions between permanently charged species, or between the ion and a permanent dipole
dipole interactions
electrostatic interactions between uncharged, but polar molecules
van der Waals interactions
- weak interactions between all atoms, regardless of polarity
- attractive (dispersion) and repulsive (steric) component
- weak individually
- universal
- stacking of bases in DNA
hydrophobic effect
- complex phenomenon associated with the ordering of water molecules around nonpolar substances
- refers to the association or folding of nonpolar moolecules in an aqueous solution
- does NOT arise due to attractive force between two nonpolar molecules
attractive force (london dispersion)
- depends on the polarizability
- dominates at longer distances (0.4-0.7 nm)
repulsive force (steric repulsion)
- depends on the size of atoms
- dominates at very short distances
Importance of van der waals interactions
- determines steric complementarity
- stabilizes biological macromolecules (stacking in DNA)
- facilitates binding of polarizable ligands
water as a good solvent
charged and polar substances
- amino acids/peptides
- small alcohols
- carbohydrates
water as a poor solvent
nonpolar substances
- nonpolar gases
- aromatic moieties
- aliphatic chains
bulk water
little order
high entropy
water near a hydrophobic solute
highly ordered
low entropy
low entropy
thermodynamically unfavorable, thus hydrophobic solutes have low solubility
amphipathic lipids
polar/hydrophilic head
nonpolar/hydrophobic tail
amphipathic lipids in water
- lipid molecules disperse in solution
- nonpolar tail surrounded by ordered water molecules
- entropy decreases