Mood Disorders
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
Episodes of severe low mood/anhedonia which impairs functioning which last 4-6 months and often recur without treatment
Very heterogeneous (experience is very different for each person)
Duration of MDD episodes
less than one month = 25%
less than 3 months = 50%
one year = 15-39%
2 years = 22%
Relapse rates of MDD
after 2 months: 20%
after 6 months: 30%
within first year: 40%
by second year: 50%
Physical/somatic symptoms of MDD
tiredness
lack of energy
agitation
slowness
sleep changes
appetite changes
loss of libido
lack of motivation
physical pain
Emotion symptoms of MDD
sadness
loss
hopelessness
worthlessness
tearfulness
anger
irritability
Cognitive symptoms of MDD
self-criticism
indecisiveness
pessimism
suicidal thoughts
memory disturbance
rumination
negative bias in self perception
inflated, grandiose thinking
psychosis
Behavioural symptoms of MDD
psychomotor slowing or agitation
dependency
crying
lack of goal-directed activities
“zombie living”
lack of self-care
self-harm
self-medication
Prevalence of MDD
3.8% (~280 million)
Causal/Maintenance factors of MDD
genetics/heritability
Freud: importance of loss
Beck’s Cognitive Model
adversity in early years
personality/individual differences
stressful life events (environmental)
lack of positive reinforcement/more negative reinforcement
What affects rates of MDD
willingness to report symptoms (women more likely so more common in women than men)
hormonal changes (women)
COVID-19
financial difficulties
relationship status (single associated more with MDD)
Beck’s Cognitive Model of MDD
Early experiences + activating event →
Core beliefs formed/assumptions →
Negative thoughts →
Physical/emotional/behavioural symptoms →
Reinforce core beliefs/assumptions
Bipolar I Disorder
Experience of at least one episode of mania thought life (state of elation or irritability)
Don’t need to experience depression but most do
Bipolar II Disorder
At least one hypomanic (less severe mania) episode and one depressive episode
Hypomania doesn’t cause significant impairment
Manic-Depressive Spectrum
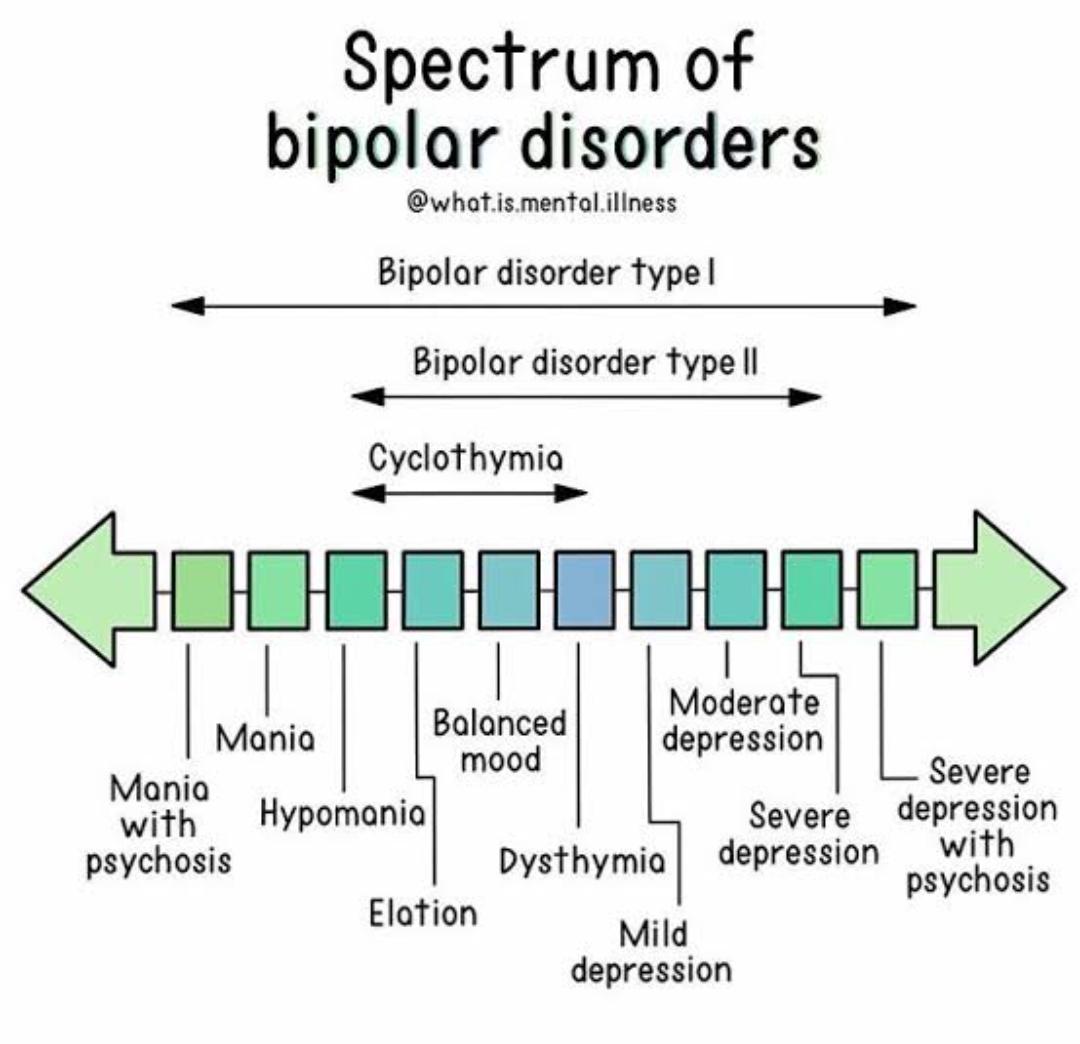
Prevalence of Bipolar Disorders
0.6% for BP I
0.4-2% for BP II
Much less common than MDD
Onset before 25
Most experience 4+ episodes in their life
Causal/maintenance factors of BPD
Similar triggers to depression:
one of the most heritable disorders
elevated cortisol levels
connection to neurotransmitters (serotonin, norepinephrine, dopamine)
early life adversity
negative life events
neuroticism
negative cognitive styles
family criticism
lack of social support
sleep disturbance
reward sensitivity
Suicide/Suicide Ideation
Leading cause of death for 10-24 year-olds
Men are 1.7 times more likely to die by suicide than women
750,000 people die each year by suicide
Prevalence of suicidal ideation
9%
Risk factors of suicidal ideation/suicide
having a mental health disorder
heritability
abnormalities of serotonin system
social factors (e.g. world events, physical/sexual assault, lack of social belonging/isolation, divorce/widowhood)
Treatment for Mood Disorders
Psychotherapy:
CBT
Behavioural activation therapy (increase participation to decrease negative reinforcement)
Psychoeducation
Medication:
antidepressants (e.g. SSRIs, tricyclics)
mood stabilisers (e.g. lithium)
antipsychotic drugs
Cultural influences of mood disorders
cultural focus on mental vs. physical symptoms
willingness to report symptoms
factors such as seasons, national income equality, family cohesion, stigma