inorganic chemistry
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
what is the name given to group 1 elements
alkali metals
describe the physical characteristics of group 1 metals
soft (can be cut with a knife)
low melting and boiling points
low density (floats on water)
shiny (tarnishes when exposed to air)
describe the chemical properties of group 1 elements
reacts vigorously with water to form metal hydroxides like NaOH
reacts with oxygen to form metal oxides eg. Li₂O
eg. 4Li + O₂ —> 2Li₂O
form ionic compounds like NaCl
react with halogens like KCl
why do all group 1 elements have similar chemical properties?
all have one electron in their outer shell
describe the observations when lithium is added to water
fizzes gently
moves across surface of water
disappears
describe the observations when sodium is added to water
melts and forms a ball
fizzes
moves across surface of water
gets smaller and disappears
leaves a white trail
describe the observations when potassium is added to water
melts and forms a ball
fizzes vigourously and explodes
sparks
burns with a lilac flame
leaves a white trail
what are the similarities of the reactions of lithium and potassium with water?
they both float, effervesce, move around on the surface of the water and disappear
what are the differences of the reactions of lithium and potassium
lithium fizzes gently but potassium explodes
lithium doesn’t burn but potassium has a lilac flame
lithium doesn’t melt but potassium melts into a ball
what is the word equation for when group 1 metals are added to cold water
metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
what’s the balanced symbol equation for when sodium is added to cold water
2Na + 2H₂O —> 2NaOH + H₂
why do group 1 metals fizz on contact with water?
hydrogen gas released
what colour would universal indicator turn if present when a g1 metal is added to water?
purple
metal hydroxide produced
hydroxides are alkalis
how should g1 elements be stored and why?
in oil
very reactive and lose properties eg shininess very quickly
what are the reactions of g1 metals with air?
lithium burns with a red flame to form lithium oxide
sodium burns with a yellow flame to form sodium oxide
potassium burns with a lilac flame to form potassium oxide
predict the properties of francium
g1 element
soft low melting and boiling point low density shiny and tarnishes when exposed to air
near bottom of g1
reactions with air and water will be more violent than other g1 metals
give the state and colour of g7 elements at room temp
fluorine = gas, yellow
chlorine = gas, green
bromine = liquid, red-brown
iodine = solid, grey (forms purple vapour when heated
describe the trends in the physical properties of the halogens
colour gets darker down the group
boiling point and melting point increase down the group
reactivity decreases down the group
all poor conductors of heat and electricity
predict the state and colour of astatine
below iodine in periodic table
solid
dark grey/black
what is a displacement reaction
when a more reactive halogen displaces a less reactive halide from its compound
halogen displacement reactions
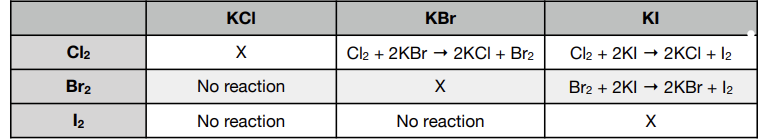
give the ionic equation of the displacement reaction between Cl2 and KBr
- Overall reaction: Cl2 (aq) + 2KBr (aq) → 2KCl (aq) + Br2 (aq)
- Separate out ionic compounds
- Cl₂ (aq) + 2K+ (aq) + 2Br- (aq) → 2K+ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq) + Br₂ (aq)
- Remove spectator ions that appear on both sides (i.e. 2K+)
- Ionic equation: Cl₂ (aq) + 2Br- (aq) → Br₂ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq)
Why are three of the reactions not carried out in the above table?
- A halogen cannot displace itself
- No reaction would occur
Why do three of the experiments not produce a reaction?
A halogen cannot displace a more reactive halogen
Describe two experiments to show the order of reactivity of bromine, chlorine and iodine
- Add chlorine (Cl2) to KBr
- Solution turns orange
- Cl₂+ 2KBr → Br₂+ 2KCl
- Add bromine (Br2) to KI
- Solution turns brown
- Br₂+ 2KI → l₂+ 2KBr
Name the gases present in the air and their approximate percentage by volume
- Nitrogen 78% - Oxygen 21% - Argon 0.96% - Carbon dioxide 0.04%
Describe how copper can be used to show the percentage of oxygen in the air
- Copper is put in a large tube that is attached to two gas syringes
- One syringe contains 100cm3 of air
- One syringe empty (pushed all the way in)
- Copper heated strongly
- Air passed over copper using syringes
- Oxygen reacts with copper
- Forms copper (II) oxide (CuO)
- Air allowed to cool
- Volume of air decreases to 80cm3
Explain why the copper between the syringes turns black
- Copper reacts with oxygen
- Forms copper (II) oxide
- 2Cu (s) + O2 (g) → 2CuO (s)
why is the air allowed to cool before measuring the change in volume?
gas expands when heated
describe how iron can be used to show the percentage of oxygen in the air
iron filing placed in a burette that is full of air
end of burette placed in a trough of water
iron reacts with oxygen
water moves into burette
how is the percentage of oxygen in the air calculate using the iron filings experiment
initial column of air height/final column of air height x 100
describe how phosphorus can be used to show the percentage of oxygen in the air
phosphorous placed on a tray inside a tube full of air
tube placed in a beaker of water
phosphorous lit with hot wire
phosphorous reacts with oxygen in the air
phosphorous + oxygen → phosphorous oxide
4P + 5O₂ —> P₄O₁₀
volume of air decreases
water moves into tube, pushing phosphorus up
Describe the observations when magnesium burns in oxygen
bright white light
white solid forms
magnesium + oxygen = magnesium oxide
2Mg (s) + O₂(g) → 2MgO (s)
Give the word and symbol equation for when magnesium oxide dissolves in water
- Magnesium oxide + water → magnesium hydroxide
- MgO (s) + H₂O (l) → Mg(OH)₂ (aq)
forms an alkaline solution
describe the observations when hydrogen burns in oxygen
pale blue flame
water forms
2H₂ (g) + O₂ (g) → 2H₂O (l)
describe the observations when sulfur burns in oxygen
blue flame
poisonous colourless sulfer dioxide gas forms
S (s) + O₂ (g) → SO₂
sulfur dioxide dissolves in water to form acidic solution of sulfurous acid
SO₂ (g) + H₂O (l) → H₂SO₃ (aq)
what type of reaction are combustion reactions
oxidation reactions
a substance gains oxygen
define thermal decomposition
breaking down of a substance using heat
what type of reaction occurs when metal carbonates are heated?
thermal decomposition
describe the thermal decomposition of copper 2 carbonate
copper II carbonate is a green solid
it decomposes to form copper oxide- a black solid
give word and symbol equations for the reaction that occurs when copper II carbonate is heated strongly
Copper(II) carbonate → copper (II) oxide + carbon dioxide
- CuCO₃ → CuO + CO₂
Explain the effect on the environment of increasing atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide
Greenhouse gas → contributes to global warming
- Polar ice caps melt - Sea levels rise - Floods low lying land - Loss of habitats and biodiversity
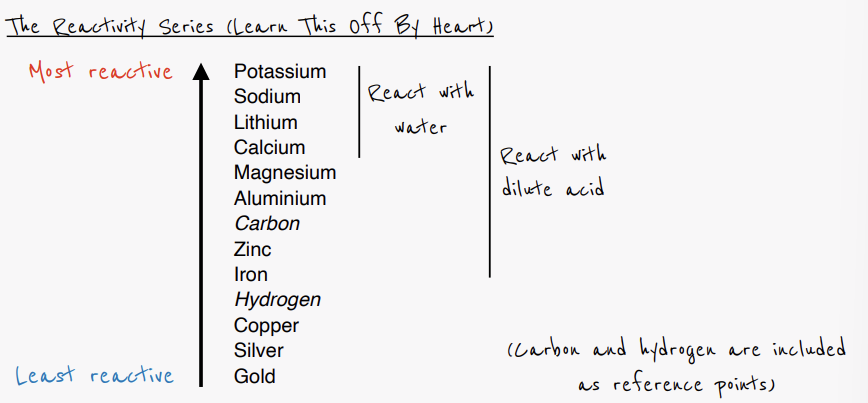
What is the reactivity series?
List of metals in order of their reactivity - Most reactive metals at the top - Least reactive at the bottom
How can you determine the reactivity of a metal?
Place in cold water (most will not react)
- those which react are the most reactive metals
- If no reaction, test with steam
- If no reaction, test with acid
(note: only metals above hydrogen in the reactivity series will react with acid)
- Note: Potassium, sodium, lithium and calcium are too reactive to react with acids (dangerous)
Explain how displacement reactions can be used to arrange metals in order of reactivity
- Occur when a less reactive element is pushed out of its compound by a more reactive element
- e.g. with metals and metal oxides:
- Magnesium + copper (II) oxide → magnesium oxide + copper
- Displacement reaction occurred, therefore magnesium more reactive than copper
- e.g. with metals and aqueous solutions of metal salts:
- Zinc + copper (II) sulfate → zinc sulfate + copper
- Displacement reaction occurred, therefore zinc more reactive than copper
what is the reactivity series
Give the word and symbol equation for when iron rusts
Iron + oxygen + water → hydrated iron (III) oxide
- 4Fe + 3O₂ + nH₂O → 2Fe₂O₃.nH₂O
what conditions are needed for rusting
water
oxygen
what methods are used to prevent iron from rusting
barrier methods
galvanising
sacrificial protection
how do barrier methods prevent iron from rusting
Provide protective layer
- Prevent water / oxygen reaching iron
- e.g. paint (bridges), grease (car engines), oil (bike chains)
- If the layer is damaged the iron will rust
Describe the process of galvanising
Coating iron in a more reactive metal
e.g. zinc - Zinc reacts with oxygen first, forming Zn2+
- Zn loses electrons instead of iron
- Used for car bodies, buckets
What is sacrificial protection?
- Method used to stop iron from rusting
- Iron coated in a more reactive metal / blocks of more reactive metal attached to iron
- More reactive metal undergoes oxidation in preference to iron
Define oxidation
Gain of oxygen - Loss of electrons
Define reduction
- Loss of oxygen
- Gain of electrons
Define redox
A reaction where both reduction and oxidation take place at the same time
Define oxidising agent
- Something which causes another substance to be oxidised
- An oxidising agent is itself reduced (it gains electrons)
Define reducing agent
-Something which causes another substance to be reduced
- A reducing agent is itself oxidised (it loses electrons)
Describe how to investigate reactions between dilute acids and metals
- Pour the same volume of a dilute acid into four boiling tubes
- Place a small piece of different metals (e.g. magnesium, zinc, iron, copper) in each tube
- Observe the changes that occur:
- A rapid fizzing and a colourless gas (hydrogen) produced
- Reaction mixture becomes warm as heat is produced (exothermic)
- More reactive metal = more fizzing and more heat
Explain why hydrogen gas is produced when a metal reacts with a dilute acid
- Metals above hydrogen in reactivity series will react with dilute acids
- Produce a salt and hydrogen in a displacement reaction
- e.g. magnesium + hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + hydrogen
- Mg (s) + 2HCl (aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Methyl Orange
Red in acid
Yellow in alkaline
Phenolphthalein
Colourless in acid
Pink in alkaline
Litmus paper
Red in acid
Blue in alkaline
Universal indicator
Red in acid
Purple in alkaline
What ion is responsible for making something acidic?
- H+
- Produced by acids in aqueous solutions
What ion is responsible for making something alkaline?
- OH-
- Produced by alkalis in aqueous solutions
Define acid
- H+ donor
Define base
- H+ acceptor
- OH- donor
- e.g. metal carbonate, hydroxide, oxides, ammonia
Define alkali
- Soluble base
What is a neutralisation reaction
- Addition of a base to an acid
- To produce a neutral solution
What is a salt
- Ionic compound formed by the neutralisation of an acid by a base
Give the ionic equation for a neutralisation reaction
- H+ + OH- → H2O
Remembering which ionic compounds (salts) are soluble/insoluble:
- All sodium, potassium and ammonium compounds are soluble
- All nitrates are soluble
- All sulfates are soluble except lead (II) sulfate, barium sulfate, and calcium sulfate
- All chlorides are soluble except lead (II) chloride and silver chloride
- All carbonates are insoluble except ammonium, potassium and sodium salts
- All hydroxides are insoluble except ammonium, potassium and sodium salts
- Calcium hydroxide is slightly soluble
Provide an example of the Brønsted-Lowry theory in context
- Dissolving hydrogen chloride in water
- H2O(l) + HCl(aq) → H3O+(aq) + Cl- (aq)
- HCl donates H+ (acts as an acid)
- H2O accepts H+ (acts as a base)
Which compounds can act as bases?
- Metal oxides / hydroxides
- Ammonia
Describe the reactivity of metals with acids
- Metals below hydrogen in the reactivity series do not react with acids
- Metals above hydrogen in the reactivity series react with acids, producing hydrogen
- Note: very reactive metals react very explosively with acids e.g. Potassium
How do you make soluble salts?
- Use the crystallisation method
- REACT until saturated
- FILTER
- EVAPORATE: heat to evaporate some water
- COOL: collect crystals that form
- DRY: allow the crystals to dry in a warm place or on filter paper
- For the reactants, you can use:
- Acid + insoluble metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide/metal carbonate
What is the test for hydrogen?
- Lit splint burns with squeaky pop
What is the test for oxygen?
Glowing splint relights
What is the test for carbon dioxide?
Limewater turns cloudy when gas bubbled through
What is the test for ammonia?
Damp red litmus paper turns blue
What is the test for chlorine?
- Bleaches damp blue litmus paper
How do you test for ammonium ions (NH4+)?
- Add sodium hydroxide solution
- No precipitate is formed, but choking gas is given off (ammonia)
- Turns damp red litmus paper blue - confirms presence of ammonia
How do you test for copper (Cu2+), iron (II) (Fe2+) and iron (III) (Fe3+)?
- Use precipitation reactions by adding sodium hydroxide
- Cu2+ → copper hydroxide, Cu(OH)2, produced = light blue precipitate
- Fe2+ → Iron(II) hydroxide, Fe(OH)2, produced = green precipitate
- Fe3+ → Iron(III) hydroxide, Fe(OH)3, produced = brown precipitate
How do you test for halides?
- Add dilute nitric acid
- Removes carbonate ions
- Add silver nitrate
- Silver halide precipitate forms
Results of adding silver nitrate to halides:
- Silver chloride = white precipitate
- Silver bromide = cream precipitate
- Silver iodide = yellow precipitate
- e.g. Ag+ (aq) + I- (aq) → AgI (s)
How do you test for sulfates?
- Add dilute hydrochloric acid (removes carbonate ions)
- Add barium chloride
- Result: barium sulfate is a white precipitate
- Ba2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) → BaSO4 (s)
How do you test for carbonates?
- Add dilute hydrochloric acid
- Fizzing indicates carbon dioxide being produced
- Test for carbon dioxide using lime water
- Turns milky/cloudy
- 2H+ (aq) + CO32- (aq) → CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
What is the chemical test for water?
- White anhydrous copper sulfate turns blue
- Hydrated copper (II) sulfate formed = blue crystal
How do you do a physical test for water?
- Check boiling point
- Water boils at 100°C
How do you show that water is pure?
- Check boiling point
- Pure water has single boiling point at 100°C