IB Biology HL - Cell division
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/14
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
1
New cards
Define cell cycle.
The cell cycle is an ordered set of events the cell goes through before dividing into two daughter cells.
2
New cards
Outline the phases of the cell cycle (name the phases and briefly state what happens in each phase).
1. Interphase - the stage of cell development and growth.
* G1 - first growth phase, the cell grows in size and conducts its normal metabolic functions
* S - synthesis phase, DNA replication occurs
* G2 - second growth phase, the cell continues to grow and prepares for division
2. M phase - the stage of cell division into two identical daughter cells.
* Mitosis - nuclear division, DNA is separated into two identical nuclei
* Cytokinesis - cytoplasmic division, cellular contents are segregated and the cell splits into two
3
New cards
What is meant by DNA supercoiling?
It is the process during which DNA becomes condensed (from chromatin to chromosomes) prior to nuclear division. In this form, it can be easily segregated, but it is inaccessible for the transcriptional machinery.
4
New cards
Outline the 4 stages of mitosis.
\*prior to mitosis (during interphase): DNA is duplicated, but still uncondensed
1. Prophase
* DNA supercoils and chromosomes condense (they are now visible under the microscope)
* Chromosomes are comprosed of genetically identical sister chromatids, joined together at the centromere (they form the characteristic “X” shape)
* Centrosomes move to the opposite poles of the cell and radiate microtubule spindle fibres
* Nuclear membrane breks down and the nucleus dissolves
2. Metaphase
* Microtubule spindle fibres brom both centromeres connect to the centromere of each chromosome
* The chromosomes align along the centre of the cell (equatorial plane)
3. Anaphase
* Microtubule depolymerisation causes the spindle fibres to shorten in length and contract, separating the sister chromatids and pulling them towards the opposite poles of the cell
* Remember: now that the sister chromatids are separated, each of them is an individual chromosome on its own :) (instead of an X-shaoed chromosome made up of two sister chromatids, we now have two individual chromosomes made of one chromatid - I)
4. Telophase
* the two sets of chromosomes arrive at the poles and spindle fibres dissolve
* Chromosomes decondense (they are no longer visible under the microscope)
* Nuclear membranes reform around each chromosome set
* Cytokinesis occurs concurrently, splitting the cell into two.
1. Prophase
* DNA supercoils and chromosomes condense (they are now visible under the microscope)
* Chromosomes are comprosed of genetically identical sister chromatids, joined together at the centromere (they form the characteristic “X” shape)
* Centrosomes move to the opposite poles of the cell and radiate microtubule spindle fibres
* Nuclear membrane breks down and the nucleus dissolves
2. Metaphase
* Microtubule spindle fibres brom both centromeres connect to the centromere of each chromosome
* The chromosomes align along the centre of the cell (equatorial plane)
3. Anaphase
* Microtubule depolymerisation causes the spindle fibres to shorten in length and contract, separating the sister chromatids and pulling them towards the opposite poles of the cell
* Remember: now that the sister chromatids are separated, each of them is an individual chromosome on its own :) (instead of an X-shaoed chromosome made up of two sister chromatids, we now have two individual chromosomes made of one chromatid - I)
4. Telophase
* the two sets of chromosomes arrive at the poles and spindle fibres dissolve
* Chromosomes decondense (they are no longer visible under the microscope)
* Nuclear membranes reform around each chromosome set
* Cytokinesis occurs concurrently, splitting the cell into two.
5
New cards
What is cytokinesis and how does it differ between animal and plant cells?
Cytokinesis is the divison of cytoplasm that occurs concurrently with the final stage of mitosis (telophase).
In animal cells: after anaphase, microtubule filaments form a concentric ring around the centre of the cell and constrict, ==forming a cleavage furrow==. When the furrow meets the centre, the two daughter cells become completely pinched off. As the separation occurs from the outside and moves towards the inside, it is said to be ==centripetal==.
In plant cells: after anaphase, carbohydrate-rich vesicles form in a row at the equatorial plane of the cell. These vesicles fuse together forming a ==cell plate== that gradually extends and eventually fuses with the cell wall, dividing the cell into two. As the separation originates at the centre and moves laterally, it is described as ==centrifugal==.
In animal cells: after anaphase, microtubule filaments form a concentric ring around the centre of the cell and constrict, ==forming a cleavage furrow==. When the furrow meets the centre, the two daughter cells become completely pinched off. As the separation occurs from the outside and moves towards the inside, it is said to be ==centripetal==.
In plant cells: after anaphase, carbohydrate-rich vesicles form in a row at the equatorial plane of the cell. These vesicles fuse together forming a ==cell plate== that gradually extends and eventually fuses with the cell wall, dividing the cell into two. As the separation originates at the centre and moves laterally, it is described as ==centrifugal==.
6
New cards
What is mitotic index and how to calculate it?
It is a measure of the proliferation status of a cell population (the ratio between the number of cells undergoing mitosis and the total number of cells).
mitotic index = number of cell in mitosis/number of all cells under investigation
mitotic index = number of cell in mitosis/number of all cells under investigation
7
New cards
What are cyclins?
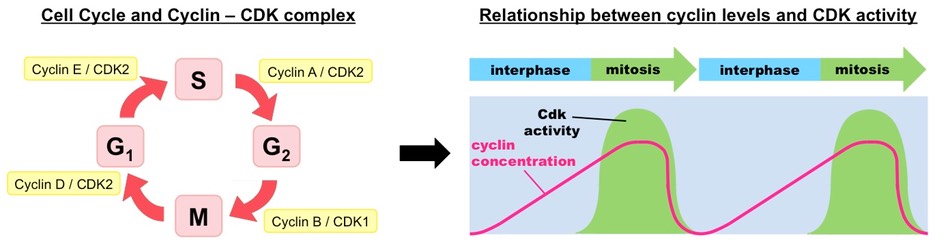
Cyclins are a family of regulatory proteins that control the progression of the cell cycle. They activate ==cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs)==, which control the cell cycle through ==phosphorilation==.
When a cyclin and CDK form a complex, the complex binds into a target protein and modifies it via phosphorilation. The phosphorilated protein will trigger some specific event (such as centrosome duplication). After the event has occured, the cyclin is degraded and the CDK is rendered inactive again.
Cyclin levels will peak when their target protein is required and lower during the rest of the time.
(image source: bioninja)
When a cyclin and CDK form a complex, the complex binds into a target protein and modifies it via phosphorilation. The phosphorilated protein will trigger some specific event (such as centrosome duplication). After the event has occured, the cyclin is degraded and the CDK is rendered inactive again.
Cyclin levels will peak when their target protein is required and lower during the rest of the time.
(image source: bioninja)
8
New cards
What is a tumour? How does it differ from cancer?
Tumours are abnormal cell growths resulting from uncontrolled cell division. They can occur in any tissue or organ and can cause diseases collectively known as ==cancers==.
9
New cards
What is a mutagen?
Mutagen is an agent that changes the genetic material of an organism by either acting on the DNA molecule or interfering into the replication process. They can lead to the formation of cancers (some of them are ==carcinogens==)
Mutagens can be:
* physical - sources of radiation (X-rays, UV light, radioactive decay)
* chemical - DNA interacting substances (reactive oxygen species - ROS, metals like arsenic)
* biological - viruses, certain bacteria, mobile genetic elements (transposons)
Mutagens can be:
* physical - sources of radiation (X-rays, UV light, radioactive decay)
* chemical - DNA interacting substances (reactive oxygen species - ROS, metals like arsenic)
* biological - viruses, certain bacteria, mobile genetic elements (transposons)
10
New cards
What is an oncogene?
Oncogene is a gene that has a potential to cause cancer if it undergoes a mutation. There are two main types:
* ==proto-oncogenes== - genes that code for proteins stimulating the cell cycle, promoting cell growth and proliferation. When a proto-oncogene is mutated or subjected to increased expression, it becomes a **cancer-causing oncogene**.
* ==tumour supressor genes== - genes that code for proteins repressing the cell cycle progression and promoting apoptosis (they are sometimes called **anti-oncogenes**, because their normal functioning is meant to actually preven cancer, i.e. if anything goes wrong during the cell cycle, they should cause the cell to die).
* ==proto-oncogenes== - genes that code for proteins stimulating the cell cycle, promoting cell growth and proliferation. When a proto-oncogene is mutated or subjected to increased expression, it becomes a **cancer-causing oncogene**.
* ==tumour supressor genes== - genes that code for proteins repressing the cell cycle progression and promoting apoptosis (they are sometimes called **anti-oncogenes**, because their normal functioning is meant to actually preven cancer, i.e. if anything goes wrong during the cell cycle, they should cause the cell to die).
11
New cards
What is metastasis?
Metastasis is the spread of cancer from one location (primary tumour) to another, forming a secondary tumour.
Tumour cells may either remain in their original location (==benign== tumours) or spread, invading neighbouring tissue (==malignant== tumours).
In is important to note that secondary tumours are made up of the same type of cell that primary tumour - so if a breast cancer spread to the liver, the patient has a secondary breast cancer in their liver (treated with breast cancer drugs).
Tumour cells may either remain in their original location (==benign== tumours) or spread, invading neighbouring tissue (==malignant== tumours).
In is important to note that secondary tumours are made up of the same type of cell that primary tumour - so if a breast cancer spread to the liver, the patient has a secondary breast cancer in their liver (treated with breast cancer drugs).
12
New cards
Does smoking increase the risk of cancer?
Yes. There is a strong positive correlation between the frequency of smoking and cancer development (lung cancer especially, but also mouth, stomach, liver, pancreas and bowel cancers). This is due to cigarette smoke containing over 60 known carcinogenes.
13
New cards
Describe meiosis.
Meiosis is a cell division which results in the production of four genetically distinct haploid daughter cells (gametes).
1. ==Meiosis I== - first mitotic division. It is a reduction division (diploid —> haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated.
* ==prophase I== - chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form ^^bivalents^^, crossing over occurs
* ==metaphase I== - spindle fibers from opposing centrosomes connect to bivalents at centromeres and align them in the middle of the cell
* ==anaphase I== - spindle fibres contract and split the bivalent cousing the homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell
* ==telophase I== - chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane **may** reform, cell divides (cytokinesis) to form two haploid (the chromosomes are still made up of two sister chromatids, so it is a single set of chromosomes in the X shape) daughter cells
\* ==interkinesis== (additional growth phase) **may** occure between meiosis I and II, but no DNA replication occurs in this stage
2. ==Meiosis II== - second mitotic division, separates the sister chromatids to form the toral of 4 haploid cells.
* ==prophase II== - chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves (if it reappeared after the meiosis I), centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell
* ==metaphase II== - spindle fibres from opposing centromeres attach to chromosomes at centromere and align them along the equator of the cell
* ==anaphase II== - spindle fibres contract and separate sister chromatids (now each of which is a separate chromosome), moving the to the opposite poles of the cell
* ==telophase II== - chromosomes decondense, nuckear membrane reforms, cytokinesis occurs
1. ==Meiosis I== - first mitotic division. It is a reduction division (diploid —> haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated.
* ==prophase I== - chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form ^^bivalents^^, crossing over occurs
* ==metaphase I== - spindle fibers from opposing centrosomes connect to bivalents at centromeres and align them in the middle of the cell
* ==anaphase I== - spindle fibres contract and split the bivalent cousing the homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell
* ==telophase I== - chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane **may** reform, cell divides (cytokinesis) to form two haploid (the chromosomes are still made up of two sister chromatids, so it is a single set of chromosomes in the X shape) daughter cells
\* ==interkinesis== (additional growth phase) **may** occure between meiosis I and II, but no DNA replication occurs in this stage
2. ==Meiosis II== - second mitotic division, separates the sister chromatids to form the toral of 4 haploid cells.
* ==prophase II== - chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves (if it reappeared after the meiosis I), centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell
* ==metaphase II== - spindle fibres from opposing centromeres attach to chromosomes at centromere and align them along the equator of the cell
* ==anaphase II== - spindle fibres contract and separate sister chromatids (now each of which is a separate chromosome), moving the to the opposite poles of the cell
* ==telophase II== - chromosomes decondense, nuckear membrane reforms, cytokinesis occurs
14
New cards
What causes the genetic variation between the gametes formed in meiosis?
* independent assortment and random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in metaphase I
* crossing over in prophase I
* crossing over in prophase I
15
New cards
How does crossing-over occur?
During prophase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes become connected in a process called ==synapsis==, forming a bivalent (two chromosomes) or a tetrad (four chromatids). Autosomes always undergo synapsis, sex chromosomes often remain unpaired.
Bivalents are connected by a protein-RNA complex known as ==synaptonemal complex==.
While in synapsis, **non-sister** chromatids remain physically connected at regions called ==chiasmata== and can break and recombine with their homologous partner - this is known as crossing-over. Therefore, an exchange of alleles can occur.
These chromosomes that consist of genetic material from both homologues are ==recombinant chromosomes==.
Bivalents are connected by a protein-RNA complex known as ==synaptonemal complex==.
While in synapsis, **non-sister** chromatids remain physically connected at regions called ==chiasmata== and can break and recombine with their homologous partner - this is known as crossing-over. Therefore, an exchange of alleles can occur.
These chromosomes that consist of genetic material from both homologues are ==recombinant chromosomes==.