10. chemically-induced, spontaneous, & surgical experimental mouse models
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are the 4 main types of treatment strategies used to mimic human disease in mice?
Chemical induction: Use of agents like urethane to initiate disease (e.g., cancer, IBD)
Genetic manipulation: Creating knockout (KO) or transgenic mice to study gene-disease relationships.
Spontaneous models: Disease arises due to spontaneous mutations or alterations in mouse colonies.
Surgical induction: Physical interventions like ACL transection to mimic degenerative diseases (e.g., osteoarthritis).
What is the urethane mouse model used fo
Used to induce lung cancer in mice.
Urethane is administered via intraperitoneal injection to initiate tumour development, typically leading to multiple lung adenomas.
how does urethane work and how can it be used to study tumour via injection
metabolized by the P450 system to form a reactive vinyl carbamate epoxide which covalently binds to DNA
causes base misincorporations during DNA replication and point mutation
mutation of P53
mislocalizaation of P27
altered DNA methylation
loss of the p19/Arf expression
What was the outcome of combining urethane exposure with a p27 knockout mouse?
Synergistic increase in lung tumour development.
Demonstrates that p27 is a key barrier to chemically induced lung cancer.
Lung tumours appeared in 30-week-old mice in the urethane-treated p27 KO group but not in WT or untreated KO mice.
3 advantages of using a chemical carcinogen mouse model
led to a concept of multistage tumour development through distinct stages of initiation, promotion, progression
DNA sequencing gives us tools to completely dissect the human genome architecture
revealed that chemically-induced cancers in mouse carry a high point mutation signatures that reflect the cause of tumour
provide a route to identify the causes of mutation signatures found in human cancers & inform therapeutic drug resistance & responses to immunotherapy (dependent on mutation load & genetic heterogenity)
What are the 4 limitations of chemically induced mouse models?
Findings may not fully translate to humans due to species differences.
Human cancers are influenced by diverse genetic and lifestyle factors not mirrored in mice.
Requires dose extrapolation from mouse to human.
Retrospective human studies often have confounding variables not present in controlled mouse experiments.
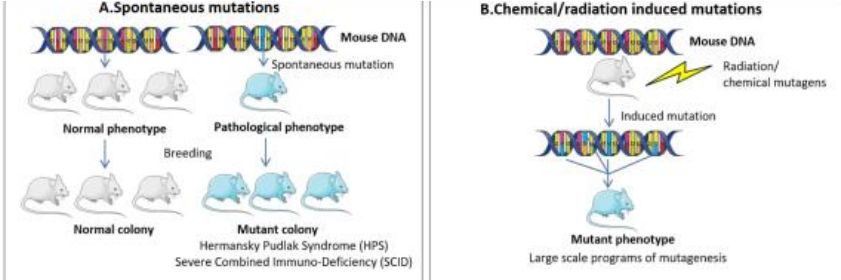
What is a spontaneous mouse model
Involves natural mutations or introduced DNA sequences that lead to disease without external triggers.
Can closely mimic the genetic profile of patients.
Used when a natural disease progression or a genetically-driven model is needed.
can occur via mutations, genetic drift, or selective breeding over generations
Name a chemically induced inflammatory disease model in mice.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) models.
Induced by chemical agents (e.g., DSS, TNBS).
Mimics chronic inflammation of the gut for studying pathogenesis and drug efficacy.
Describe a mouse surgical model of disease and its application.
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) transection model in rats/mice used to study osteoarthritis (OA) to look at therapies that improve joint paint & prevent joint deterioration
Involves surgically cutting the anterior cruciate ligament, sparing the meniscus.
Causes joint instability, followed by progressive cartilage damage and inflammation.
OA signs appear after 4–5 weeks; useful for testing joint pain therapies.
What is the relevance of surgically induced OA models to human disease?
Mimics OA resulting from sports injuries or trauma.
Models the common joint degeneration process found in human OA.
Allows study of disease progression and potential therapeutic interventions.
What ethical and legal considerations must be addressed before conducting a urethane-induced lung cancer study in mice?
Obtain ethical approval from an institutional animal care and use committee.
Ensure compliance with legal regulations (e.g., UK Animals [Scientific Procedures] Act 1986).
Perform a harm-benefit analysis to justify the study.
Apply the 3Rs: Replacement, Reduction, Refinement.
Prepare protocols for animal monitoring, humane endpoints, and experimental validity.