NVCC BIO 102 Exam 4 Review Part 1 Ch 26
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Nerve nets
Are nervous impulses spread over the entire body surface
Ganglia
clusters of neurons
nerve ladder
connects to paired muscles on each side of the body, allowing the worm to move rhythmically
Nerve cord
helps the animal coordinate movements
peripheral nervous system
carries information to or from the central nervous system
Central nervous system
interprets signals it receives from the peripheral nervous system
cell body
contains the nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles.
Dendrites
are short, branched extensions that transmit information toward the cell body
axon
conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body
synapses
tiny gaps between dentrites and axons of different neurons
Myelin sheath
made of fatty neuroglia cells, coats sections of the axon and speeds neural impulses.
Sensory neurons
bring information from the body's organs toward the central nervous system
Inter neurons
receive signals from sensory neurons.The message is processed, and a signal is sent to a motor neuron.
motor neuron
conducts a message from the central nervous system to a muscle or gland, stimulating contraction or secretion
membrane potential
the voltage difference across a membrane
resting potential
is the membrane potential of a neuronnot sending signals
What is the concentration of K+ inside a neuron?
High
What is the concentration of Na+ inside a neuron?
Low
What is the concentration of K+ outside a neuron?
Low
What is the concentration of Na+ outside a neuron?
High
Sodium-potassium (Na+-K+) pumps
use energy from ATP to actively move Na+ out of the neuron and K+ into the neuron
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
hyperpolarization
the membrane temporarily dips below resting potential, until the sodium-potassium pumps reestablish it.
Synaptic integration
determines the cell's response: if the majority of stimuli are excitatory, then the post synapticcell will likely initiate an action potential
central nervous system
integrates sensory information and coordinates the body's responses
peripheral nervous system
carries information between the central nervous system and the rest of the body
Somatic motor neurons
carry signals to voluntary muscles
Autonomic motor neurons
carry signals to involuntary muscles and glands
sympathetic nervous system
dominates under stress and emergencies
parasympathetic nervous system FUNCTION
decrease heart rate and breathing rate, constrict arteries
sympathetic nervous system FUNCTION
increase heart rate and breathing rate and dilate arteries
Gray matter
cell bodies and dendrites
White matter
myelinated axons
reflexes
Controlled by spinal cord without interacting with the brain
Forebrain consists of
cerebrum, Thalamus, Hypothalamus
Midbrain
relays info about voluntary movements from forebrain to spinal cord
Hindbrain consists of
medulla oblongata, pons, cerebellum
cerebrum
controls the qualities of what we consider the "mind.
limbic system
is also contained within the cerebrum. This"emotional center" of the brain is actually scattered through different brain areas.
hippocampus
is part of the limbic system responsible for forming long-term memories
amygdala
is part of the limbic system.It is responsible for forming emotions such as fear and pleasure
Neuronal plasticity
is the capacity of the nervous system to be remodeled, especially in response to its own activity. Also is essential to formation of memories
blood-brain barrier
protects the brain from extreme chemical fluctuations
meninges
are layered membranes that help protect the CNS
Cerebrospinal fluid
bathes and cushions thebrain and spinal cord
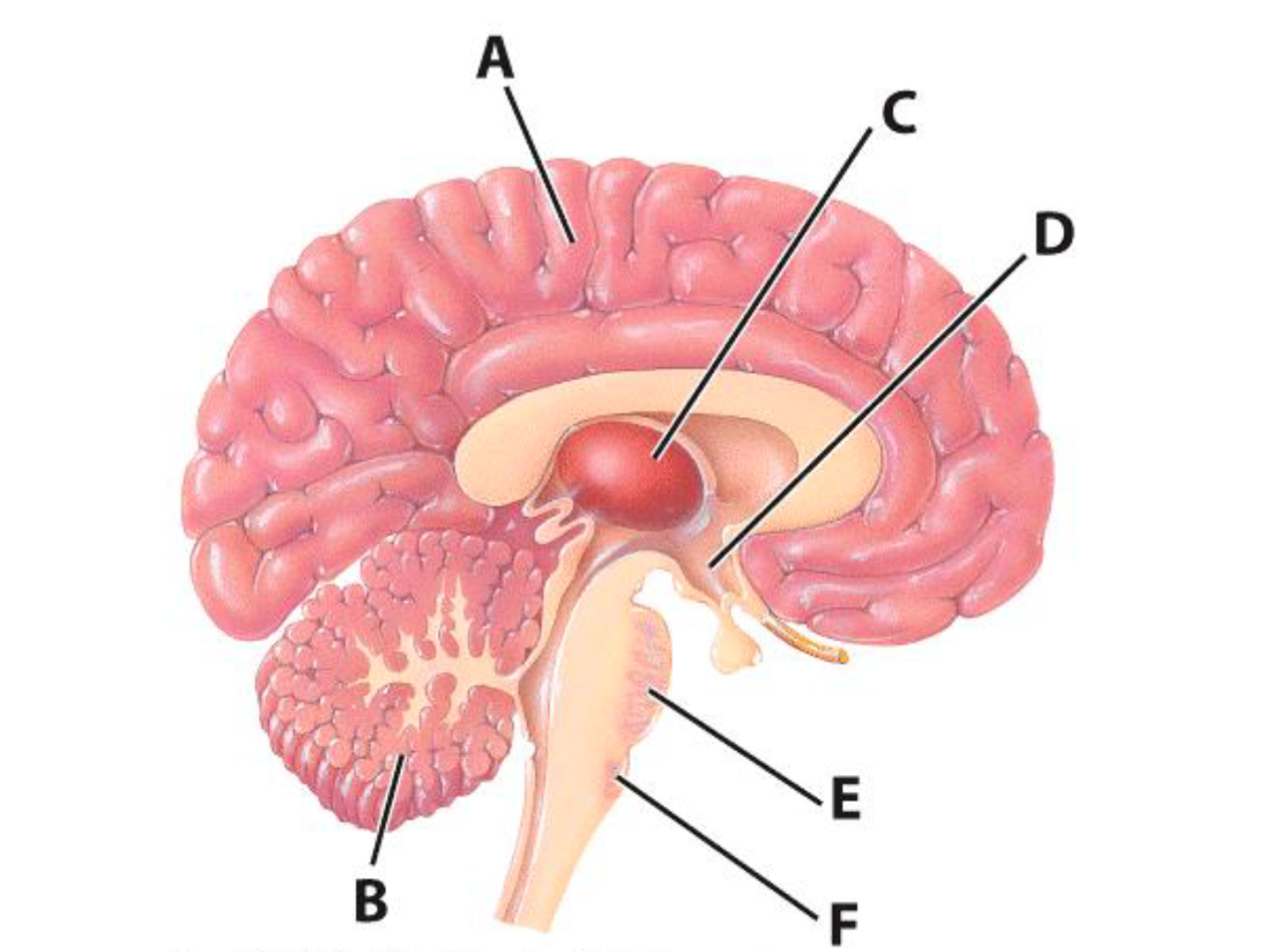
A
Cerebrum
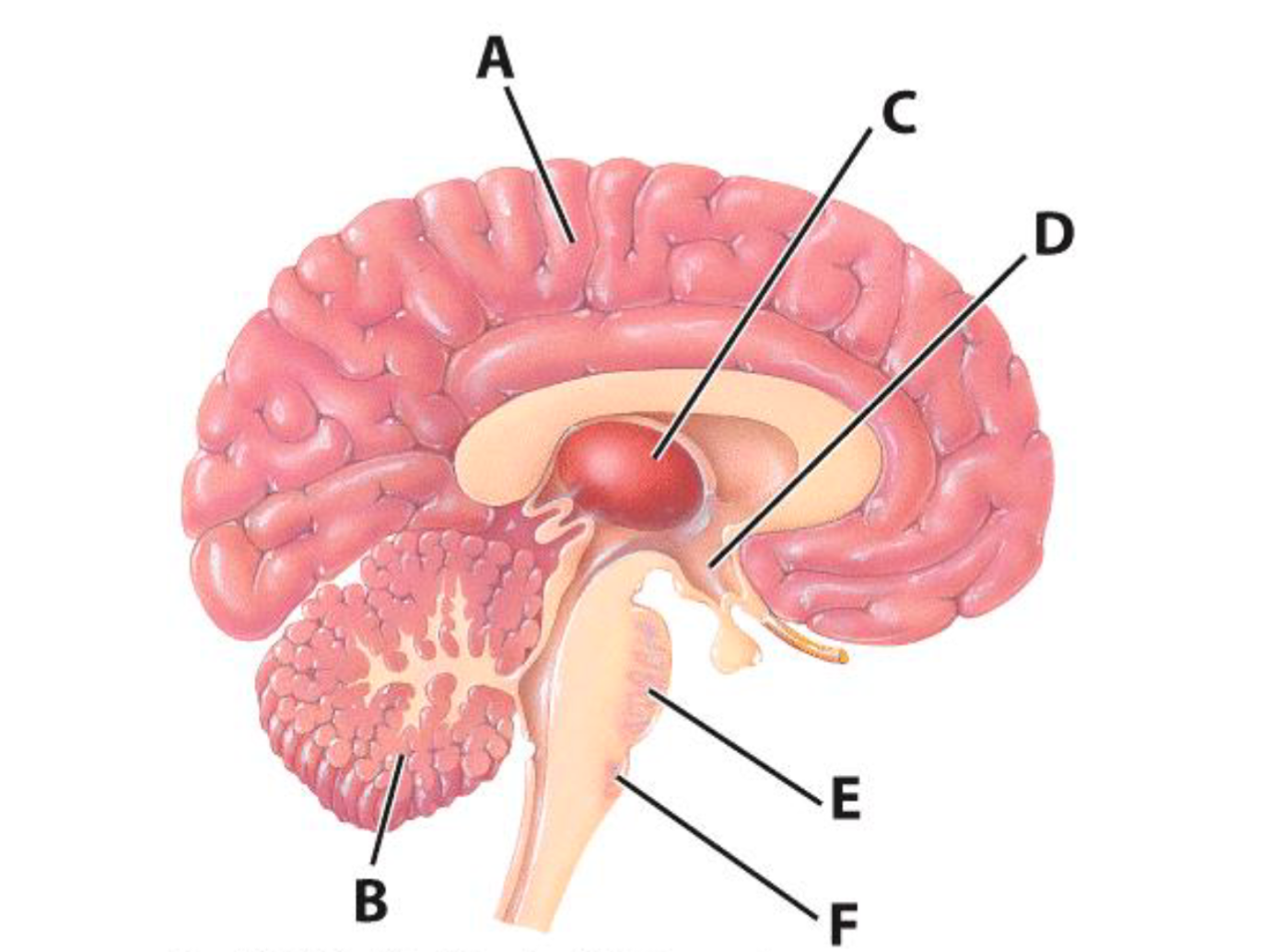
B
Cerebellum
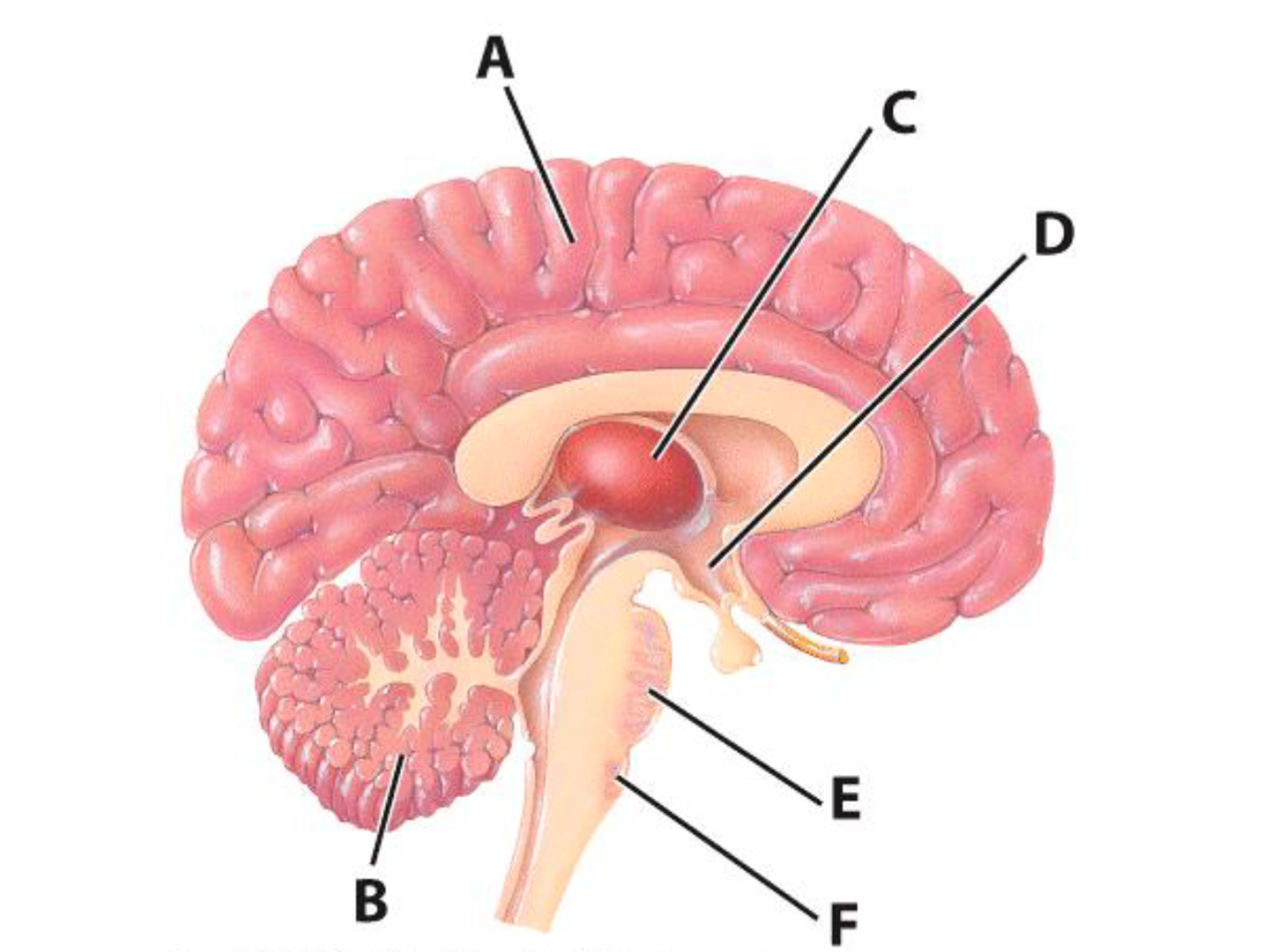
E
Pons
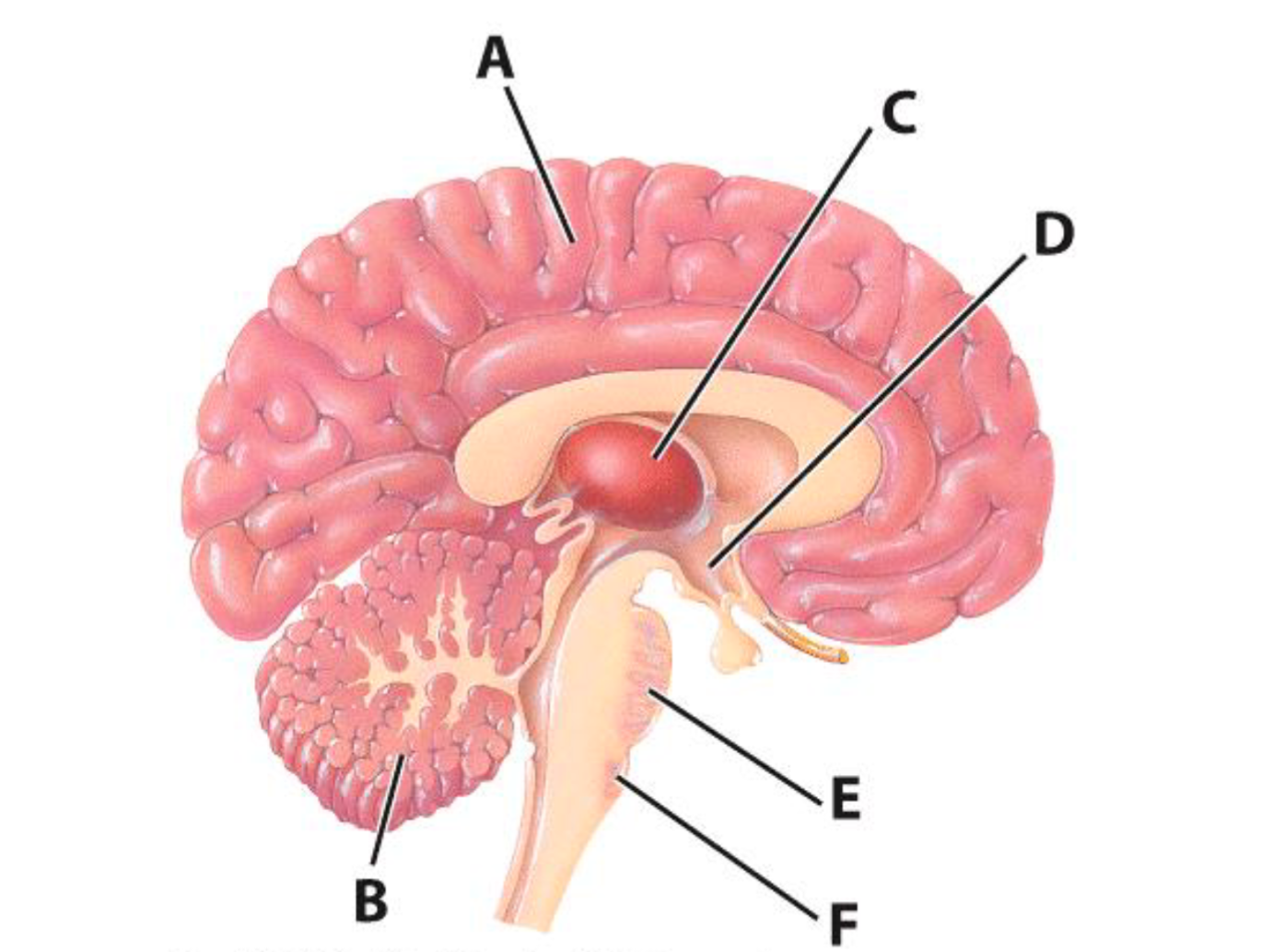
C
Thalamus
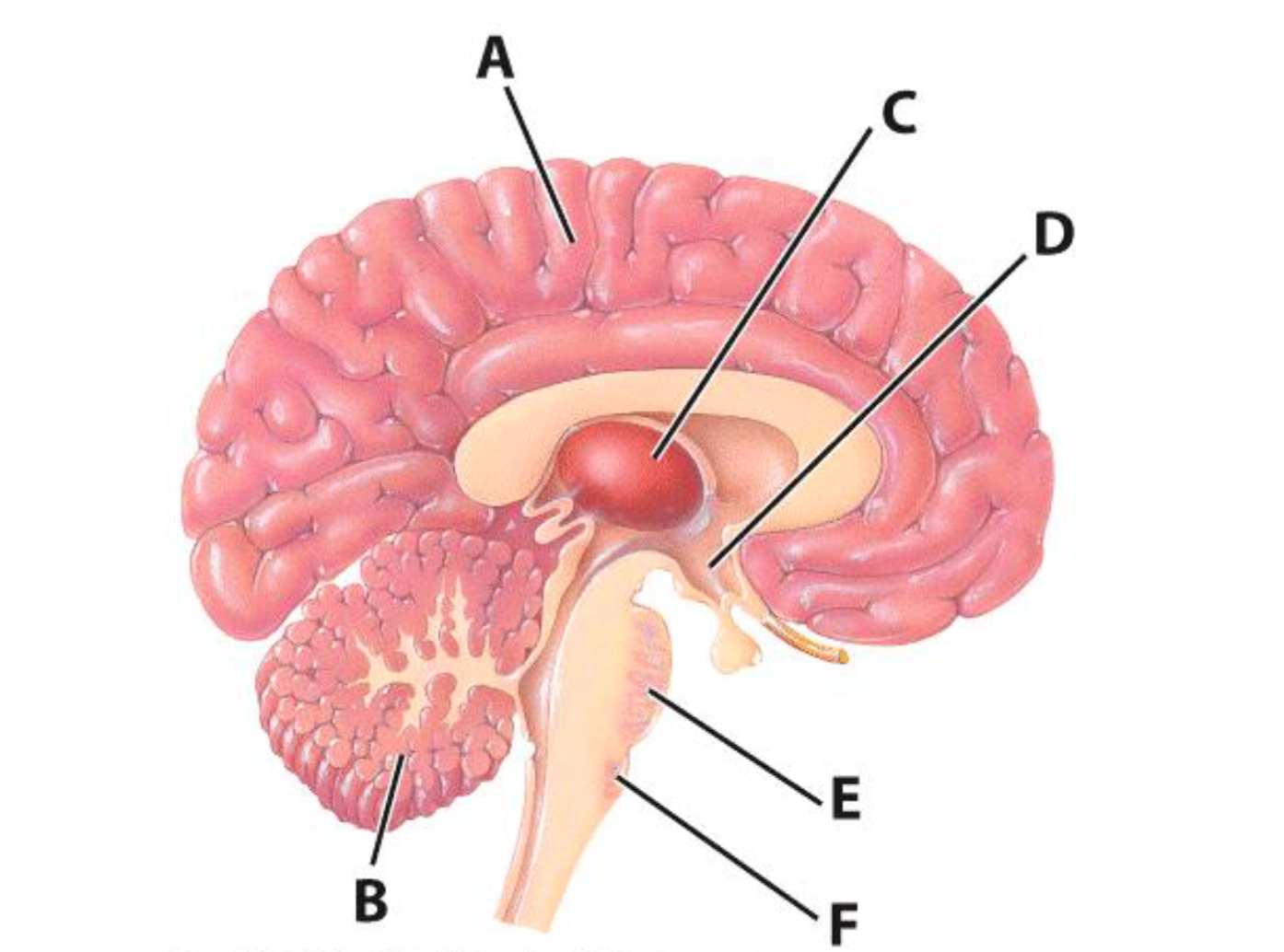
D
Hypothalamus
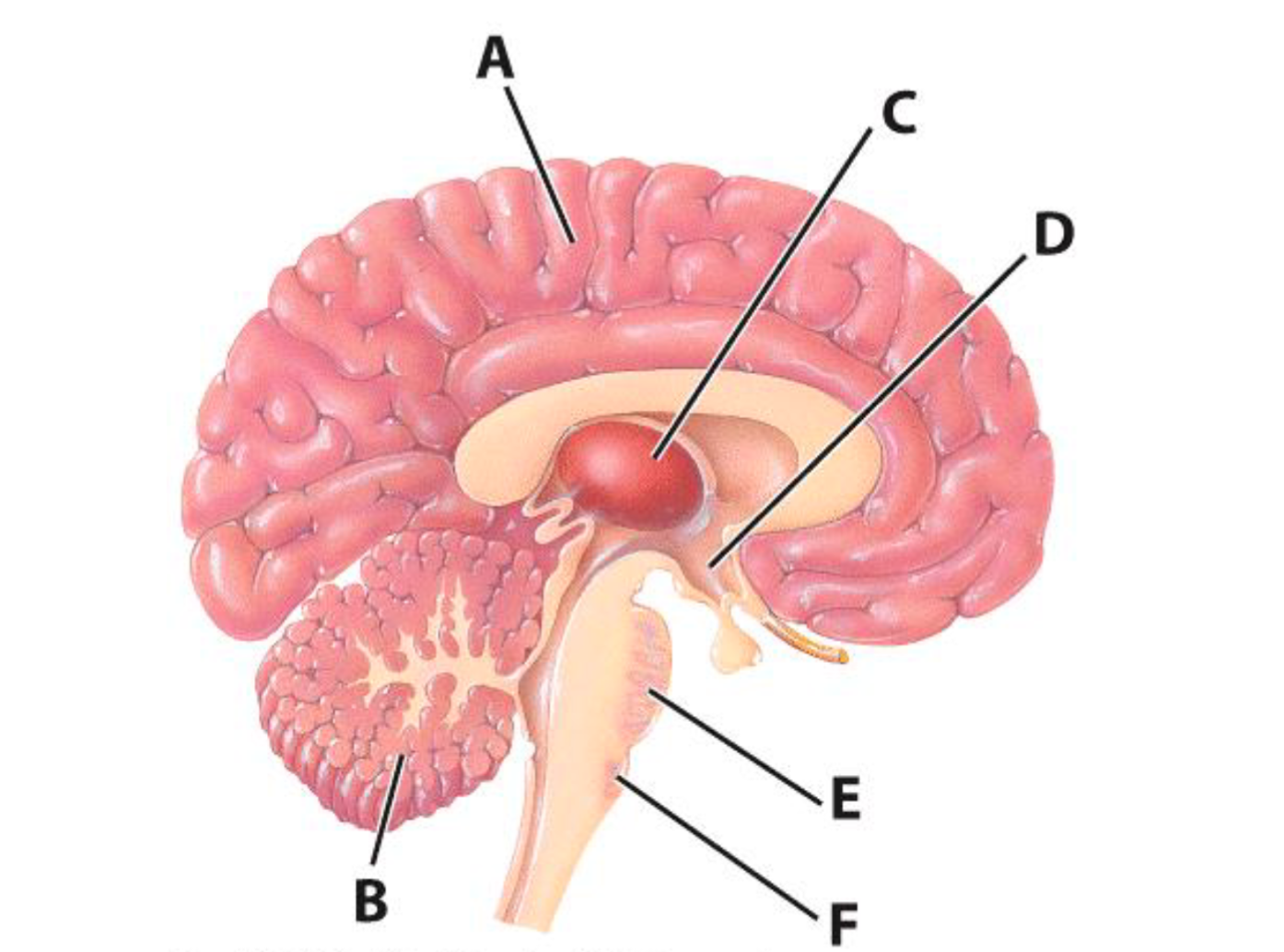
F
Medulla Oblongata