Topic 4 SL
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Groundwater
Water stored beneath the Earth’s surface in soil and rock crevices.
Saline
Salty.
Hydrological cycle
The biogeochemical cycle by which water continuously cycles on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
Evaporation
The transformation of a liquid into a vapor, for example liquid water into water vapor.
Transpiration
The release of water by plants as water vapour.
Evapotranspiration
The process by which water moves from land to the atmosphere by evaporation and from plants by transpiration.
Advection
Wind-blown movement of water vapor or condensed/frozen water droplets (clouds).
Sublimation
The transformation of solid to vapour, for example ice to water vapour.
Condensation
The transformation of a gas into a liquid, such as water vapor into liquid water.
Precipitation
Water that falls to the Earth’s surface or condenses in various forms of rain, snow, hail, or sleet; in chemistry it describes the transformation of a dissolved substance to an insoluble solid.
Infiltration
Movement of water from the surface into the soil.
Percolation
The transfer of water downward through layers of soil or rock.
Run-off
The transfer of water from a solid surface into a body of water.
Surface run-off
Flow of excess water over land after rainfall, melting of snow, etc.
Streamflow
Flow of water in a river or artificial body, such as a canal.
Irrigation
The transfer of water by humans from surface or groundwater storages to crops.
Drought
A long period of abnormally low rainfall that leads to a shortage of water for organisms in an area.
Drip irrigation
The controlled supply of water directly to individual plants through a network of tubes or pipes.
Fertilisers
Substances mainly composed of nitrates, phosphorus, and potassium, added to increase soil fertility.
Eutrophication
The natural or artificial enrichment of a body of water, particularly with nitrates and phosphates, that results in depletion of the water’s oxygen content. It is accelerated by human activities that add detergents, sewage, or agricultural fertilizers to bodies of water.
Algae
Aquatic organisms that perform photosynthesis to produce their own food.
Flash flood
Unexpected intense flood caused mainly due to excessive rainfall.
Deforestation
The action of removing trees from a wide area of land.
Sedimentation
The process of particles settling to the bottom of a body of water.
Afforestation
Planting large numbers of trees on land which has few or no trees.
Urbanization
The process of making a landscape more built-up, industrialized and dominated by close human settlements.
Sponge Cities
Urban environments constructed to prevent run-off and flooding, and to recharge groundwater, by provision of green spaces.
Water Security
Having access to sufficient amounts of safe drinking water.
Water Scarcity
Limited availability of water to human societies.
Mitigation
Action to reduce the severity of something; e.g. strategies involve reduction, stabilization of GHG emissions and their removal from the atmosphere.
Dams
A wall with gates built across a water body to stop the flow and collect the water.
Reservoirs
An area where water is collected and stored for later use.
Rainwater Catchment
An area to which excess rainwater drains.
Desalination
Processes that remove the excess salt and other minerals from water in order to obtain freshwater suitable for consumption or irrigation.
Ways to Increase Supply of Water
Dams and reservoirs
Desalination technology
Improving natural wetlands
Rainwater Catchment systems
Ways to Reduce Demand for Water
Metering
Rationing
Products that uses less water
Grey-water recycling
Metering
Measuring and recording a quantity using a meter. This can be used to keep track of water usage in households.
Rationing
Limiting the quantity a person or group may use.
Grey-Water Recycling
Waste water from showers and sinks can be recycled for purposes other than drinking, such as water plants.
Ways of Conserving Water in Food Production
Drip irrigation
Greenhouses
Aquaponics
Drought-resistant crops
Aquaponics
A form of aquaculture that combines raising fish in tanks with the culture of soilless plants. Waste water from fish tanks goes to plants, then the purified water from plants goes back to fishes.
Phytoplankton
Microscopic aquatic plants that carry out photosynthesis.
Natural Capital
The natural resources that have economic value or provide a service to humans.
Natural Income
Materials in nature that can be used by humans to meet their needs and wants.
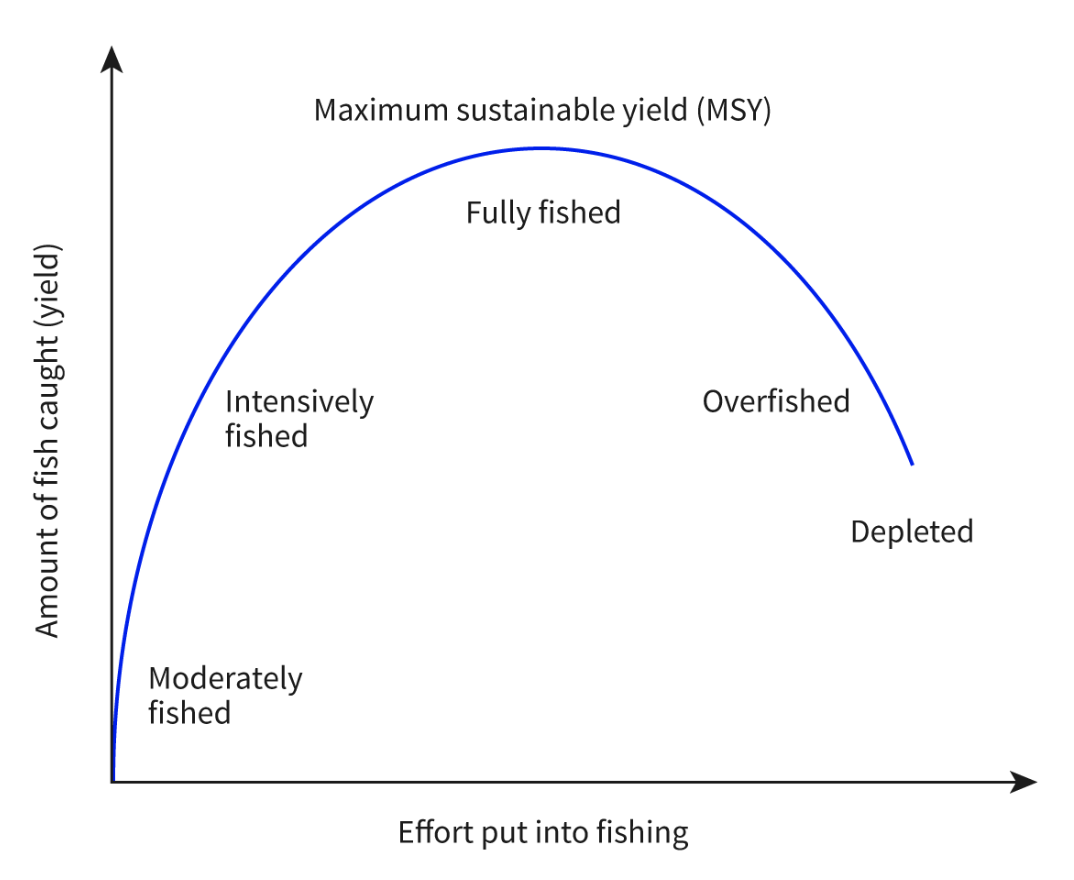
Maximum Sustainable Yield (MSY)
The largest yield or catch that can theoretically be taken from a species’ stock without permanently depleting the stock.
Fishing quotas
A permitted or required quantity, for example of fish that can be caught in a year by a particular ship.
Ocean acidification
A reduction of the ocean’s pH over time (becoming more acidic), caused mainly by dissolution of CO2 from the atmosphere.
Coral Bleaching
Occurs when corals expel the colorful algae living within the coral polyps, making the coral turn white.
Marine Protected Area
Region in the ocean where human activities, such as fishing or development, are regulated to conserve and protect marine ecosystems.
Aquaculture
The farming of aquatic organisms, including fish, mollusks, crustaceans and aquatic plants.
Why are fish species overexploited?
Lacking fishing regulation
Hi-tech fishing gears catch unsustainable amount of fishes
Global markets hides fishes origins
Fishing sustainability is affected by…
Number of fish caught in a time period.
Damage done to habitats from fishing.
Level of bycatch
Stakeholders in Managing Fish Stocks
Countries (international cooperation)
Individual action
NGOs.
National governance
Negative Impacts of Aquaculture
Harm to local habitats
Diseases
Antifouling agents can be harmful
Fishmeal comes from wild fish