Expanded Concepts for PSYC 2317 - Comprehensive Final Exam Review
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
There are no included computation questions for this review set, only the ideas that Professor Bruton said we would need to cover.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Population
The entire group of interest to a researcher.
Sampling error
The natural discrepancy that occurs between a sample and a population.
Nominal scale
Simple named categories without a specific order.
Ordinal scale
Named categories with ranks attached; examples include rankings like first, second, and third.
Interval scale
Numbered measurements where zero is just a reference point, such as temperature.
Ratio scale
Numbered measurements where zero indicates the absence of the thing being measured.
sampling with replacement.
The first of the three requirements for a random sample is
that the probabilities for selecting the next person for a sample cannot change after another individual is selected.
The second of the three requirements for a random sample is
that every individual must have an equal chance of being selected.
The third of the three requirements for a random sample is
larger
Without sampling with replacement, the probabilities get _______ (larger/smaller) during the series of selections, with each selection having a different probability of being selected.
Thus, the sample would not sufficiently represent the population.
Normal Distribution
What kind(s) of distribution(s) is(are) this (these)?
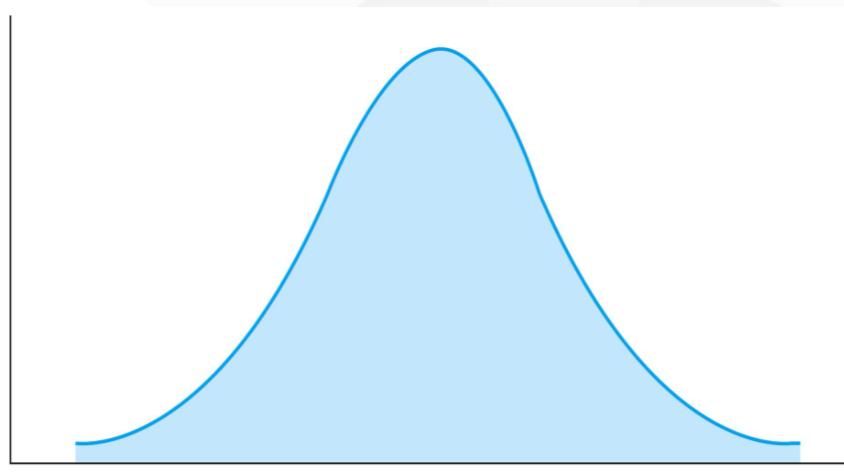
Symmetrical Distribution(s)
What kind(s) of distribution(s) is(are) this (these)?
Positively Skewed Distribution(s)
What kind(s) of distribution(s) is(are) this (these)?
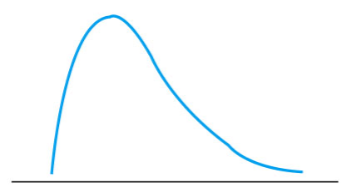
Negatively Skewed Distribution(s)
What kind(s) of distribution(s) is(are) this (these)?
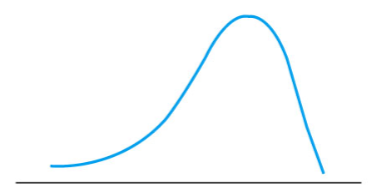
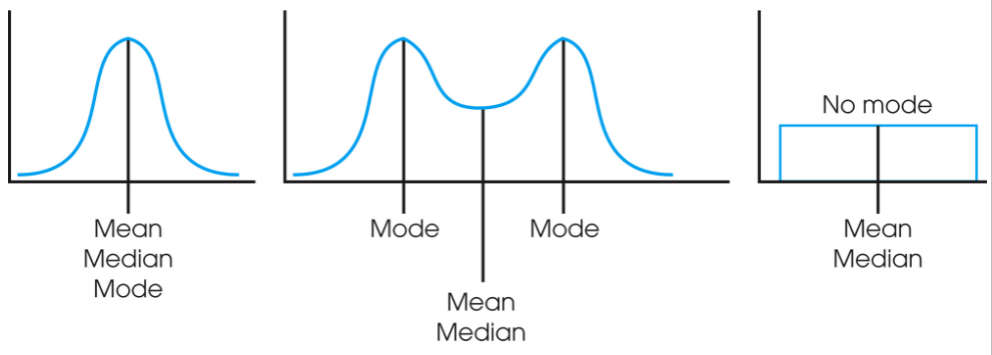
0 or more; the same place in the center of the distribution
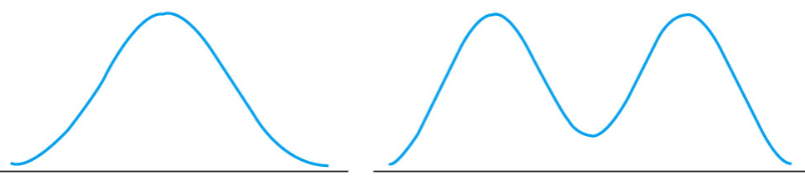
For a symmetrical distribution, it can have ____________ mode(s), and the mean and median appear in ________________________________________.
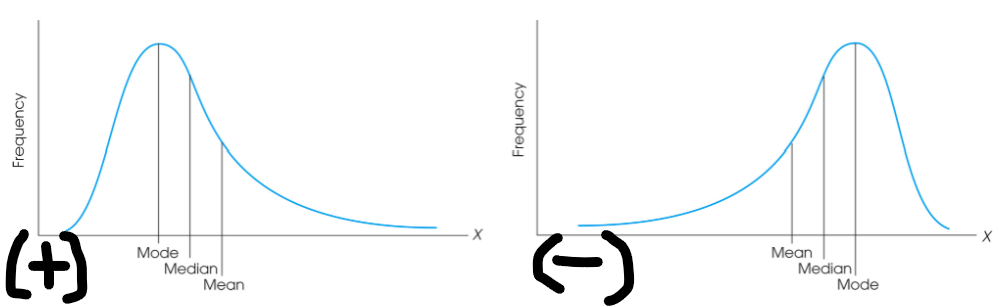
only 1; different places, with the mean at the “balance point” and the median at the center of the distribution.
For a skewed distribution, it can have ________ mode(s), and the mean and median appear in ______________________________________________________.
Expected value of M (μM)
the mean of the sampling distribution, equal to the population mean (μ).
Standard error of M (σM)
the “standard deviation” of the sampling distribution; tells you about the average discrepancy between the sample means (M) and the population mean (σ)—in other words, the measurement of sampling error.
Null hypothesis (H0)
The hypothesis that states there is no treatment effect or no relationship between variables.
Alternative hypothesis (H1)
The hypothesis that states there is a treatment effect or a relationship between variables.
Type I error
The error made when a true null hypothesis (H0) is rejected; the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true.
greater
The greater or larger the alpha level (α), the ______ (greater/less) the critical region.
easier
The greater the critical region, it is ________ (easier/harder) to reject the null hypothesis (H0).
increases
Increasing the alpha level (α) __________ (increases/decreases) the risk of Type I error.
simple
It is more _______ (simple/difficult) to reject the null hypothesis (H0) for a one-tailed test compared to a two-tailed test if the direction of the treatment effect is consistent with the researcher’s hypothesis.
smaller
The larger the sample size (n), the more the sample size undercuts the error, which makes the estimated standard error (s(M1-M2)) ______ (bigger/smaller).
larger
The larger the sample standard deviation (s), the ______ (larger/smaller) the estimated standard error (s(M1-M2)) will be.
independent-measures t-test
a test used in a situation in which you have two groups of participants being compared to one other.