Cell Communication and Cell Cycle
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
m phase (mitotic phase)
phase of the cell cycle where mitosis and cytokinesis occur, resulting in the division of a parent cell into two genetically identical daughter cells.
Juxtacrine signaling
Cell signaling that requires direct contact between cells, either through membrane-bound molecules or direct channels like gap junctions.
: How do G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) work in cell signaling?
A ligand binds to the GPCR on the cell membrane, activating an attached G protein. The G protein exchanges GDP for GTP, becoming active. The activated G protein then triggers the production of secondary messengers (like cAMP), which relay the signal through phosphorylation cascades, ultimately leading to a specific cellular response such as gene expression, enzyme activation, or cell division.
Phosphatase
enzymes that remove phosphate groups (dephosphorylate), often turning off the proteins.
secondary messengers
(like cyclic AMP) are molcules that relay and amplify the intracellular signal
an example of a secondary messenger in action is when epinephrine (adrenaline) binds to a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) on the surface of a target cell. This activates the associated G protein by causing GDP to be replaced with GTP. The activated G protein (specifically the alpha subunit) then moves along the membrane and activates the enzyme adenylate cyclase. Adenylate cyclase converts ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP), which acts as the secondary messenger. cAMP then activates protein kinase A (PKA), which triggers a phosphorylation cascade that ultimately leads to glycogen breakdown
signaling cascades
pathways that relay signals from receptors to target cells. amplifying the incoming signals, resulting in the appropriate responses by the cell, like cell growth, secretion of molecules, or gene expression
interphase
phase of the cell cycle between cell divisions, where the cell grows, performs normal functions, and prepares for division. It includes G1, S, and G2 phases.
g1 phase
first gap phase of interphase where the cell grows, synthesizes proteins, and prepares for DNA replication.
phosphorylation cascades
a series of events where one enzyme phosphorylates another, activating it, which then phosphorylates another, and so on. T
amplify and relay signals through a chain of phosphorylation events, ultimately leading to a specific cellular response.
role of protein modification in signal transduction pathways
Protein modifications like phosphorylation help activate or inhibit proteins, allowing the cell to relay, amplify, and regulate responses to external signals.
g0 phase
resting state where cells exit the cell cycle and do not divide. Some cells may re-enter the cycle, while others remain permanently in G0.
s phase
synthesis phase of interphase where DNA is replicated, ensuring that each daughter cell will have an identical set of chromosomes.
hormones
chemical messengers that move around the body to stimulate activity
g2 phase
second gap phase of interphase where the cell continues to grow and prepares for mitosis by synthesizing necessary proteins and organelles.
what is the cell cycle controled by
controlled by regulatory proteins and checkpoints that ensure proper progression and prevent errors, such as damaged DNA or incomplete replication.
cell cycle checkpoints
Specific control points in the cell cycle (G1, G2, and M checkpoints) that assess conditions like DNA damage, correct replication, and proper attachment of chromosomes to the spindle.
kinase
enzymes that active/deactivate other proteins by phosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to another molecule)
always in the cell, usually inactive
attached to a cyclin = activated
cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)
family of enzymes that, when bound to cyclins, regulate the cell cycle's progression by phosphorylating target proteins (activating or deactivating them), which then promotes cell cycle activities

organisms need to regulate pathways to respond to changes in the environment
signalling pathways can target gene expression and alter the amount of a particular protein produced in a cell (apoptosis can be the result of a signal transduction)

example of using signal transduction to respond to the environment
quorum sensing: a signal mechanism used by bacteria, where they release signals to neighboring bacteria to detect changes in population density
allows bacteria to act as a group in response to changes in the environment
g1 phase: checkpoint
critical checkpoint in the G1 phase where the cell decides to proceed with division, enter G0, or undergo apoptosis, based on environmental and internal signals.
check cell size, nutrients, growth factor, dna damage
cyclins
Regulatory proteins associated with different phases of the cell cycle
different cyclins are involved in different phases of the cellcycle
concentrations can fluctuate depending on cell activity → produced to promote cell cycle progression, degraded to inhibit it
bind to CDKs to activate them, controlling the timing and sequence of cell cycle events. (cyclins are specific to the cdks they activate)
What is signal amplification in signal transduction, and how does it work?
occurs when a single signaling molecule triggers a cascade, activating multiple downstream molecules, leading to a larger cellular response.
one signaling molecule activates multiple enzymes
each enzyme acts on multiple substrates, producing more active molecules
the cascade repeats, exponentially increasing the response
ex: PHO pathway
Low Pi → Pho81 inhibits Pho80-Pho85
Pho4 remains active → Induces multiple Pho target genes
Increased PHO1 expression → More APase enzyme → Greater phosphate regulation
Result: A small signal leads to a large response by amplifying the effect at each step.
gap junction
direct connections between the cytoplasm of adjacent animal cells that allow ions, nutrients, and signaling molecules to pass freely between them.
paracrine signalling
communication of cells over relatively short distances
important during development (growth factors, immune cells)
why is paracrine signalling crucial for immune cells?
allows for the rapid and localized transmission of chemical signals (such as cytokines and interleukins). This fast, short-distance communication enables immune cells to coordinate effective responses to pathogens or harmful substances in a targeted area, without activating the entire body unnecessarily.
endocrine signalling
long distance cell signaling (like via blood)
hormones like insulin
quorum sensing
bacteria monitor the density of the population based on chemical signals
autocrine signaling
a cell signals to itself, releasing a ligand that binds to receptors on its own surface
helps cells take on and reinforce their correct identities (like cancer)
ex: T-cell signaling itself
signal transduction
relay proteins + secondary messengers that relay extracellular signals to activate cellular responses
3 stages of cell communication: reception, transduction, and response
ligands
signalling molecules that bind to receptors and trigger a response by changing the shape of the receptor protein
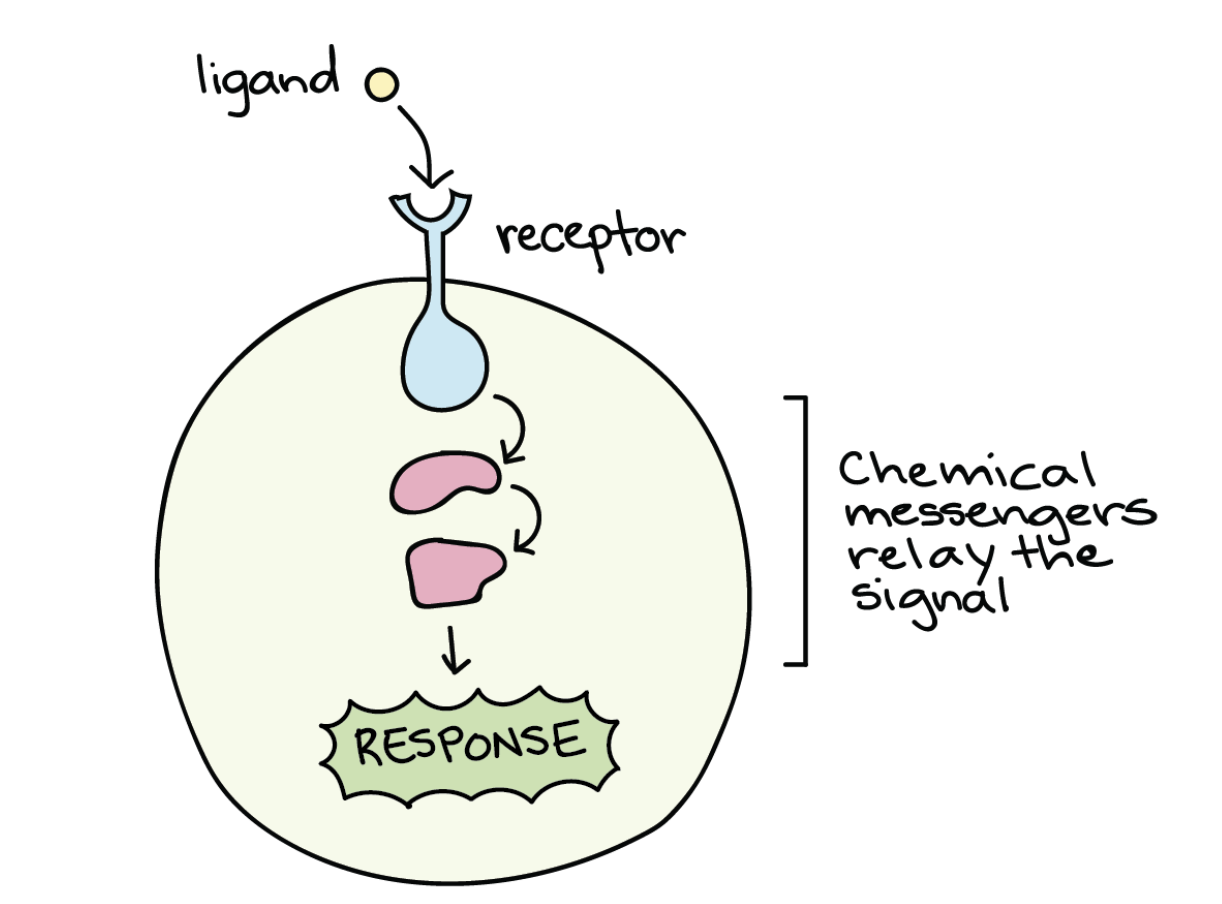
what are the four basic categories of chemical signalling in multicellular organisms?
paracrine signaling, autocrine signaling, endocrine signaling, and signaling by direct contact
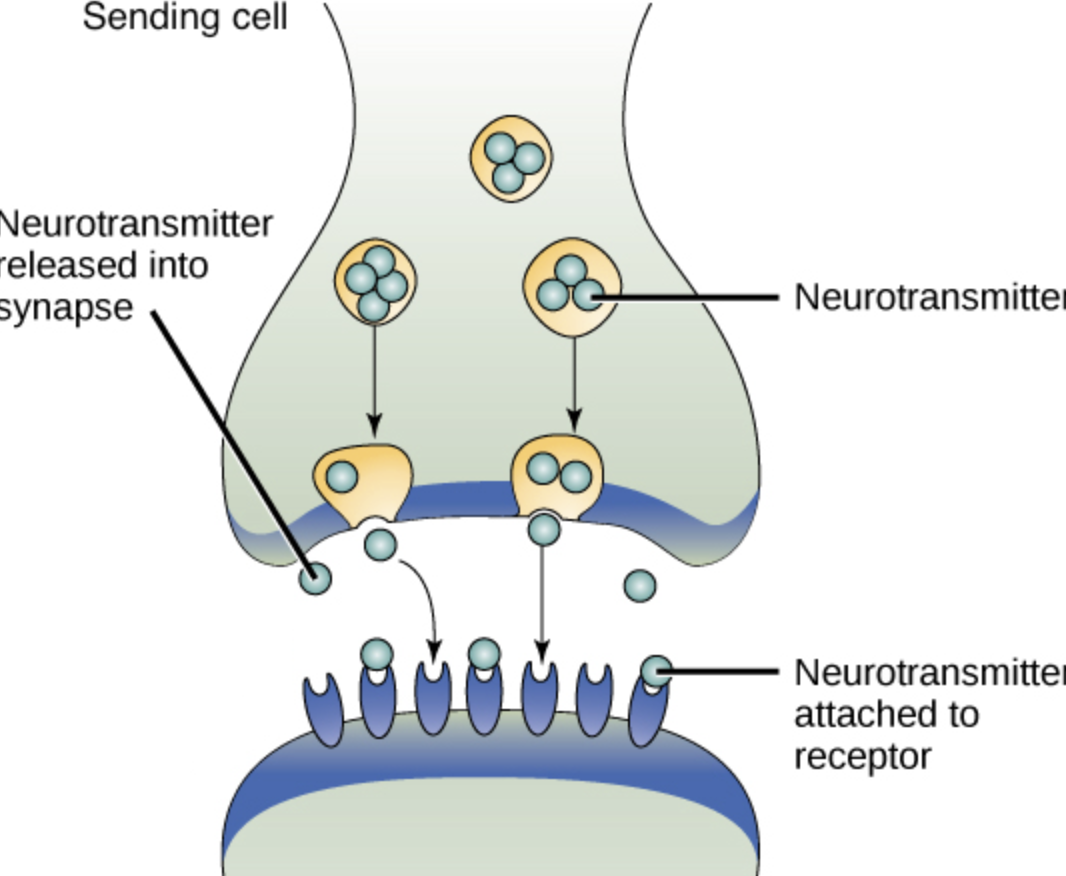
synaptic signaling
a type of paracrine signaling; nerve cells transmitting signals
autoinducers
signaling molecules continually secreted by bacteria to announce their presence to their neighbours
short distance communication
typically involves cells of the same or nearby type and uses local regulators — signaling molecules that are secreted and received over a short distance (often by diffusion). These signals are important for processes like growth, immune responses, and development.
feedback mechanism
a biological process in which the output or result of a system regulates that same system, helping maintain homeostasis.
g2 checkpoint
end of g2, dna replication and damage check
m spindle checkpoint
fiber attachment to chromosomes check
how do disruptions to the cell cycle result in cancer/programmed cell death?
the original code for making proteins is stored in the DNA, and if its altered, the structure and the function of the protein can be altered
if there is change in the dna that codes for one of the proteins needed to regulate the cell cycle, then the cell cycle could go unregulated
cancer is the result of an unregulated cell cycle with uncontrolled cell division
cell signalling depends on what?
the ability to detect a signal molecule. ex: Not all cells have receptors for epinephrine. Only cells with such receptors are capable of responding.