TOPIC 7- Antimicrobial Drugs and Resistance
1/21
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
antimicrobial
compound that inhibits growth (-static) or kills (-cidal) a microorganism in a human or an animal
selective toxicity- only attacks foreign cells and not the human’s cells
narrow spectrum
affects only microbes within a limited functional group
penicillin only attacks gram positive bacteria
very narrow spectrum
affects only a very specific group (phyla / species) of bacteria
isoniazid is only effective against mycobacteria
broad spectrum
works against a wide range of microbes from a singular domain
tetracycline works on both gram negative and gram positive bacteria
growth factor analogous
type of synthetic antimicrobial drug that:

quinolenes
type of synthetic antimicrobial:
interferes with DNA replication
broad spectrum
Ex: Ciprofloxacin which targets DNA gyrase
DNA gyrase
enzyme involved in the supercoiling of DNA
antibiotic
antimicrobial agent produced by other microorganisms
beta-lactam antibiotic
antibiotic that includes a beta-lactam ring
the function of the beta-lactam ring is to block crosslinking so the cell walls of the bacteria are weak
binds to a periplasmic protein called the penicillin binding protein
only works when the bacteria is actively growing
methicillin
semi-synthetic penicillin
designed to fight the antibiotic-resistant S. aureus
resistant to beta-lactam
resulted in MRSA, methicillin-resistant S. aureus
beta-lactamase
enzyme produced by beta-lactam resistant bacteria which cuts the beta-lactam ring thus rendering the antibiotic ineffective
amipicillin
semi-synthetic penicillin
broad spectrum and acid stable
cephalosporine
a type of beta-lactam antibiotic:
more resistant to beta-lactamase
better against gram negative bacteria bcuz they can penetrate the membrane better
used to treat infections by penicillin resistant bacteria
vancomycin
cell wall synthesis inhibitor
blocks the cross-linking of penicillin but don’t include beta-lactam ring
narrow spectrum; blocks MRSA (only specific gram positive)
big molecule so it is more likely to cause an allergic reaction
aminoglycosides
disrupts protein synthesis

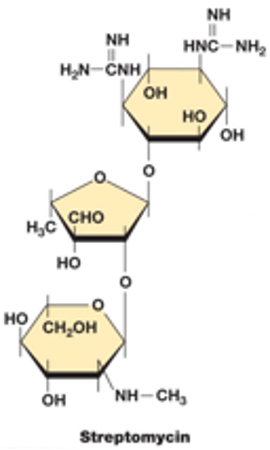
macrolides
protein synthesis inhibitor
made by streptomycin
structure is based on the lactone ring
erythromycin
a type of protein synthesis inhibitor, macrolides

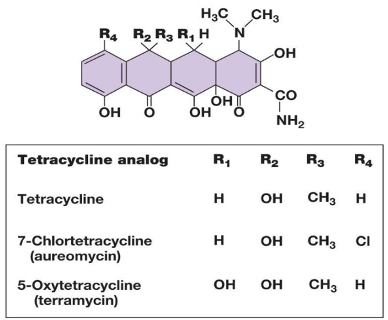
tetracycline
type of protein synthesis inhibitor

daptomycin
made by S. roseosporus
made by non-ribosomal protein synthase (assembles amino acids into chain, not a ribosome)
depolarizes the membrane by forming a hole in it
narrow spectrum against gram positive bacteria
last resort against MRSA
platensimycin

mechanisms of antibiotic resistance
inactivation of the drug
metabolic bypass
modification of the drug bypass
decreased uptake
efflux pumps
ways to prevent antibiotic resistant
infection prevention
rapid and conclusive diagnosis
appropriate and prudent use of antibiotics
prevention of transmission of disease