Chemistry Structure and Bonding - 91164
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Level 2 NCEA 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
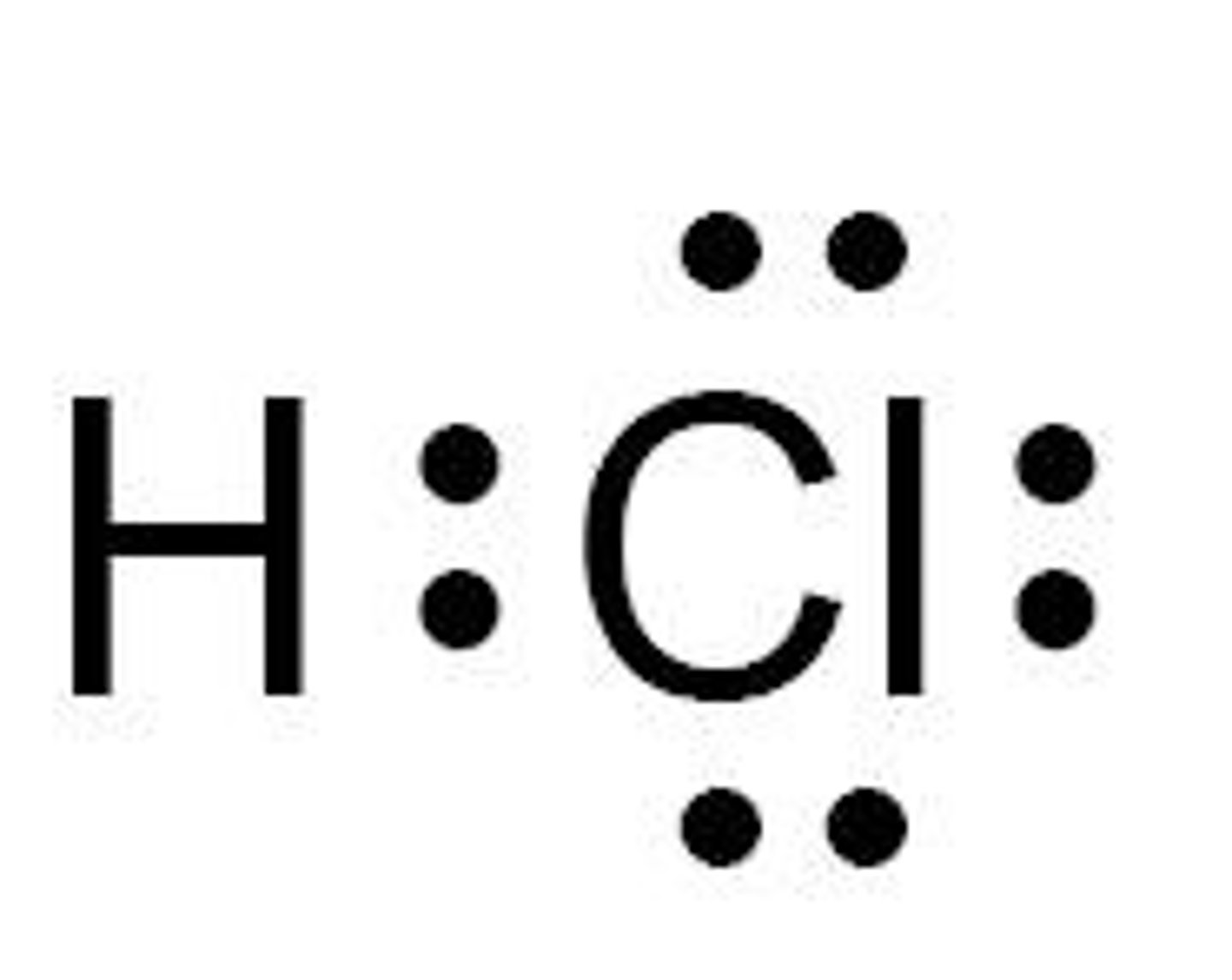
What is the molecular shape of HCl?
Linear
What type of bond is present in Na2O?
Ionic bond
What is the shape of SF2?
Bent or V-shaped
What is the molecular geometry of CO2?
Linear
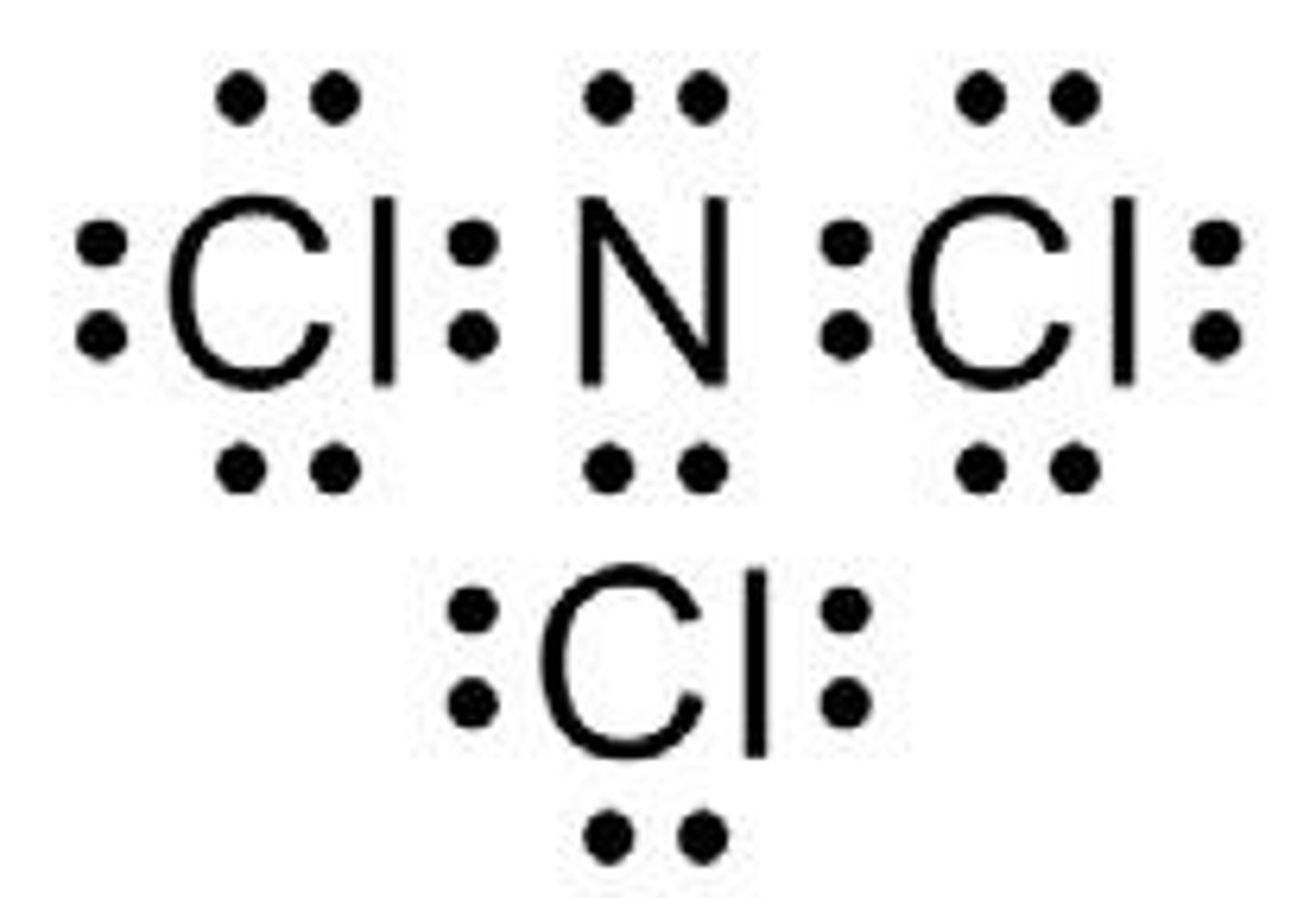
What is the shape of NCl3?
Trigonal pyramidal
What type of particles are found in MgCl2?
Ions
What is the molecular shape of SO2?
Bent or V-shaped
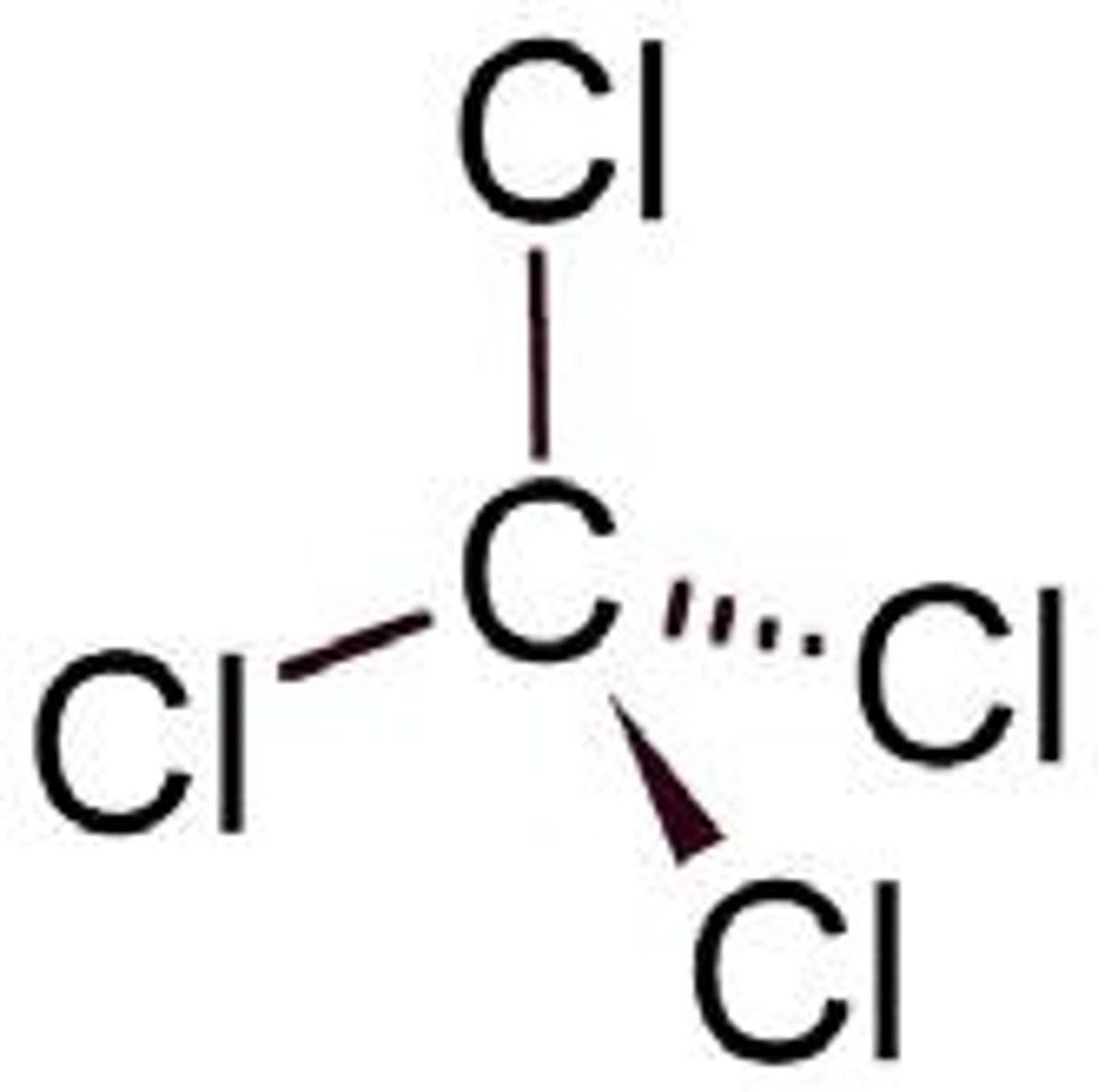
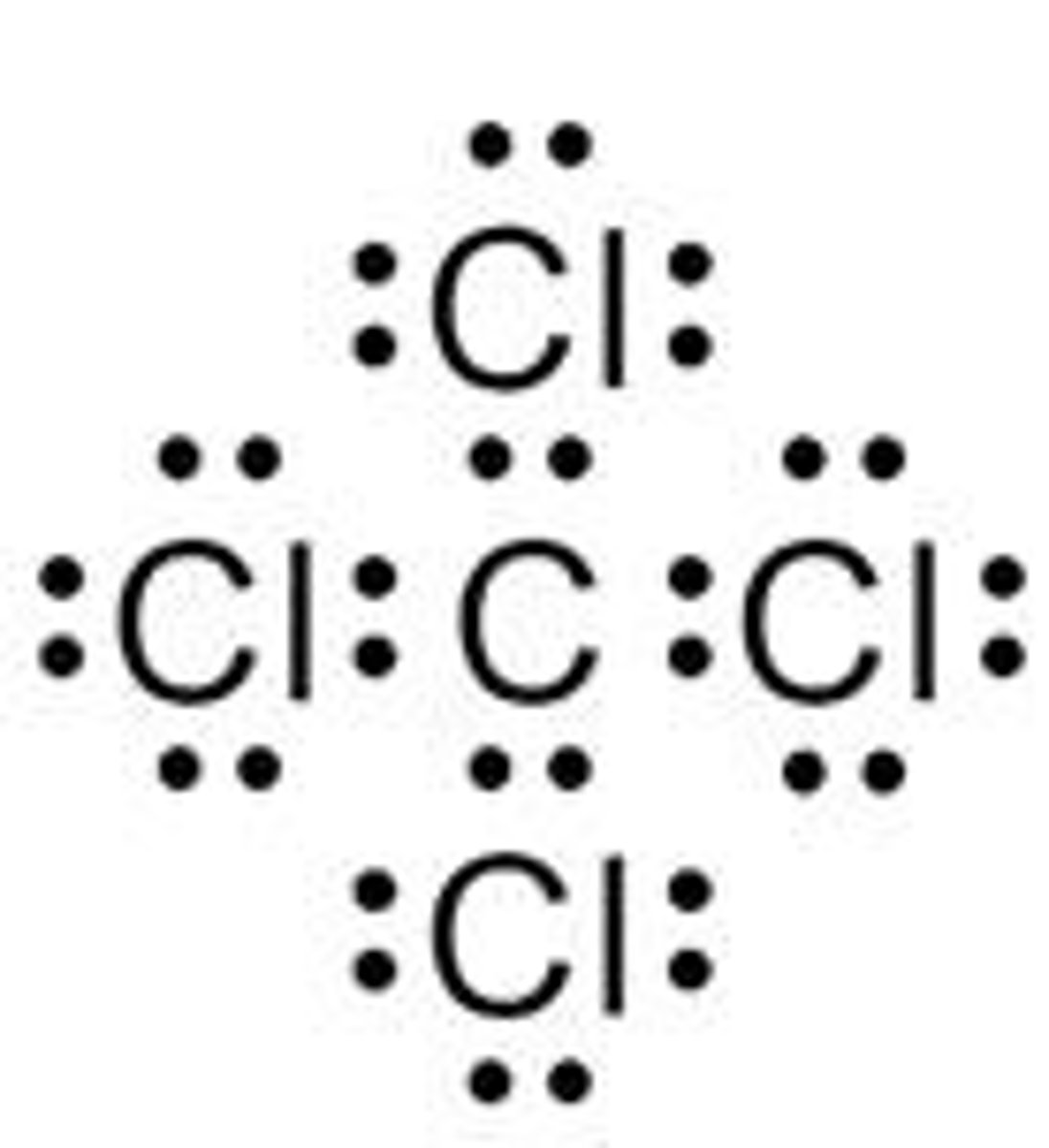
What type of bond is found in CCl4?
Covalent bond
What is the shape of CH2Cl2?
Tetrahedral
What is the molecular geometry of PH3?
Trigonal pyramidal
What is the shape of H2S?
Bent or V-shaped
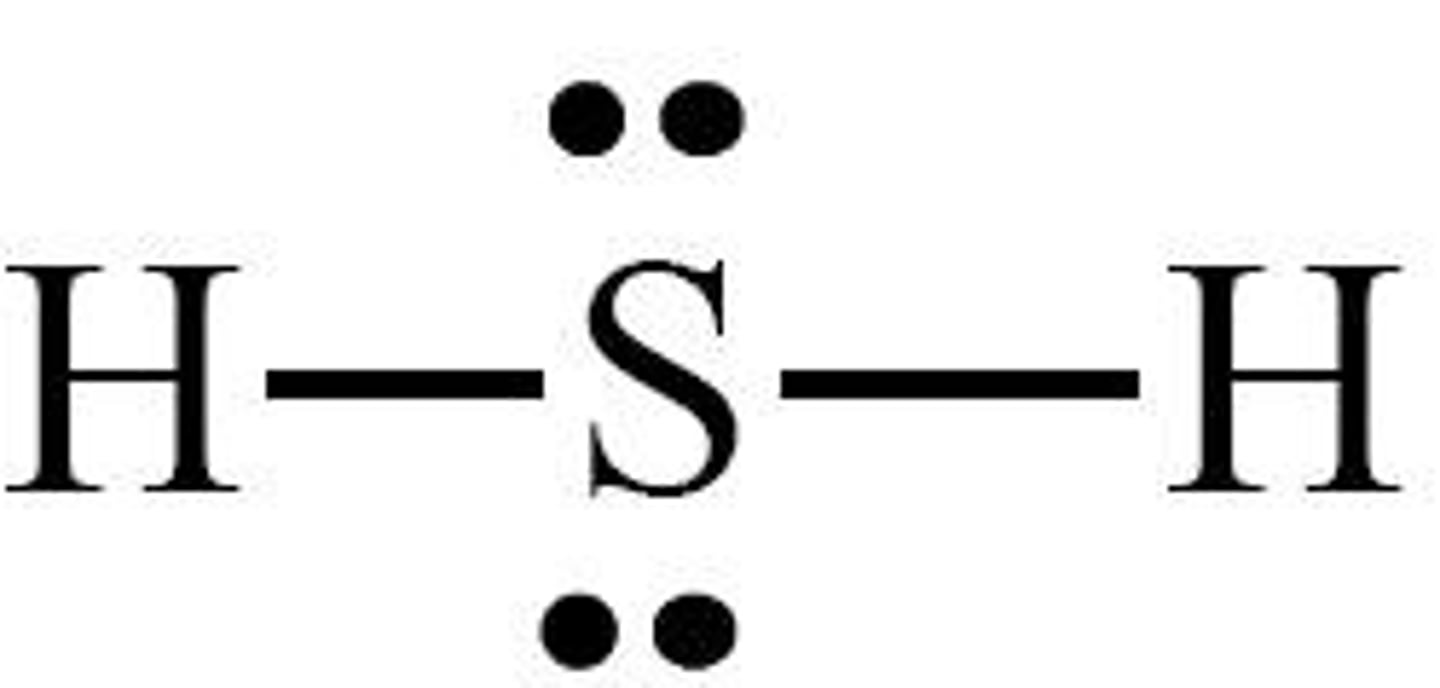
What type of bond is present in SiO2?
Covalent bond
What is the molecular shape of H2O?
Bent or V-shaped
What type of bond is found in SCl2?
Covalent bond
What is the shape of SO3?
Trigonal planar
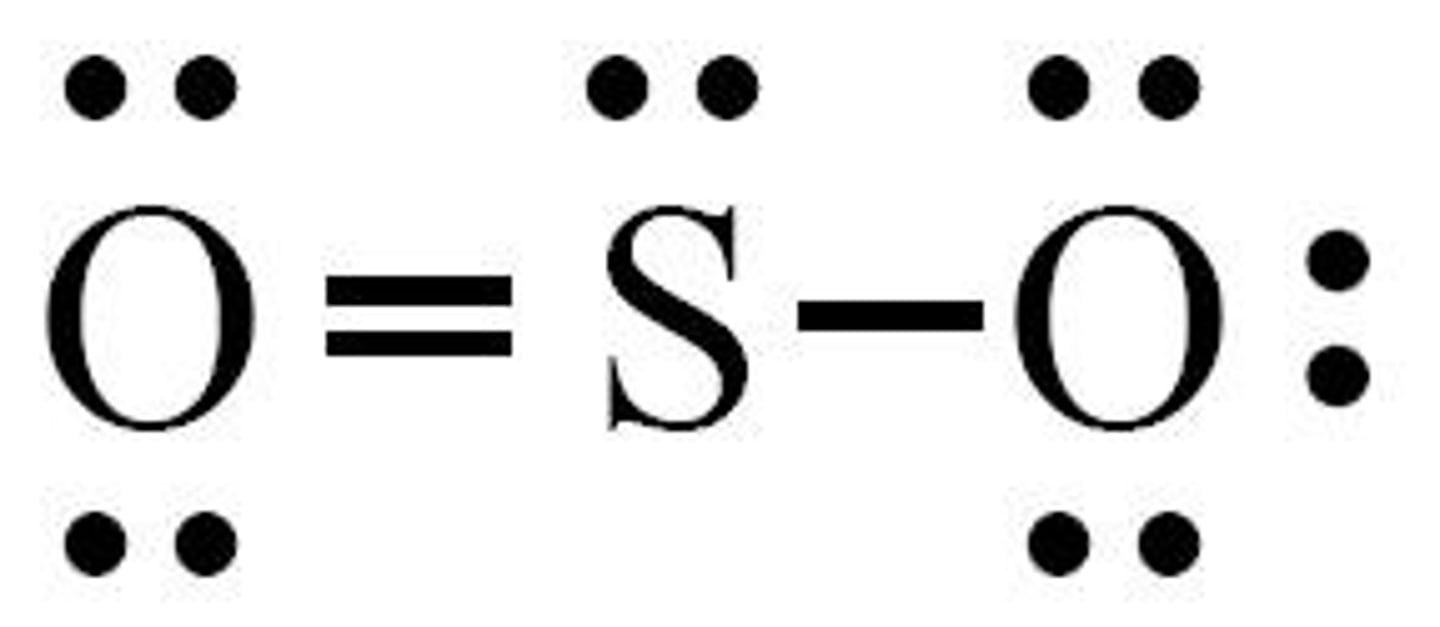
What is the molecular geometry of CH3Br?
Trigonal pyramidal
What type of bond is present in Cu?
Metallic bond
What is the shape of SiCl4?
Tetrahedral
What type of particles are in S8?
Molecules
What is the electronegativity trend for the most electronegative elements?
F, O, N, Cl, S.
What determines the shape of a molecule?
The number of bonding and non-bonding regions around the central atom.
What is a polar bond?
A bond between atoms with an unequal distribution of electrons, resulting in regions of negative charge.
What type of solutes dissolve in polar solvents?
Ionic solutes like NaCl and polar solutes such as sugar.
What is the significance of the melting point in molecular solids?
It reflects the strength of bonds between particles.
What is a covalent network solid?
A type of solid where atoms are held together by strong covalent bonds, e.g., diamond and SiO2.
What characterizes metallic bonding?
Metal atoms with loosely held valence electrons that can drift, allowing for electrical conductivity.
What is the structure of ionic solids?
They form a 3D crystal lattice of cations and anions held together by electrostatic attractions.
What is VSEPR theory used for?
To predict the shape of molecules based on electron pair repulsion.
What is a dipole?
A separation of electric charge within a molecule, leading to positive and negative ends.
What defines a non-polar molecule?
A molecule with no overall charge due to the cancellation of polar bonds.
What are van der Waals forces?
Weak attractive forces between molecules.
What is the role of electronegativity in bonding?
It measures an atom's tendency to attract electrons in a bond.
What is a covalent bond?
A bond formed by the sharing of a pair of electrons between two atoms.
What is an ionic bond?
A bond formed between oppositely charged ions.
What is the shape of a molecule with a bent or V-shaped geometry?
An example is H2O, which has a polar bond.
What is a hydrocarbon?
A molecule containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds form between charged particles, while covalent bonds form by sharing electrons.
What is the significance of the crystal lattice structure in ionic solids?
It provides stability and strength due to the electrostatic attractions between ions.
What are the characteristics of metallic solids?
They consist of layers of metal atoms with weak attractive forces between them.
What type of solid is characterized by small covalently bonded molecules?
Molecular solids, such as sugar.
What is the trend in bonding as you move across the Periodic Table?
The trend goes from ionic to covalent to metallic bonding.
What is a molecular structure diagram?
A representation showing bonding between atoms in a molecule and any lone pairs of electrons.
What is the definition of a solute?
A substance that dissolves in a solvent to form a solution.
What is the definition of a solvent?
A liquid that dissolves a solute to form a solution.
What is the molecular shape of SF2?
Bent or V-shaped
What is the molecular shape of CO2?
Linear or straight
What is the molecular shape of NCl3?
Trigonal or triangular pyramid
What is the molecular shape of CH2Cl2?
Tetrahedral
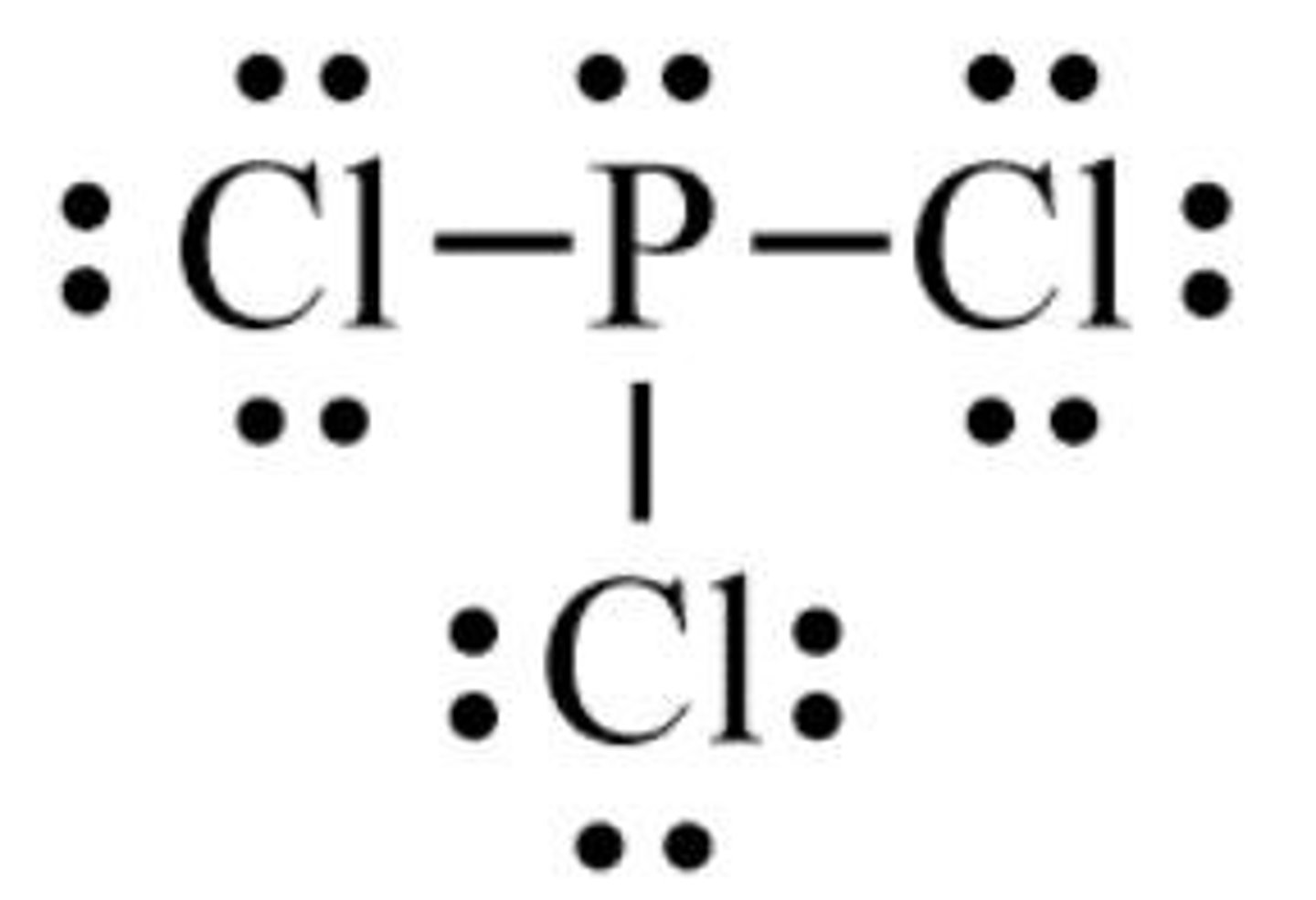
What is the molecular shape of PCl3?
Trigonal or triangular pyramid
What is the molecular shape of PH3?
Trigonal or triangular pyramid
What is the molecular shape of CH3Br?
Bent or V-shaped
What type of bond is found in Na2O or NaCl?
Ionic bond
What type of particles are found in SO3?
Molecules
What is the molecular shape of CCl4?
Tetrahedral
What type of bond is found in SiO2?
Covalent
What type of bond is found in MgCl2 or MgO?
Ionic bond
What type of bond is found in H2CO / HCHO?
Covalent
What type of bond is found in SiCl4?
Covalent
What are the two types of intermolecular attractions?
Van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds.
What are the five most electronegative elements?
F, O, N, Cl, S.
What is a polar covalent bond?
Uneven sharing of electrons between atoms with different electronegativities.
What is the difference between intramolecular and intermolecular forces?
Intramolecular forces are within molecules, while intermolecular forces are between molecules.
What characterizes a polar bond?
A polar bond has unequal sharing of electrons, resulting in regions of negative and positive charge.
What is the significance of molecular shape in chemistry?
The shape of a molecule affects its polarity and interactions with other molecules.
What is a characteristic of small covalently bonded molecules?
They typically have low melting points and are often found in liquid or gaseous states.
What is a crystal lattice?
A regular 3D arrangement of ions held together by electrostatic attractions.
What type of solid is characterized by strong covalent bonds between atoms?
Covalent network solids, such as diamond and SiO2.
What defines metallic bonding?
Metallic bonding involves a sea of loosely held valence electrons that can drift randomly, allowing for electrical conductivity.
How do dipole interactions occur?
Dipole interactions occur due to the attraction between regions of positive and negative charge in polar molecules.
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to draw electrons toward itself in a bond.
What is a non-polar molecule?
A molecule with an even distribution of charge, often containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
What is the role of solvents in chemical reactions?
Solvents dissolve solutes, facilitating chemical reactions by allowing molecules to interact.
What is the shape of a water molecule?
The shape of a water molecule is bent or V-shaped due to its polar bonds.
What is the effect of multiple polar bonds on molecular polarity?
If several polar bonds do not cancel each other out, the molecule will be polar.
What is a polar molecule?
A molecule that has a net dipole moment due to the presence of polar bonds.
What is the relationship between ionic solids and electrical conductivity?
Ionic solids conduct electricity when melted or dissolved in water due to the movement of ions.
What is a linear molecular shape?
A molecular shape where atoms are arranged in a straight line, typical of diatomic molecules like Cl2.
What are particles are molecular solids made up of?
Molecules
What are the attractive forces between molecules?
Intermolecular forces
What particles are metallic solids made up of?
Atoms and cations in a sea of delocalised electrons.
What particles are ionic solids made up of?
Ions
What particles are covelent networks made up of?
Atoms
What are the attractive forces between atoms in a covalent network?
Covalent bonds
What are the attractive forces between atoms and cations in a sea of delocalised electrons?
Metallic bonds
What are the attractive forces between cations and anions in ionic bonds?
Ionic bonds
What is the melting point of SiO2 (silicon dioxide) ?
1700
What is the melting point of SiCl4 (silicon tetrachloride) ?
-69
What is the melting point of CuCl2 (copper (II) chloride)
620
What is the melting point of Al (aluminium)?
660
Is this enthalpy change exothermic or endothermic Δr H = –72 kJ mol–? WHY?
Exothermic because the enthalpy value is negative showing that the reactions releases energy.