Lecture 12: Snakes Lecture Review
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts and facts about snakes based on lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What is the primary focus when discussing venomous snakes in the lecture?
The focus is on husbandry and ensuring safety when working with them.
What is a Gila monster?
A venomous lizard found in Arizona, known for being non-aggressive but venomous.
What key anatomy feature distinguishes venomous snakes from non-venomous ones?
Venomous snakes typically have a triangular-shaped head and heat-sensing pits.
What is the proper way to handle a venomous snake to ensure safety?
It's important to avoid getting too close to the snake's head and to be aware of your surroundings.
What are some common signs of respiratory disease in snakes?
Open mouth breathing, nasal discharge, and lethargy.
What type of blood cells are unique to reptiles, including snakes?
Nucleated red blood cells.
In snakes, how are the cloaca used to determine the sex?
If probing into the cloaca reveals a hemipenis pocket, it indicates a male; if not, it's likely a female.
What are the most common bacterial causes of disease in snakes?
Aeromonas and Pseudomonas.
What is inclusion body disease (IBD) and what physical symptoms does it cause in snakes?
IBD is caused by a virus affecting boas and pythons, leading to neurological symptoms like failure to right themselves.
What is the recommended practice for feeding snakes to prevent obesity?
Ensure the food is not larger than the snake's head and avoid overfeeding.
How should substrate for snake enclosures be managed?
Natural substrates can harbor parasites; paper is recommended as a safer alternative.
What are common parasites affecting snakes?
Amoebas, mites, and ticks.
How does humidity impact snake care as discussed in the lecture?
Low humidity can lead to conditions like retained spectacles and skin issues.
What is the significance of retained spectacles in snakes?
They can impair vision and affect the snake's ability to hunt.
What is the proper method for milking a snake for anti-venom?
Stay away from the fangs and ensure safety when handling.
What are the two primary non-infectious causes of disease in snakes?
Malnutrition and obesity.
Why is it discouraged to feed live prey to snakes?
Live prey can injure the snake and may turn on it if the snake is not hungry.
What is one of the major impacts of IVD in snakes?
Poor wound healing and abnormal physical presentation like stargazing.
What behavioral sign can indicate a stressed or unhealthy snake?
Lethargy and not engaging in normal activities.
Why is proper husbandry critical for snake care?
It significantly affects snake health and can prevent many diseases.
How are you able to advance the sexing rode in further?
Male snakes
What is the equivalent to neutrophils in snakes?
Heterophils
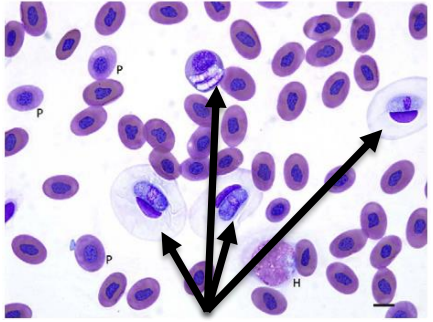
Hepatozoon
Leukemia
Inclusion body disease
What are azurophils?
A mix between monocyte and neutrophils
When should you feed juveniles?
Every 2-7 days
When do you feed adults?
7-21 days
Where are mites often found?
Gular fold
How do you assess dehydration?
“Tent” the skin
How do you check cadiovascular system?
Doppler
How long can snakes go between feedings?
6 weeks
How long should you wait to handle after feeding?
3 days
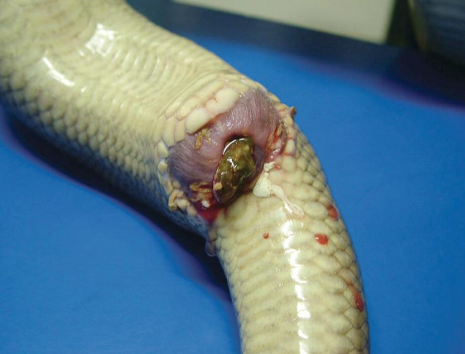
Clinical presentation of cloacoliths?
Inspissated purulent material and urates
Associated with cloacitis
Malodurous and/or bloody cloacal discharge
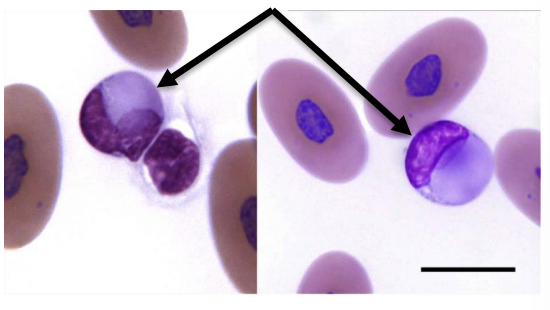
What lesions are seen with cloacoliths?
Swollen cloaca and surrounding tissues
Intestinal hemorrhage and necrotic plagues
Common sequela with cloacoliths
Ascending infections
What is constipation associated with?
Dehydration, overfeeding, low temperature
Clinical presentation of constipation
Lethargy, hardened feces
What is dysecdysis secondary to?
Fungal (Ophidomyces ophiodiicola and Paranannizziopsis)
IBD (viral)
How is dysescedysis diagnosed?
Histopathology
What is retained spectacles caused by?
Improper husbandry
Mites
Mouth rot
Infections
Dark brown to black
Melanophores
Red to yellow
Xanthophores
Crystaline green/blue
Iridophores
Most common chromatophormas?
Melanophoroma/melanoma
What other neoplasia commonly occurs?
Fibrosarcoma and SCC
Differentials for neoplasia
Granulomas
Parasitic masses
Steatitis
Cryptosporidium
What is septicemia secondary to?
Trauma, localized infection, parasitism, environmental stressors
Most common causes of septicemia
Aeromonas and Psuedomonas
Signs of septicemia
Ventral petechiae/eryghemia
Respiratory distress
Lethargy
Convulsions and incoordination
Blister-like ventral skin lesions
Blister disease
Causes of blister disease
Excessive humidity
Inadequate substrate
Suboptimal temperature
Same causes as blister disease and can also be secondary to scale disease
Scale rot
Lesions seen with infectious or ulcerative stomatitis
Oral mucosa petechiae
Causous material
Ulceration or granulation formation
Osteomyelitis
Causes of infectious/ulcerative stomatitis
Aeromonas and psuedomonas
Sequela of infectious stomatitis
Respiratory and intestinal infection
Treatment of infectious or ulcerative stomatitis
Surgical debridement
Irrigation with antiseptics
Systemic antibodies
Supportive therapy
Vitamin (A and C) supplementation
What causes pneumonia?
Husbandry, Aeromans and Psuedomonas
Clinical presentation of pneumonia
Open mouth breathing
Treatment of pneumonia
Improving husbandry
Systemic antibiotics
Nebuilzations
Increased temperature
Who is IBD most common in?
Boas and pythons
How is Reptarenvirus (IBD) transferred?
Body fluids
What can trigger immunosuppression?
Poor wound healing
Dysecdysis
Regurgitation
Leukocytosis
Neurologic symptoms
Diagnosis of IBD
Leukocyte cytoplasmic on blood smear
What kind of disease does adenovirus cause?
Hepatic or GI diseas
CS of adenovirus
Sudden death, high morbidity
Lesions seen with adenovirus
Intranuclear inclusion bodies in liver
What paramyxovirus causes pneumonia?
Ferlavirus
What iridovirus causes anemia?
Snake erythorcyte virus (SEV)
What causes zoonotic dysentery?
Entamoeba (Amebiasis)
CS of Amebiasis
Bloody/mucoid diarrhea
lesions of amebiasis
Ulcerative/fibrinonecrotizing colitis
Hepatitis
Differentials for Amebiasis
Bacteria
Protozoa
Coccidia
CS of trich
Diarrhea
Diagnosis of trich
Fecal smear, postmortem
What is mites secondary to?
Systemic disease
What do ticks cause?
Anemia
How do you treat external parasites?
Permethrin and Ivermectin
Best spots of venipuncture
Cardiac, coccigeal v., jugular
A client presents a young arboreal snake. Based on proper husbandry guidelines from the sources, what type of enclosure should you recommend? a) A long, shallow enclosure to allow for stretching. b) A tall enclosure with climbing structures. c) A terrestrial enclosure with ample floor space. d) A small, confined enclosure to reduce stress.
b) A tall enclosure with climbing structures. c) A terrestrial enclosure with ample floor space.
You are performing a physical exam on a snake. You observe tiny, dark spots moving between the scales. Based on the sources, what is the most likely external parasite you are seeing, and what diagnostic step should you take to confirm? a) Ticks; remove and identify grossly. b) Ophionyssus natricis mites; remove a spot and examine under a microscope. c) Larval cestodes; perform a fecal float. d) Fungal spores; perform a skin scraping and culture
b) Ophionyssus natricis mites; remove a spot and examine under a microscope.
A snake is presented with an opaque spectacle covering its eye that does not appear shiny. The owner reports recently decreasing the humidity in the enclosure. Based on the sources, what is the most likely issue, and what is an initial treatment approach? a) Mouth rot; systemic antibiotics. b) Dysecdysis; wait for the next shed cycle. c) Retained spectacle; soak the snake in shallow water and gently attempt removal. d) Septicemia; improve sanitation and administer antibiotics.
c) Retained spectacle; soak the snake in shallow water and gently attempt removal.
A client feeds their adult ball python exclusively frozen-thawed adult mice once a week. The snake has recently become lethargic and anorexic, and the feces observed outside the enclosure appear hardened. Based on the sources, what husbandry-related issue is a likely contributor to these signs? a) Overfeeding. b) Feeding frozen-thawed prey that were not properly warmed. c) Feeding frequency is too high for an adult. d) Feeding frozen meals which can contribute to dehydration.
d) Feeding frozen meals which can contribute to dehydration.
During a necropsy of a snake suspected of having a bacterial infection, you observe redness and petechiae on the ventral scales. According to the sources, this finding is most suggestive of: a) Scale rot. b) Blister disease. c) Septicemia. d) Infectious stomatitis.
c) Septicemia.
A boa constrictor is presented with severe neurological signs, including stargazing and inability to right itself when placed on its back. The owner mentions another boa in the collection recently died after exhibiting similar signs. Based on the sources, what is the most likely diagnosis? a) Adenovirus. b) Septicemia. c) Inclusion Body Disease (IBD). d) Amebiasis with CNS involvement.
c) Inclusion Body Disease (IBD).
You are performing a blood smear evaluation on a snake. You observe small inclusions within the cytoplasm of the erythrocytes (red blood cells). According to the sources, this finding is most consistent with: a) Inclusion Body Disease (IBD). b) Hepatozoon species infection. c) Snake Erythrocyte Virus (SEV). d) Leukemia.
c) Snake Erythrocyte Virus (SEV).
A juvenile snake is presented for a wellness exam. According to the sources, how frequently should juvenile snakes typically be offered food? a) Every 7-21 days. b) Every 2-7 days. c) Once a month. d) They should have continuous access to food.
b) Every 2-7 days.
You are asked to perform venipuncture on a 350-gram ball python. Based on the sources, what is considered the best site for a blood draw in a snake of this weight? a) The jugular vein. b) The caudal (coccygeal) vein. c) The cardiac site. d) The palatine vein in the mouth.
c) The cardiac site.
.
A snake owner presents their pet trapped on a sticky rodent trap. Based on the practical clinical applications mentioned in the sources, what is the recommended method for removing the snake from the trap? a) Gently pull the snake off the trap. b) Cut the parts of the trap away from the snake. c) Apply mineral oil or immersion oil to the adhesive and gently free the snake. d) Submerge the snake and the trap in warm water until it releases.
c) Apply mineral oil or immersion oil to the adhesive and gently free the snake.
A client calls concerned because their snake is open-mouth breathing. According to the sources, open-mouth breathing in a snake is a common sign of: a) Obesity. b) Dysecdysis. c) Pneumonia or other respiratory issues. d) Constipation.
c) Pneumonia or other respiratory issues.
You are attempting to sex a snake. According to the sources, what method involves probing the cloaca? a) If the probe goes deep, it is likely a female; if it goes shallow, it is likely a male. b) If the probe goes deep, it is likely a male due to the hemipenis pocket; if it goes shallow, it is likely a female. c) The presence of hemipenes is diagnostic for females. d) Only visual inspection of the tail base can determine sex.
b) If the probe goes deep, it is likely a male due to the hemipenis pocket; if it goes shallow, it is likely a female.
A snake presents with brown discoloration at the edges of its scales in multiple locations. The owner uses aspen chips as substrate and maintains high humidity. Based on the sources, what is the most likely diagnosis? a) Blister disease. b) Scale rot (dermatitis). c) Infectious stomatitis. d) Amebiasis.
b) Scale rot (dermatitis).
A python is presented with a large, black mass on its body. Biopsy is recommended. According to the sources, what type of neoplasia is most common in snakes and should be high on your differential list for a black mass? a) Fibrosarcoma. b) Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). c) Melanophoroma (melanoma). d) Iridophoroma.
c) Melanophoroma (melanoma).
A snake is presented with malodorous, bloody discharge from the cloaca and apparent swelling of the cloacal area. According to the sources, what condition is most likely present? a) Constipation. b) Dysecdysis. c) Cloacoliths. d) Amebiasis.
c) Cloacoliths.
A client reports feeding their snake "pinkies". According to the sources, what is a potential health issue associated with feeding pinkies exclusively, and why? a) Obesity, because they are high in fat. b) Metabolic bone disease, because they are underdeveloped and lack calcium. c) Septicemia, because they can transmit bacteria. d) Dysecdysis, because they lack necessary vitamins for skin shedding.
b) Metabolic bone disease, because they are underdeveloped and lack calcium.
A client presents a snake with a history of severe, bloody, and mucoid diarrhea. A fecal exam reveals motile trophozoites. Based on the sources, what parasitic disease is most likely? a) Trichomoniasis. b) Amebiasis (Entamoeba histolytica). c) Cryptosporidiosis. d) Ticks and mites.
b) Amebiasis (Entamoeba histolytica).
You are treating a snake for a bacterial infection. According to the sources, what are two of the most common bacterial culprits in snake diseases? a) Salmonella and E. coli. b) Staphylococcus and Streptococcus. c) Aeromonas and Pseudomonas. d) Clostridium and Bacteroides.
c) Aeromonas and Pseudomonas.
You are performing a physical exam and lift the gular fold of a snake. According to the sources, why is it important to check this area? a) It can be a site for retained spectacles. b) It is where the heart is located. c) Mites often hide in this fold. d) It is a common site for cloacoliths.
c) Mites often hide in this fold.