DPT 745 Week 5 Lecture Notes Pt. 1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
mandible, neck, manubrum, platysma
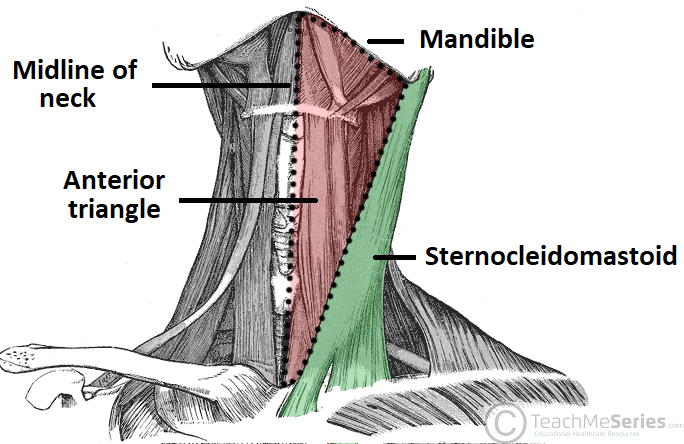
Anterior Triangle Borders
– Inferior border of _____, midline of _____, jugular notch of _____, anterior border of SCM, _____ (roof) pre-tracheal fascia (floor)
clavicle, trapezius, platysma
Posterior Triangle Borders
(a.k.a. lateral cervical region)
– Posterior border of SCM, middle 1/3 of _____, anterior border of _____, _____ (roof), deeper musculature (floor)
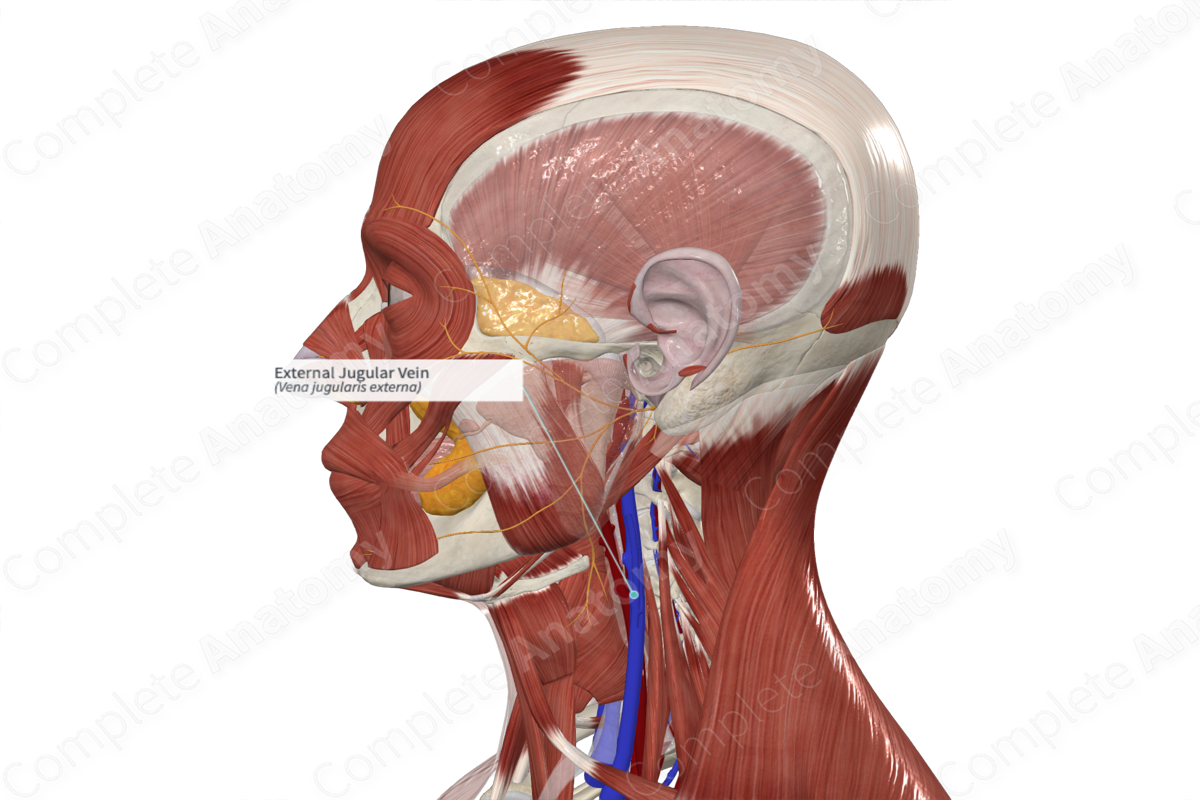
External jugular vein
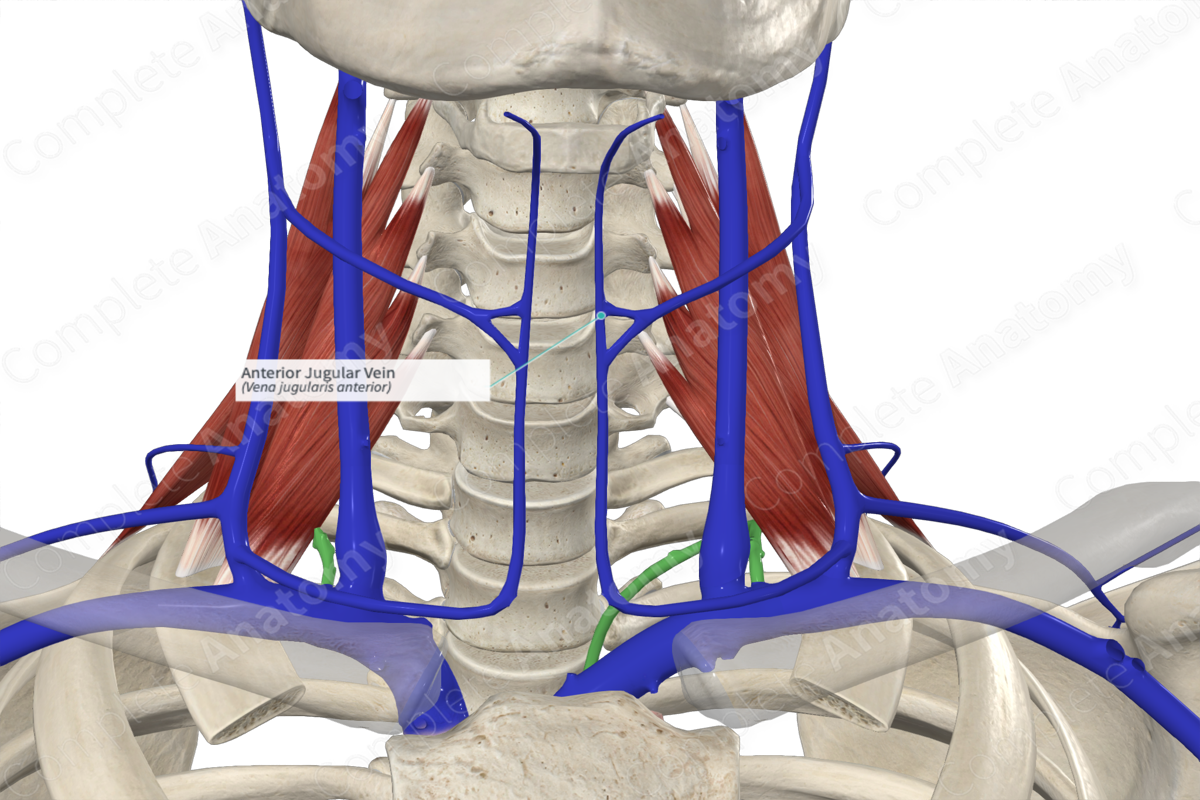
Anterior jugular vein
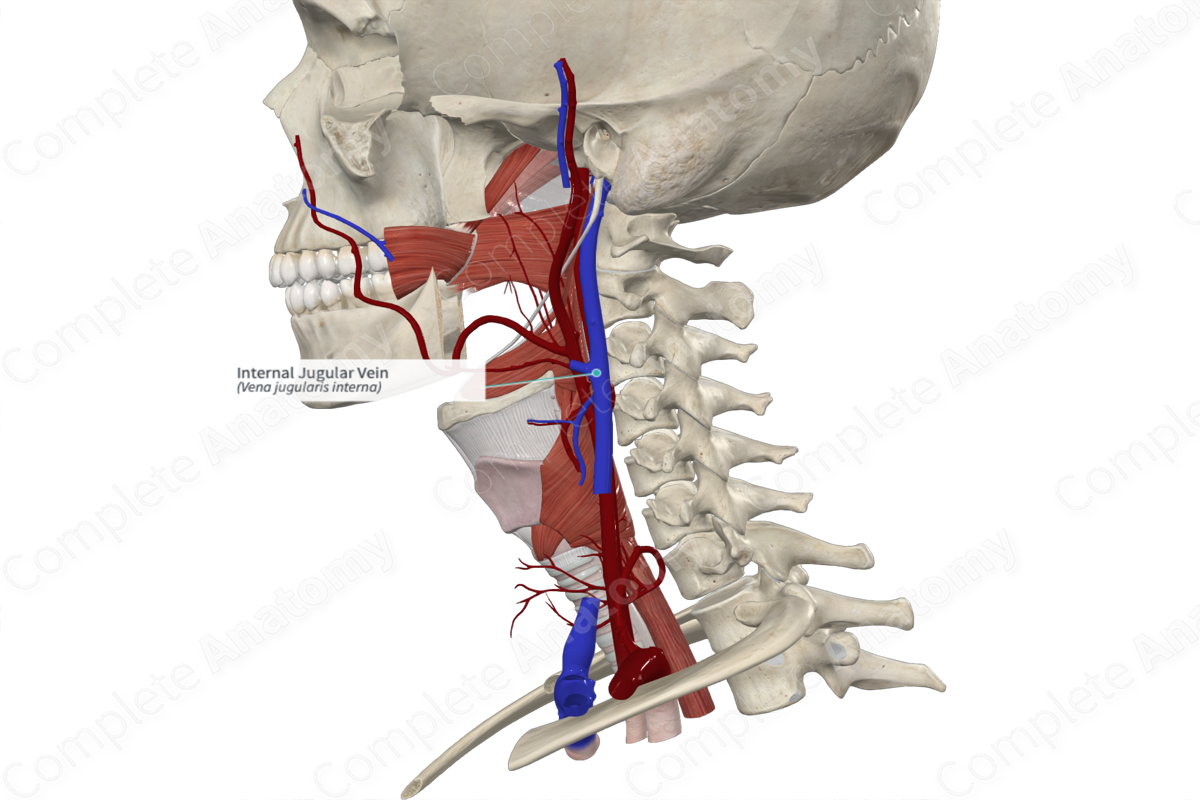
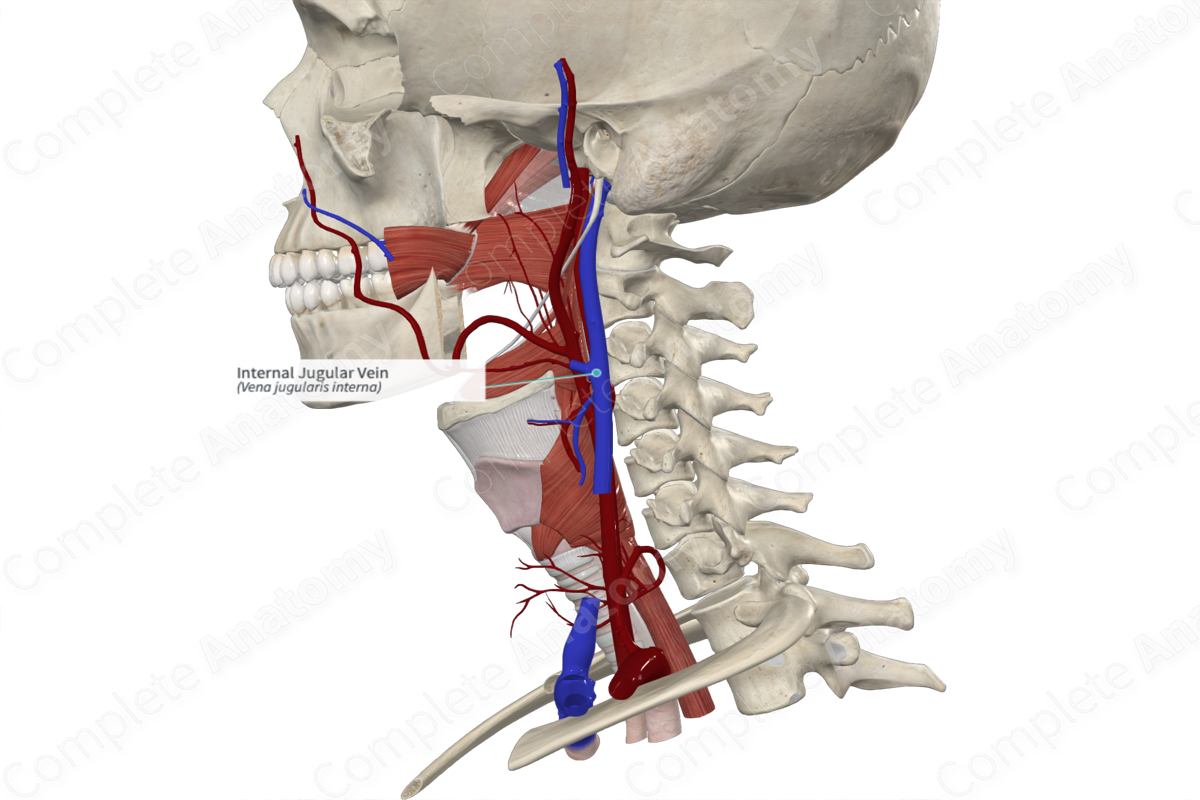
Internal jugular vein
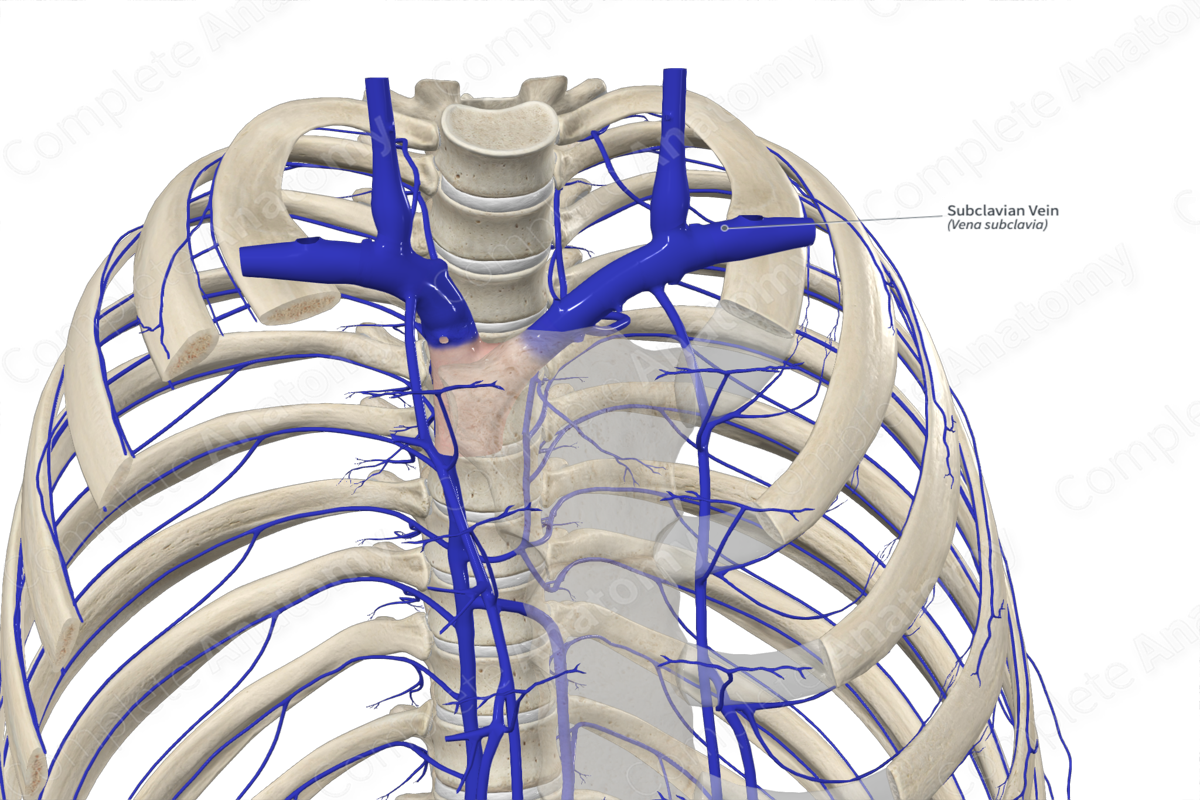
Subclavian vein
Brachiocephalic vein
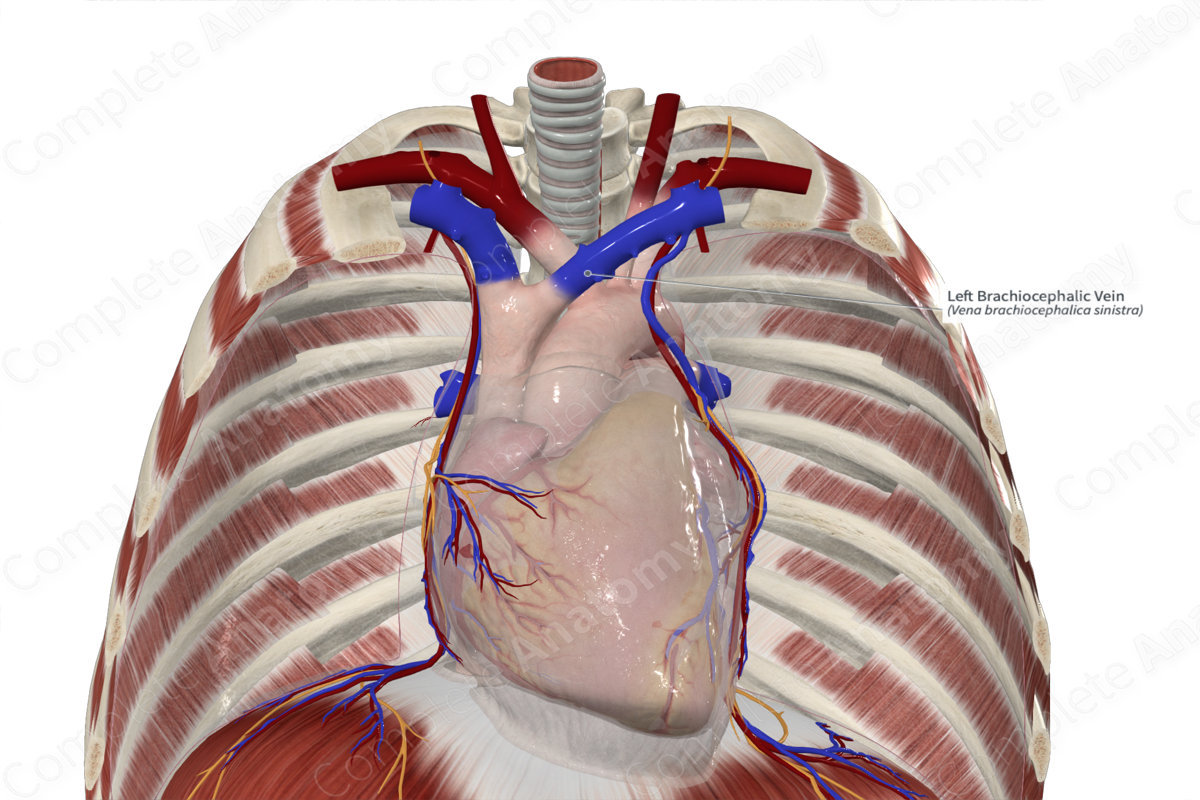
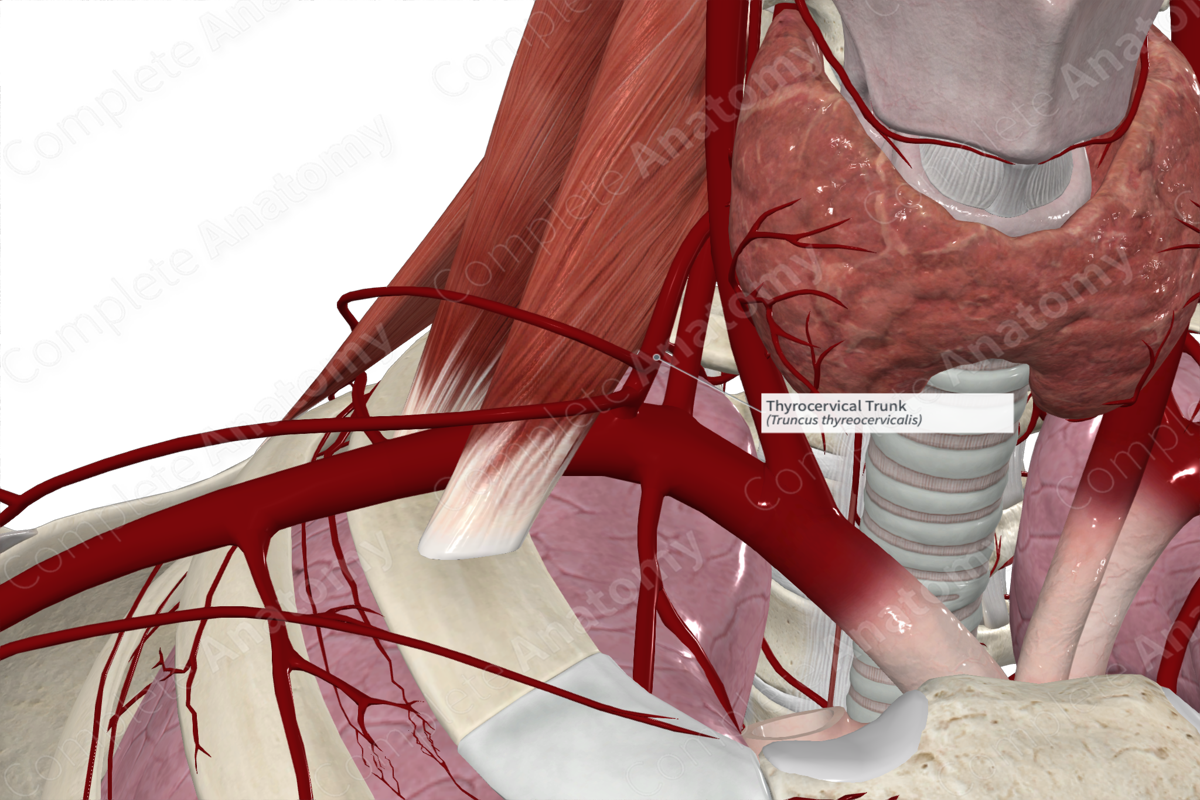
Common carotid artery

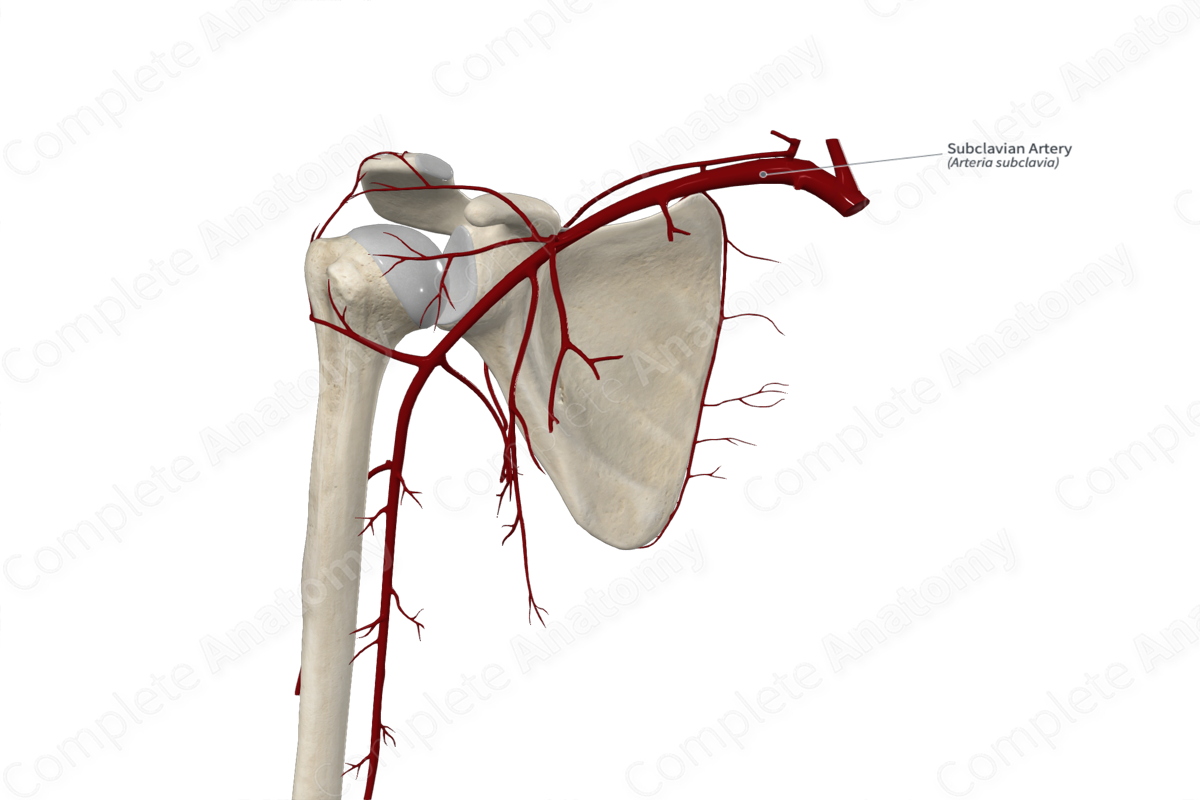
Subclavian artery
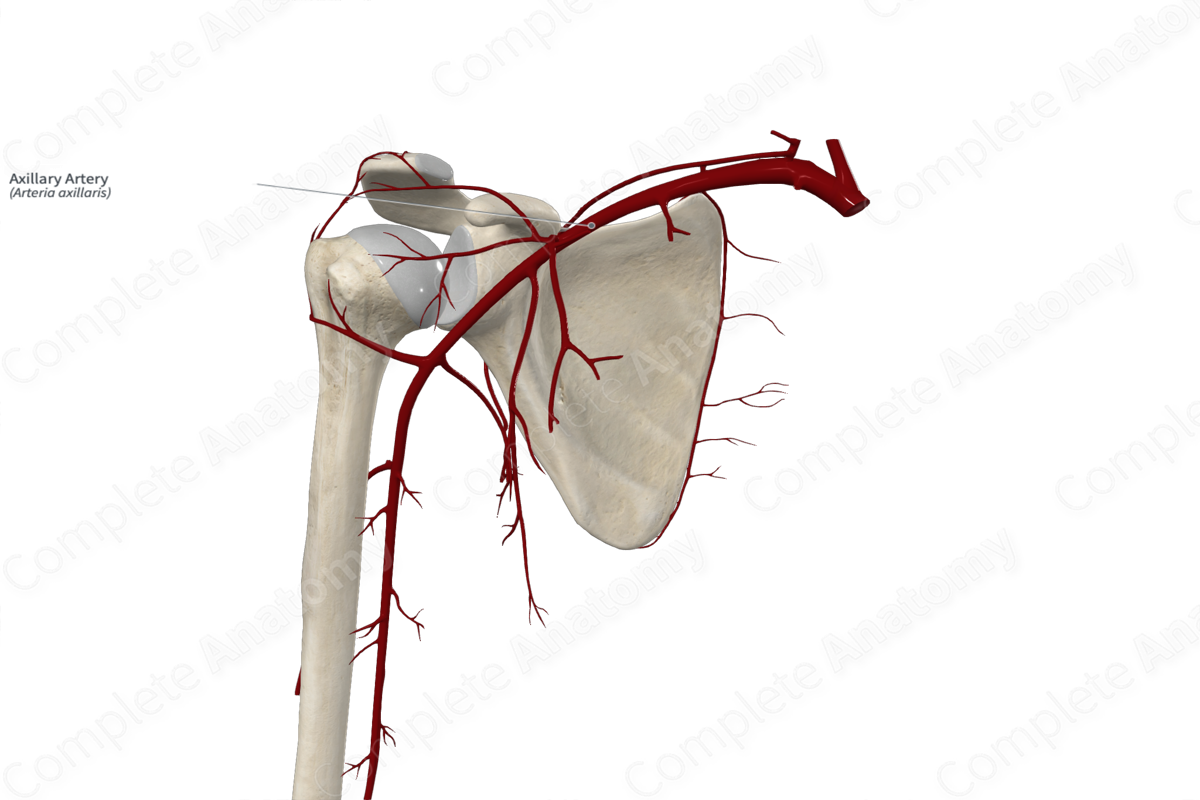
Axillary artery
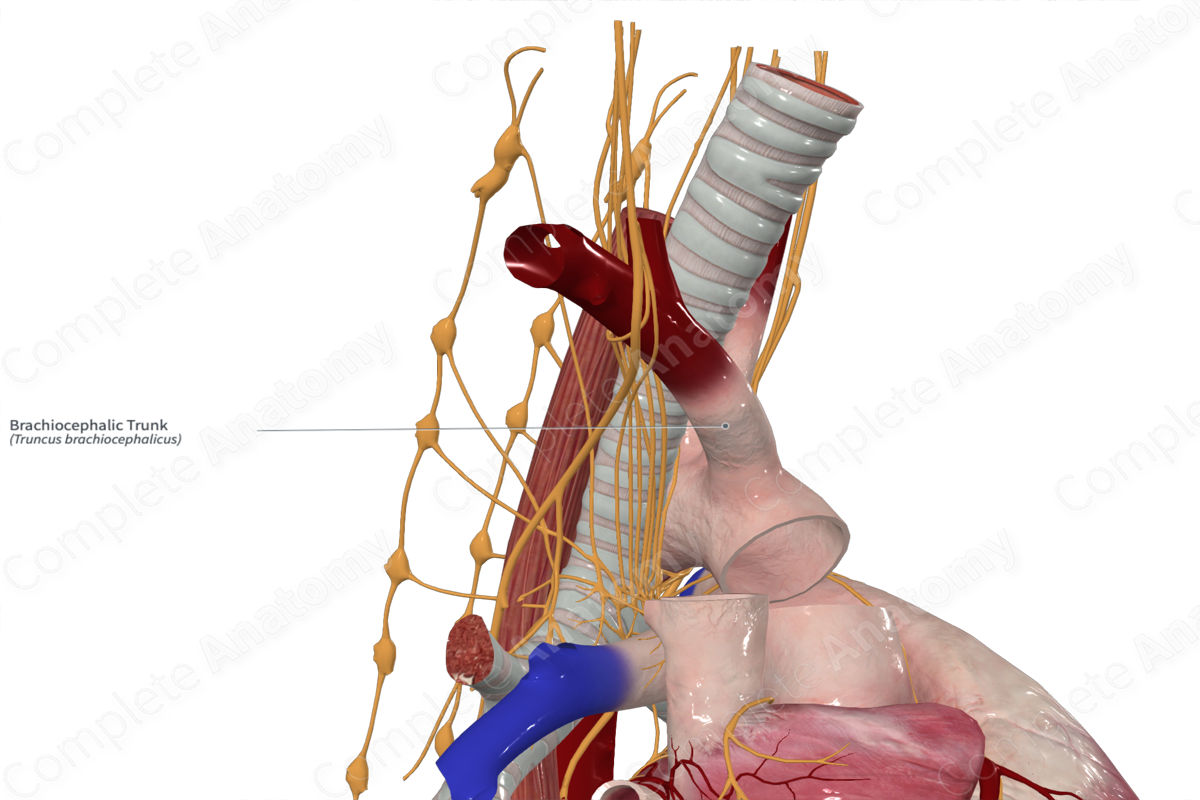
Brachiocephalic trunk
Thyrocervical trunk
Spinal
Cervical
Brachial
Nerves of the Posterior Triangle
• ____ Accessory Nerve
• _____ Plexus
• _____ Plexus
Hypoglossal nerve
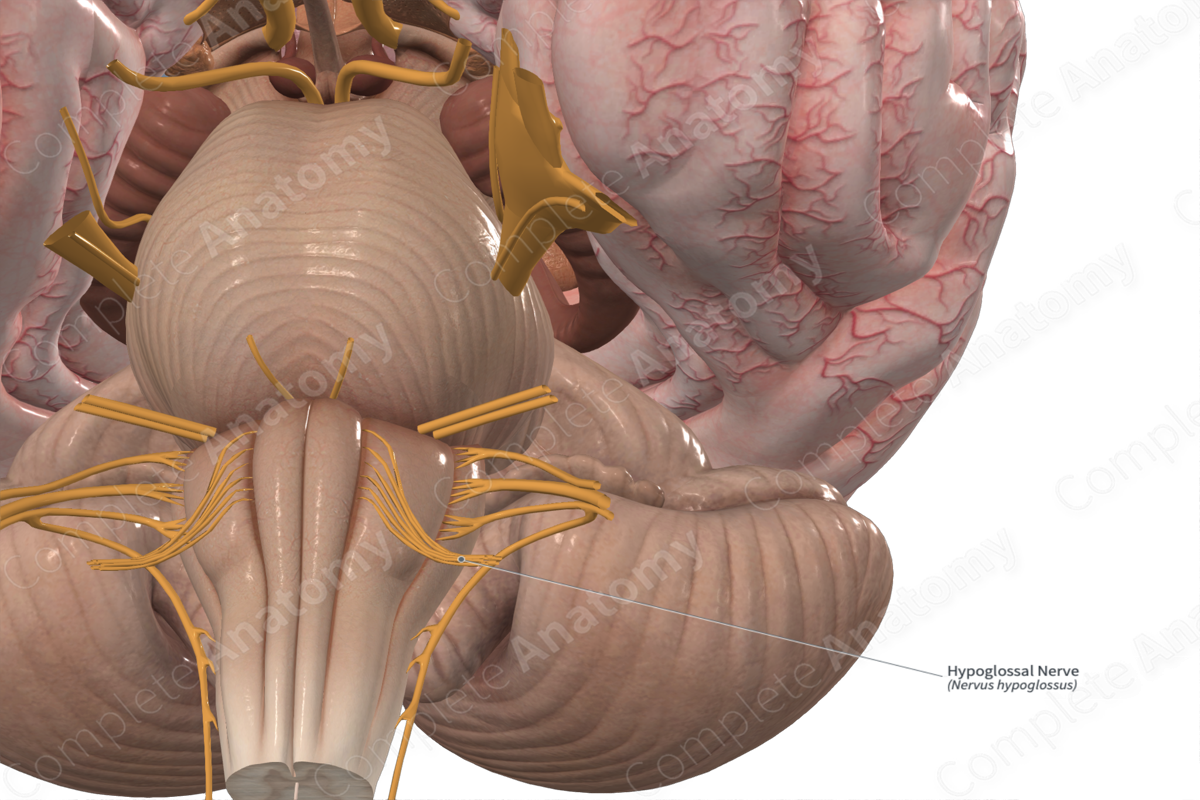
Ansa cervicalis
1
2, 3
_____ _____
Superior root C___
Inferior root C___-___
Capitis
Omo
Muscles of the Posterior Triangle
• Splenius _____
• Levator scapulae
• Posterior, Middle, & Anterior scalenes
• ___hyoid
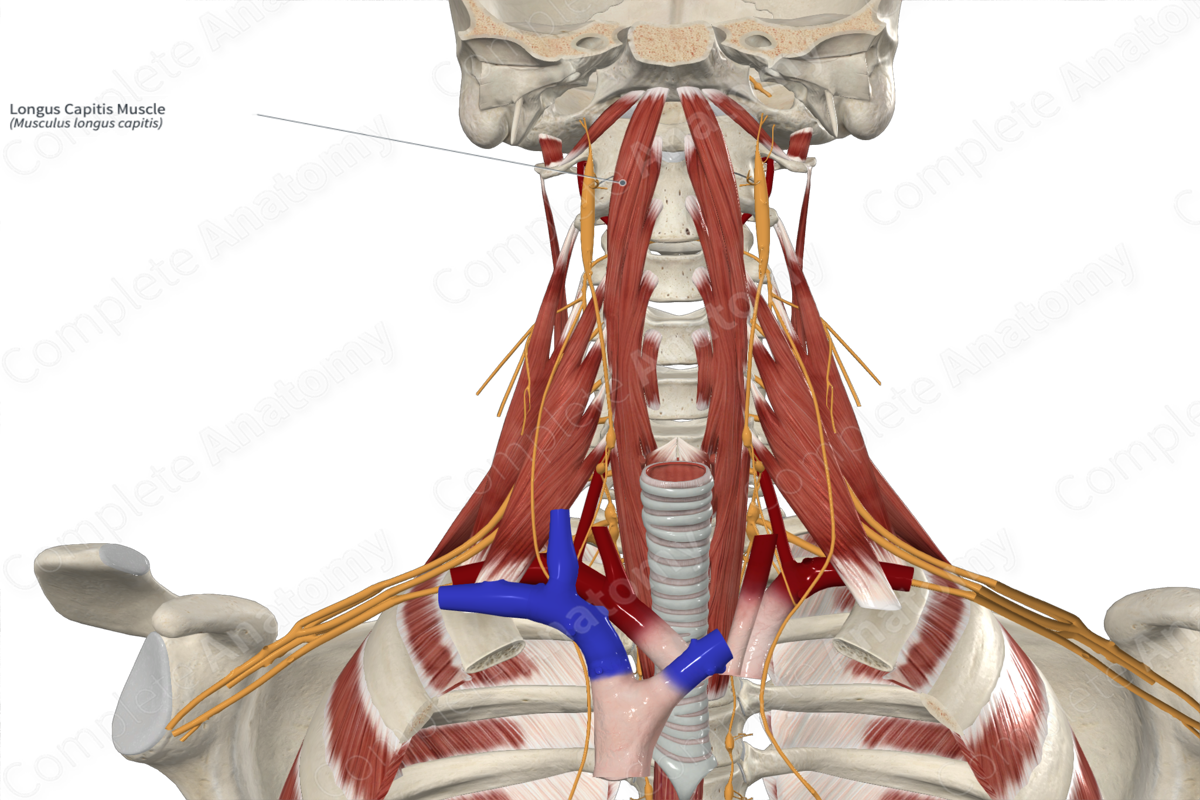
Longus capitis
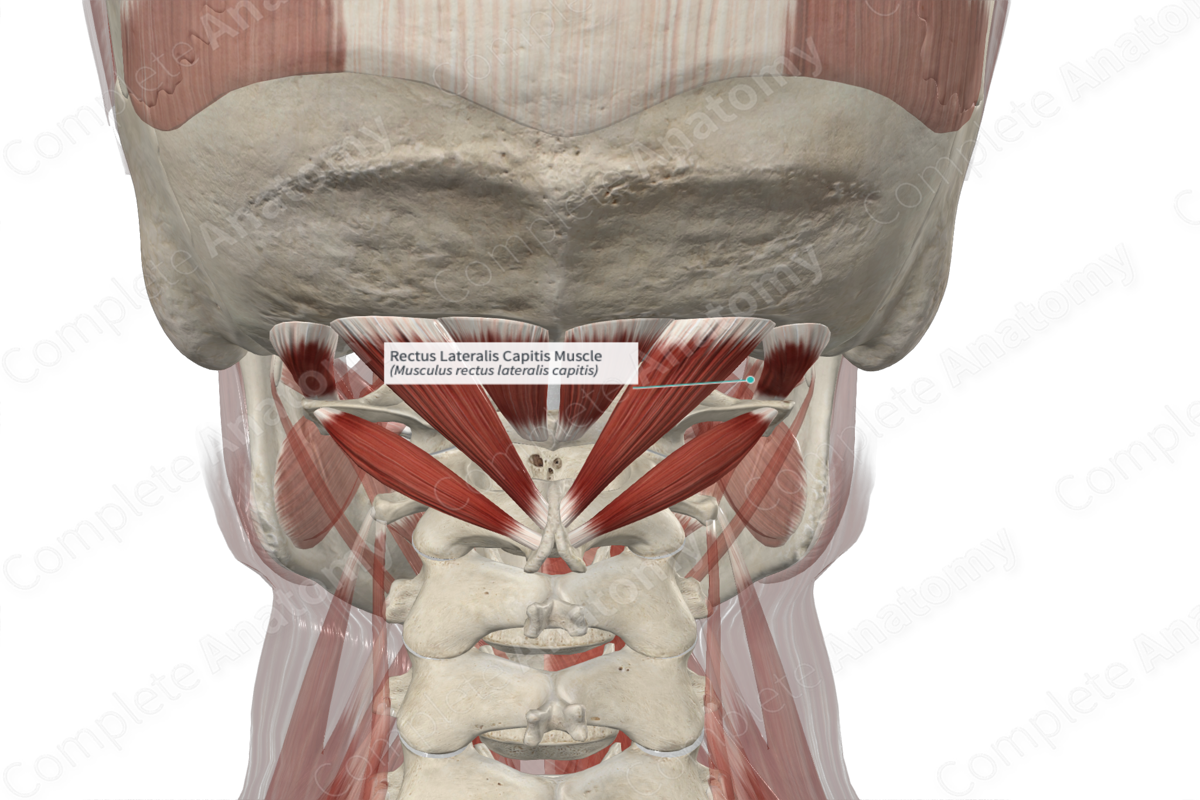
Rectus capitis lateralis
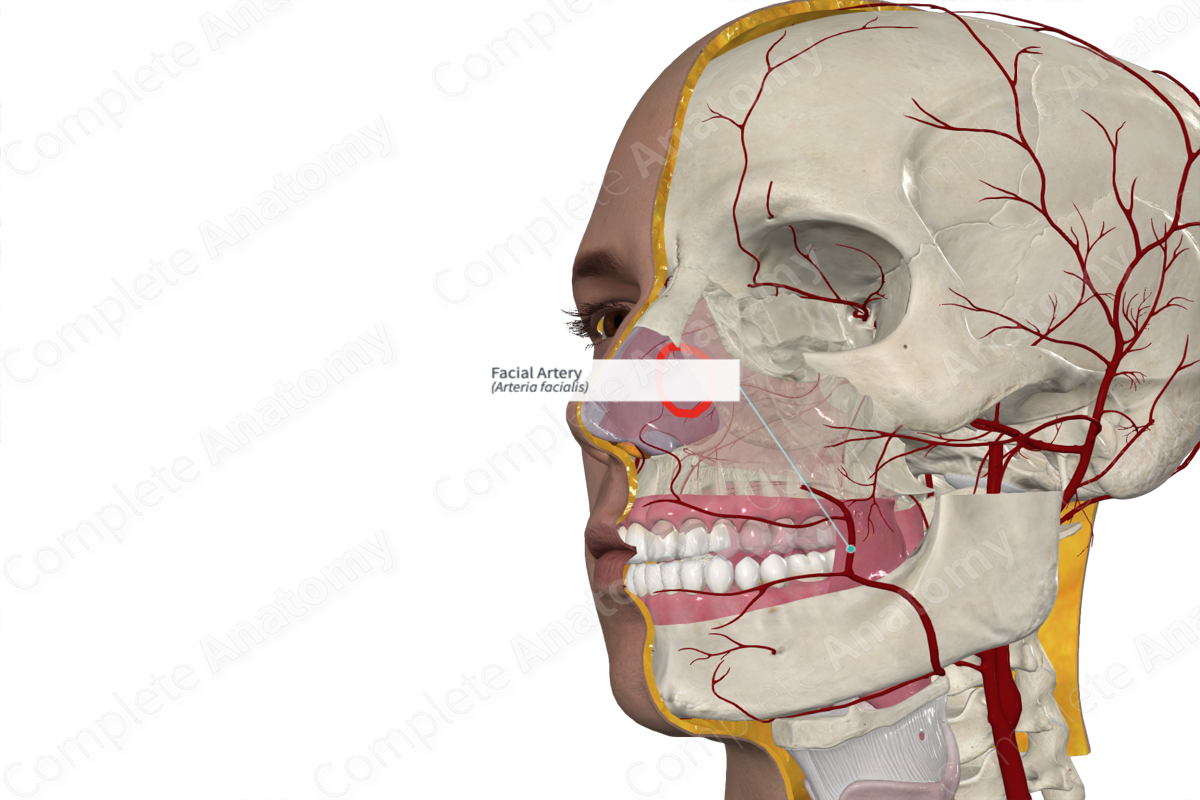
Facial artery
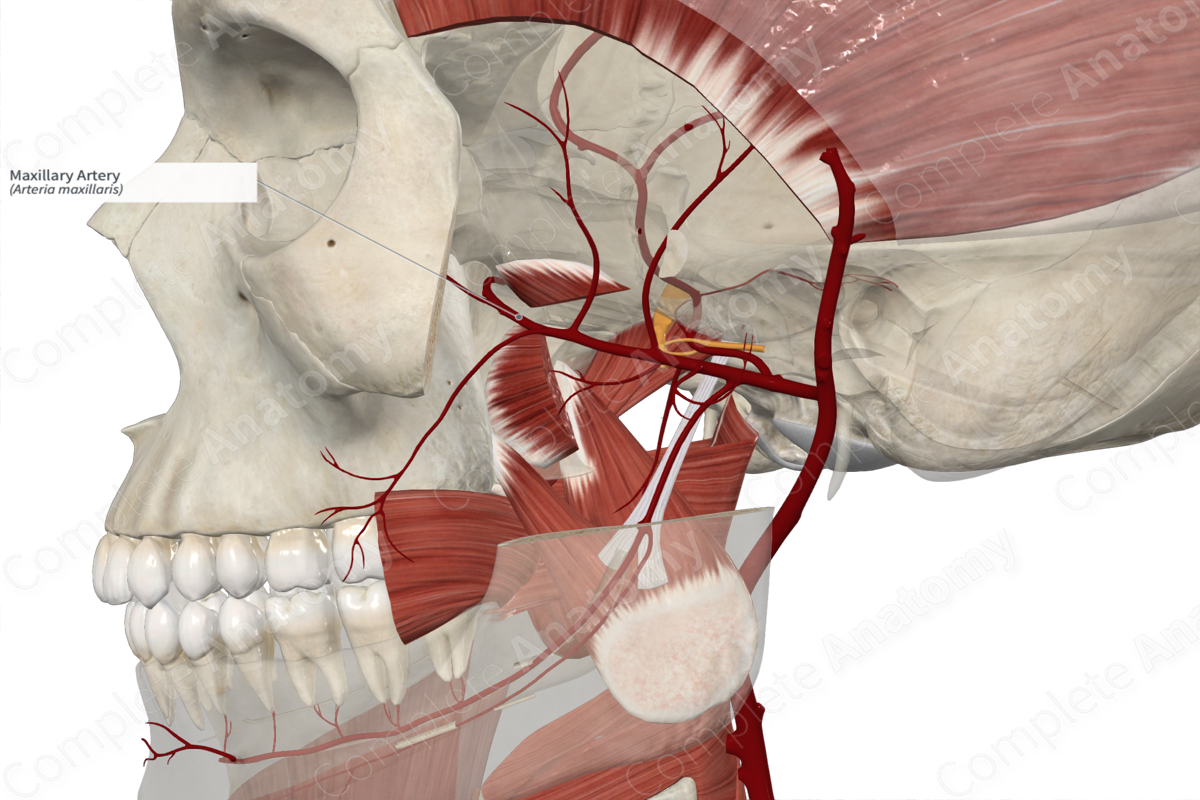
Maxillary artery
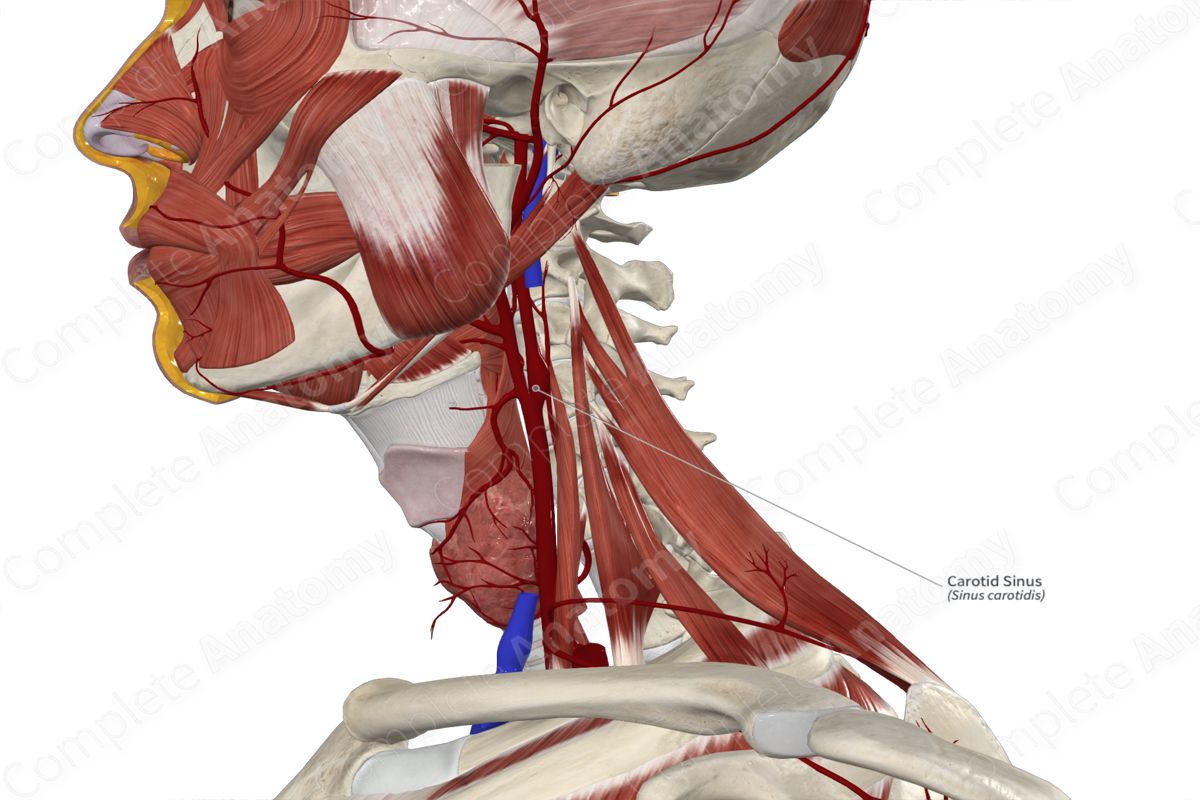
Carotid sinus
Baroceptor in Blood pressure
Carotid body
Chemoreceptor for O2 levels in blood
Facial vein
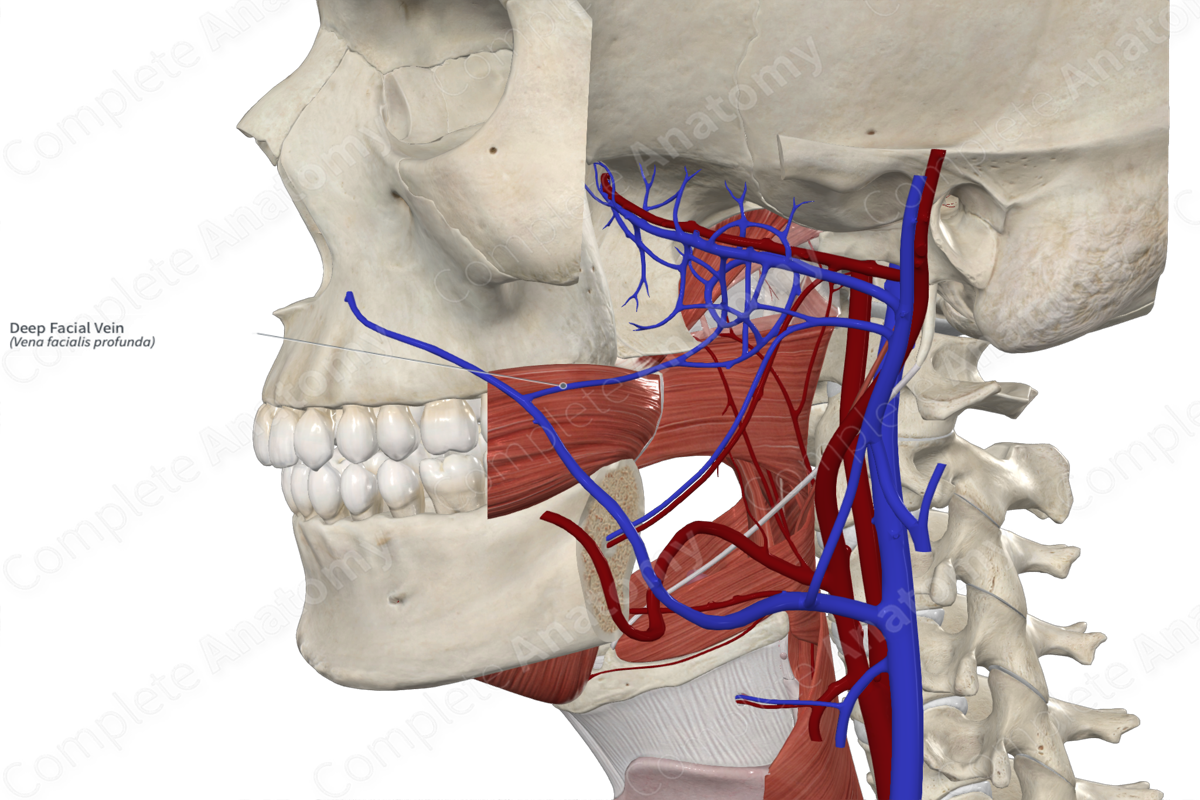
Internal jugular vein
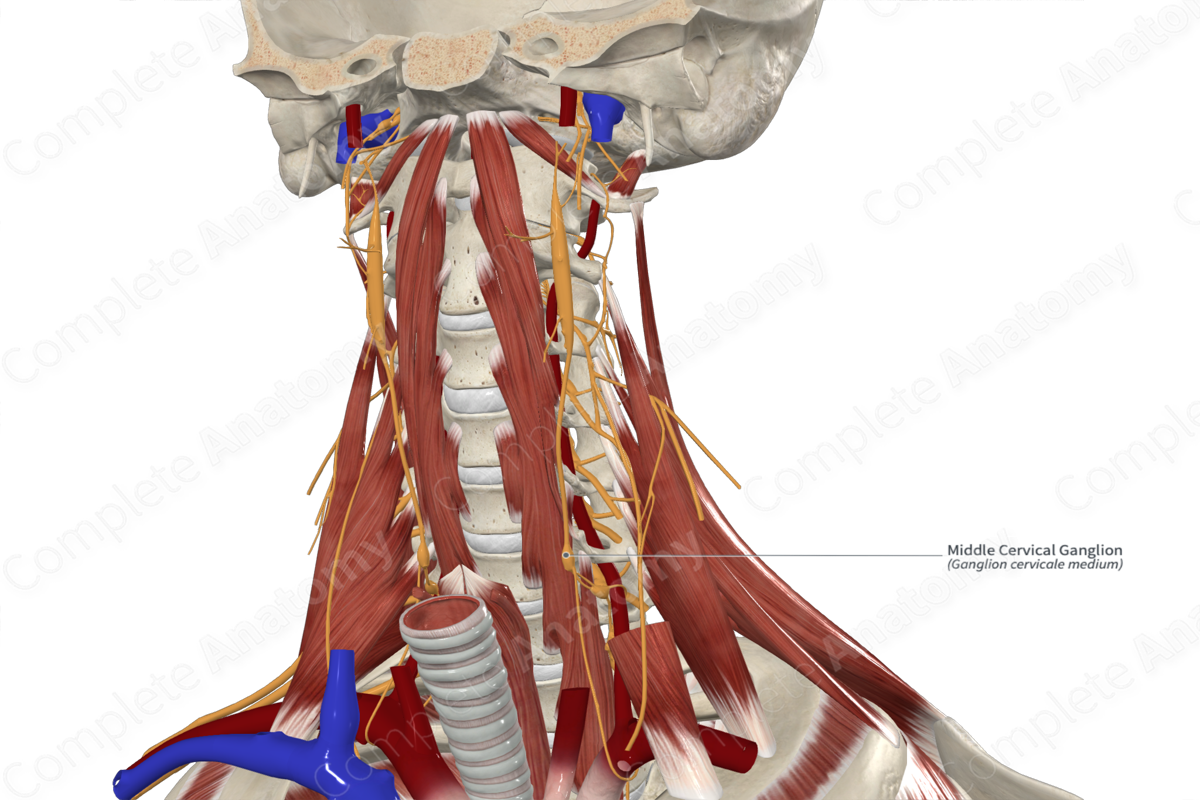
Cervical
Sympathetic
Nerves of the Anterior Triangle
• _____ Plexus
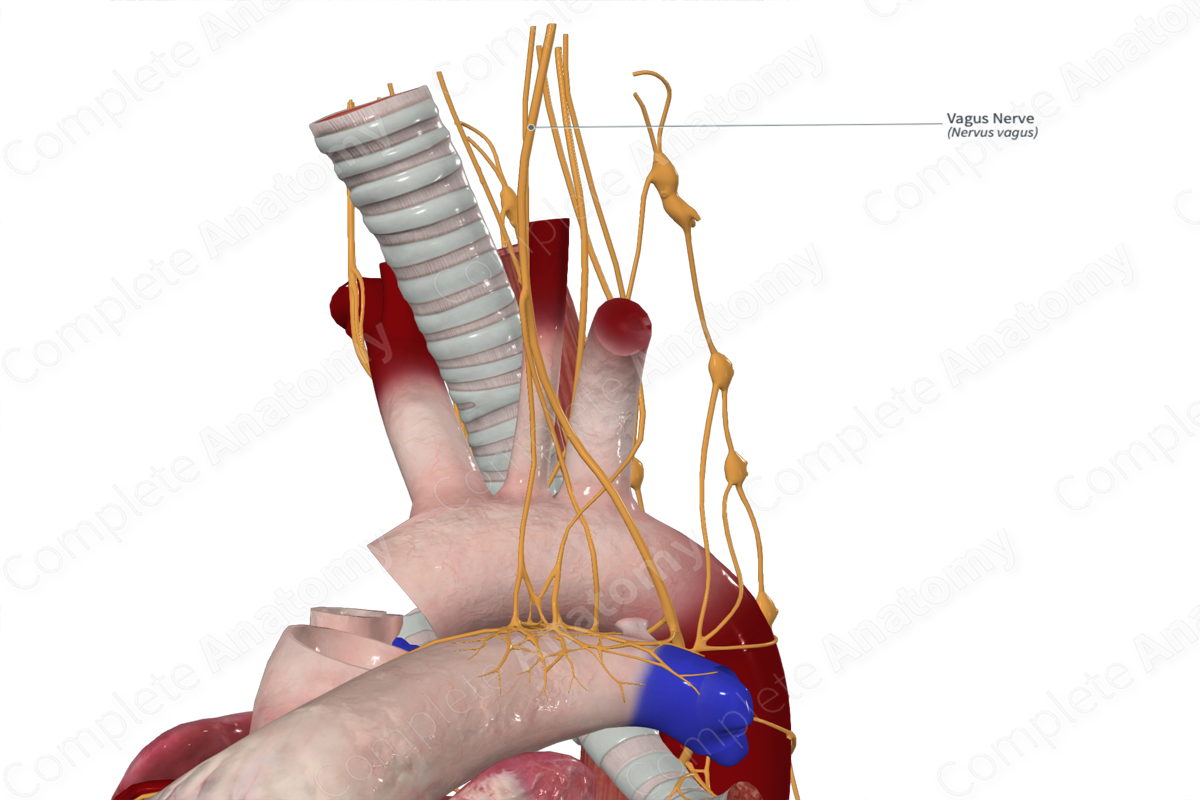
• Vagus
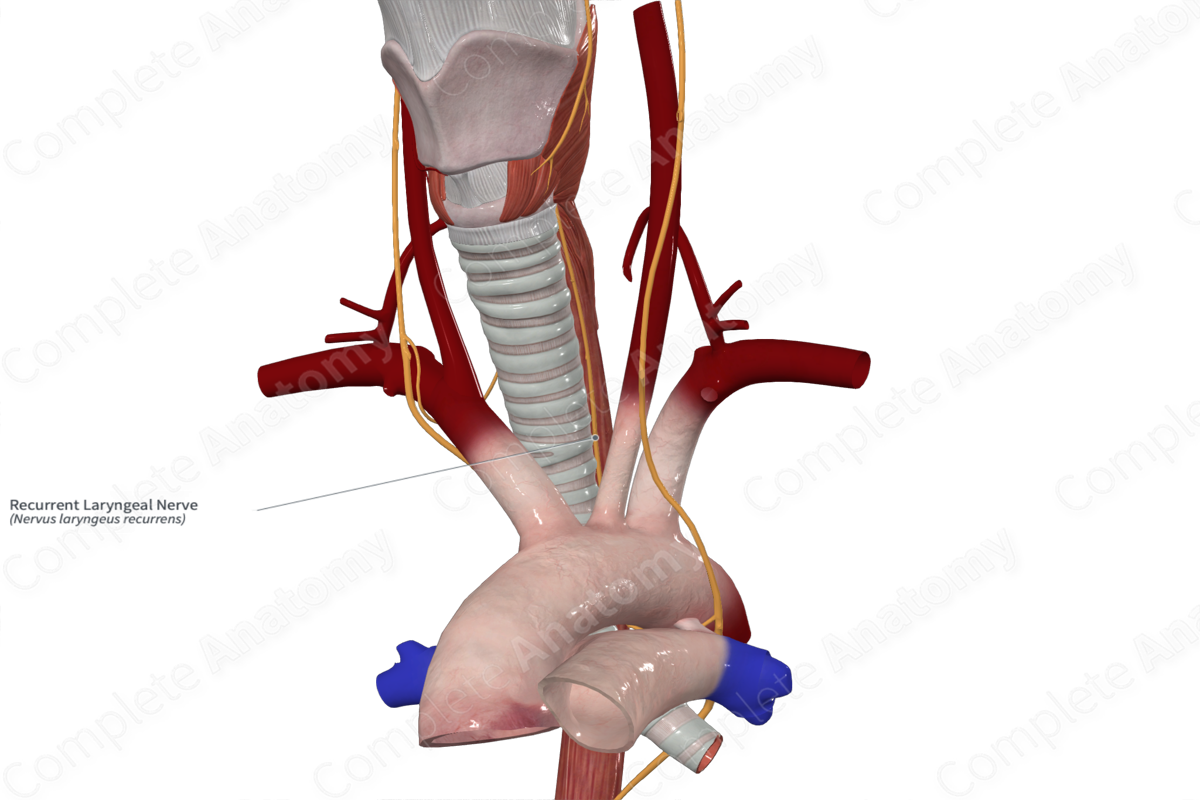
– Recurrent laryngeal nerves
• _____ Chain
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
Right vagus nerve
Right cervical ganglion
Trachea-esophageal groove
Location of left recurrent laryngeal nerve
Digastric
Muscles of the Anterior Triangle
• Mylohyoid
• Geniohyoid
• Stylohyoid
• _____
• Sternohyoid
• Omohyoid
• Sternothyroid
• Thyrohyoid
Thyroid
Para
Larynx
Esophagus
Other Important Structures of the Anterior Triangle
• _____ gland
• _____thyroid gland
• _____
• Trachea
• Pharynx
• _____
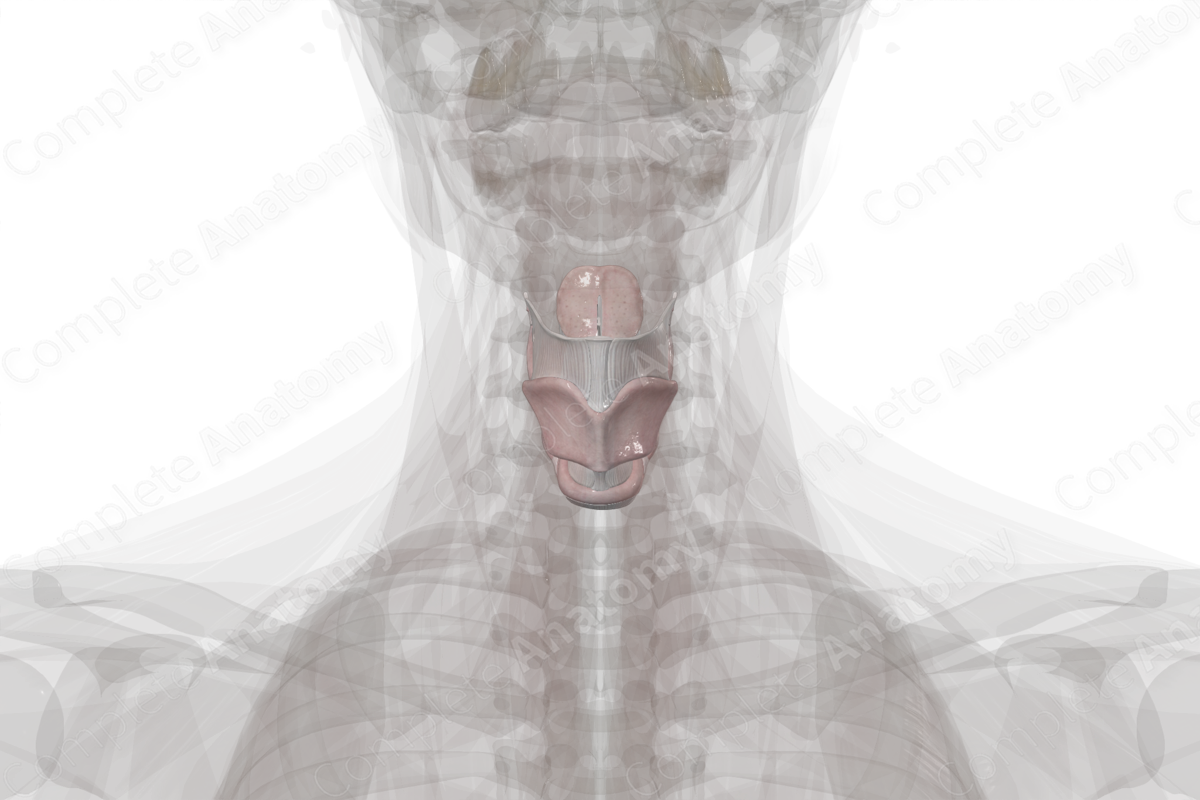
Larynx
_____ (voice box)
• Part of the respiratory system specially designed for vocalizing. It is a series of cartilages and attached muscles, ligaments, and fibroelastic membranes. It opens into the oropharynx and sits anterior to the laryngopharynx
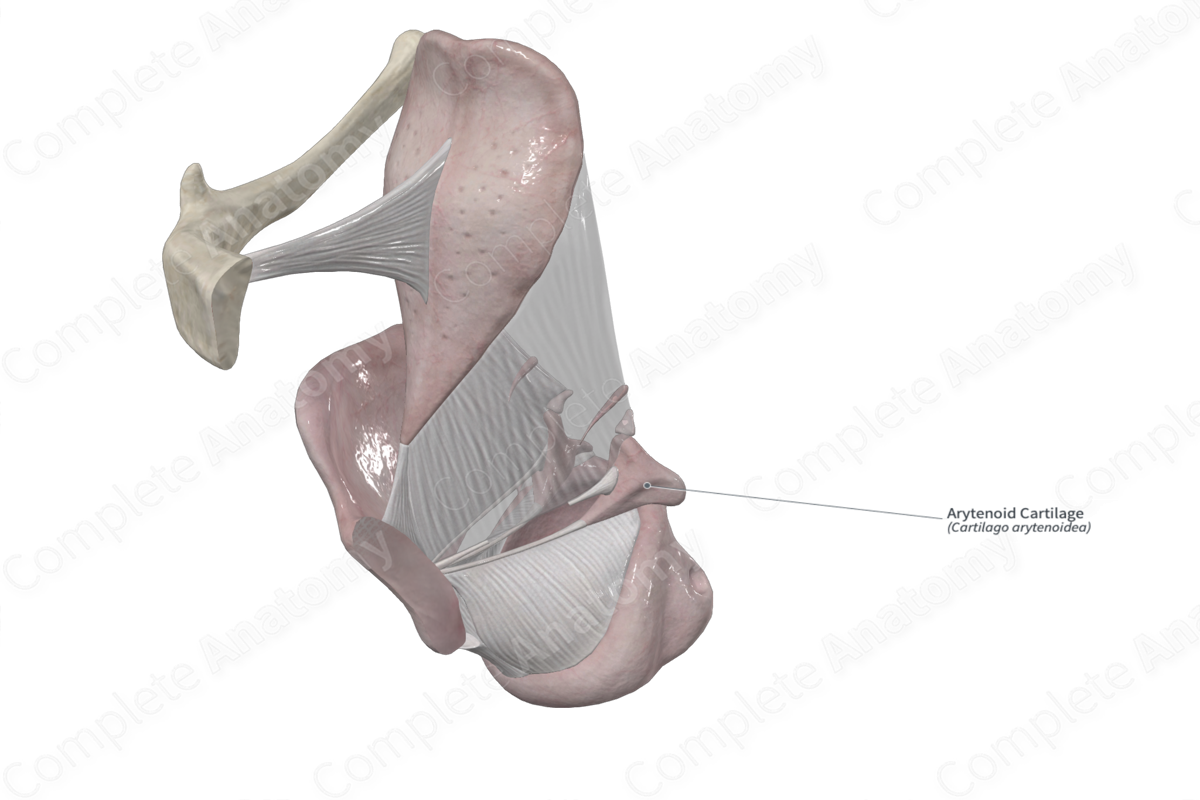
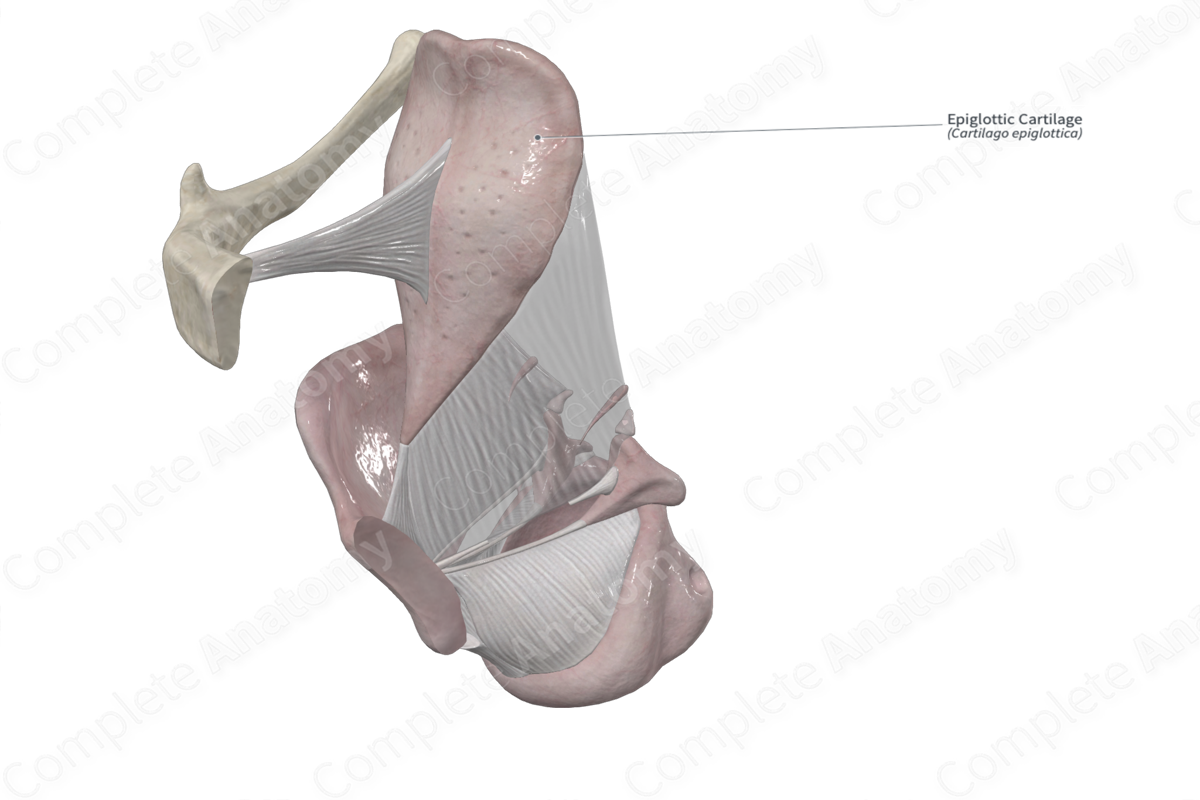
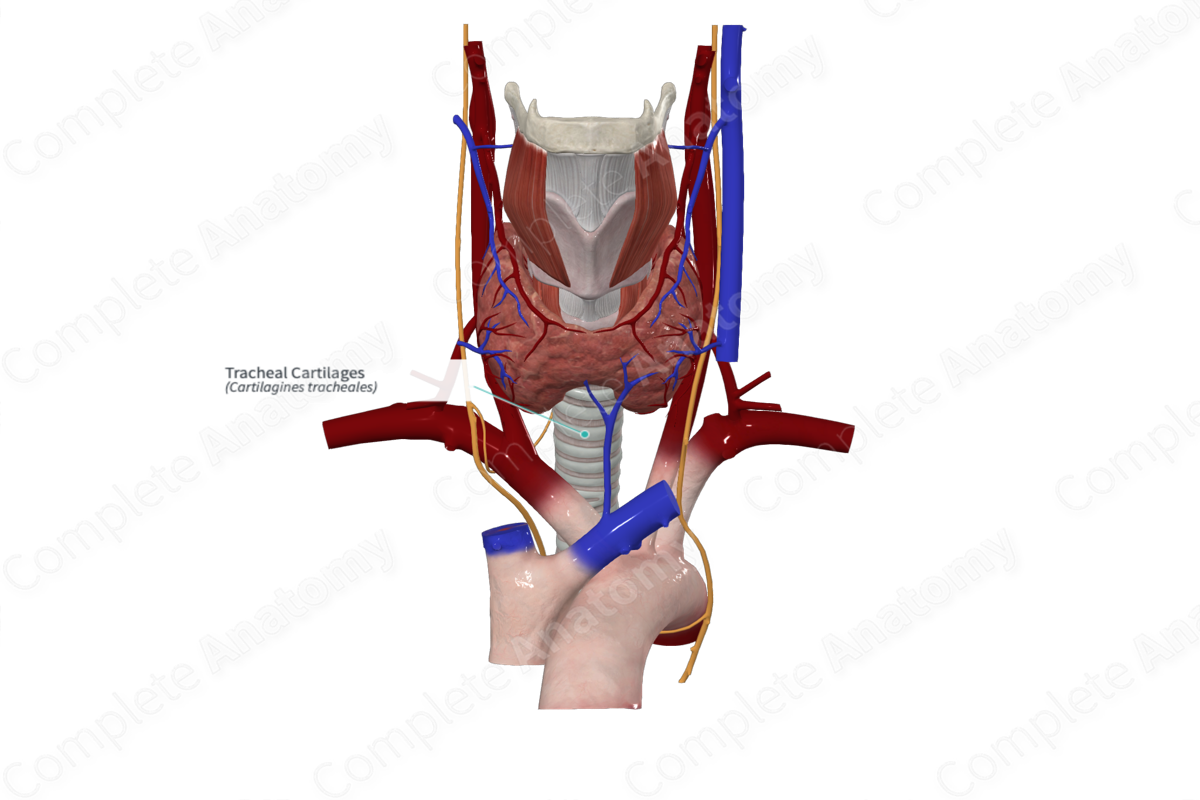
• Cartilages of larynx
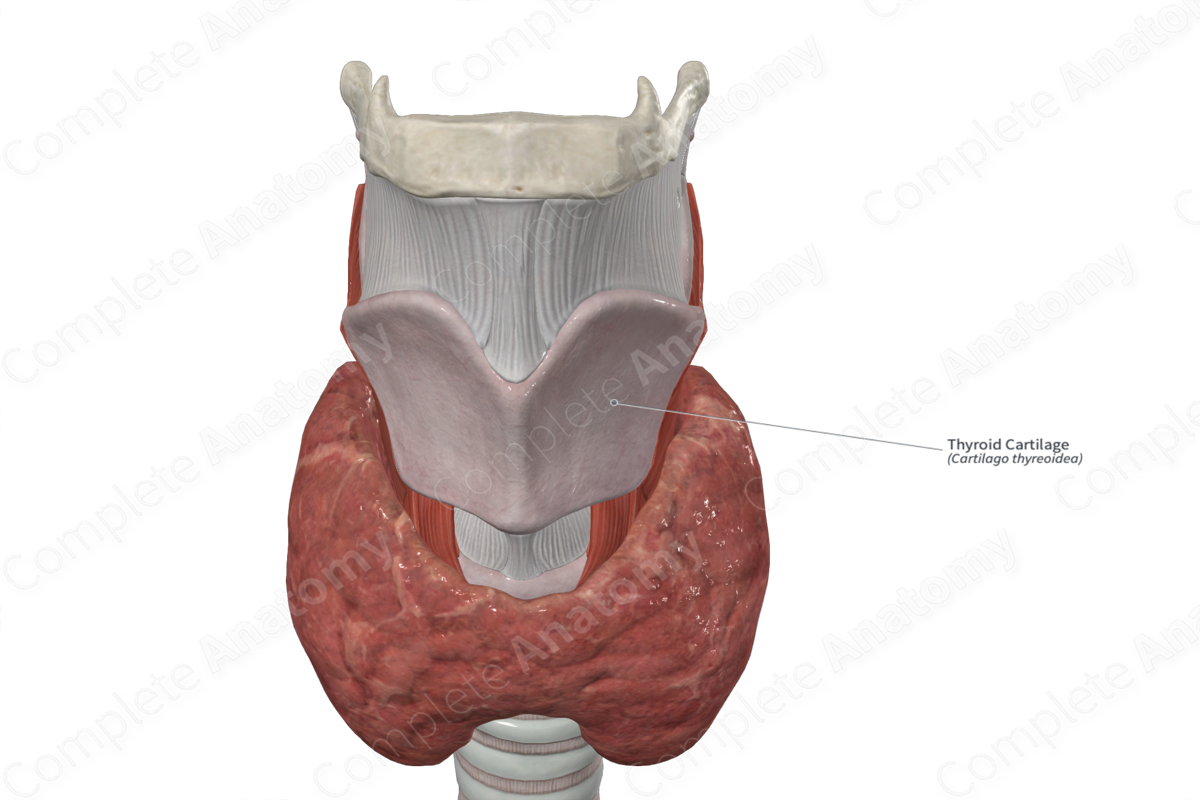
– Thyroid
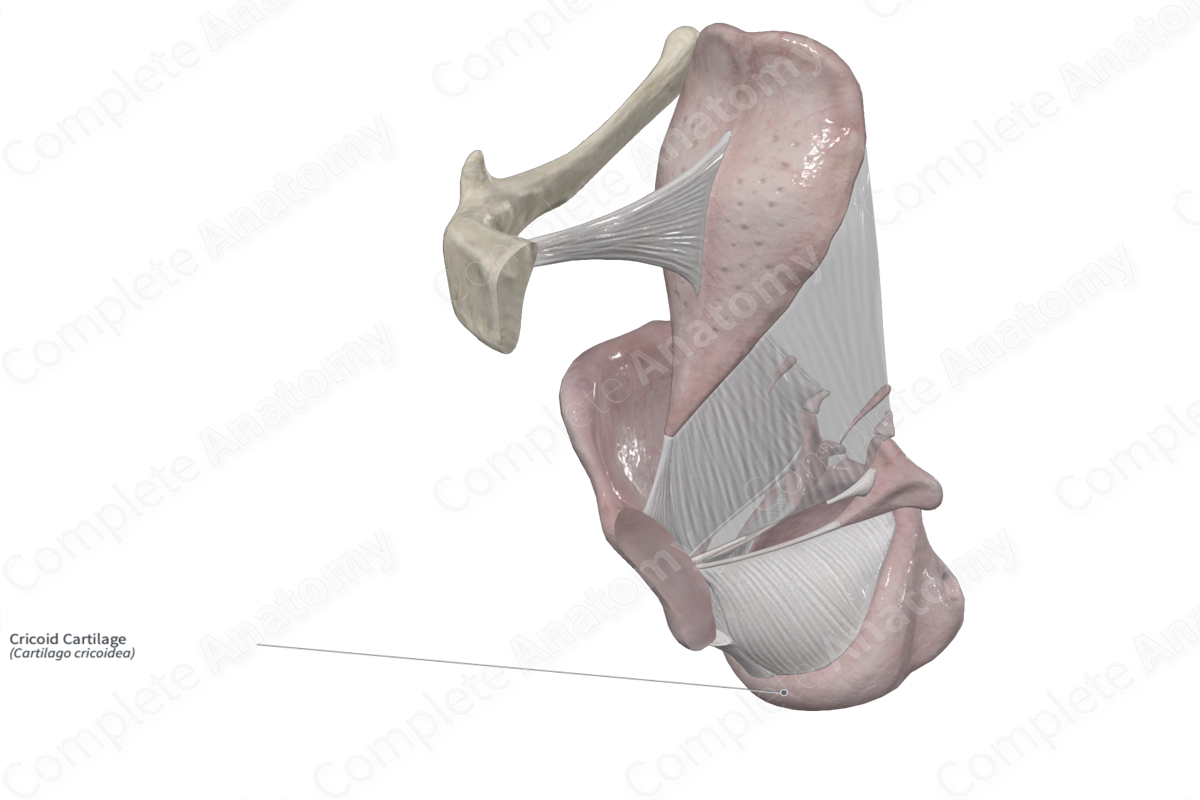
– Cricoid
– Arytenoid
– Epiglottic
– Tracheal
Oropharynx
Nasopharynx
Laryngopharynx
Thyroid cartilage
Cricoid cartilage
Arytenoid cartilage
Epiglottic cartilage
Tracheal cartilage
Superior, thyroid
Inferior, thyroid
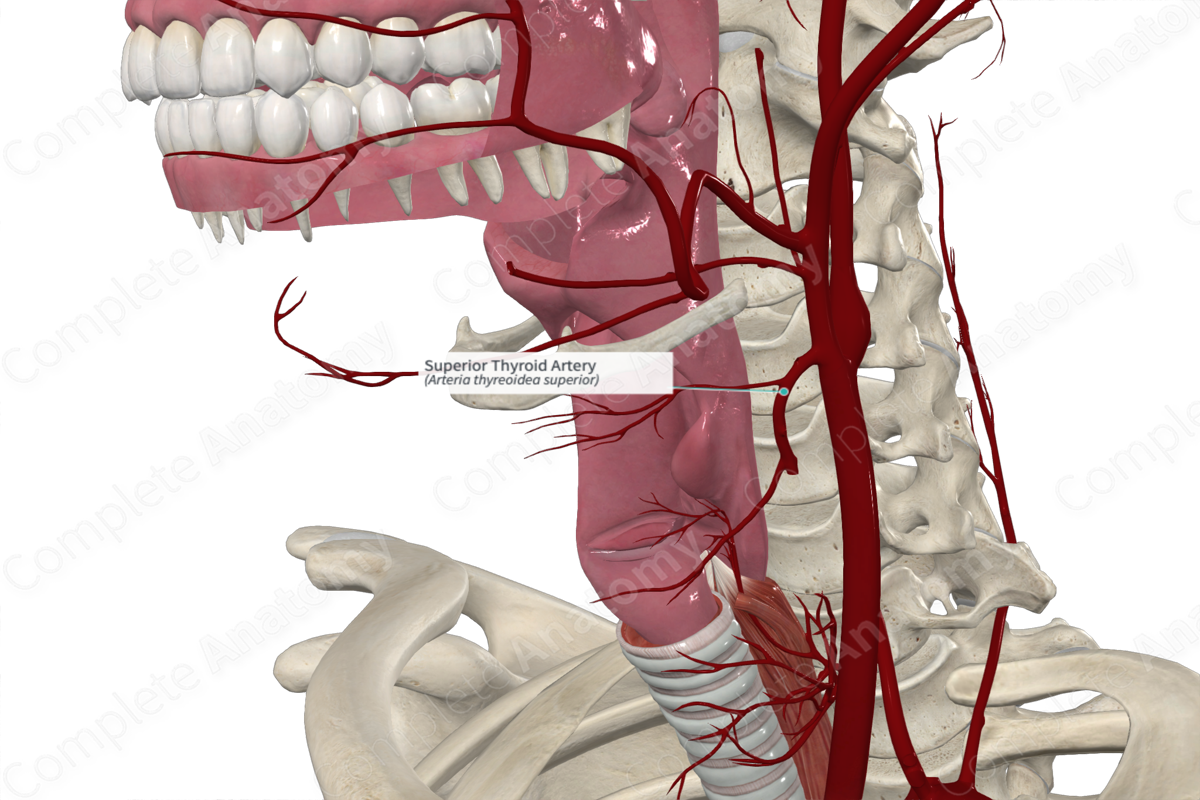
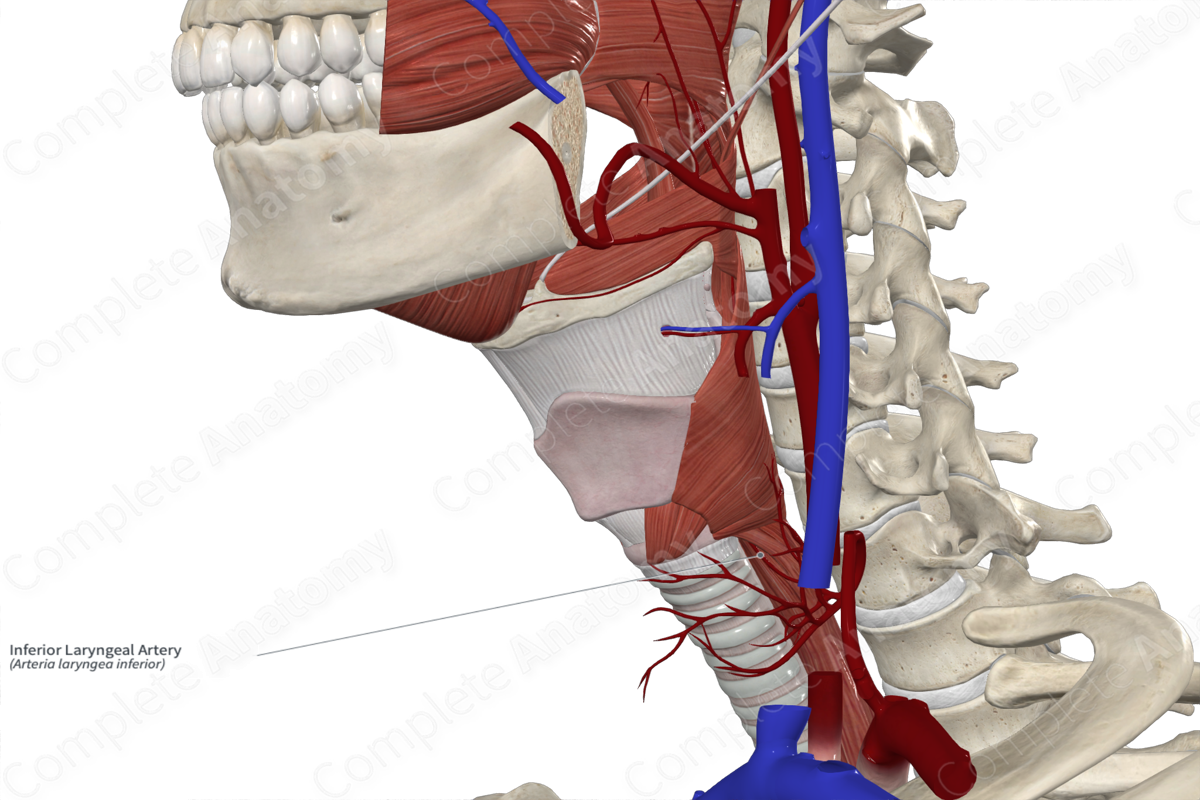
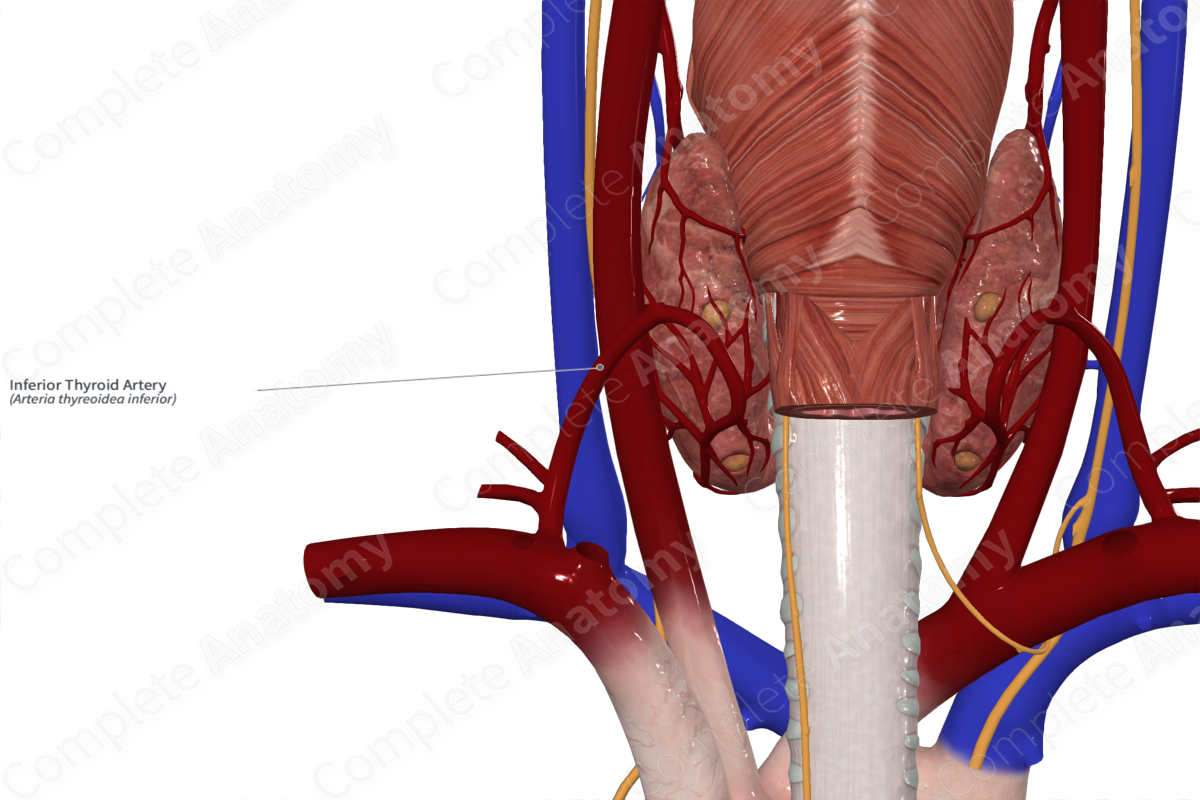
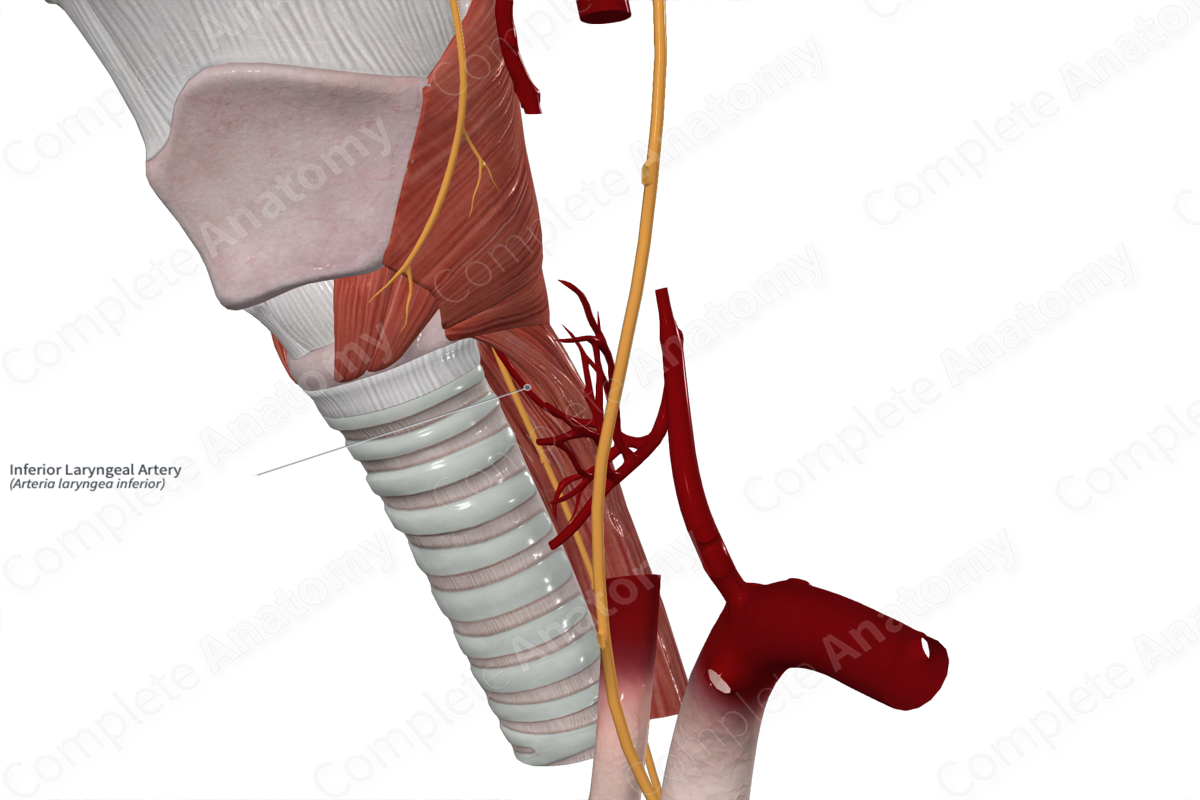
Vascularization of the Larynx
• _____ laryngeal artery branch of the superior _____ a.
• _____ laryngeal a. branch of the inferior _____ a.
• Laryngeal veins accompany the arteries
Superior laryngeal artery
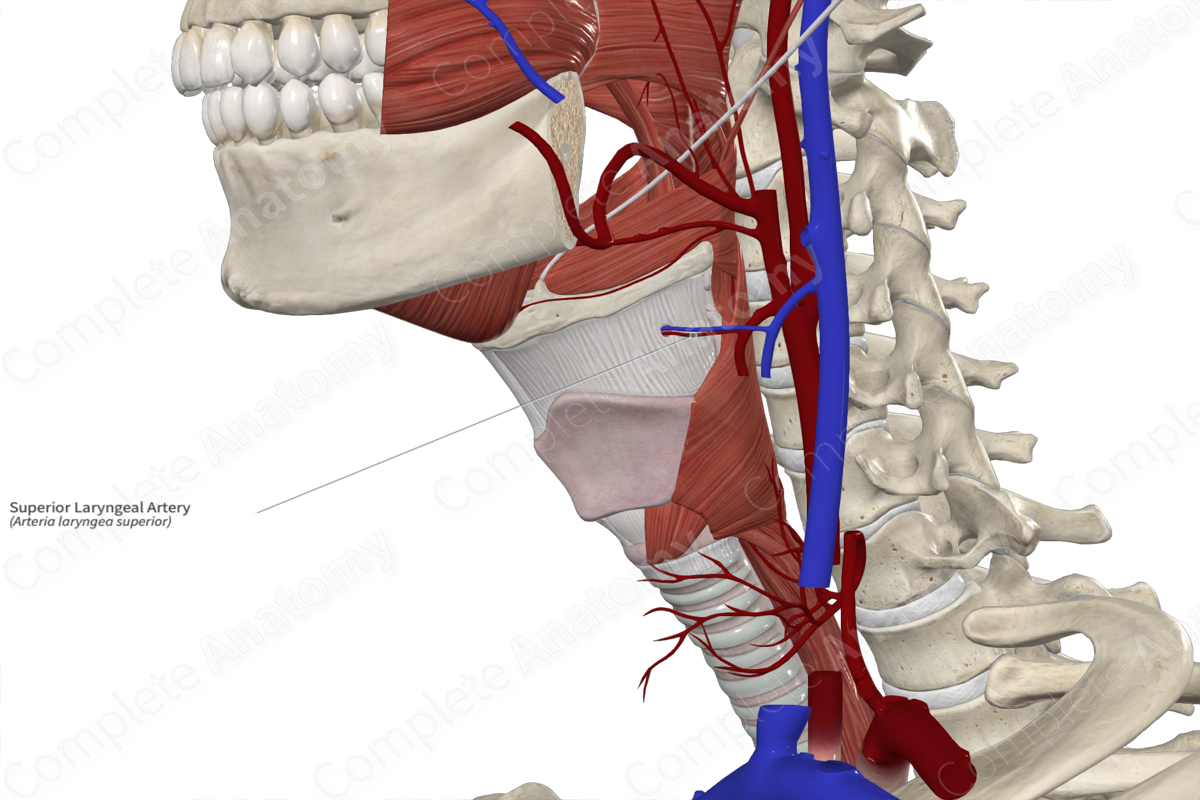
Superior thyroid artery
Inferior laryngeal artery
Inferior thyroid artery
superior
recurrent
Innervation of the Larynx
• Sensory
– _____ laryngeal - superior to the vocal folds
– _____ laryngeal - inferior to the vocal folds
• Motor
– superior laryngeal and recurrent laryngeal
Superior laryngeal nerve
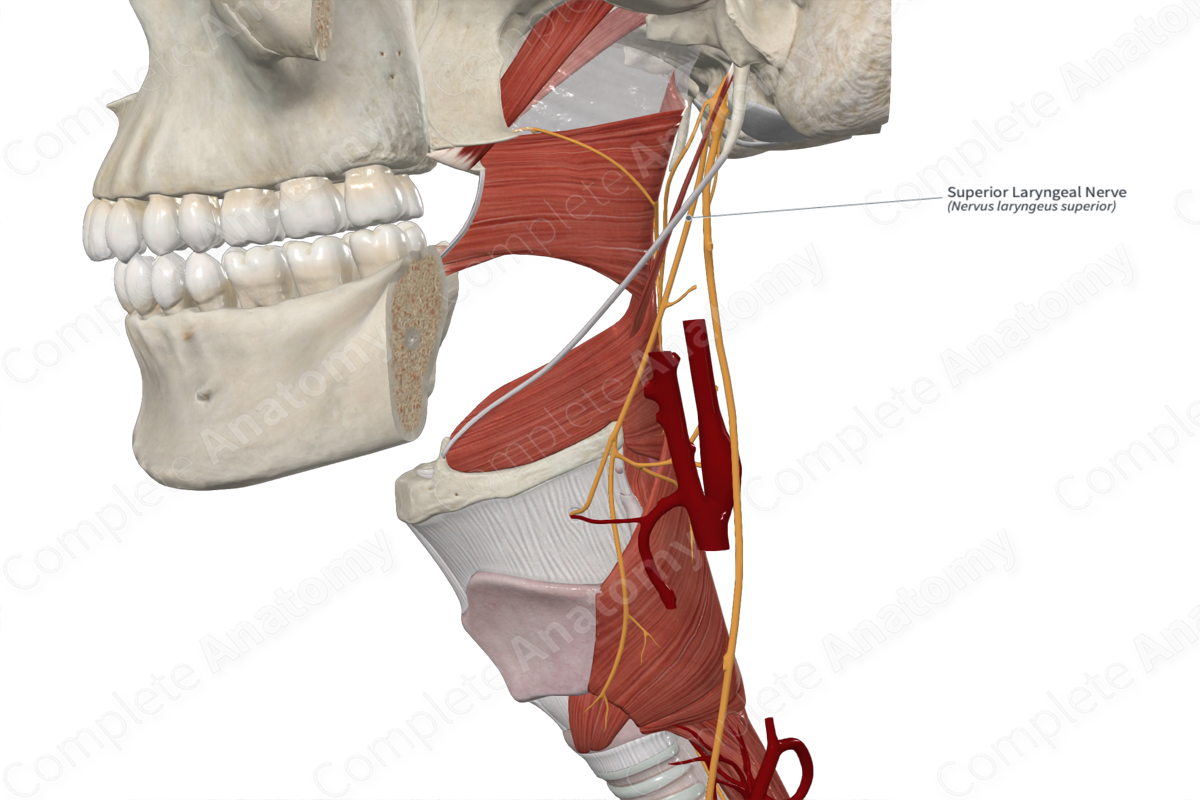
Inferior laryngeal nerve
Pharynx
Air
Food
_____
• Muscular tube that extends from the base of the skull to the esophagus
• It has posterior and lateral walls
• It is open anteriorly to the nasal cavity, oral cavity and larynx
• It serves two roles:
– _____ passage - is always open except during swallowing
– _____ passage - to swallow food, one must hold their breath
• Location - in midline anterior to the vertebralcolumn
• The pharynx is divided up into three sections;
– Nasopharynx
– Oropharynx
– Laryngopharynx
constrictors
elevate
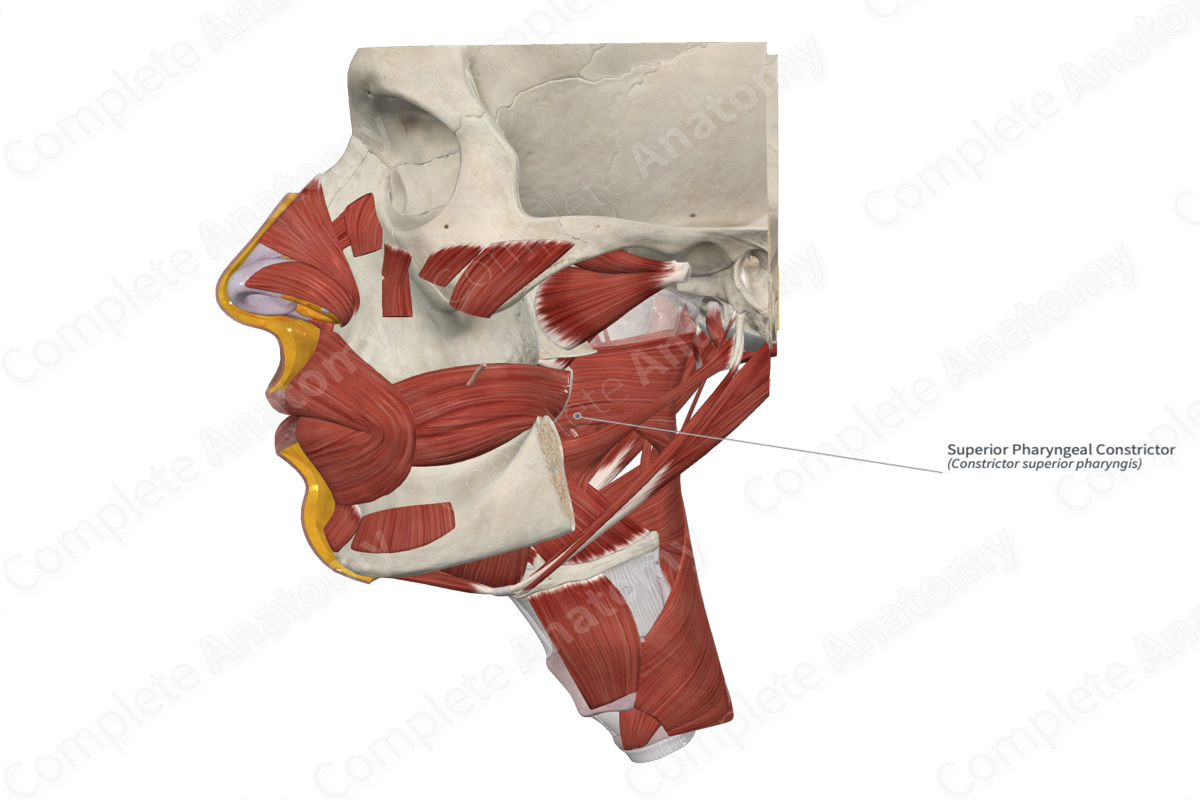
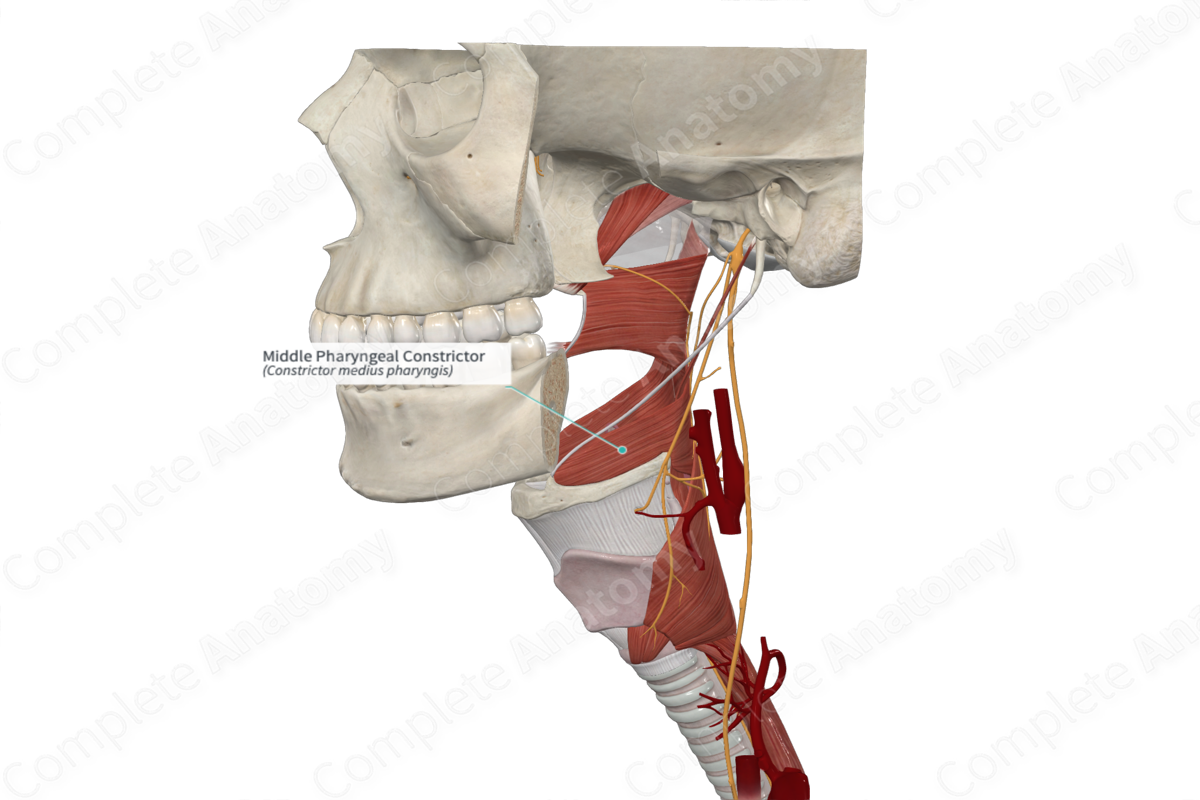
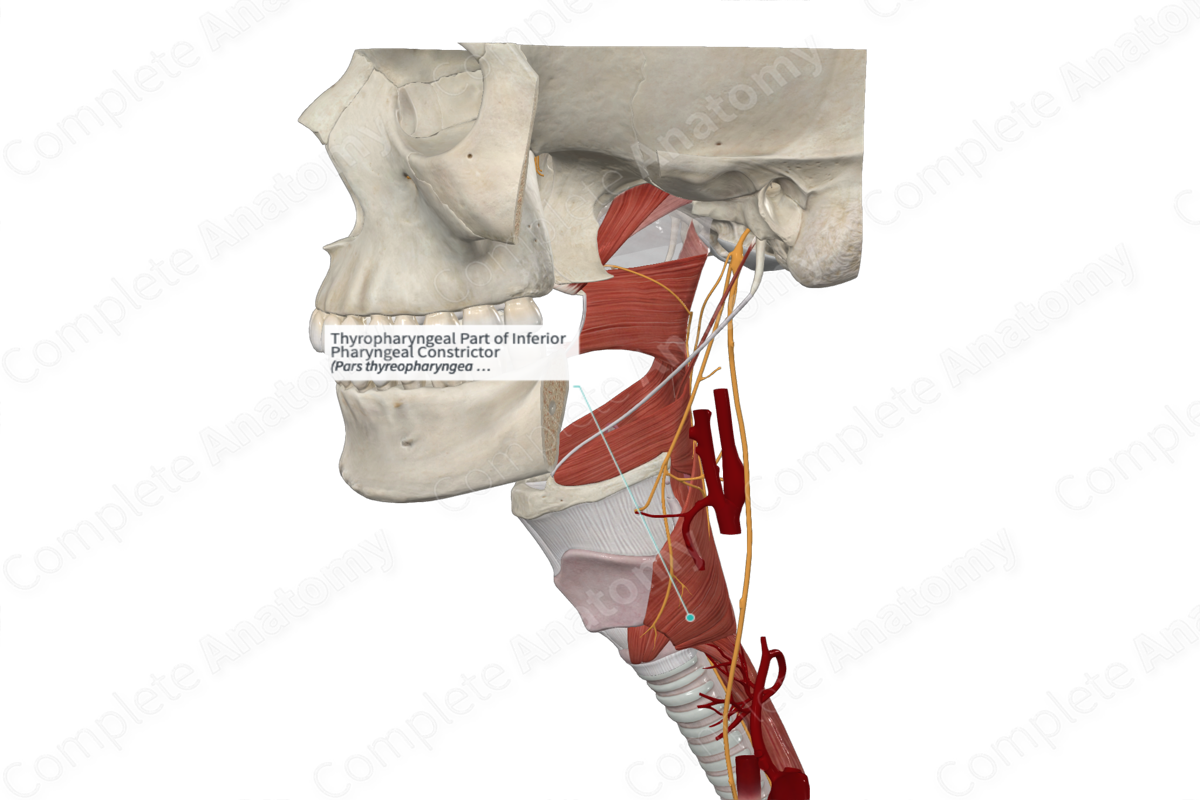
Muscles of the Pharynx
• Superior, middle, and inferior ______
– These muscles act to constrict the pharynx and propel food to the esophagus
• Pharyngeus muscles
– Longitudinal muscles of the pharynx; Function to _____ the pharynx and larynx during swallowing
Superior pharyngeal constrictor
Middle pharyngeal constrictor
Inferior pharyngeal constrictor
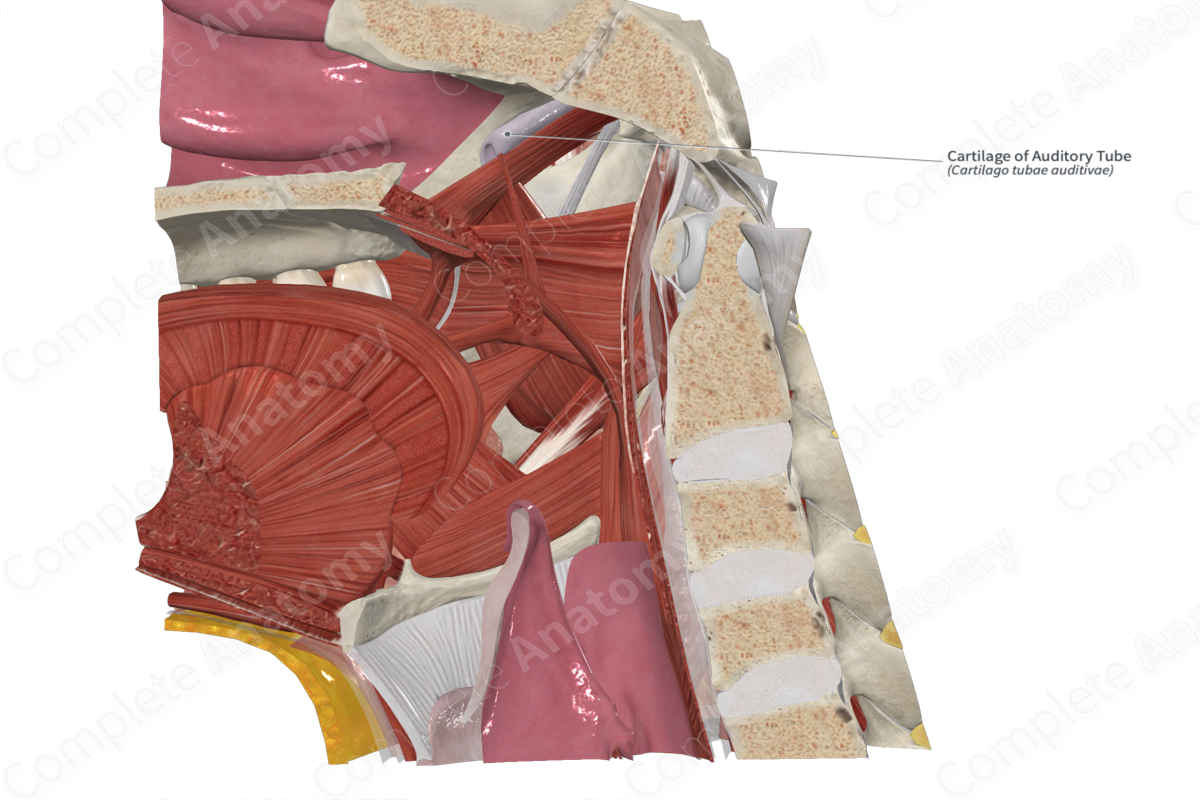
Pharyngotympanic tube
Pharyngeal
Motor, Vagus
Sensory, Glossopharyngeal
Innervation of the Pharynx
• _____ plexus
– _____ innervation is by the _____ nerve (CN X)
– ______ innervation by the _____ nerve (CN IX)
Deglutition
longitudinal
______
• A bolus of food is masticated in the oral cavity and passed into the oral pharynx by the tongue
• The nasopharynx is protected by muscular contraction of the soft palate to prevent entry into the nasal cavity.
• Contraction of the _____ muscles of the pharynx raises the pharynx to receive the bolus
• Constrictors propel the bolus into the esophagus
• Inlet constrictors to the larynx prevent passage of the bolus into the trachea (aspiration)