Psychoactive Substances Ch 2
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes cells of the nervous system and communication within/between a neuron(s)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
What are the types of neurons?
Sensory, interneurons, and motor neurons
Sensory neuron
Detect changes in the internal or external environment
Motor neuron
Controls muscular contraction or glandular secretion
Interneuron
Between sensory and motor neurons, located entirely within the CNS
What are the divisions of the nervous system?
Central and peripheral nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
Made up of the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
Includes the nerves outside the skull/spinal cord and the sensory organs
Soma
The cell body of a neuron, which contains the nucleus
Its shape varies considerably in different kinds of neurons
integrates information
Dendrite
a branched, treelike structure attached to the soma of a neuron
receives information from the terminal buttons of other neurons
Synapse
The junction between the terminal buttons of one neuron and the somatic or dendritic membrane of the receiving cell
Axon
the long, thin, cylindrical structure covered with myelin
carries the action potential and transmits information from the cell body to the terminal buttons
Action potential
The basic message carried by the axon
How are neurons classified?
Based on axons and dendrites leaving the soma
multipolar
bipolar
unipolar
Multipolar neuron
1 axon
many dendrites attached to the soma
motor and interneurons neurons
Bipolar neuron
1 axon
1 dendrite attached to its soma
transmits smell, sight, taste, and hearing
Unipolar neuron
1 axon attached to its soma
the axon divides, one branch receiving sensory information and the other sending information into the CNS
fastest transmission of information
transmits somatosensory information
sensory neuron
Nerves
Bundles of individual neurons/axons contained within a protective membrane
What are the sites of neurotransmitter release?
Terminal buttons and synaptic connections
Terminal button
the bud at the end of a branch of an axon
forms synapses with another neuron and sends information to that second neuron
calcium channels are embedded here
Neurotransmitter
A chemical that is released by a terminal button
has an excitatory or inhibitory effect on another neuron
Cell membrane
a structure consisting principally of lipid molecules that defines the outer boundaries of the cell
contains proteins
Cytoplasm
jelly-like fluid containing organelles
contains mitochondria
How do mitochondria work within the cytoplasm of a neuron?
extract energy from nutrients
synthesize adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
contain their own genetic material
replicate independently of the rest of the cell
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
a molecule of prime importance to cellular energy metabolism
its breakdown liberates energy
Nucleus
A structure in the central region a cell, containing the chromosomes
Describe chromosomes within the nucleus of neurons
consist of long strands of DNA
contain genes (which code for proteins)
Where are proteins found in the neuron?
cytoskeleton
enzymes
microtubules involved in axoplasmic transport
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
a long, complex macromolecule consisting of 2 interconnected helical strands
along with associated proteins, strands of DNA constitute the chromosomes
Gene
The functional unit of the chromosome, which directs synthesis of one or more proteins
Cytoskeleton
Formed of microtubules and other protein fibers, linked to each other and forming a cohesive mass that gives a cell its shape
Enzyme
A molecule that controls a chemical reaction, combining 2 substances or breaking a substance into 2 parts
Microtubule
A long strand of bundles of protein filaments arranged around a hollow core
part of the cytoskeleton and involved in transporting substances from place to place within the cell
Axoplasmic transport
an active process by which substances are propelled along microtubules that run the length of the axon
includes anterograde and retrograde transport
Anterograde transport
Runs from the soma to the terminals
Retrograde transport
Runs from the terminals to cell body
Where are glia cells located?
central nervous system
What are the types of glia?
astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglia
Astrocyte
controls chemical composition around neurons
processes area around neurons and blood vessels
help nourish neurons
acts as “glue”
surrounds and isolates synapses
removes debris via phagocytosis
Phagocytosis
The process by which cells engulf and digest other cells or debris caused by cellular degeneration
How do astrocytes help nourish neurons?
convert bloodstream glucose into lactate, which is then used by neurons
stores glycogen
Oligodendrocytes
produce the myelin sheath IN THE CNS
one cell makes up to 50 myelin segments
Myelin sheath
Surrounds axons and insulates them
speeds up the transmittance of information
prevents messages from spreading between adjacent axons
How do oligodendrocytes form myelin sheaths?
form processes shaped like canoe paddles
each of these paddle-shaped processes then wraps itself many times around a segment of an axon, producing layers of myelin
each paddle becomes a segment of an axon’s myelin sheath
Node of Ranvier
A naked portion of a myelinated axon, between adjacent oligodendroglia or Schwann cells
Microglia
the smallest of glial cells
phagocytes
protects the brain from invading organisms (immune system function)
Where are Schwann cells located?
peripheral nervous system
Schwann Cells
produce myelin IN THE PNS
each segment of myelin is one Schwann cell
True or False? The chemical composition of myelin in the PNS is the same as that of the CNS
False
Describe the BBB (Blood-Brain Barrier)
selectively permeable
more permeable in some areas (e.g., area postrema)
capillaries within the brain do not have gaps
How do molecules pass through the BBB?
active transport carries many molecules into the CNS
drugs are inert (non-effective) if they cannot pass through
Area postrema
part of the brain that controls vomiting
BBB is much weaker here, permitting neurons in this region to detect the presence of toxic substances in the blood
Describe Ehrlich’s experiment
discovered the BBB
if a blue dye is injected into an animal’s bloodstream, all tissues except the brain and spinal cord will be tinted blue
Membrane potential
the electrical charge across a cell membrane
the difference in electrical potential inside and outside the cell
Resting potential
The membrane potential of a neuron when it is not being altered by excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
-60 to -70 mV
What is the charge of the resting potential?
Approximately 70 mV in the giant squid axon
At rest, what molecules have the highest concentration OUTSIDE the cell?
Chloride and sodium
At rest, what molecules have the highest concentration INSIDE the cell?
Potassium and anion proteins
Depolarization
Reduction (toward 0) of the membrane potential of a cell from its normal resting potential
Hyperpolarization
An increase in membrane potential, making it more negative than the resting potential.
refractory period at -90 mV
Action potential
The brief electrical impulse that provides the basis for conduction of information along an axon
Threshold of excitation
The value of the membrane potential that must be reached to produce an action potential
Force of diffusion
When there are no forces or barriers to prevent them from doing so, molecules will diffure from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration
Electrolytes
An aqueous solution of a material that ionizes (namely, a soluble acid, base, or salt)
Ions
A charged molecule (cations vs. anions)
Cations
Positively charged ions
Anions
Negatively charged ions
Electrostatic pressure
The attractive force between atomic particles charged with opposite signs or the repulsive force between atomic particles with the same sign
When at rest, what ion has force of diffusion and electrostatic pressure going in the same direction?
Sodium ions move into the cell
Which is the stronger force; force of diffusion or electrostatic pressure?
Force of diffusion
How is the resting potential of the cell restored?
Sodium potassium pump (321 NOKIA)
Intracellular fluid
The fluid contained within cells
Extracellular fluid
Fluids located outside of cells
Sodium-potassium transporters
A protein found in the membrane of all cells that extrudes sodium ions out of the cell and transports potassium ions into the cell
Ion channels
A specialized protein molecule that form pores through the membrane that permits specific ions to enter or leave cells
TRUE or FALSE? When an action potential is triggered, its size decreases
False; it remains the same as it travels down the axon
All-or-none law
The principle that once an action potential is triggered in an axon, it is propagated, without decreasing, to the end of the fiber
Rate law
The principle that variations in the intensity of a stimulus are represented by variations in the firing rate of action potentials, NOT the amplitude of the action potential.
rate of firing is the basic element of information
Where is the only place where a myelinated axons comes into contact with the extracellular fluid?
At the node of Ranvier, where the axon is naked
Why is there no inward flow of Na+ when the sodium channels open in the myelinated areas?
Because there is no extracellular sodium
Saltatory conduction
conduction of action potentials by myelinated axons
the action potential appears to jump from one node of Ranvier to the next
What are some advantages to saltatory conduction?
the neuron expands less energy (ATP) to maintain ion balance
faster conduction
Synaptic transmission
the primary means of communication between neurons
the transmission of messages from one neuron to another through a synapse
relies on neurotransmitters
Postsynaptic potential
Alterations in the membrane potential of a postsynaptic neuron, produced by liberation of neurotransmitter at the synapse
Binding site
The location on a receptor protein to which a ligand binds
Ligand
A chemical that binds with the binding site of a receptor
Dendritic spine
A small bud on the surface of a dendrite, with which a terminal button of another neuron forms a synapse
What strutures make up the synapse?
presynaptic membrane
postsynaptic membrane
synaptic cleft
synaptic vesicles
release zone
postsynaptic density
Presynaptic membrane
membrane of the terminal button that lies adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane
neurotransmitter is released here
Postsynaptic membrane
the cell membrane opposite the terminal button in a synapse
the membrane of the cell that receives the message
Synaptic cleft
The space between the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane
Synaptic vesicles
Contain neurotransmitter
Release zone
The location of neurotransmitter release
Postsynaptic density
Contains receptors and the proteins that hold them in place
Describe how neurotransmitters are released
Several synaptic vesicles located just inside the presynaptic membrane fuse with the menbrane and then break open, spilling their contents into the synaptic cleft
Omega structure
Synaptic vesicles fused with the membrane during neurotransmitter release
Postsynaptic receptor
A receptor molecule in the postsynaptic membrane of a synapse that contains a binding site for a neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter-dependent ion channel
An ion channel that opens when a molecule of a neurotransmitter binds with a postsynaptic receptor
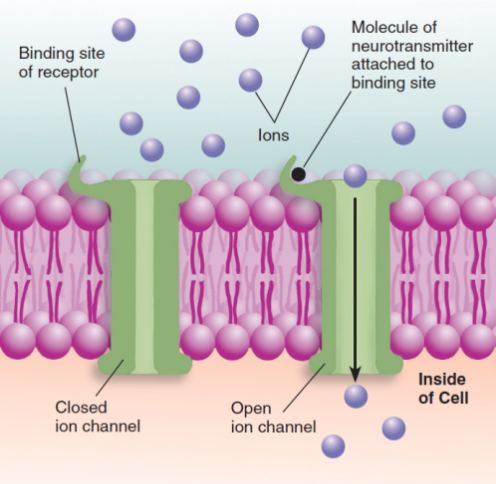
Ionotropic receptor
A receptor that contains a binding site for a neurotransmitter and an ion channel that opens when a molecule of the neurotransmitter attaches to the binding site
can only open ONE ion channel
glutamate, GABA, etc.
What’s another term for ionotropic receptor?
Ion channel
Is an ionotropic receptor or metabotropic receptor fast acting/short lasting?
Ionotropic receptor