Negative Externalities
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Externality
A third-party spill-over effect
Negative externality
A negative spillover.
Negative consumption externality
A negative third party spill over derived from the consumption of a good.
Negative production externality
A negative third party spill over derived from the production of a good.
S =
Marginal Cost
D =
Marginal Benefit
Social Cost formula
Private Cost + External Cost
Social Benefit formula
Private Benefit + External Benefit
Socially efficient equilibrium
The equilibrium best for society
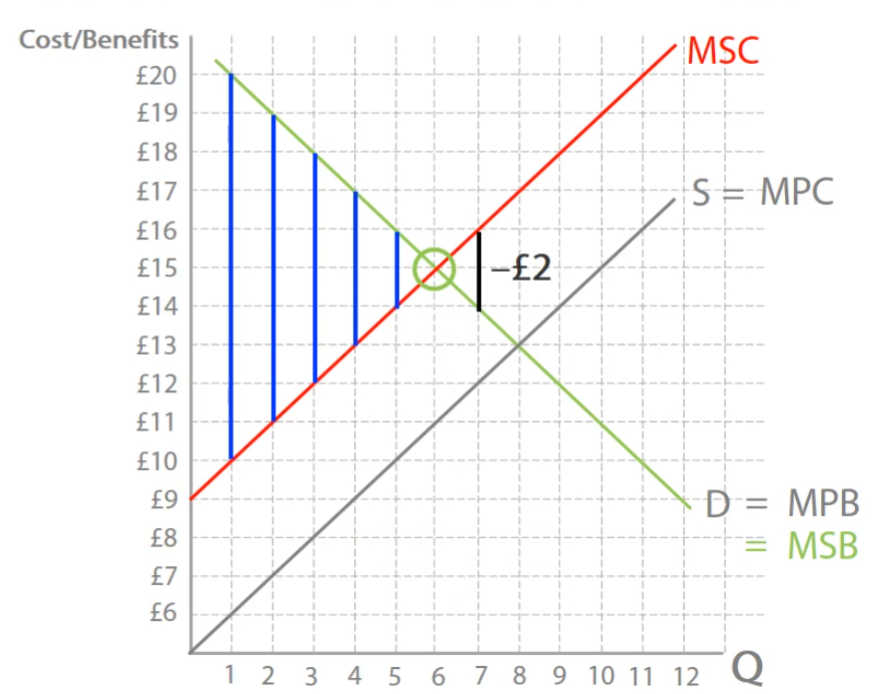
Market equilibrium
S = D leading to welfare loss
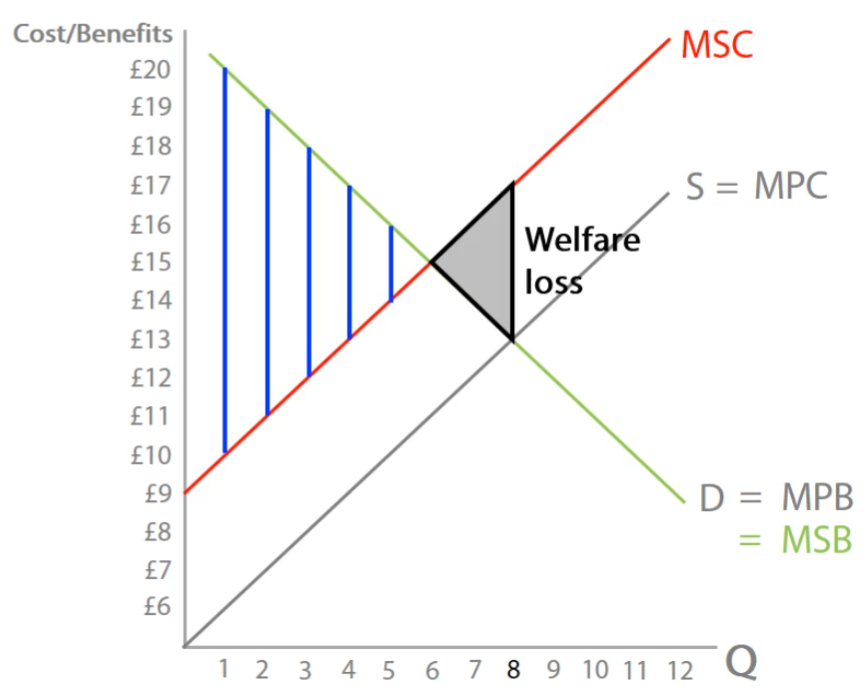
Socially Optimal Level/Cost
Marginal Social Cost = Marginal Social Benefit
Welfare loss
When there is overconsumption or overproduction
How to solve welfare loss?
Indirect taxations such as specific and ad valorem tax.
Tradable pollution permits
Minimum Price
Regulation
Main aim of taxation
To internalize external costs.
How does indirect tax affect firms
Makes production more costly, therefore shifts MPC upwards and internalizes overconsumption and welfare loss.
Assumptions of government taxation on negative production
Correct size of tax
Tradable Pollution Permits
Sets a cap on how much pollution a year is allowed. Raises government tax revenue through permits which are divided up until the cap is reached.
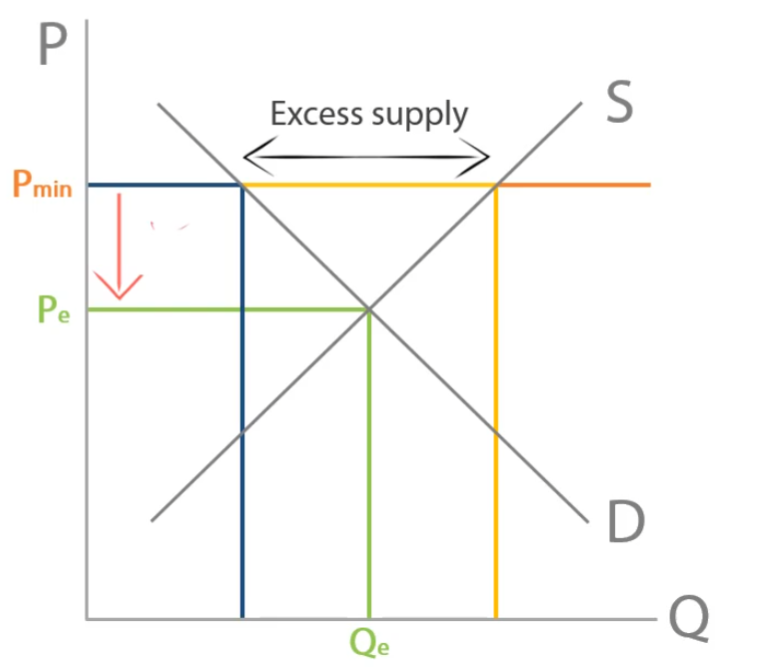
Minimum Price
The lowest price a supplier of a good can legally sell for to contract demand and reach socially optimum level. Leading to excess supply and therefore disequilibrium as it must be set above equilibrium price.
Regulation
When government makes changes to the law to correct market failure. Such as banning hard drugs to totally reduce consumption of hard drugs.