Electrochemical Cells
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What do electrochemical cells do?
interconvert electrical and chemical energy
Name types of cells. Name each form of the types present.
Primary Cells
galvanic
voltaic
secondary (rechargeable)
fuel cells
Electrolytic
How do Primary Cells Function?
generate electricity from spontaneous, irreversible, exothermic chemical reactions
How do Electrolytic Cells Function?
electrical energy is used to drive forward non- spontaneous, reversible, chemical reactions
What is a Battery?
two or more electrochemical cells in a single container
What is a Primary Cell?
a device that changes chemical energy (from a redox reaction) into electrical energy
Reaction materials will be consumed, and either the anode/electrolyte or both will need to be replaced or the battery thrown away.
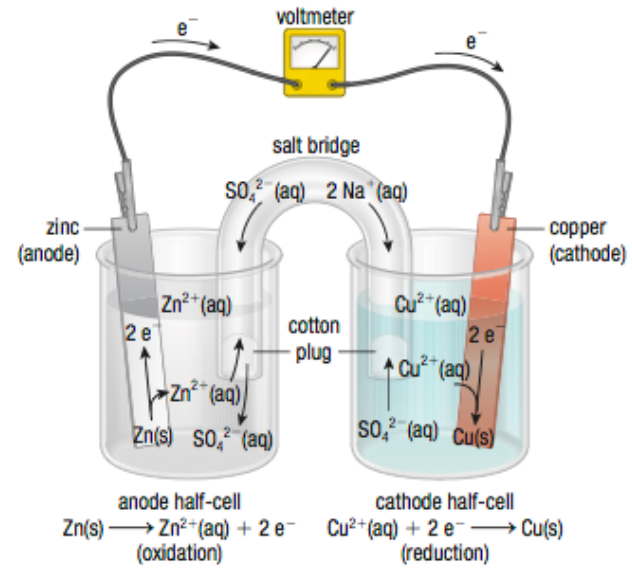
Oxidation and reduction reactions are separated into two half- cells/compartments, but are connected by an external wire to allow for electrons to flow between them
Primary Cell Components
Each half cell has a conductor (electrode)
The electrode where OXIDATION occurs is the anode (-)
The electrode where REDUCTION occurs is the cathode (+)
Each half cell is connected by a salt bridge to neutralize build-up of charges and maintain potential difference
anions flow from cathode → anode through salt bridge, cations from anode → cathode. NO SALT BRIDGE— NO VOLTAGE
potential difference created when circuit is complete and can. be measured with a voltmeter
What is a Salt Bridge?
a glass tube or absorptive paper containing aqueous, non-reactive, solution of ions
What do primary cells look like?
What are Electron Potentials?
charge separation between the metal and its ions in solution within the half cells
What physically occurs in cell wrt Electron Potentials?
atoms will form ions by releasing e⁻, making the surface of the metal negative wrt the solution all while ions in the solution gain e⁻ to form atoms (equilibrium)
How is reactivity related to Electron Potentials?
The reactivity of the metal determines the magnitude of electrode potential and position of equilibrium in the half cell
RULE: more reactive metal = more negative electrode potential
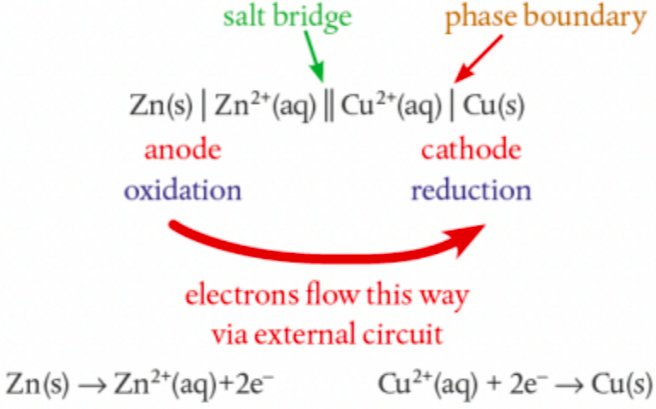
What is a Cell Diagram Convention? How do you draw one?
a shorthand way to represent primary cells
Anode on the left, cathode on the right (e⁻ flow from left to right)
double vertical line represents salt bridge
single vertical line is phase boundary (eg. solid electrode and aqueous solution)
aqueous solutions of each electrode are next to the salt bridge
If a half-cell has two ions, separate with comma since they are in the same phase

What would a Cell Diagram Convention of Zinc and Copper look like?
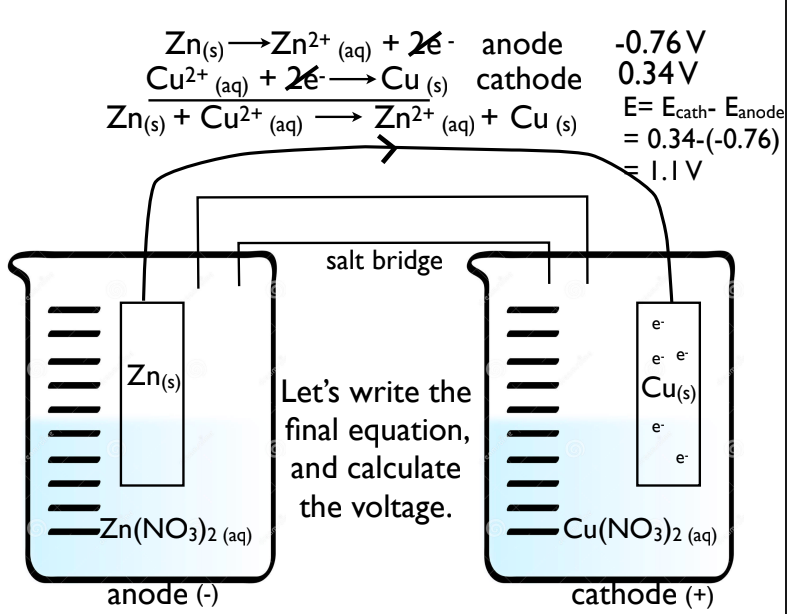
How do you predict Cell Reactions?
You look at the two metals in the half cells
direction of electron flow and voltage is determined by the relative strength of the reducing agents
Find which metal is higher on the Activity Series
Whichever element is higher will oxidize (anode- stronger
reducing agent), and the lower
is being reduced (cathode -
weaker reducing agent).
Draw galvanic cell using zinc and copper metal
Trick:
Red Cat
An Ox
wrt Secondary Cells, how can electricity generating reactions be reversed?
by applying current
wrt Secondary Cells, what are their pros and cons?
Pro | Con |
satisfy higher current demands | have a higher rate of self-discharge |
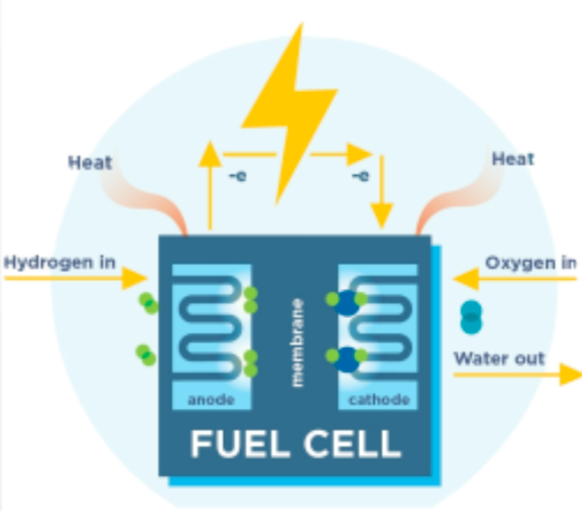
Tell me about Fuel Cells
converts hydrogen, methanol, or ethanol and oxygen into water, carbon dioxide and heat.
cause little pollution and are very efficient
not rechargeable but need steady supply of fuel