Oral histology and embryology LO 1
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Prenatal development
Begins with the start of pregnancy and continues until the birth of the child; the 9 months of gestation is usually divided into trimesters or 3 month time spans.
Embryology
The study of prenatal development.
Preimplantation period, embryonic period, fetal period
What are the 3 periods of prenatal development?
First week
When is the preimplantation period?
Week 2 to week 8 (end of 2nd month)
When is the embryonic period?
Week 9 (3rd month) to 9th month
When is the fetal period?
First
What trimester? Proliferative and embryonic period.
Fetal period
The ————— period happens during the 2nd and 3rd trimester
1
How many cells are in a zygote?
46 (eggs 23 + sperms 23)
How many chromosomes are in a zygote?
Morula or "blastula"
After 3 days, the baby is now a ball of cells and is almost at the uterus. This is called a:
Blastocyst
When the blastula arrives to the uterus, it is now called a:
Induction
Action of one group of cells on another that leads to the establishment of the developmental pathway in the responding tissue. A physiological process: the first physiological process involved during prenatal development is the process of ———————. Triggering of development due to the interaction of embryological cells (ovum and sperm).
Proliferation
Controlled cellular growth and accumulation of byproducts. A physiological process that follows induction as well as the other processes is the dramatic process of ———————, controlled levels of cellular growth present during most of prenatal development. Cells increase in number.
interstitial growth
This happens in the proliferation period. Growth may be by ——————— growth, which occurs from deep within a tissue or organ. Deep within a tissue: soft tissue.
Appositional growth
Happens in the proliferation period as well. In contrast, growth may be by ——————— growth, in which a tissue enlarges its size by the addition of layers on the outside of a structure. Bone or dental tissue.
Differentiation
Change in identical embryonic cells to become distinct structurally and functionally. A change occurs in the embryonic cells, which are identical genetically but later become quite distinct structurally and functionally. ——————— occurs at various rates in the embryo. Many parts of the embryo are affected: cells, tissue types, organs, and systems.
Cytodifferentiation.
This type of differentiation in the development of different cell types.
Morphodifferentiation
This type of differentiation is the development of the different or shape for each organ or system. This is accomplished by morphogenesis.
Morphogenesis
Development of specific tissue structure or or shape differing form due to embryonic cell migration and inductive interactions.
Maturation
Attainment of adult function and size due to proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenesis. The physiological process of ——————— of the tissue types and organs begins during the embryological period and continues later in the fetal period.
Embryonic period (2nd to 8th week)
The fetus is most susceptible to developmental disturbances during the ——————— period.
3 weeks
W.H.O says 50% of fertilized ova are lost within the first — weeks.
15%
WHO says ——% of recognizable pregnancies have spontaneous abortion.
3%-6%
WHO says there are birth defects in —% to —% of all newborns.
65%
——% of all birth defects have no known or identifiable cause.
Teratogenic agents
Agents that can lead to birth defects.
Genetic or environmental.
Teratogenic agents can be divided into 2 categories: ——————— or ———————, based on their etiology.
Chromosomal abnormalities
Genetic teratogenic agents are caused by:
Environmental agents and factors
——————— teratogenic agents and factors are things like: medications, drugs, infectious agents, and radiation.
Genetic abnormality
Are environmental or genetic teratogenic factors the major contributors to the pathologic process.
Drugs, chemicals, infections, radiation
What are the 4 known teratogens involved in congenital malformation.
Nicotine (tobacco), ethanol (alcohol), excessive vitamin D, radiation therapy (>5 rads).
Environmental teratogens are things like social drugs, medications, nonprescription products, etc. what are 4 examples?
Cytomegalovirus, herpes virus, rubella virus, syphilis
4 infections that can cause developmental malformations:
Diabetes, folic acid deficiency (spina bifida) , iodine deficiency, maternal starvation, obesity
5 metabolic imbalances that can lead to developmental malformations:
Fertilization
——————— is completed with formation of the zygote.
Preimplantation period
The result of this process is the joining of the ovum’s chromosomes with those of the sperm. This joining of chromosomes from both biological parents forms a new individual with “shuffled” chromosomes. To allow this formation of a new individual, the sperm and ovum, when joined, have the proper number of chromosomes (from diploid number of 46=zygote).
Down syndrome
If any disturbances occur in meiosis during fertilization, major congenital malformations result from the chromosome abnormality in around 10% of cases. An example of this is ———— ———————, where an extral chromosome number 21 is present after meiotic division.
Implantation
This is the end of the preimplantation period. By the end of the first week, the blastocyst stops traveling and undergoes ——————— and thus becomes embedded in the prepared endometrium, the innermost lining of the uterus on its back wall.
Trophoblast layer
This is the peripheral (outer) layer of cells of the blastocyst. This part of the blastocyst invades the endometrium to implant itself.
Embryoblast layer
This is the inner mass of embryonic cells in a blastocyst.
Embryonic period
The ——————— period of prenatal development, extends from the beginning of the 2nd week to the end of the 8th week. During the 2nd week of prenatal development, the implanted blastocyst grows by increased proliferation of the embryonic cells. Differentiation is also occurring, resulting in morphogenesis.
Embryonic cell layers (germ layer)
Increased number of embryonic cells creates the ——————— cell layers within the blastocyst.
Bilaminar embryonic disc
Developed in the blastocyst. Developed from the blastocyst and appears as a flattened, essentially circular plate of bilayered cells.
Superior: epiblast layer inferior: hypoblast
The bilaminar embryonic disc has a superior and inferior layer. The superior layer is the ————— layer and is composed of light columnar cells. The inferior layer is the ————— layer is composed of small cuboidal cells.
Yolk sac and the amniotic cavity.
2 cavities develop on either side of the bilaminar embryonic disc. These cavities are:
Epiblast layer
The ectoderm is formed from the ————— layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc.
Mesoderm
Migrating cells from the epiblast layer eventually form into the:
Hypoblast layer
The mesoderm is formed from what layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc.
Third week
The beginning of the ————— week, some cells from the epiblast layer move or migrate toward the hypoblast layer only in the area of the primitive streak.
Ectodermal cell layer
In the 3rd week, the epiblast differentiates into the ——————— cell layer.
Endodermal cell layer
In the 3rd week, the hypoblast differentiates into the ——————— cell layer.
Mesodermal cell layer
Developing between the epiblast and the hypoblast, are mesenchyme cells that become the ——————— cell layer.
Primitive streak
What is the middle line pointing to?
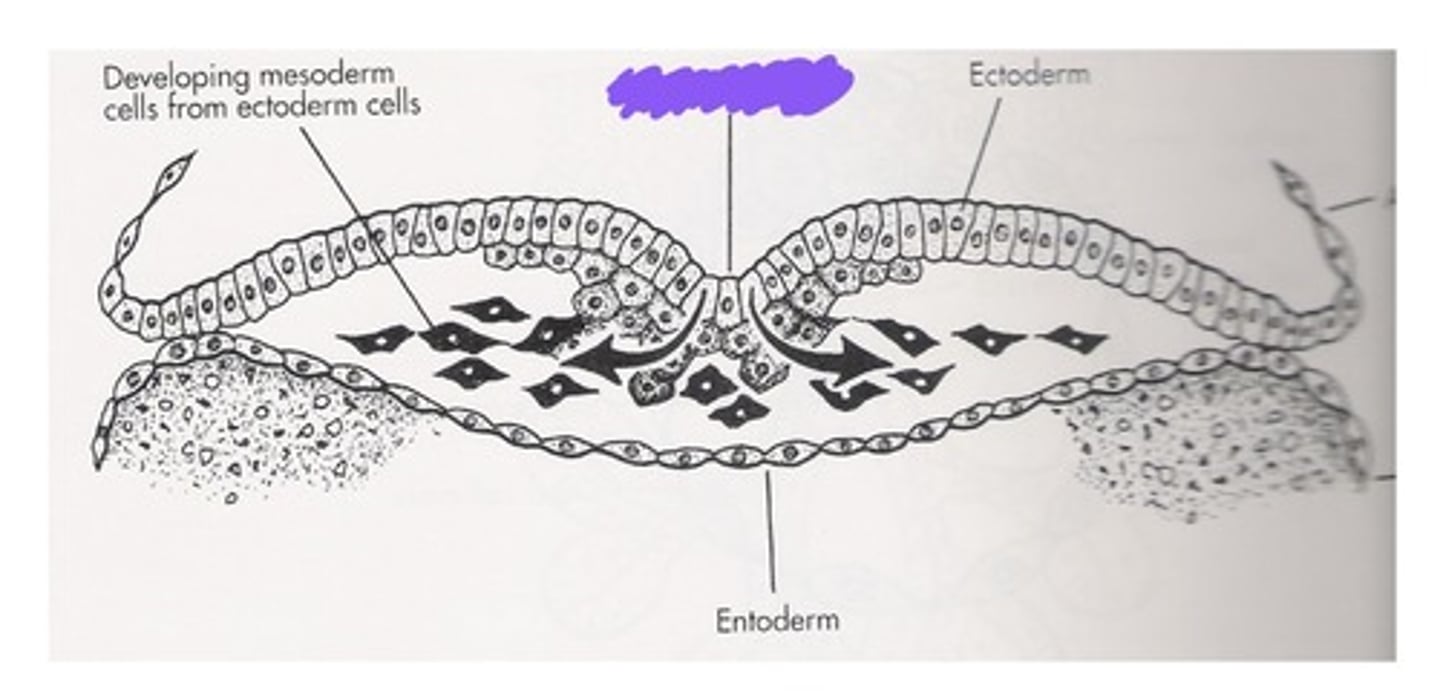
Ectoderm
Nervous system, sensory epithelium of the eye, ear, nose, epidermis, hair, nails, mammary and cutaneous glands, epithelium of sinuses, oral and nasal cavities, intraoral glands, tooth enamel. All of these things are formed out of the: (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm?)
Endoderm
GI tract epithelium and associated glands. These things are formed out of the: (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm?)
Mesoderm
Muscles, CT derivatives (bone, cartilage, blood, dentin, pulp, cementum, PDL). These things are formed out of the: (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm?)
Trophoblast layer
The ——————— layer gives rise to the prenatal support tissues like the placenta.
Trilaminar disc
Embryo at the end of the third week of gestation.
Central nervous system
In the 3rd week, what system begins to develop in the embryo?
Neural plate of cells
In the 3rd week, a specialized group of ectodermal cells on the dorsal surface differentiate to form neuroectodermal cells. This central band of cells that extents the length of the embryo, from the cephalon end (top) to the caudal end (tail end). These cells form the:
Neural groove
As it grows, the lateral edges of the neural plate begin to elevate. Morphodifferentiation of the embryo's flat sheet of cells differentiate into the ————— —————. Near the end of the 3rd week, the ————— ————— deepens further and is surrounded by the neural folds.
Neural crest cells
In addition during the 3rd week, another specialized group of cells, the ————— ———— ————, develop from the neuroectoderm. These cells migrate from the crests of the neural folds and then disperse within the mesenchyme. These differentiate into diverse cell types such as components of the nervous system, melanocyte pigment cells, connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and all dental tissues except enamel.
Somites
Differentiated mesoderm gives rise to the ————— that are located on the sides of the developing CNS. These differentiate into mesenchymal cells which differentiate into connective tissue forming cells, skeletal (bone and cartilage) structures of the head, neck, trunk, associated muscles, and dermis.
Neural tube
1. The neuroectoderm forms from the ectoderm and is located at the neural plate. The neural plate then thickens to form the neural groove, surrounded by the neural folds. Then these folds meet and fuse, forming the:
Neuroblasts
Neuroepithelial cells proliferate and differentiate into ———————. ——————— are primitive nerve cells which develop into neurons. These cells do not have potential for mitosis.
Embryonic folding
In the 4th week, the disk undergoes ——————— —————: the trilaminar disc has folded into the embryo as a result of extensive growth of ectoderm. This places forming tissue types into their proper positions for further embryonic development as well as producing a somewhat-tubular embryo.
Ectodermal layer
The ——————— layer turns into the epidermis, sensory organs, and nerve tissue like eyes, ears, nose, and the nervous system, neural crest cells, mammary glans and cutaneous glands.
4th
During the ————— week of pregnancy, the face and neck begin to develop, with the primitive eyes, ears, nose, oral cavity, and jaw areas.
Foregut
The ————— gives rise to the primitive pharynx, which will form the oropharynx.
12th week
Facial development begins in the fourth week of pregnancy and completed in the ————— week.