Data Creation and Management in Geospatial Systems
1/495
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
496 Terms
What are the primary sources of geospatial data mentioned in the course overview?
Enterprise Geodatabases, Shared Folders, and Hosted Services.
What are some examples of Enterprise Geodatabases listed?
DOTB6GISDB01, DOTB6GISDBST01, GTI_PUB_UTM, RIL_LRS_PUB.
What types of data formats are discussed in the course?
Shapefile, Feature Class, Hosted Services, Raster.
What is the main focus of the course on Data Management?
How data management is applied to GIS and the creation of shared folder directories.
What are the key components of creating a Shared Folder Directory?
Creating a Shared Folder Directory, learning about Hierarchical Folder Structure, determining the difference between folders and files, discussing best practices, and how to share folders.
What best practices are emphasized for creating a File Geodatabase?
Understanding what File Geodatabases are, how to create them, and their organization and structure.
What is the significance of good data in relation to geospatial products?
Good data is essential for creating reliable and stable map products, similar to a strong foundation for a building.
How is information defined in the context of GIS?
Information is data that has been refined, structured, and converted into useful facts and figures that can be further analyzed into knowledge.
What characteristics are included in the definition of information?
Characteristics that describe or identify a feature name, type, unique identifier, and measurements in meaningful units.
What is the difference between data and information?
Data are raw, unorganized facts that lack meaning, while information is structured data that conveys logical meaning and can aid in decision-making.
How is data organized and stored?
Data are organized and stored in tables, Excel spreadsheets, database tables, and databases.
What does geospatial data refer to?
Data that describe features, objects, or events that can be physically located on earth and have some sort of spatial reference assigned to them.
What is the recommended setup for the course to facilitate learning?
Having at least two monitors—one for reading and one for doing exercises.
What is the instructor's approach to accommodating student needs?
The instructor encourages students to ask for help and to slow down if needed.
What is the relationship between the user, software, and data in GIS?
The user is the foreman, the software is like the workers, and both need to collaborate effectively to produce a desired product.
What does the term 'information' imply in terms of decision-making?
Information aids in decision-making by providing references and highlighting features or themes.
What is the importance of measurements in information?
Measurements in meaningful units such as length, area, and height provide context and understanding of the data.
What does the course emphasize about hands-on learning?
The course is entirely hands-on, requiring active participation and completion of exercises.
What is the challenge associated with data in GIS?
Data must be of high quality to ensure that the resulting map or product is reliable.
What is the role of the user in the context of data and information?
The user is responsible for managing and utilizing data effectively to create meaningful information.
What is the significance of a hierarchical folder structure in data management?
It helps organize data systematically, making it easier to access and manage.
What is the expected outcome of analyzing data?
Data needs to be analyzed and converted into information before it can be used for decision-making.
What are the data formats in which geospatial data is stored?
Vector, Raster, Surfaces, and Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN).
What are the data types used to share geospatial data?
Shapefiles, Feature Classes, KML/KMZ, ArcGIS services.
Where can different geospatial data types be housed?
Geodatabases, Database, File Folders.
What is vector data in ArcGIS Pro?
A coordinate-based data model representing geographic features, consisting of geometry and attribute data.
What are the three geometries defined by vector data?
Point (single vertex), Line (sequence of interconnected vertices), Polygon (multiple interconnected vertices with the same start and end position).
What are the characteristics of vector data?
Easily created and edited, displays discrete real-world features, scalable, and used for Spatial Analysis.
What does raster data represent?
Continuous data from satellites, remote sensing devices, or scanned maps, representing real-world phenomena.
What are some examples of thematic raster data?
Soils, land surface, vegetation cover.
What is the structure of raster data?
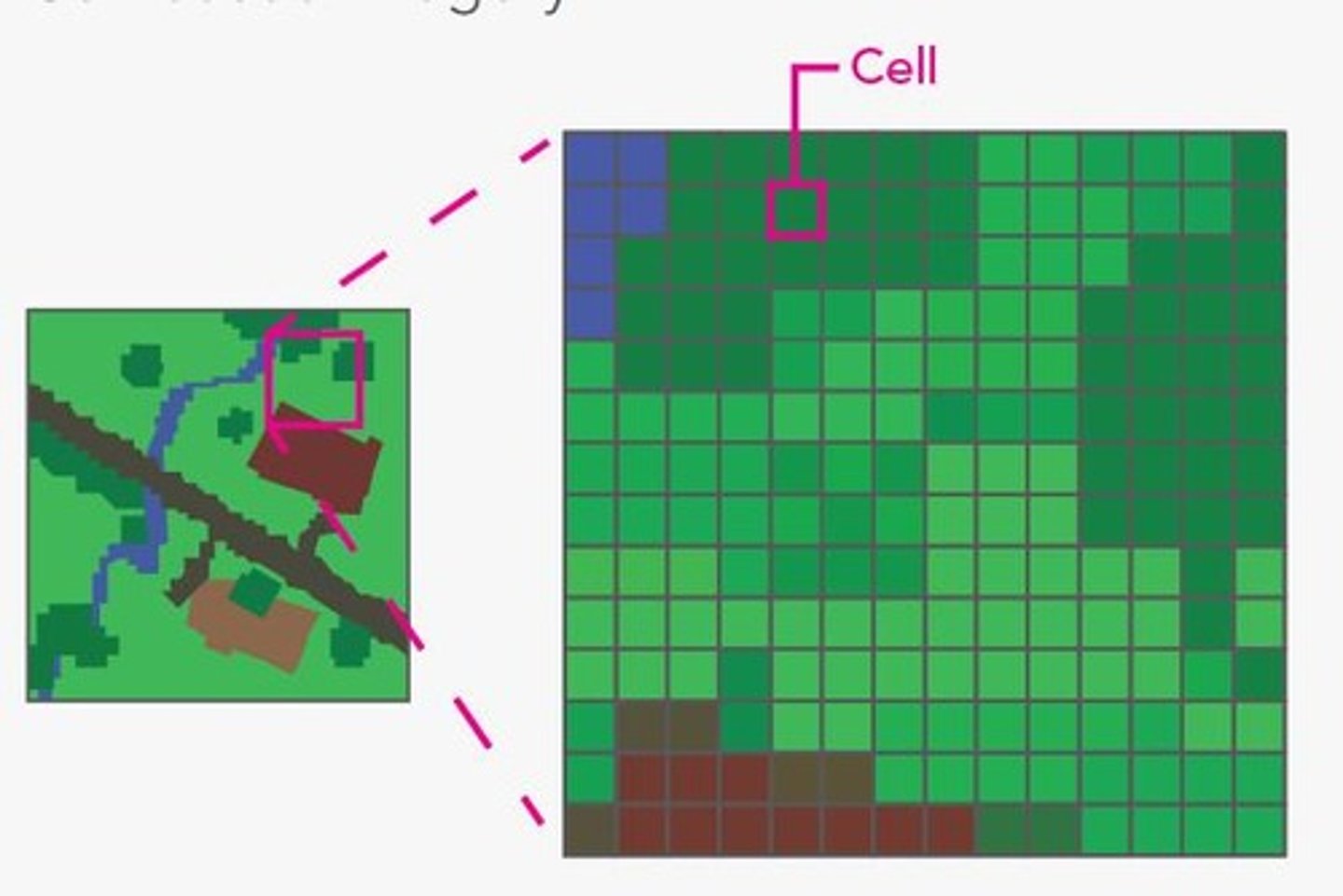
Composed of cells organized into a matrix of rows and columns called a grid.
What are the primary uses of raster data?
Basemaps, surface or elevation maps, thematic maps, and 3D raster images.
What happens to raster images when zooming in and out?
They are not scalable; images pixilate when zooming in and become clearer when zooming out.
What is a cell in raster data?
The smallest unit of information in a raster dataset, also referred to as a pixel.
What types of values can raster cells represent?
Real number values (with decimals) and Integer number values (without decimals), which can be both positive and negative.
What does resolution refer to in raster data?
The size of the cells in a raster dataset and the ratio of screen pixels to image pixels.
How is spatial resolution determined?
By cell size, which affects the clarity of the image; smaller cells yield smoother images.
What are the four kinds of resolution in raster data?
Radiometric resolution (ability to distinguish differences in spectrum), Spatial resolution (smallest object resolvable), and others not specified in the notes.
What is the impact of smaller raster cell size on processing time?
Smaller cell sizes take longer to process in GIS software.
What does radiometric resolution describe?
The ability of a sensor to distinguish slight differences in the spectrum between adjacent points.
What does spatial resolution determine?
The level of detail represented by an image and the dimension of the area on the ground represented by a single cell.
What does spectral resolution describe in remote sensing?
It describes the ability of a sensor to distinguish between wavelength intervals in the electromagnetic spectrum.
How does higher spectral resolution affect wavelength range?
The higher the spectral resolution, the narrower the wavelength range for a particular band.
What does temporal resolution refer to in geospatial imaging?
It refers to the frequency at which the image was captured over the same place on the earth's surface.
What is a Triangle Irregular Network (TIN)?
A TIN is used to represent height values and surface morphology by triangulating interconnected sets of vertices (vector-based XYZ points) to form a network of interconnected triangles.
What are the advantages of using a Triangle Irregular Network (TIN)?
TINs create more accurate surfaces by capturing accurate linear features through interconnected non-overlapping triangles.
In what units is TIN measured?
TIN is measured in English and metric units, not decimal degrees.
What are the common formats for raster data storage?
Common raster formats include Img, jpeg2, GIF, and LAS.
What are the key vector formats mentioned in the notes?
Key vector formats include Shapefile, Feature Class in a Personal, File, Enterprise Geodatabase, and KML.
What is a shapefile in geospatial data storage?
A shapefile is a simple and portable format for geospatial data storage, consisting of multiple files including a database file (DBF), shape index file (SHX), and shapefile (SHP).
What does the database file (DBF) in a shapefile contain?
The DBF houses the information and data for the shapefile.
What is the purpose of the shape index file (SHX) in a shapefile?
The SHX contains the column headers and indexes used to organize the data in the database file (DBF) for fast retrieval.
What does the shapefile (SHP) contain?
The SHP contains the feature's geometry and some of the data.
What is the advantage of using shapefiles?
Shapefiles are easy to create, portable, and can be used by various GIS software.
What are some disadvantages of shapefiles?
Disadvantages include inability to store complex geographical information, character limits, lack of versioning, and a maximum size of 2GB.
What is a Feature Class in geospatial data storage?
A Feature Class is a collection of homogenous geographic feature data that share the same geometry type and attribute fields, residing in a Geodatabase.
What types of geometric shapes can a Feature Class contain?
A Feature Class can contain Point, Line, and Polygon shapes.
What is the purpose of annotation in a Feature Class?
Annotation is saved map text or strings of text associated with a point, polyline, or point feature.
What does the M value represent in a Feature Class?
The M value represents linear measurements to interpolate distances along linear features and is used in linear referencing.
What is dynamic segmentation in geospatial data?
Dynamic segmentation is the process of geolocating an event along a measurement system using the M value.
What is the significance of the multiple patch feature in a Feature Class?
A multiple patch feature represents a 3D geometry such as a building front or tree.
Can a Feature Class contain multiple parts of a polygon?
Yes, a Feature Class can contain both single and multiple parts of a polygon or polyline.
What is the role of X, Y, Z coordinates in a Feature Class?
X, Y, Z coordinates define the geometric shape of the feature in three-dimensional space.
What is the relationship between Feature Classes and feature datasets?
Feature Classes can be organized into groups called feature datasets.
What is a geodatabase?
A geodatabase is a collection of spatial and non-spatial data held in a common folder on a disk or database management system.
How does a geodatabase maintain data?
It maintains data through a series of interrelated tables that contain the information and geometries, using a unique identification (primary key) to interlink the data.
What types of data can a geodatabase house?
A geodatabase can house vector, raster, tabular data, and TIN networks.
What are the three types of geodatabases?
1. Personal Geodatabase (PGDB or MDB) 2. File Geodatabase (FGDB) 3. Enterprise Geodatabase (SDE or EGDB)
What is a Personal Geodatabase?
The simplest geodatabase type, based on a Microsoft Access database that can store up to 2GB of both spatial and non-spatial data.
What features can a Personal Geodatabase include?
Attachments, Annotation, Feature Classes and Datasets, Geometric Networks, Mosaics, Network Datasets, Parcel Fabric, Relationship Classes, Raster Catalog and Datasets, Schematic, Table (nonspatial), Terrain, Toolboxes, and Topology.
What are the limitations of a Personal Geodatabase?
Only one user can use it at a time, and it is not supported in ArcGIS Pro.
What is a File Geodatabase?
A middle-range geodatabase type that is the native version in ArcGIS, accessible only from ArcGIS software.
What is the storage capacity of a File Geodatabase?
It can store up to 1 TB but can be upgraded to 256 TB of both spatial and non-spatial data.
What features can a File Geodatabase include?
Similar to Personal Geodatabase: Annotation, Attachments, Feature Classes and Datasets, Geometric Networks, Mosaics, Network Datasets, Parcel Fabrics, Raster Catalog and Datasets, Relationship Classes, Schematic Datasets, Table, Terrains, Toolboxes.
What are the advantages of a File Geodatabase?
It does not need to be stored on a database server, can be accessed simultaneously, and supports subtypes and domains.
What is an Enterprise Geodatabase?
The most complex type of geodatabase, housed on a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) and designed for medium to large scale use.
What are some examples of RDBMS that can house an Enterprise Geodatabase?
SQL Server, PostgreSQL, Oracle, DB2, SAP.
What are the advantages of using an Enterprise Geodatabase?
Better data security, backup and recovery capabilities, multiuser/multi-editor environment, and archiving capabilities.
Who are the different user roles in an Enterprise Geodatabase?
1. Geodatabase Administrator 2. Data Creator 3. Publisher 4. Editors 5. Analysts 6. Viewer.
What is the role of a Geodatabase Administrator?
The individual who creates and owns all the database objects and maintains the enterprise geodatabase.
What does the term 'versioning' refer to in an Enterprise Geodatabase?
The use of multiple individual snapshots of a database at a given point in time to allow editing.
What is the maximum data size limit for an Enterprise Geodatabase?
There is no limit in data size.
What types of replication can a Personal Geodatabase participate in?
Check-in and checkout replication, and one-way replications.
What is a key feature of the File Geodatabase regarding user access?
It allows simultaneous access, but if being edited, each user must work on different datasets.
What is the primary key's role in a geodatabase?
It serves as a unique identification to interlink the data across interrelated tables.
What types of datasets can be included in a File Geodatabase?
Feature Classes, Datasets, Geometric Networks, Mosaics, Network Datasets, and more.
What is the purpose of the two SQL servers implemented by WVDOT?
To house both enterprise geospatial and non-geospatial data.
What are the names of the two SQL servers used by WVDOT?
DOTB6GISDB01 (Production Enterprise Geodatabase) and DOTB6GISDBST01 (Staging Enterprise Geodatabase).
What type of data does the Production Enterprise Geodatabase (DOTB6GISDB01) house?
All data currently used in mapping projects and applications, geospatial data products shared with the public, and the most current data updated semiannually.
How many enterprise geodatabases are housed in the Production Enterprise Geodatabase?
82 enterprise geodatabases, with 64 operational (online).
What are the two most commonly used enterprise geodatabases by WVDOT?
GTI_PUB_UTM and RIL_LRS_PUB.
What is the purpose of the Staging Enterprise Geodatabase (DOTB6GISDBST01)?
To house data used for developing new applications, web maps, new datasets, and testing applications.
How many enterprise geodatabases are in the Staging Enterprise Geodatabase?
59 enterprise geodatabases.
What is the main purpose of the GTI_PUB_UTM geodatabase?
To house all feature datasets and feature classes related to creating maps and mapping products in West Virginia.
What types of datasets are contained within the GTI_PUB_UTM geodatabase?
Statewide transportation and route data features, statewide boundaries, cultural, economic, environmental, and hydrological datasets.
What is the relationship between GTI_PUB_UTM and GTI_PUB_WM?
GTI_PUB_WM is a mirror of GTI_PUB_UTM, used for web mapping and application creation.
What is the main purpose of the RIL_LRS_PUB geodatabase?
To house all feature classes and corresponding attribute tables related to the WVDOT roadway network.
What key datasets are included in the GTI_PUB_UTM geodatabase for boundaries?
Counties, Incorporated_Places_20XX, and WVDOH_Districts.
What economic datasets are included in the GTI_PUB_UTM geodatabase?
Parcels_20XX and WVDOT_Parcels.
What hydrology datasets are included in the GTI_PUB_UTM geodatabase?
Major_Rivers_Other_NHD, Rivers_Streams_NHD, and Lakes_Other_Waterbodies_NHD.