Neurology Chapter 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Neuroanatomy
Structures of the nervous system and their relationship to each other
Neurophysiology
how the nervous system functions
Molecular level
Focus on subcellular structures like proteins, ions, or lipids
work on the chemistry and physics of the nervous system structure and function
neuroscientists work on the chemistry and physics of nervous system structure and function.
Protiens, ions, lipids
Cellular level
Neurons, glia, pericytes, ependymal cells
focus on how the cells of the nervous function individually or in cooperation
might be investigating how glial support cells affect synaptic signaling.
Systems Level
They are groups of neurons and glia that perform a particular function. Accomplishing this often requires signaling through chains of neurons across different areas of the nervous system
neuroscientist might study how the somatosensory, motor, or autonomic systems work.
Motor, autonomic, visual systems
Regional Level
Midbrain, cortex, cerebellum, hippocampus
regions are anatomically defined areas and divisions. Functioning associated with nervous system regions may involve signals coming into or leaving, as well as signaling within that region
neuroscientist might seek to understand how the midbrain affects autonomic function.
Cognitive level
Involves the processes mediating emotions, thinking, learning, morality and attention. These are mediated by the cerebral and limbic cortices, and are particularly well developed in humans
A neuroscientist might be interested in how we learn new skills.
Learning, memory, emotion, attention
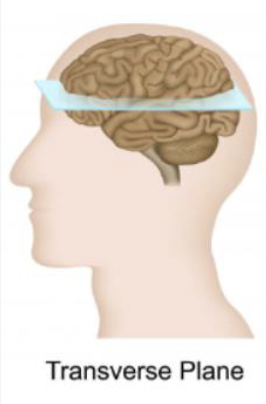
Transverse plane
a horizontal "sheet" that divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) sections
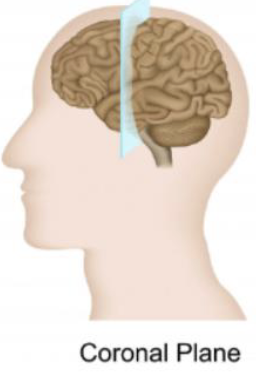
Coronal Plane
a vertical plane that divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) sections
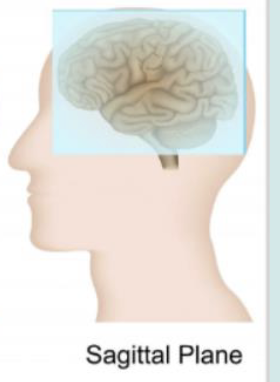
Sagittal plane
a vertical anatomical plane that divides the brain into left and right sections, allowing for a side view of its structures
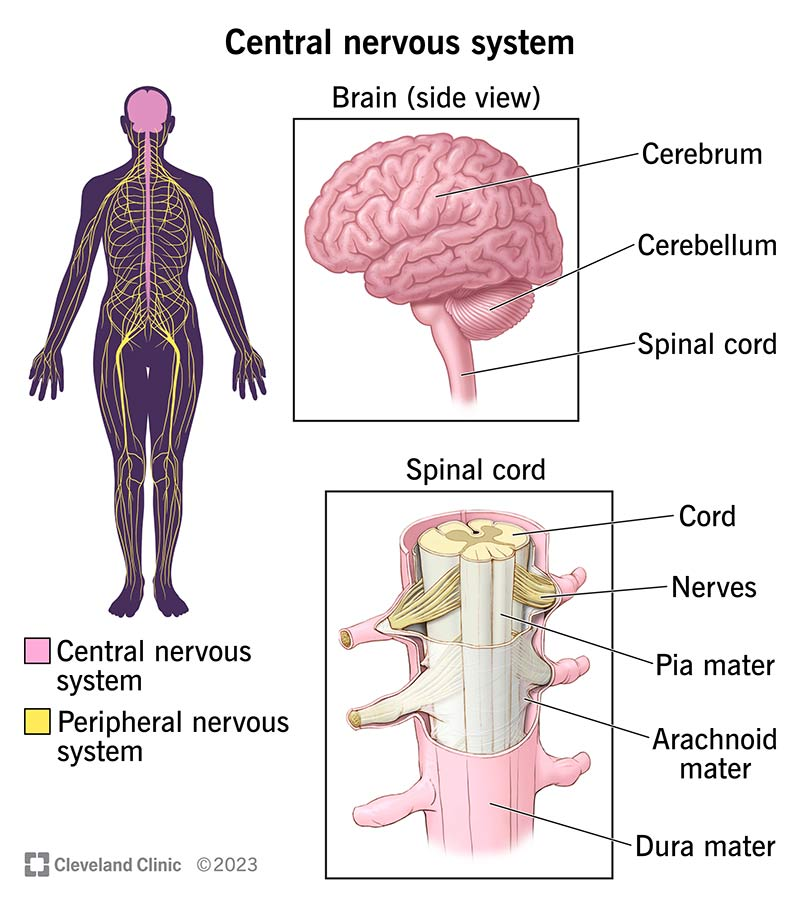
CNS
Central Nervous System
consists of the brain and spinal cord, acting as the body's control center for processing sensory information and coordinating responses. It receives input from the peripheral nervous system, then integrates this information to regulate thought, memory, movement, and involuntary functions like breathing and heartbeat.
PNS
Made up of nerves and neurons located outside in the CNS
the network of nerves and ganglia located outside the brain and spinal cord, forming a vital communication link between the central nervous system (CNS) and the rest of the body. It is responsible for transmitting sensory information to the CNS and motor commands from the CNS to the body's limbs and organs.
can be divided into somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
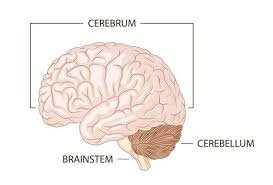
Cerebrum
the large folded hemispheres and thalamic structures buried within them that make up the bulk of the brain tissue
History
family background
symptoms
onset
progression
Genetic influence
Acute or Chronic
Observation
Mental Status
etiology and syndrome
preliminary diagnosis
clinical tests
final diagnosis
prognosis
treatment plan
Neurological Exam
Sensory systems
motor systems
autonomic system
reflexes
focal or diffuse
lesion location?
In vitro
“in glass'“ and refers to the experiments that do not require intact organisms
ex vivo
outside the body
In vivo
literally “ in life” and referring to experiments in living organisms
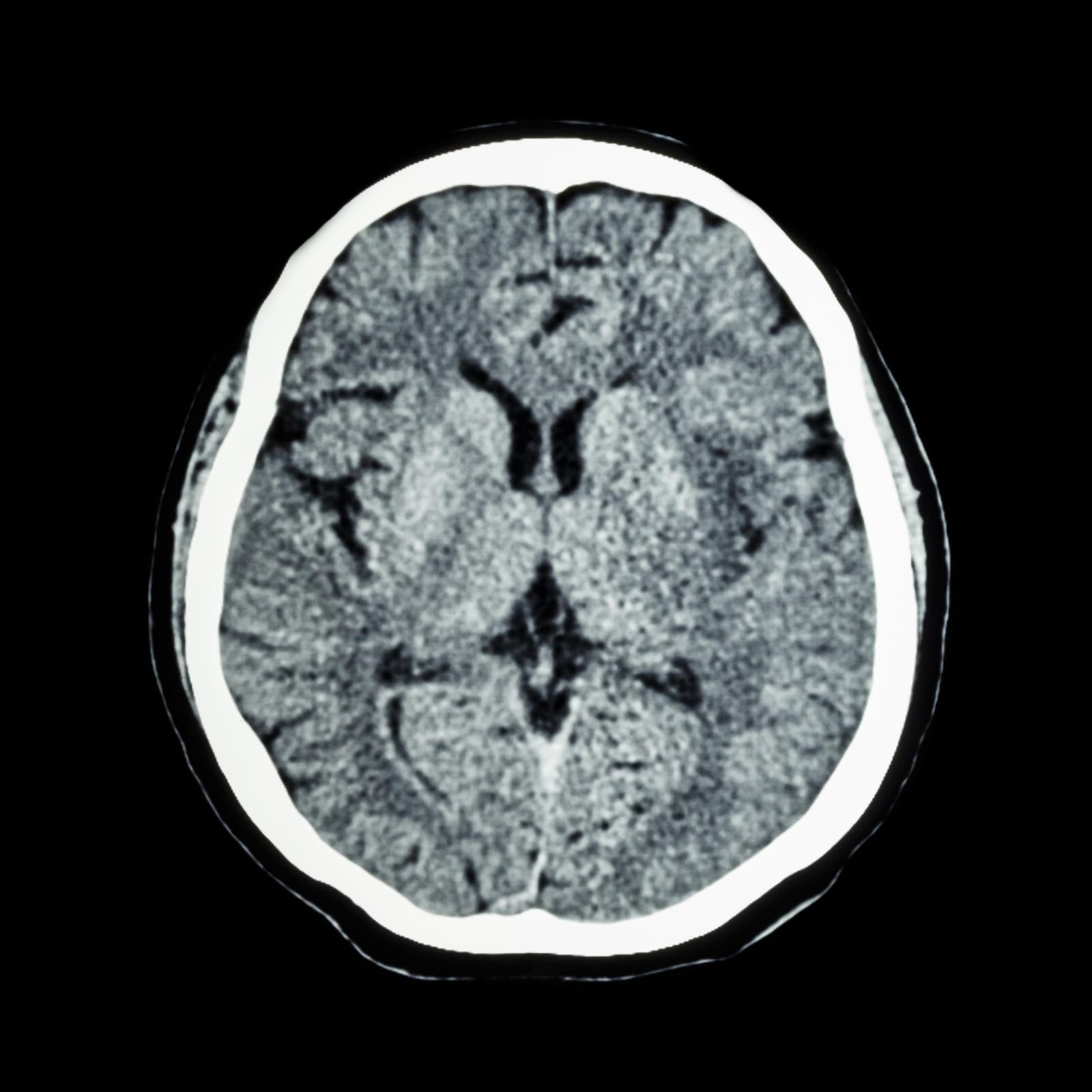
Computed Tomography
CT scans
uses X-rays to provide information about structures based on density
The denser the structure, the lighter the image
great at diagnosing large dense lesions like solid tumors
not good at identifying small lesions or lesions that do not change tissue density.
Ideal for tumors, fractures, large lesions
X- ray radiation may be a risk factor
Limited Resolution
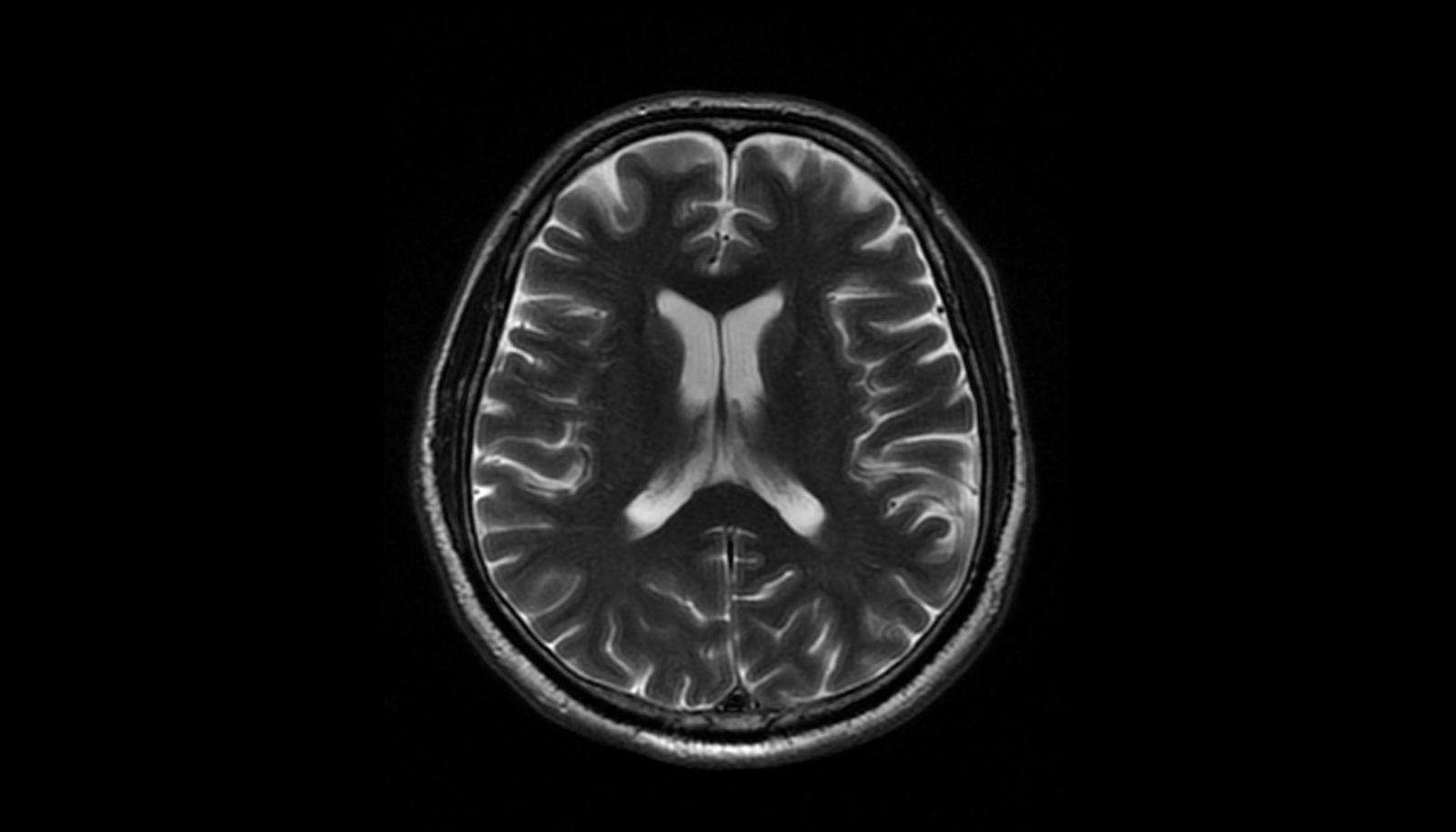
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI
Images are generated from decay of a radio frequency pulse that aligns the protons in water.
skull not well imaged in water
very fine nervous system structures can be assessed due to better resolution.
Uses radiofrequency pulses
no x-ray radiation
contrasting agent can be used for increased structural resolution
much more clear
Functional MRI
fMRI
measures change in blood flow
hemodynamic response
best spatial resolution for function
temporal resolution is low in seconds
expensive and stressful
easy to see changes that are happening
Positron Emission Tomography
PET
Measures changes in blood flow
functional imaging using radiotracers
detects gamma rays emitted from a positron during decay of radiotracer
Can be linked to molecular probes like NT receptors
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
diffusion-weighted MRI
Relies on hydrogen diffusion
great for white matter and axon damage
limited clinical use
Electroencephalogram
EEG
Optimal temporal resolution
Only true clinical way to detect neural activity