Module A1 - Cytology of neurons (Class Notes)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What is best to describe a reflex?
A reflex is a simple involuntary and instantaneous motor responses to a given stimulus
What is the local neural circuits made reflex possible?
Reflex arcs ( operate at spinal level - simple)
Do reflex depend on conscious thoughts or processing by the brain?
No
What is mono synaptic reflex?
Simple reflex
2 Neurons and 1 synapse
For patellar reflex, what is the stimulus
Tap tendon below knee
For patellar reflex - what is the response
Contraction of quadriceps m.
What are the components of a reflex
Receptor
Sensory neuron
Motor Neuron
Effector
Synapse
What do receptors do on a reflex?
-Communicate information back to CNS
-Generate action potential
What is Effector do on a reflex?
Muscle constraction
Why are reflexes being evaluated?
Provide information about the background tone of the Nervous system
General Rule:
Dysfunction in the PNS
Hyporeflexia (decrease in reflex)
General rule:
Dysfunction to CNS
Hypereflexia (increase in reflexes)
Best estimate: how many neurons are in human brain
100 billion
neurons can be classified as ____ types, they share _____features
10,000 (10 thousand)
Common
Why do neurons with similar properties can produce very different actions
Precise connection with each other ( sensory receptors and muscle)
What are the 2 distinct classes of cells do Nervous system have
-Neurons
-Glial cells
What are the components of Neurons
Excitable-communication
have resting state
What are the components for Glial Cells
support system- help with communication (can’t communicate itself
Non-excitable
Myelinated Axons
What are the morphologically of a typical neuron
Cell body (soma)
Dendrites
Axon/Myelin
Terminal Site
describe cell body
-Soma
-Contain Nucleus (metabolic center)
-10% of neuron
describe Dendrites
-comes out of cell body
-Receive information from other neuron
Describe Axon/ Myelin
Action potential travel: Axon——>Terminal site
What are the range of Axon’s Diameter
2-20ųm micrometer
How long are Axon
40in (1m)
Components of Terminal site
-Communicate with other neuron
-Chemical message
Nature neurons do not undergo______
Proitferation
Damage to neuron
- irreversible damage
-Most disease process that affect neuron associated with neuronal degradation and loss
Neuron Doctrine
Neurons are the basic butting block of nervous system
Principle of dynamic polarization
Information always flows in a specific direction
action potential: generate in cell body and travels down to the terminal site
Principle of connection specificity
Neuron make specific precise connection to certain neuron and not others
Sensory nerve and motor nerve connect to the same muscle
Nodes of Ranvier
Exposed internodal area between the nodes cover with myelin
Axon Hillock
also known as trigger zone
Start of Action potential
Start of Axon
Synapse:
Space between neuron
Use chemical to commicate
Sensory nerve
Ascending pathway
Information into CNS
Motor Nerve
Descending pathway
Information leaves CNS to PNS to activate muscles
Reflex arc
muscle stretch—>muscle contraction without using the brain
Eg. Patellar reflex
Monosynaptic reflex
Soma
body of Neuron
metabolic center
Neuron differentiation
Distinguish neuron by: shape, number of neuritis
Unipolar cells
1 neurites from cell body
Not common in mammals
Common in cold blood animals ( shellfish)
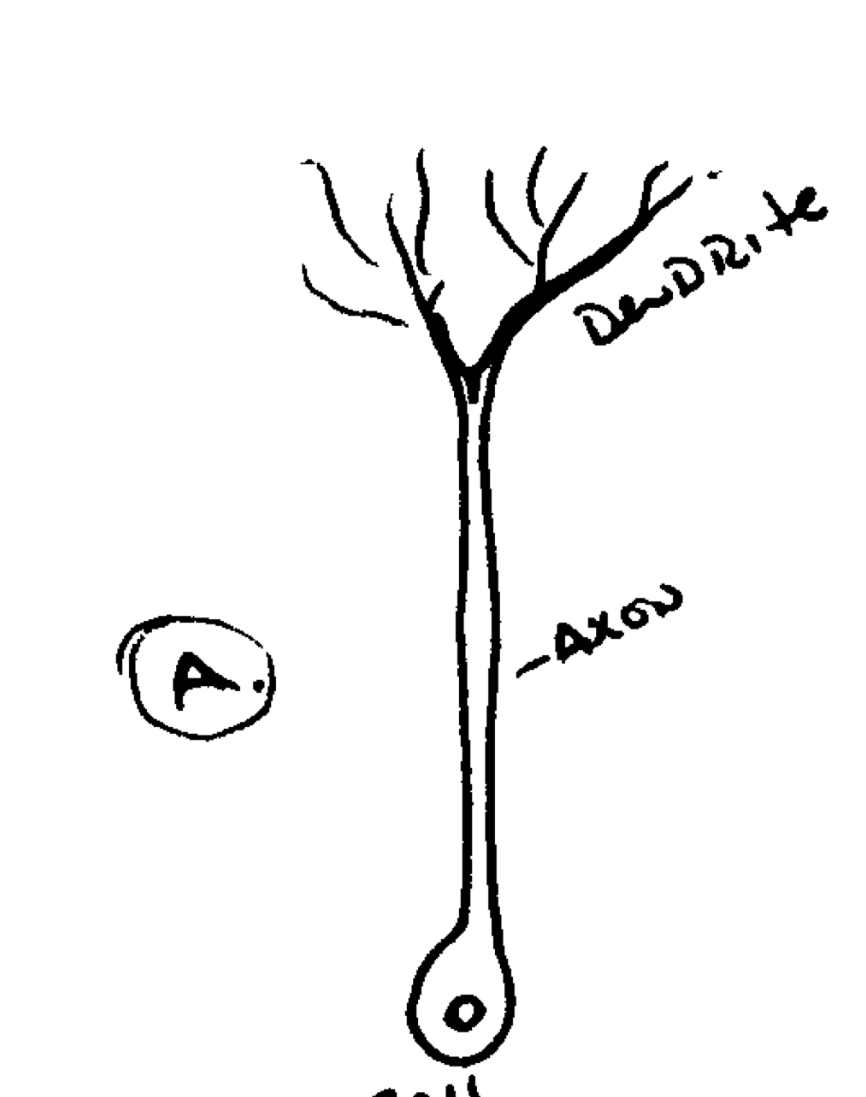
Bipolar Neurons
2 Neurites from cell body
Common in mammals (sensory)
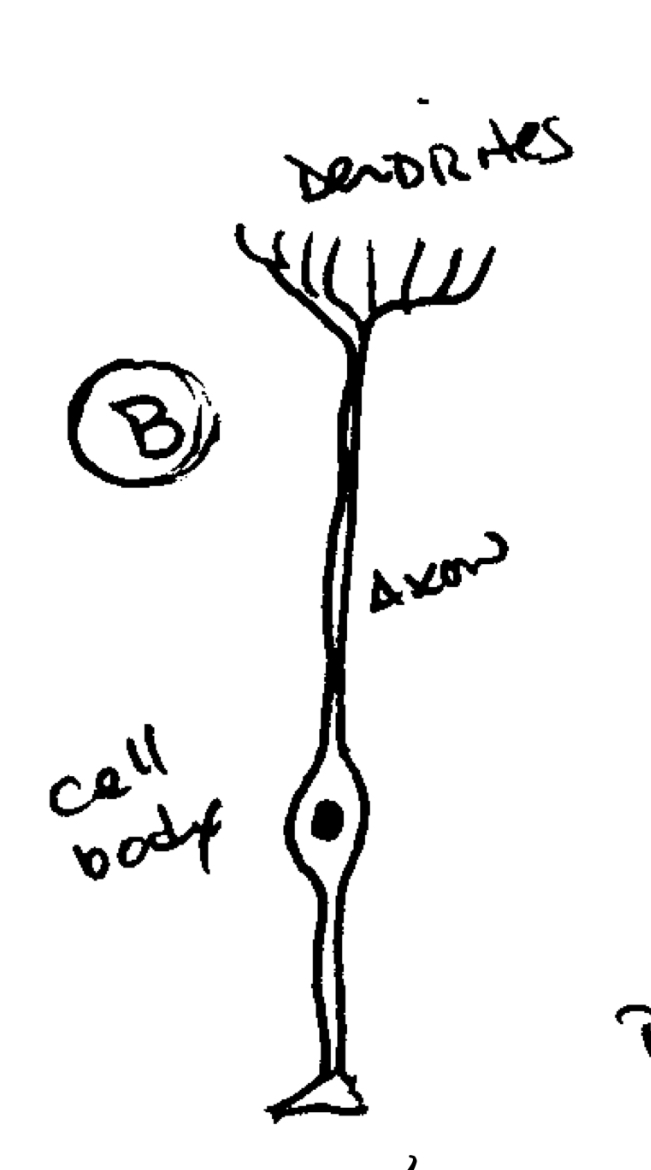
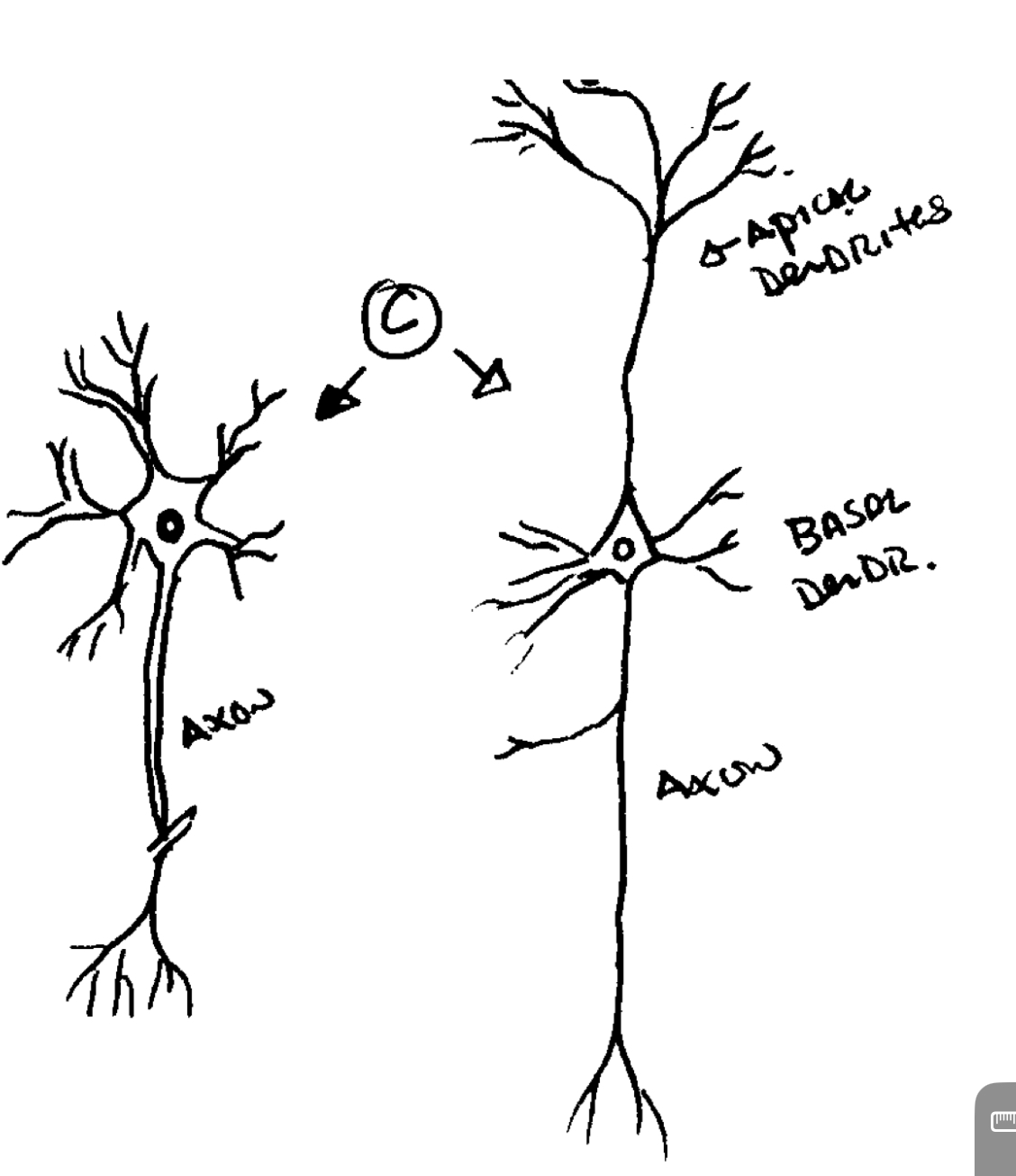
Multipolar cell
more than two neurites from cell body
MOTOR NERVE
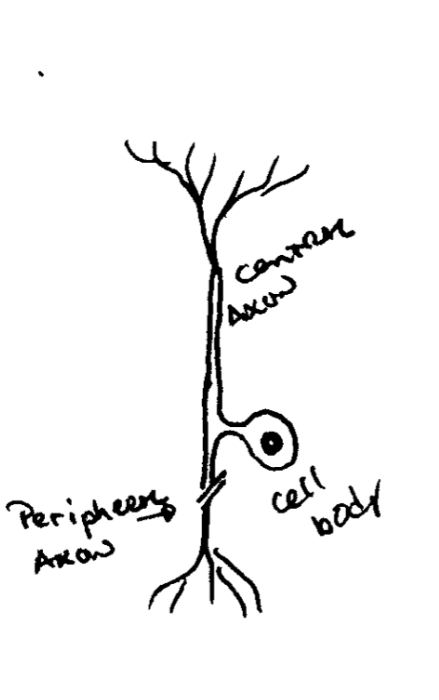
Pseudounipolar cell
one neurites comes from the cell body
Starts off as bipolar; after maturation cell body goes into dorsal root ganglion
SENSORY NERVE
Neurons can be further classified_______ into three major groups
Functional
3 groups neuron can be classified as:
Afferent
Efferent
Interneurons
Afferent neuron (Ascending)
carry info into CNS
Sensory n.
Efferent neuron ( Descending)
carry info out CNS
Motor n.
Interneurons
Most common
Carry info b/w Afferent and efferent
What are Somas and axons surrounded by?
Glial cells
Glia means ______ in Greek
Glue
How many more glial cells than neurons in CNS of vertebrates
10-50x more
Glial cells____
are non-excitable
Support cells
Can replicate
Functions of Glial cells
Supporting Elements
Form myelin
Scavengers in CNS
Buffer ions and neurotransmitters
Guide neuron during development
Functions of Glial cells: Supporting elements
Provide firmness to the brain
Functions of Glial cells: Form myelin
Oligodendrocytes: CNS
To multiple axons~15 different areas
Schwann cells: PNS
To one nodal area
Multiple sclerosis
demyelinating disorder in CNS
Effect the Oligodendrocytes
Functions of Glial cells: Scavengers in CNS
Clean up and repair injury
-activate during an injury
Functions of Glial cells: Buffer ions and Neurotransmitters
When large # of neuron activity; stabilize it
Functions of Glial cells: Guide neurons during development
Guide neuron to their proper location
Functions of Glial cells: form Blood brain barrier/CSF
Prevent chemicals into the brain (Ependymal cells)
Functions of Glial cells: Nutritive Function
Depending on their _____, Glial cell are divide into ___ major classes
Size
2
2 classes of Glial cells are:
Microglia
Macroglia
Function: Microglia
Immune system for nervous system
Function: macroglia
Oligodendrocytes
Schwann cells
Astrocytes
Function: Astrocyte
most abundant
Do not produce myelin
Perform all the rest functions
Brain cancer (Gliomas)
most are associated with glial cells
B/c they can replicate
How many ways which constituents move within the axon?
3 ways
What are the 3 ways constituents move within the axon?
Fast Anterograde
Slow Anterograde
Fast Retrograde
What is the lifespan of Axonal transport
70-100years
Function of fast Axonal transport
Energy dependent process
Uses micro tubules for transport
Soma to terminal site
What protein does fast anterograde uses
Kinesin
What protein does fast retrograde use
Dynein
Rate for Fast anterograde:
400-1000 mm/day
Rate for slow anterograde
3mm/day
Rate for fast retrograde is
150-400mm/day
Function of slow anterograde
using fluid; not microtubules
Soma to terminal site
Function of fast retrograde
Energy dependent
Active process by Microtubules
Neurotropic Viruses travels through axon
Herpes simplex (cold sores)
Polio
Rabies
Tentanus