Maths - Mechanics Y2
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What do moments measure?
The turning effect of a force
Formula to calculate the moment of a force, F, about a point, P?
F x d (force x perpendicular distance)
How do you find velocity from the speed and the direction vector?
Find magnitude of direction vector
Velocity = speed / |direction vector|
Coplanar forces
Forces that act in the same plane
Resultant moment
The sum of the moments acting on a body
What does it mean if a rigid body is in equilibrium?
The resultant force in any direction is 0 N and the resultant moment about any point is 0 Nm
Units for moment
Newton metres (Nm)
What does it mean if the resultant moment is 0 Nm?
The sum of clockwise moments = sum of anticlockwise moments
What does it mean if a rod is uniform?
The centre of mass is always at the midpoint and the mass is evenly distributed along the rod
What does it mean if a rod is non-uniform?
The centre of mass is not at the midpoint
What does it mean if a rod is tilting about a pivot?
The reaction at any other support / the tension in any other wire or string is 0.
What do you need to do to solve a question about moments for a rod in equilibrium? (4)
To diagram, draw distances from centre of mass + draw arrow for each force
Draw normal reaction force, R at the pivots (R1, R2)
Resolve at one of the pivots to eliminate one of the Rs
Total normal reaction force = total forces acting in opposite direction as its in equilibrium
For a uniform rod at equilibrium, what do the normal reaction forces equal?
The forces acting on the rod
What do you need to do to solve a question about moments for a hanging rod? (4)
1. To diagram, draw distances from centre of mass + draw arrow for each force
2. Draw tension, T at the pivots (T1, T2 - tension instead of normal reaction force)
3. Resolve at one of the pivots to eliminate one of the Ts
4. Total tension = total tension as its in equilibrium
Friction
A force that opposes motion between two rough surfaces. It occurs when the two surfaces are moving relative to each other, or when there is a tendency for them to move relative to each other.
What does it mean if there is a tendency for two surfaces to move relative to each other?
There is a force being applied to the object in the direction, but the object doesn't move as the force of friction is equal and opposite to the force being applied.
When will a stationary object move?
When the magnitude of the applied force reaches a maximum / limiting value
Does the force of friction change when the magnitude of the applied force increases above the limiting value?
No - it stays constant at its maximum value
What does the limiting value of the friction depend on? (2)
The normal reaction R between the two surfaces in contact
The roughness of the two surfaces in contact
Symbol for coefficient of friction
μ
How do you measure the roughness of the two surfaces in contact?
The coefficient of friction
What happens to the value of μ as the surfaces become rougher?
It becomes larger
What is the value of μ for smooth surfaces?
0 - there is no friction
Formula for the maximum / limiting value of friction between two rough surfaces
F (max) = the coefficient of friction x the normal reaction between the surfaces
F (max) = μR
How do you model the motion of horizontal projection? (3)
- The projectile has constant velocity, so a = 0
- It is acted on by a single force (gravity) which acts vertically and downwards - it is constant, so vertical acceleration is constant and due to gravity (a = g)
- The effects of air resistance and any rotational movement on the particle can be ignored
In projectiles, how do you represent the angle of projection?
Angle α
When a particle is projected with initial velocity U, at an angle α above the horizontal, what are its horizontal and vertical components?
Horizontal: U cosα
Vertical: U sinα
What is the velocity of the vertical component of a projectile at its point of greatest height?
0
When has a projectile reached its point of greatest height?
When the vertical component of its velocity is equal to 0
3 features of a rigid body in static equilibrium
The body is stationary
The resultant force in any direction is 0
The resultant moment is 0
When is a body or particle in static equilibrium?
If the particle/body is at rest and the resultant force acting on it is 0
Vectors equation for displacement
r = r0 + vt
r = position vector, r0 = initial position vector, v = velocity (must be constant velocity)
2 SUVAT formulae you may use with vectors
v = u + at
r = ut + ½ at2
If a brick at rest on a rough slope were to be replaced by a brick with a much higher mass but the same coefficient of friction, will the brick remain at rest on the plane? Why?
Yes - the friction will increase by the same proportion as the object’s weight
Due north?
On the same vertical line - i vectors equal
Due east?
On the same horizontal line - j vectors equal
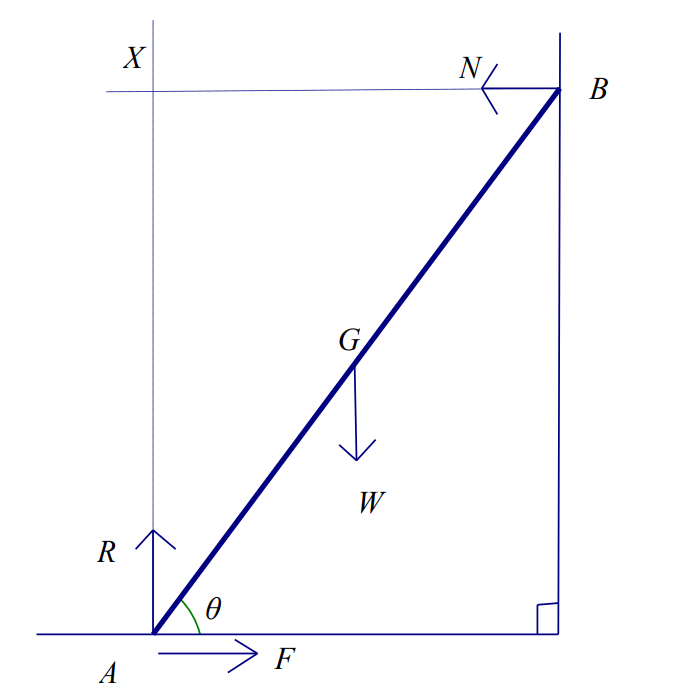
In the below diagram, if the ladder were not modelled as uniform, what would happen to the calculated value of µ? (2)
The position of the centre of mass affects the value of N, so would affect the value of µ.
If closer to A, µ smaller. If further from A, µ larger.