Economic methodology and the economic problem
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What is economics?
The study of how people allocate scarce resources for production, distribution and consumption
What type of science is economics?
a social science - studies societies and human interactions
What is a positive statement?
A statement of fact that can be scientifically tested to see if it is correct or incorrect - objective
What is a normative statement?
A statement that includes a value judgement and can’t be refuted just by looking at the evidence - subjective
What is a need?
Something that is necessary for human survival e.g food
What is a want?
Something that is desirable but not necessary for survival e.g a phone
What is the central purpose of economics?
To produce goods and services to satisfy people’s needs and wants
Define economic welfare
The economic well-being of an individual, a group within society, or an economy
Define production
A process, or set of processes, that converts inputs into output of goods
What is a capital good?
A good which is used in the production of other goods or services
What is another term for a capital good?
Producer good
What is a consumer good?
A good which is consumed by individuals or households to satisfy their need or wants
Define factors of production
inputs into the production process
What are the four factors of production?
Capital
Enterprise
Labour
Land
Capital
goods that can be used in the production process e.g equipment, buildings, money
What is the reward/incentive for capital?
Interest from the investment
Labour
human capital, which is the workforce of the economy e.g people, time
What is the reward/incentive for labour?
wages
Land
natural resources e.g oil, coal, wheat water
What is the reward/incentive for land?
rent
Enterprise
Managerial ability. The entrepreneur is someone who takes risks, innovates, and uses the factors of production e.g ‘spark’, risk-taker, decision-maker
What is the reward/incentive for enterprise?
Profit- an incentive to take risks
What is the law of diminishing marginal returns?
a concept where at least one factor of production is fixed, showing that as an additional input is added, the additional product gained falls
What is a renewable resource?
A resource that can be replenished as it is used e.g solar
What is a non-renewable resource?
A resource that is scarce and runs out as it is used e.g oil
What is another word for a non-renewable resource?
Finite resource
What are free goods?
Goods that do not use up any factor inputs when supplied e.g fresh air. They have no opportunity costs
What is the fundamental economic problem?
How best to make decisions about the allocation of scarce resources among competing uses so as to improve and maximise human happiness and welfare
Define scarcity
When the demand for a good or service is greater than the availability of the good or service
What is an economic agent?
An entity that engages in economic activity e.g producers, consumers and governments
What is rationing?
A way of allocating scarce goods and services when market demand out-weighs the available supply e.g by age
Define opportunity cost
The cost of giving up the next best alternative
What are the key economic decisions?
What to produce? How to produce it? To whom the goods should be allocated to?
Why is the environment a scarce resource?
As there are limited natural resources on earth
What is economic methodology?
It involves the application of tested economic theories to explain real-world economic behaviour
What is a free market economy? Add an example
An economy without government intervention or regulation e.g US
What are features of a free market economy?
The market allocates resources
They are driven by the profit motive
The private sector dominates
There is limited role for state (government)
What is a command economy? Add an example
A system in which a central government makes all economic decisions e.g China
What are features of a command economy?
Most resources are state owned
Planning allocates resources
Little role for market prices
What is a mixed economy? Add an example
An economy that accepts both private businesses and nationalised government services e.g UK
What are features of a mixed economy?
Mix of state and private ownership
Government intervention in markets
What is a production possibility frontier (PPF)?
a curve that shows various combinations of two goods or services attainable when all resources are fully and efficiently employed
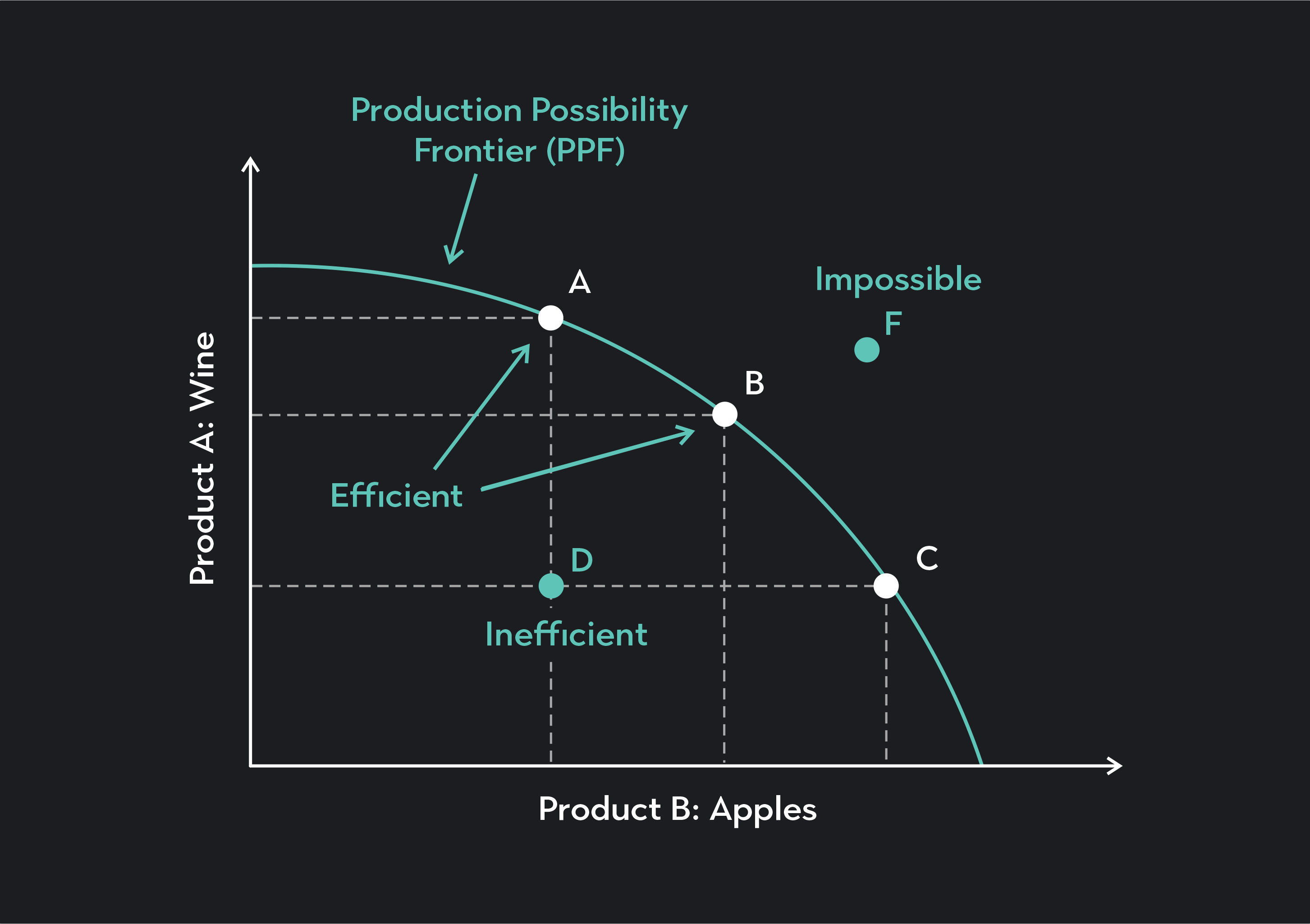
Define productively efficient
When a firm is using all its resources in the most efficient way possible producing the maximum output with the minimum input
What part of a PPF is productively efficient?
All the points on the curve
What part of a PPF is productively inefficient?
Points inside the curve, not all resources are being fully utilised
What does it mean when a point is outside the PPF?
The combination is not yet attainable with the current resources
What is allocative efficiency?
When the particular mix of goods a society produces represents the combination that society most desires
What can cause a PPF to shift outwards?
Change in the quantity or quality of factors of production
Change in technology
Trade between countries
What can cause a PPF to shift inwards?
Resource depreciation
Recourse depletion
What is resource depreciation?
machinery falling apart due to not being maintained
What is resource depletion?
resources destroyed due to things like war and natural disasters
What does a straight line PPF mean?
It means there is a constant opportunity cost
What does a curved PPF mean?
It means there is an increasing opportunity cost
Define economic growth
the increase in the potential level of real output the economy can produce over a period of time
Define unemployment
when not all of those who are able and willing to work are employed
Define full employment
when all who are able and able to work are employed