Visual Pathways
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
name the pathway from the eye to the brain
Retina
Optic Nerve
Optic Chiasm
Optic Tract Lateral
Geniculate Body
Optic Radiation
Visual Cortex
what are receptive fields
• Circular receptive field centre
• Peripheral area
what are ON-neurons
neurons that are excited by light hitting the centre and inhibited by light hitting the peripheral area
what are OFFneurons
Neurons that have the opposite reaction to the light are known
Rods contains?
rhodopsin (Opsin and retinal (Vit A aldehyde))
what sort of vision does rods have
scotopic; more sensitive
Cones have what type of vision?
photopic
What do retinal ganglion cells express?
photopigment melanopsin
what does retinal ganglion cells convey?
general level of illumination
what are the 3 neurons in the retina called?
photoreceptor, bipolar cell, and ganglion cell
what do Bodies of bipolar cells form?
inner nuclear layer
what are dendrites in contact with in the bipolar cell layer
base of rods and cones
when are on cells activated
light hits the photoreceptor and are inhibited in the dark
when are off cells activated
dark and inhibited in light
when are bipolar cells hyperpolarized in rods
when the light hits the rods
for the 3rd neuron, what are dendrites of ganglion cells in contact with?
with ON or OFF synaptic centers via axons of bipolar cells.
what do m and p cells have to do with 3rd neuron
types of neurons in the visual pathway that relay information to the third-order neurons in the brain's visual cortex
M-cells full name?
magnocellular
P-cells full name?
parvocellular
what do M cells process
process visual information related to motion and flicker,
what do P (parvocellular) cells process
details like color and high-resolution shape
describe the characteristics of P-cells
smaller cell bodies, a less extensive dendritic tree, and a thinner axon than M-cells
name a major difference between P and M cells
P-cells respond preferentially to light with a particular wavelength. P-cells are color-specific, whereas M-cells do not have such specificity
name 2 interneurons of retina
amacrine cells and horizontal cells
what is Amacrine cells responsible
interaction between ON and OFF synaptic centres
what do amacrine cells increase
contrast and the detection of motion
what do horizontal cell regulate
transmission from the photoreceptors to the bipolar cells
what is horizontal cells responsibility
typical receptive fields of the bipolar cells and ganglion cells with central excitation and lateral inhibition
how do ganglion cells exit the eye
extending their axons through the optic disk to form the optic nerve
what is the horizontal diameter of the disc
1.7 mm
what is the vertical diameter
1.9 mm
what is a physiologic blind spot
disc contains no photoreceptor cells, light incident on the disc does not elicit a response
optic nerve length
5-6 cm
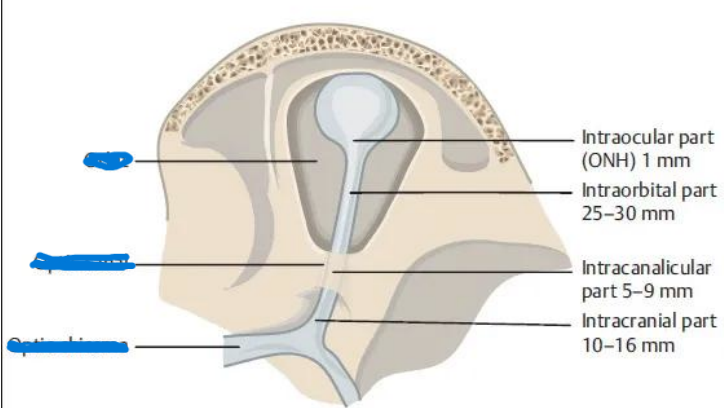
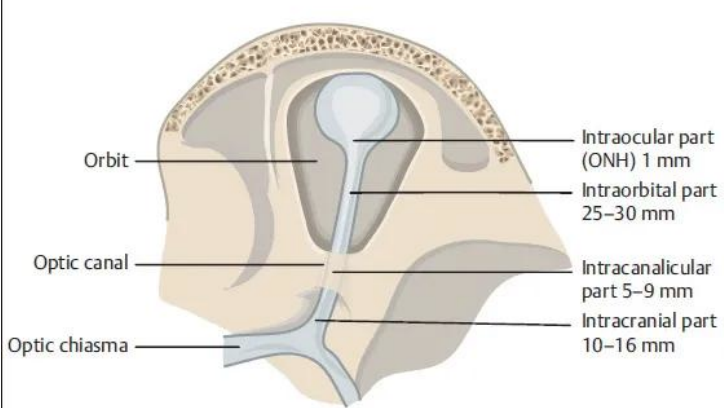
Optic Nerve Intraocular
0.7 – 1mm
Optic Nerve Intraorbital
30 mm
Optic Nerve Intracanalicular
6 – 10 mm
Optic Nerve Intracranial
10 – 16 mm
what is the Optic Chiasm surrounded by
Meningeal sheaths and cerebrospinal fluid
Optic Chiasm lies within where?
circle of Willis, a circle of blood vessels that is a common location for aneurysms
what is the Optic tract
Cylindric, slightly flattened band of fibers approximately 3.5 mm high and 5.1 mm long
where does the optic tract run from?
the posterolateral corner of the optic chiasm to the LGN
where does optic tract terminate at
LGN
where is visual information processed
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus, then is relayed to higher cortical centres
what is terminated in Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
etinal axons
name the 3 layers that LGN is structured
Magnocellular layers
parvocellular layers
koniocellular layers
what cells does magnocellular layer contain?
large
what cells does parvocellular layer contain?
medium
what cells does koniocellular layer contain?
small
where does Optic Radiation extend from
from LGN to Striate cortex
what is Optic Radiation grouped into
Temporal radiations (form the Meyer's loop)
Parietal radiations
what do Temporal radiations represent
contralateral superior field
what is contralateral superior field
upper-half of the visual field on the opposite side of the brain from a lesion
what do parietal radiations represent
contralateral inferior field
what are parietal radiations
deficit in the lower-left or lower-right quarter of one's vision, caused by damage to the opposite side of the brain
what is Visual cortex also known as
Striate cortex (V1)
how many systems are responsible for visual cortex
3
how is the first system formed
by three cortical columns
for the first system in visual cortex, what are the three cortical columns specific for?
specific for perception from left and right eye for binocular vision and depth perception
what is the second system in visual cortex composed for?
cells that receive information from identical retinal positions and have the same axes of orientation;
what does the second system in visual cortex provide?
perception of movement
how is the 3rd visual cortex organised into
into columns that form the irregular spots on the transverse sections called “blobs”.
what are the “blobs” in the 3rd visual cortex responsible for
perception of color
what are the areas between the “blobs” in the 3rd visual cortex called
“interblobs” which are localized neurons
specific for the perception of shape
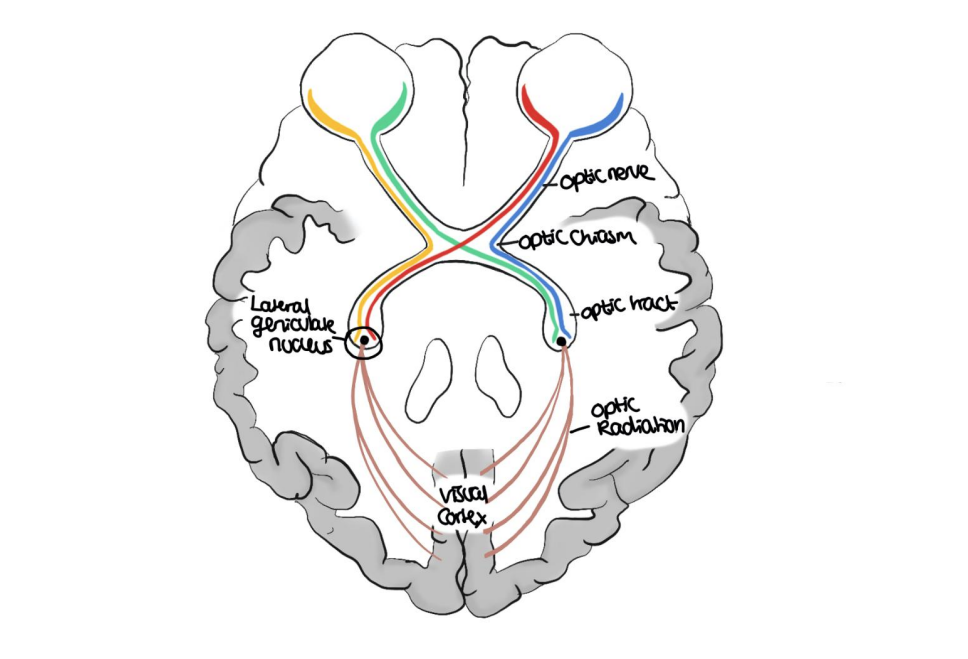

NAME
left abopia
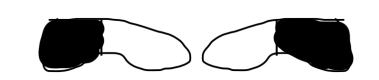
NAME
Bitemporal Hemianopia

NAME
Right Homonymous Hemianopia

NAME
Right Homonymous Superior Quadrantopia
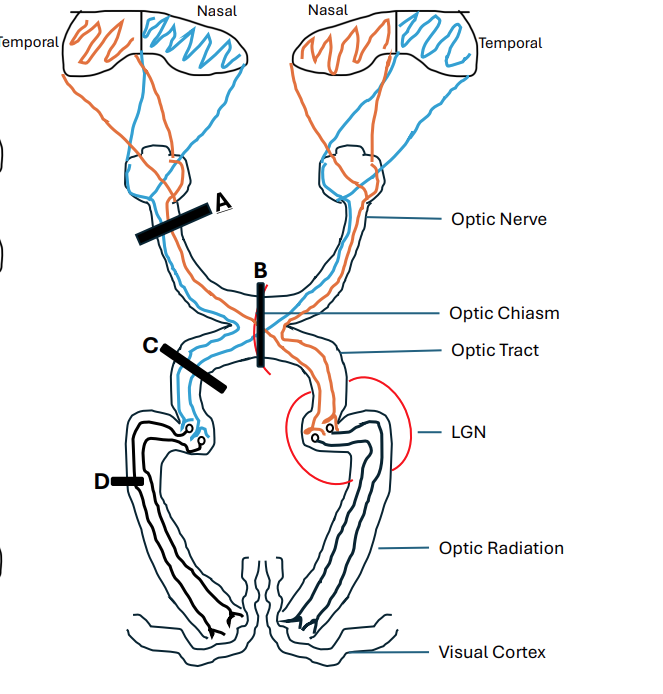
name A
Left Anopia
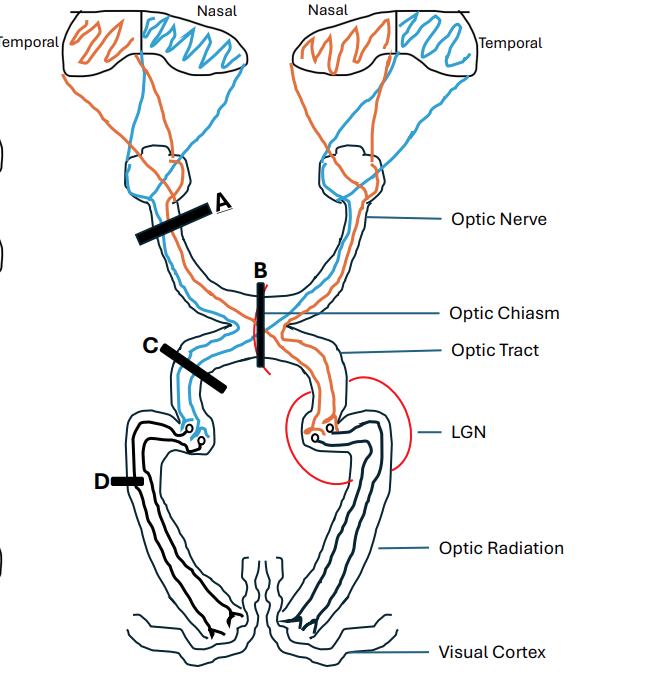
name B
Bitemporal Hemianopia
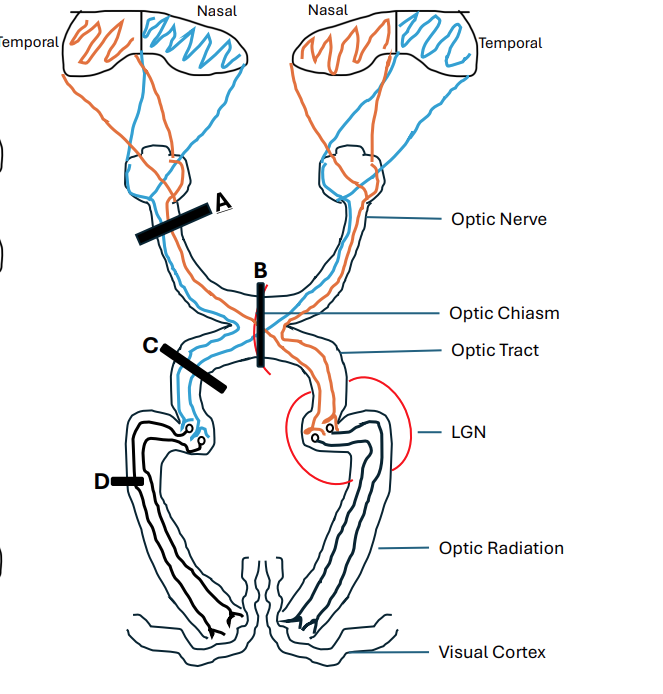
name C
Right Homonymous Hemianopia
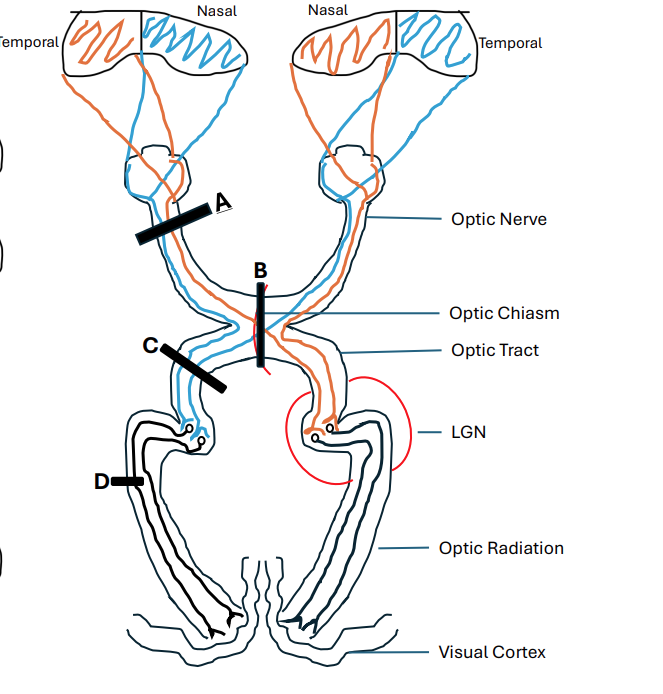
name D
Right Homonymous Superior Quadrantopia