Physio Lect 20 - Systemic Circulation
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
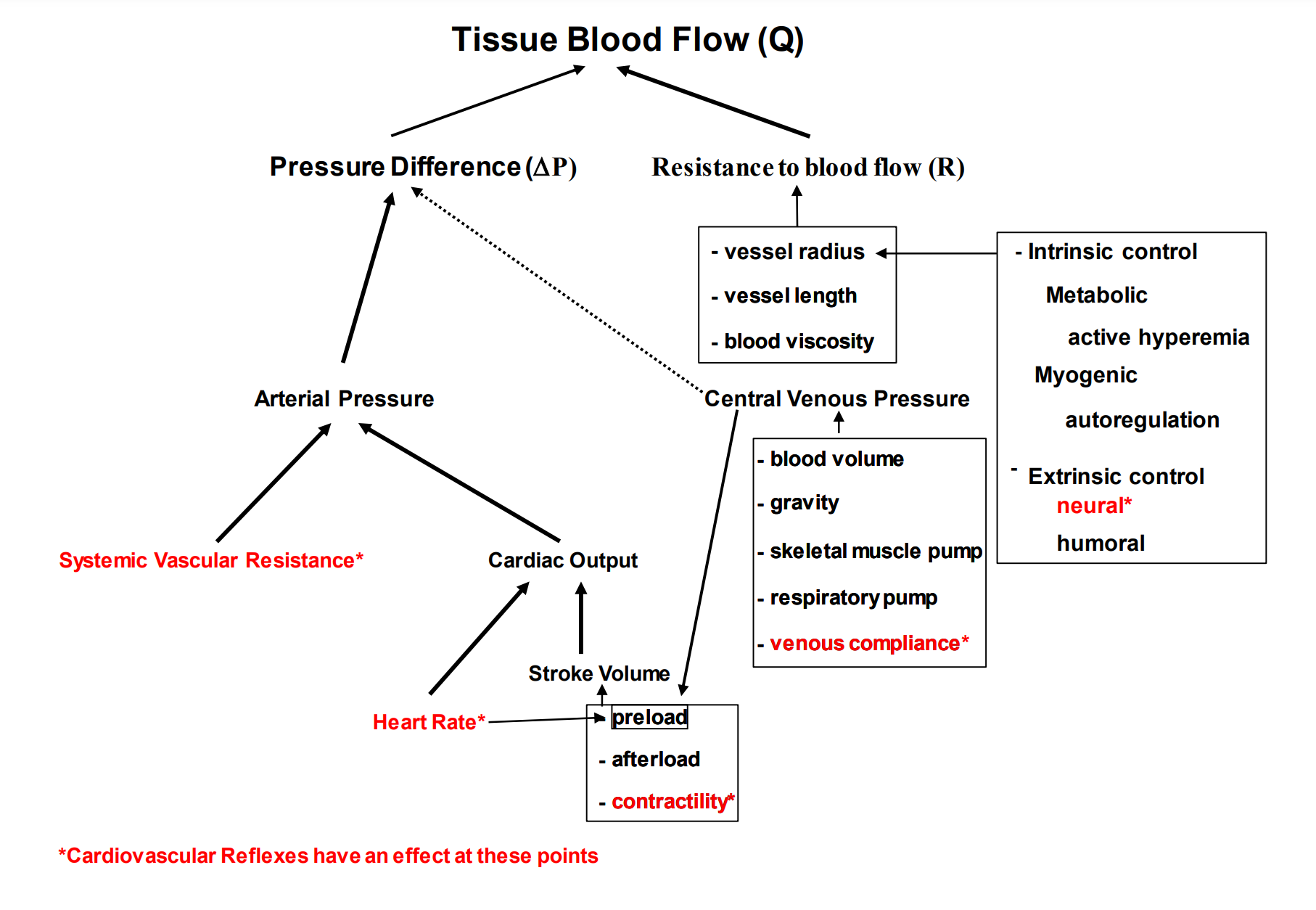
Take note of where we are in this chart
Know that cardiovascular reflexes have an effect at all of the areas highlighted in red
How do we measure arterial pressure?
Use of a pressure cuff - proportional to artery pressure
The cuff causes turbulent flow which we can hear using a stethoscope
What is perfusion pressure?
Pressure for flow through a tissue
How do we find pulse pressure?
Arterial systolic pressure - arterial diastolic pressure
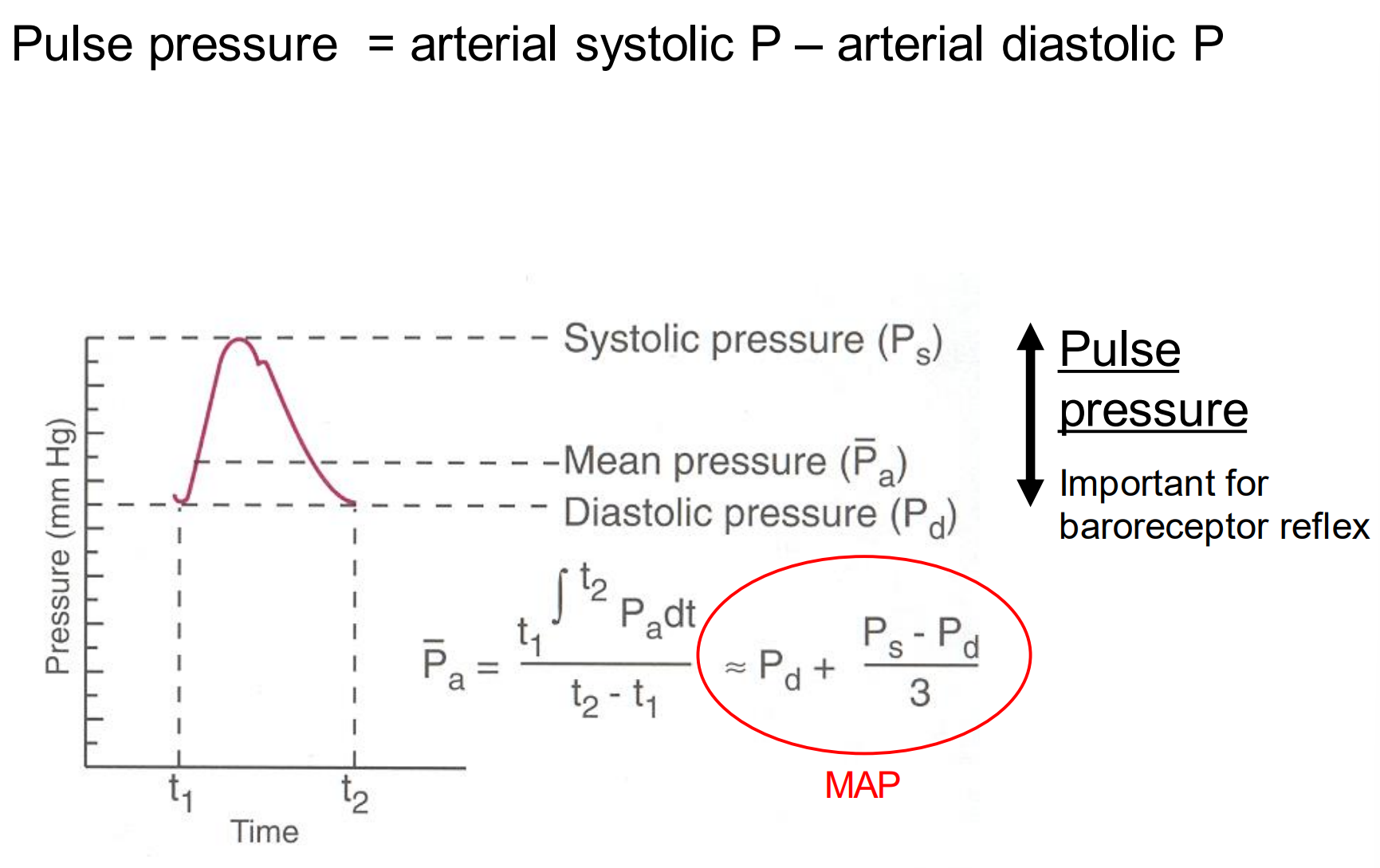
What are the determinants of pulse pressure?
Stroke volume
Compliance of arteries

What happens to stroke volume if we decrease heartrate and keep cardiac output constant?
increase in stroke volume
If cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance are constant and heartrate is decreased, what happens to mean arterial pressure?
no change in MAP
If we increase stroke volume, then CO is going to ________ which will cause a(n) ________ in MAP. There will be (no/a) change in SVR and HR.
increase
increase
no
If we increase cardiac output, heart rate, and stroke volume what will the impact be on MAP and SVR?
MAP will remain unchanged. SVR will decrease as CO increases.
SV determines what?
pulse pressure
When can we see an increase in pulse pressure? Why?
with age - decrease in arterial compliance and no change in stroke volume
Does mean arterial pressure increase with age?
yes - increases with age due to an increase in systemic vascular resistance
T/F: A normal blood volume is necessary for the normal function of the cardiovascular system
T
T/F: Control of blood volume provides long term control of the arterial pressure.
T
T/F: Pressure is always measured at the level of the heart
T
T/F: The weight of the blood adds to arterial and venous pressure as the distance below heart level increases
T - when you’re standing gravity is working to pull the blood towards your feet
What does recumbent mean?
Laying down
T/F: When you’re laying down the pressure in your head vs your heart vs your feet is about the same.
T - when they’re all at the same level gravity is working on them about the same way
When standing the pressure in your heart vs your head vs your feet ______
changes dramatically
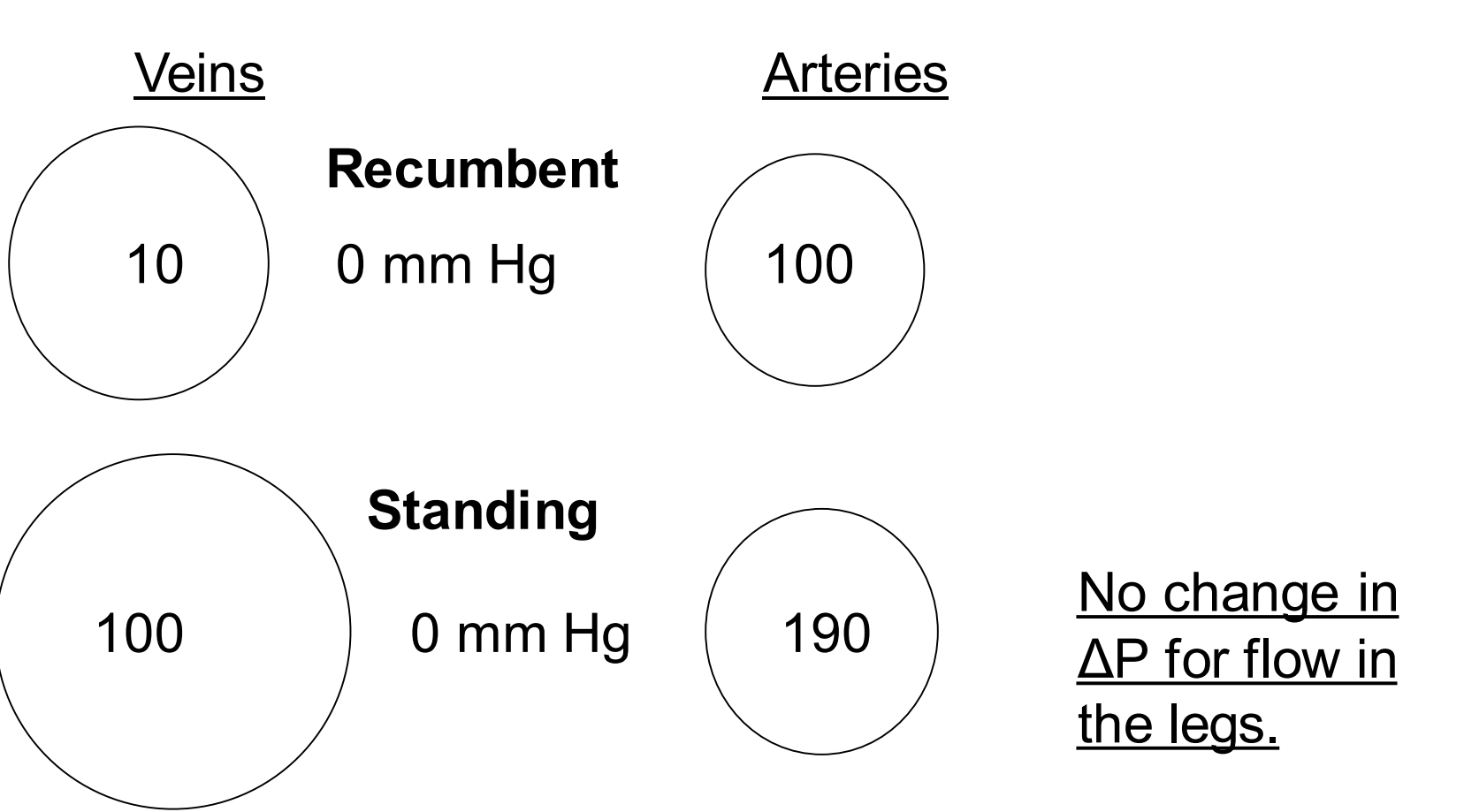
What pressures can you expect in your head, heart, and feet when standing?
60 mmHg
100 mmHg
190 mmHg
What pressures can you expect in your head, heart and feet when you are laying down?
97 mmHg
100 mmHg
95 mmHg
What is something unique to the veins when we compare them to the arteries regarding the column of blood?
Veins have valves running through them to break up the column of blood, sort of into segments
T/F: The increase in pressure due to standing causes a much greater distension of the veins than the arteries. Increase in blood volume in the veins is known as venous pooling.
T - take note of how in the image the cross-sectional area of the veins becomes much larger
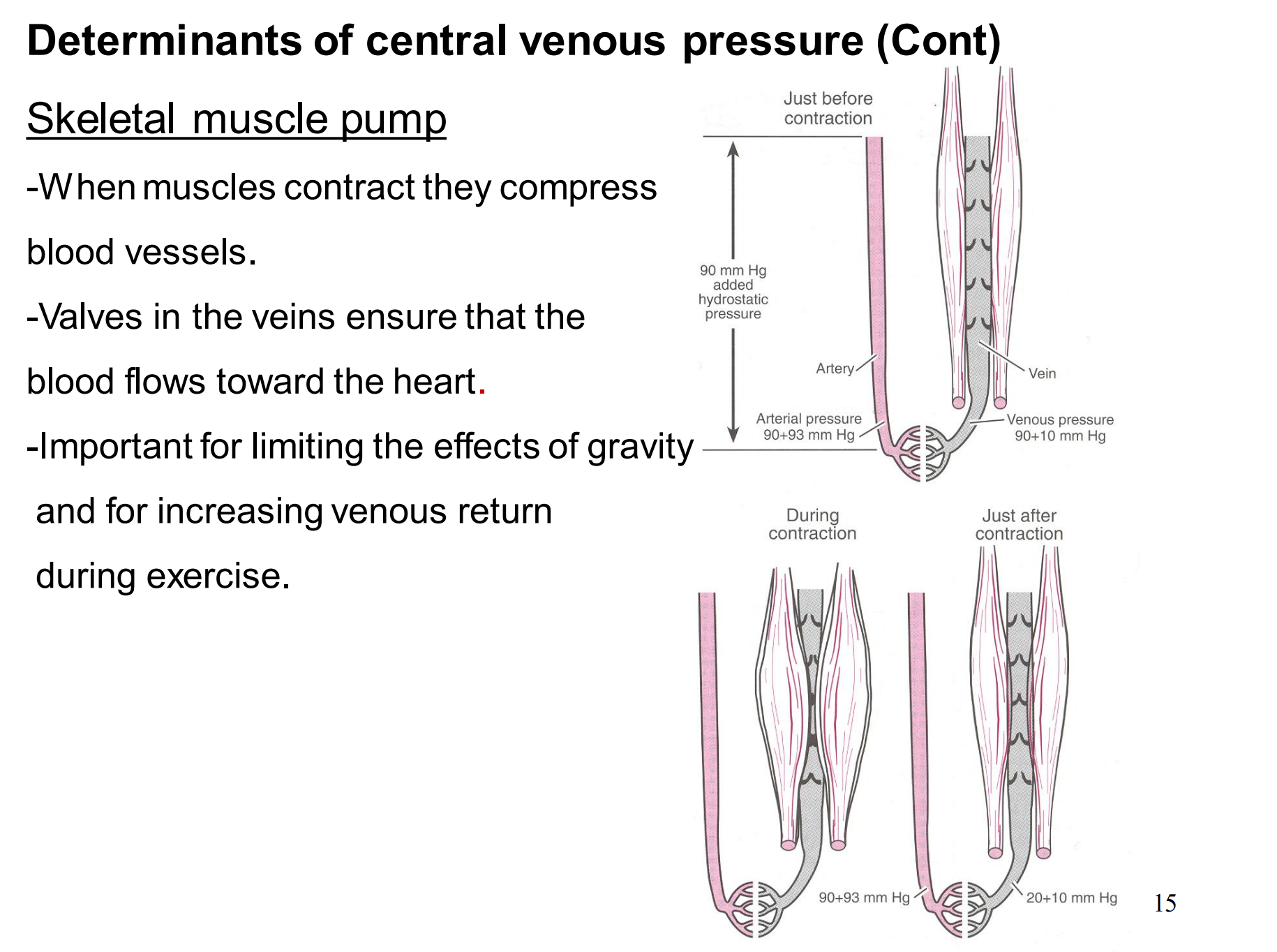
This is fairly easy to understand, just make sure that you get that when the muscles contract they force the blood back towards the heart
great work!
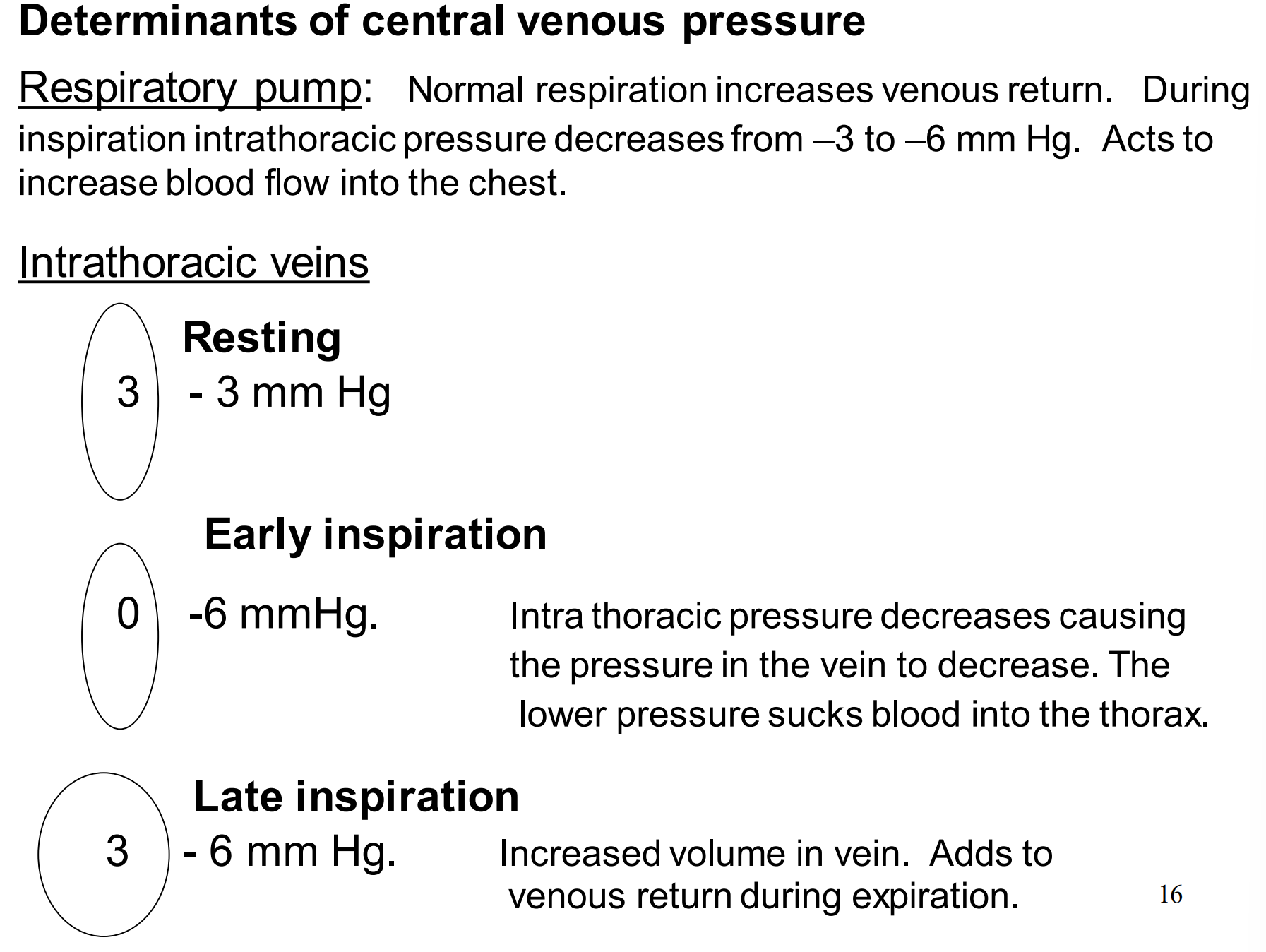
What are the 5 determinants of central venous pressure?
blood volume
gravity
skeletal muscle pump
respiratory pump
intrathoracic veins
Describe how the respiratory pump and intrathoracic veins function
nice
Regarding vascular tone for the control of blood flow, what can we say about arterioles?
They are always in a state of partial constriction (constant activity)
What are the two influences on vascular tone?
constrictor influences
dilator influences
What are the two types of vascular tone that we focus on?
basal tone
neural (sympathetic) tone
What is basal tone?
the vascular tone due to intrinsic mechanisms
What is neural tone?
vascular tone due to sympathetic activity
Basal tone is both ______ and _______.
metabolic
myogenic
What impact does increasing sympathetic activity have on resistance?
increases
What impact does decreasing sympathetic activity have on resistance?
decreases
T/F: Basal tone and neural tone are always functioning.
T - they’re independent of each other but they’re impacting the same place (vascular smooth muscle in the blood vessels)
T/F: Blocking neural tone blocks basal tone
F - basal and neural tone are not dependent on each other
T/F: Neural tone has a parasympathetic effect
F - in terms of regulating the arterioles it is always sympathetic tone, not parasympathetic
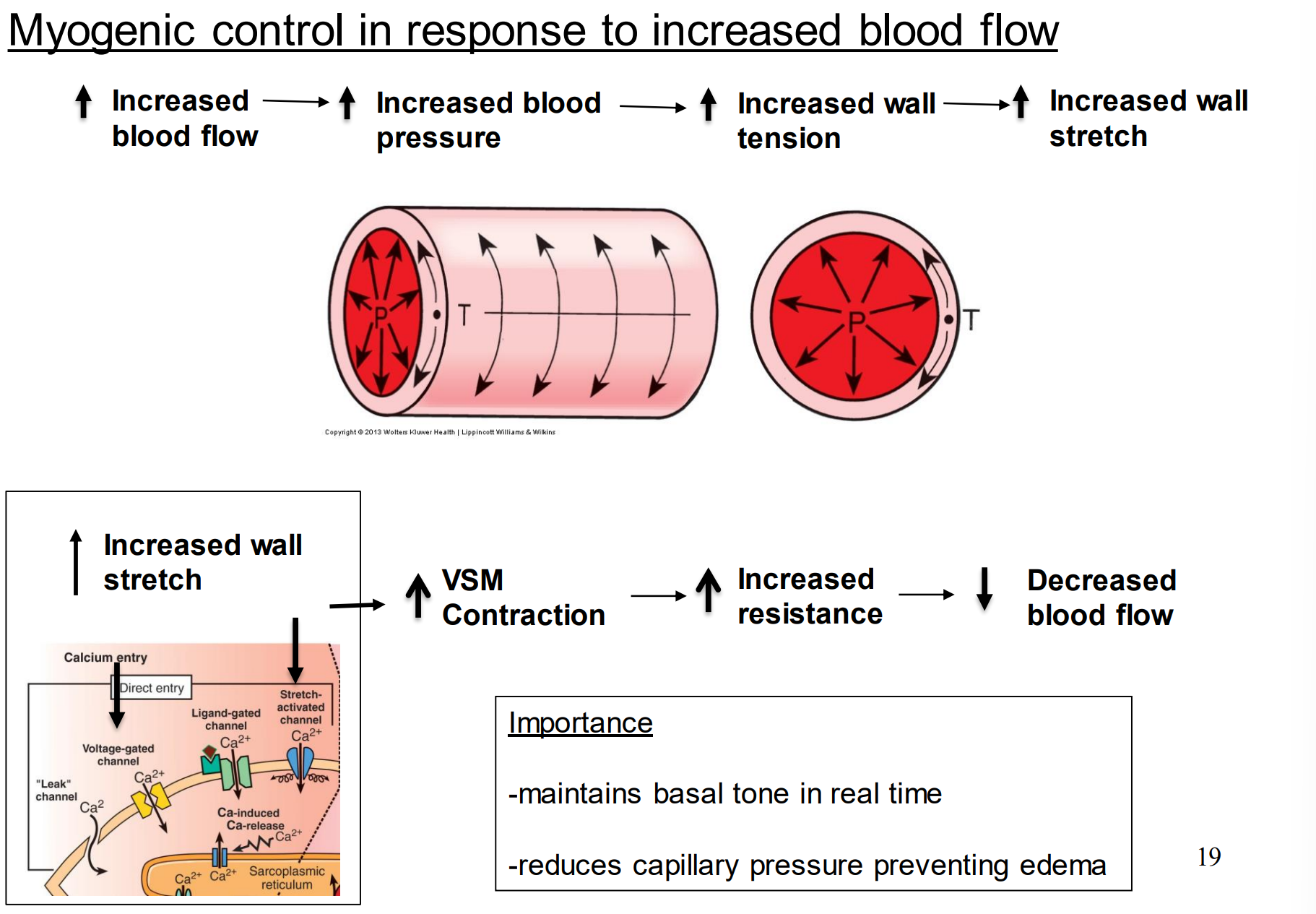
When does myogenic control of the basal tone occur?
In response to increased blood flow
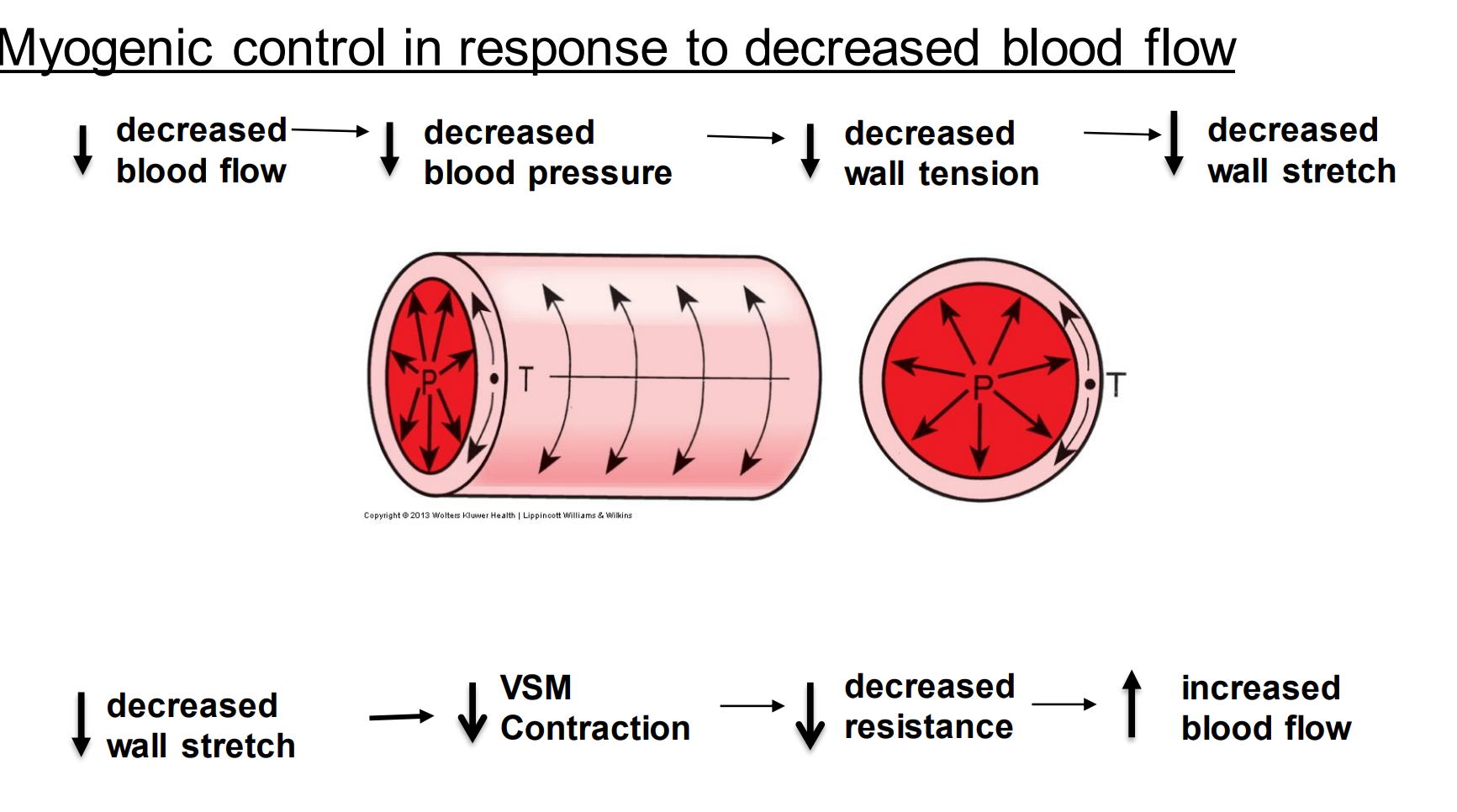
Myogenic control of the basal tone also occurs in response to decreased blood flow, why?
Maintains basal tone in real time
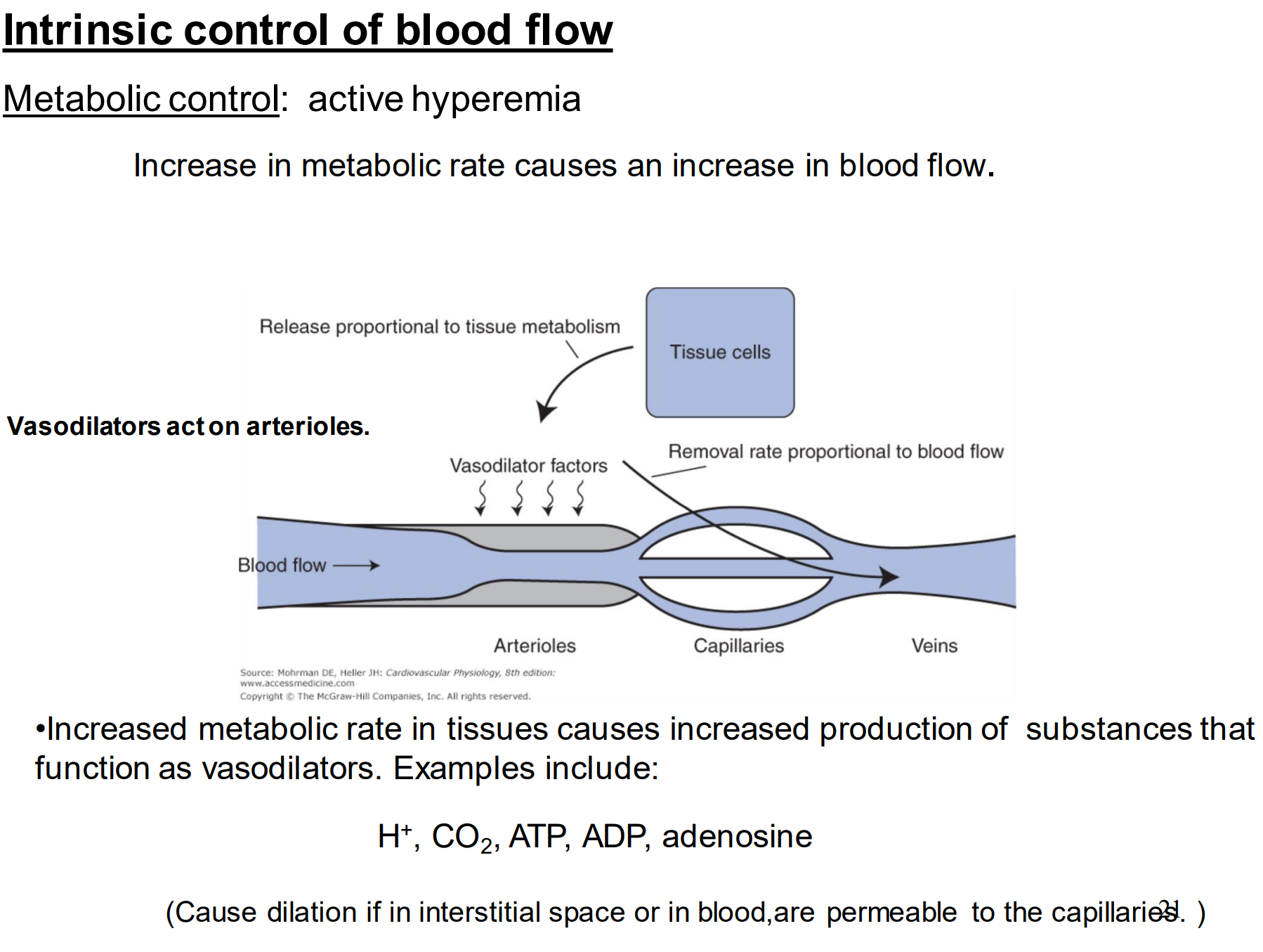
Increase in metabolic rate causes a(n) ______ in blood flow. Why?
increase
while the tissues are creating these metabolites they’re dumping them into the blood vessels —> they then act as vasodilators which decreases resistance
What are some of the metabolites that act like vasodilators?
H+, CO2, ATP, ADP and adenosine
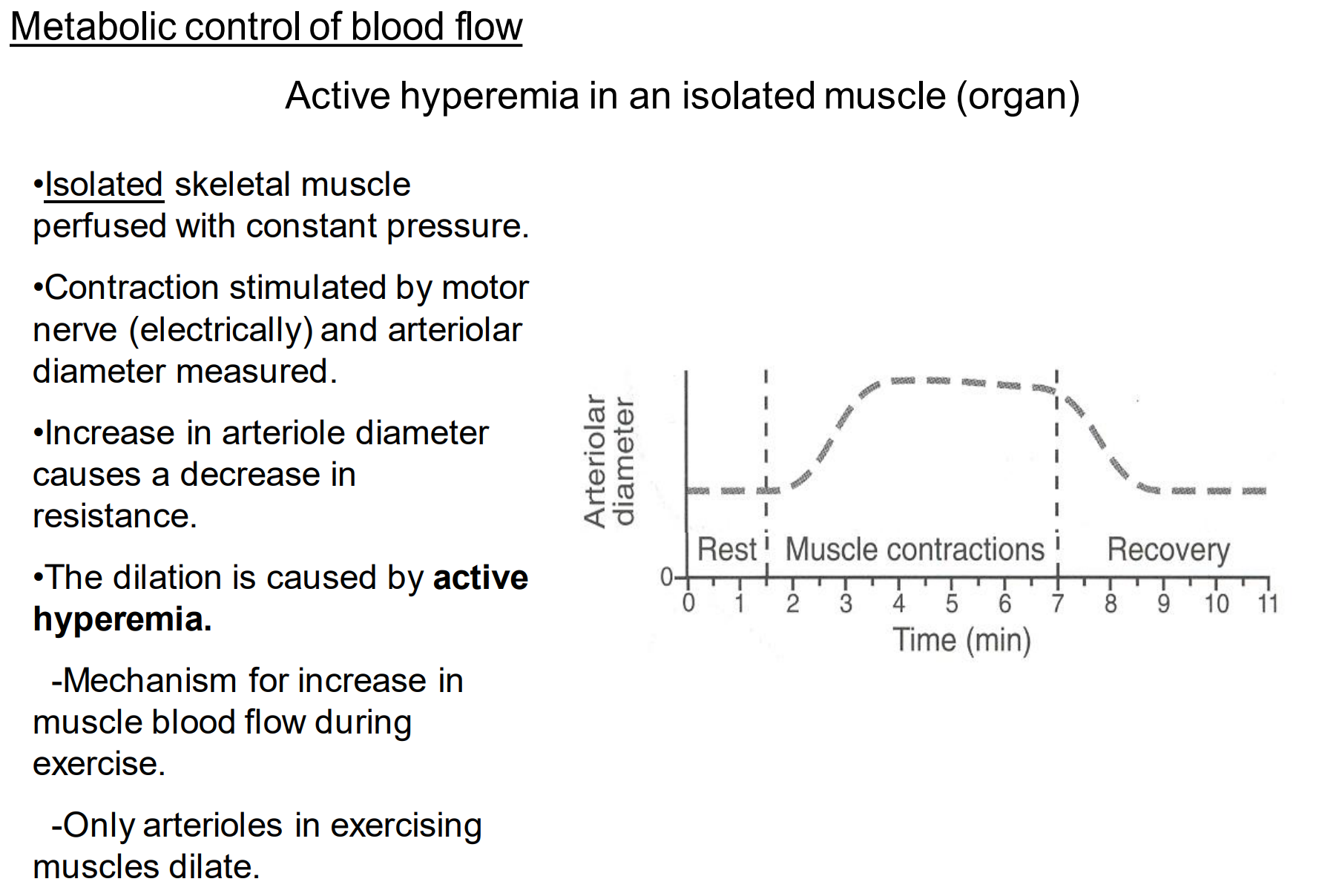
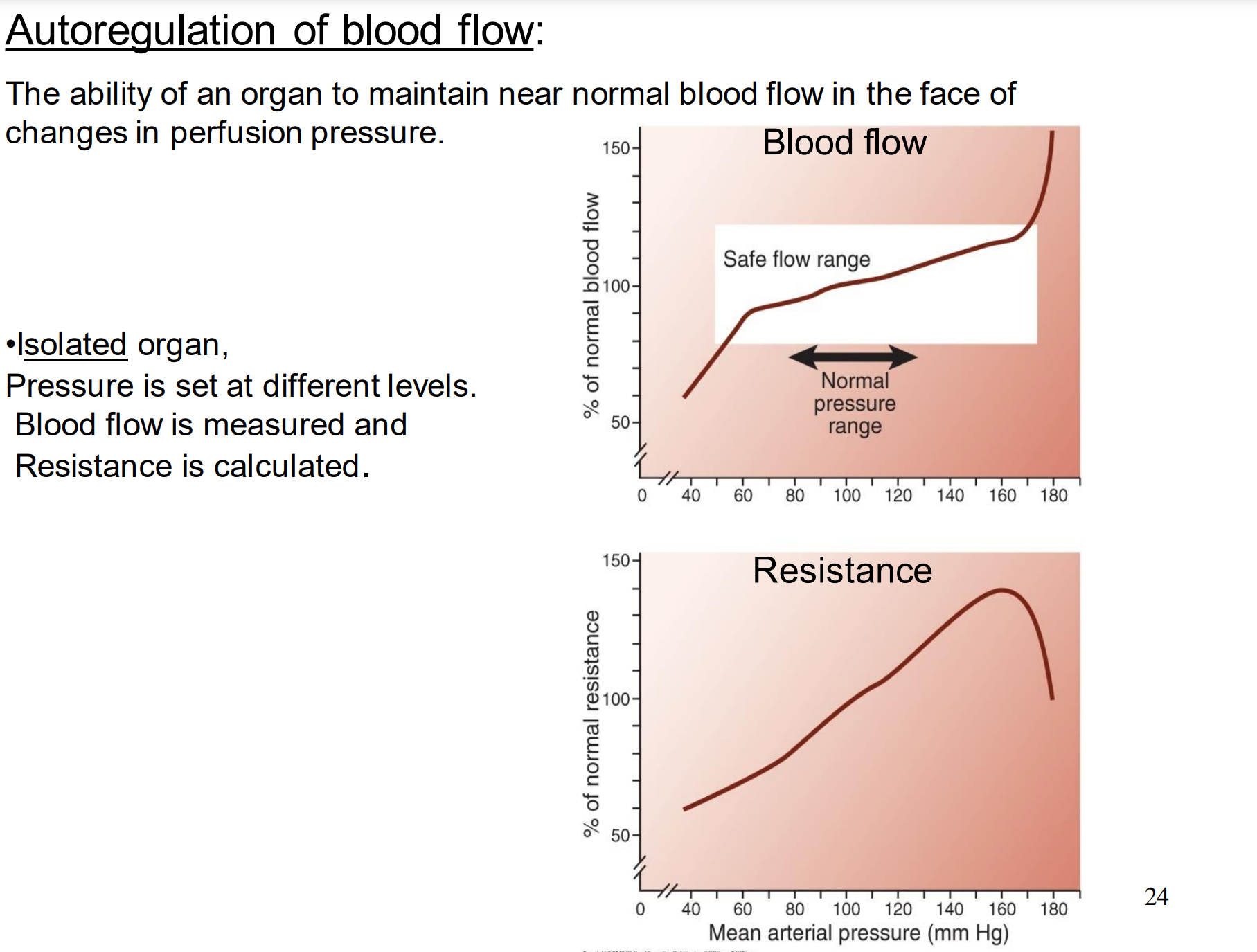
What is autoregulation of blood flow?
The ability of an organ to maintain near normal blood flow in the face of changes in perfusion pressure
Define metabolic and myogenic mechanisms used in autoregulation of blood flow
change in pressure changes blood flow which changes concentration of vasodilating metabolites which changes resistance
change in pressure changes arteriolar stretch which changes resistance
What is the limit of autoregulation of blood flow?
60 to 160 mmHg
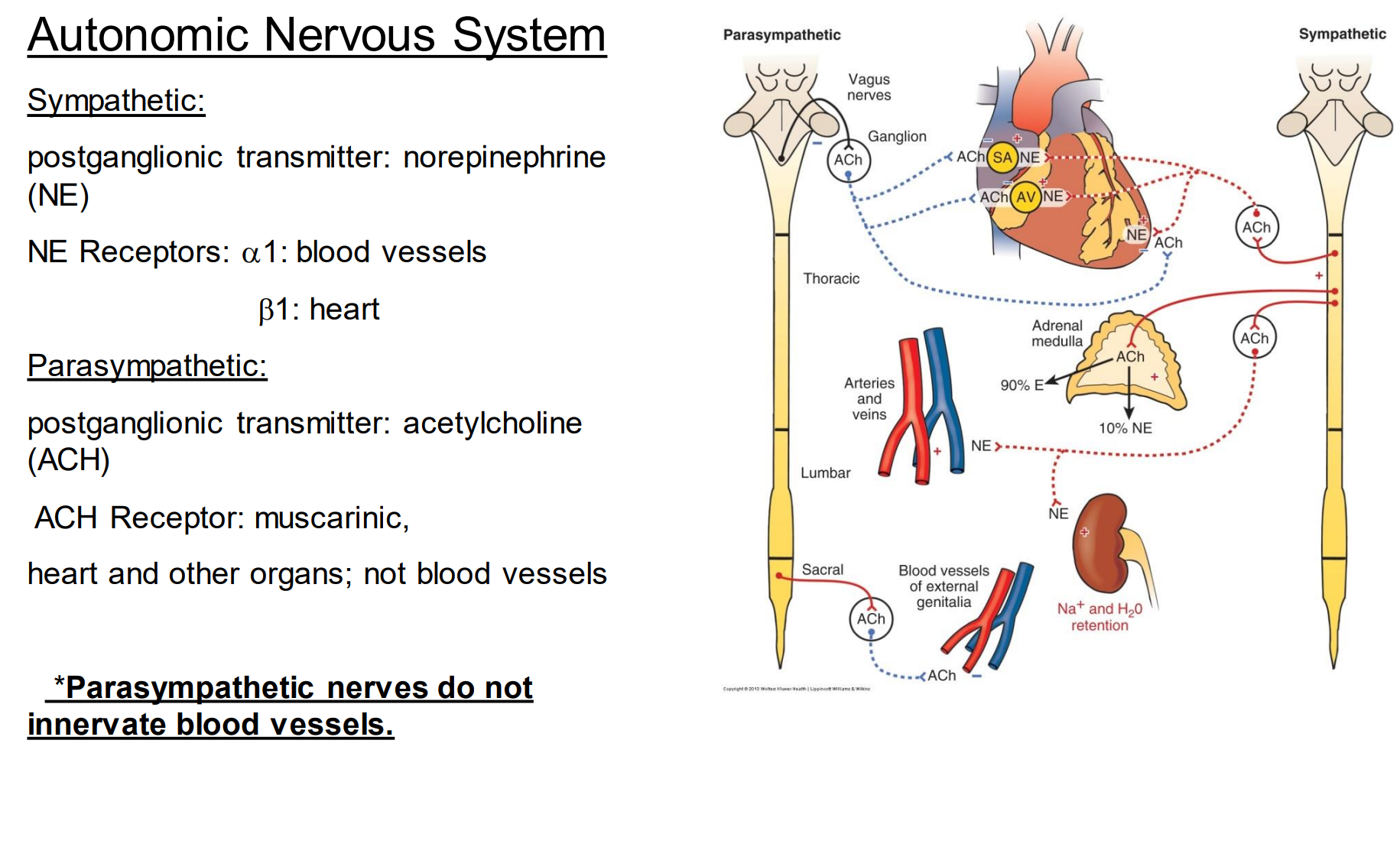
When we think about regulation of blood flow we primarily are talking about the _______ nervous system.
sympathetic
parasympathetic nerves do not innervate blood flow
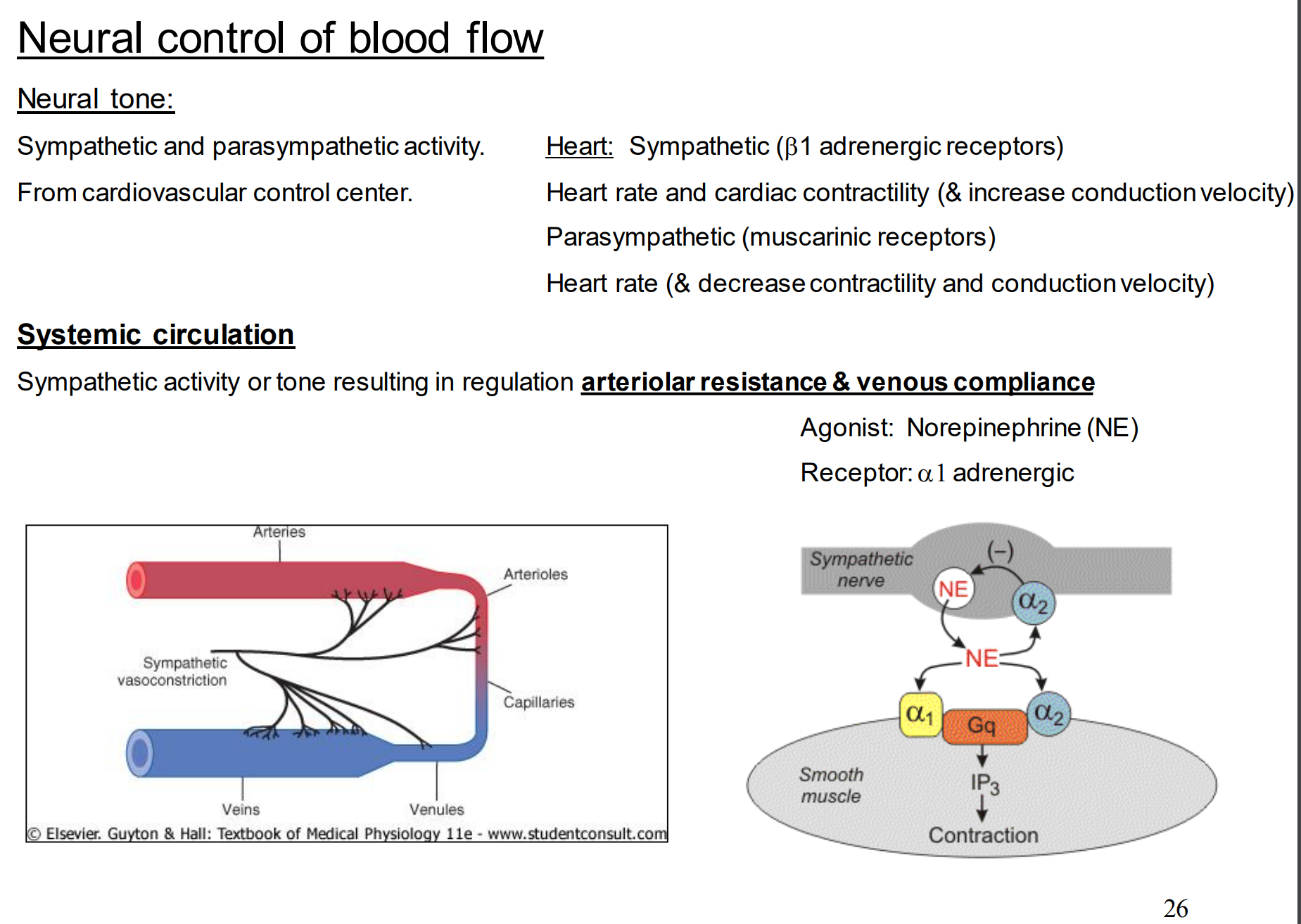
Recap of neural tone:
take note that parasympathetic influence has a negative impact on heart rate