ECG Advance
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
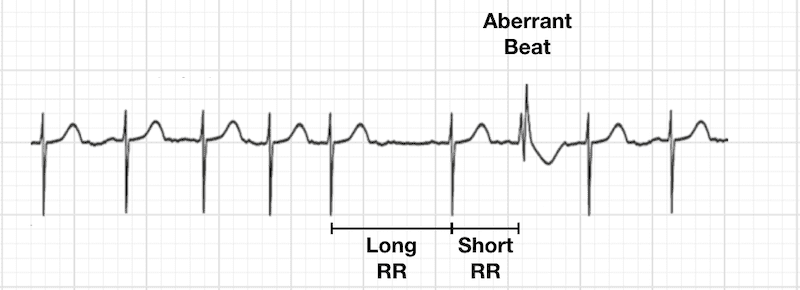
Ashman’s Phenomenon
aberrant ventricular conduction (RBBB morphology)
LONG-SHORT RULE: long beat then a short beat = a PAC will aberrant conduction.
Setting of sinus have non-compensatory pause
Common in AF settings.
RBBB diagnosis:
QRS > 12 seconds
Strain in V1 and V2
Slurring S in I, V6
Upright Fat R in V1 ***
RAD
LBBB diagnosis
QRS > 0.12s
S in V1 and V2
R in I, V5, V6
which has longer refractory period LBBB or RBBB?
RBBB
How is wave depolarization sent in BBB setting?
from the unaffected side to afefcted side via cell to cell transmission (sequential)
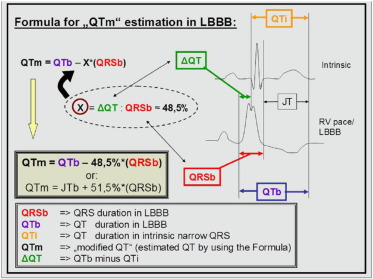
How is QT measured in the setting of BBB
Bogossian Method
QTm = QTBBB - 50%duration of BBB QRS
RVH diagnosis:
R > 7 mm w/o strain
Strain in V2 to V4
RAE/RAD may be present
R/S > 1 with skinny QRS
absent of RBBB
can mimic LAPFB
LVH diagnosis
voltage + non-voltage criteria
S wave in V1 and V2 > 30 mm
R wave in V1 and V2 > 30 mm
limb leads > 20 mm (straight 3)
ST depression; strain (3 points)
LAE in V1 (3 points)
LAD (2 points)
Probable (4 points) / Definite (5 points)
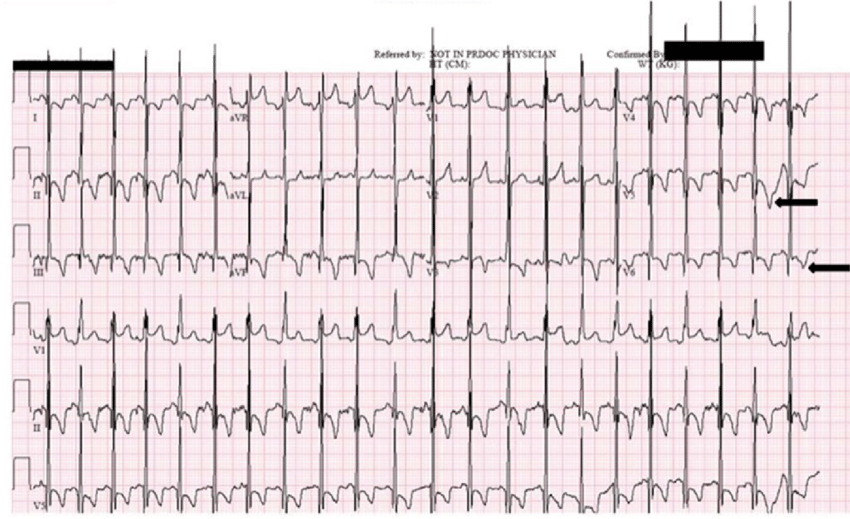
BVH diagnosis:
Katz-Watchel Phenomennon;
Large biphasic QRS V2 to V5
R+S in v3/v4 > 500
common in pediatrics with VSDs
Adults with amyloidosis
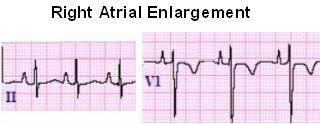
RAE diagnosis:
peaked p wave > 2.5mm in II // >1,5 mm in V1
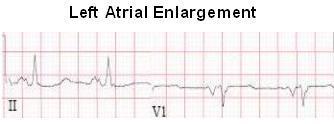
LAE diagnosis:
p > 0.11second in II // negative portion in v1 > 1mm deep
Pulmonary Embolism
clot in the artery in the lungs blocked.
Type of chest pain that almost always occurs with deep vein thrombosis
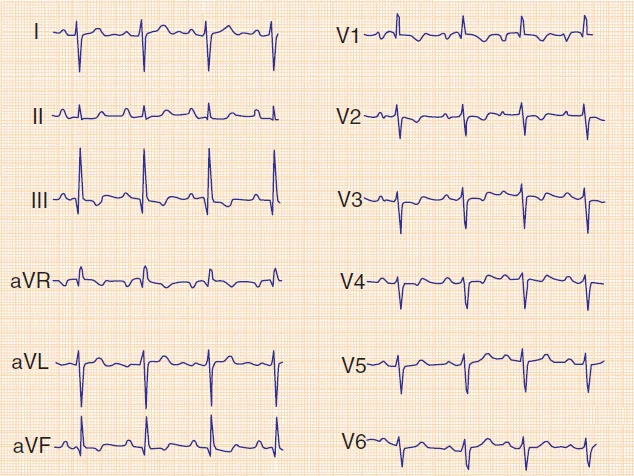
PE ECG Signs:
1.Tachycardia at rest**
2. S1Q3T3 pattern*
3. T wave inversion inferior/V1-V4*
3. Right sided changes; RAD/R with strain/RBBB (due to RV overload)
4. Hypotension
Cor-Pulmonale:
causes right sided HF associated with RV dilation
Other diagnostic tools for PE
D-dimer test (protein leftover after clot breaks down) High levels present with PE
X-Ray
Troponin Test (Elevated)
Echo/ CT scan (RV dilation/Dsyfunction)
Differentials for PE:
Pericarditis
Fever
Ischemia
Anxiety
Chest Pain Differentials:
Cardiac: Infarct, Angina (Wellens), Aortic Dissection, Pericarditis
Stomach: GERD
Musculoskeletal
Respiratory: PE, Pulmonary HTN
Miscellaneous: Anxiety, Shingles
Aortic Dissection
tear int eh inner aorta that causes blood to flow between the layers of the aorta.
Severe chest pain/upper back pain
Weak pulse
Negative cardiac biomarkers
ST elevation stages:
Hyperacute: ST elevation only
Acute: significant Q and STE
Old: Sig Q with T wave changes
Sig Q: 1/3 of R wave and 1 mm wide (transmural death)
What 2 causes Chest Pain at rest?
Unstable Angina and Wellen’s Syndrome
Wellen’s Syndrome
Chest pain at rest typically due to proximal LAD stenosis > anterior MI (need PCI/CABG!)
DO NOT DO GXT.
ECG Wellen’s
T wave changes**
History of Angina**
Minimal Elevation < 1mm
Type A: V2-V3 Biphasic negative QRS (±/-)
DO NOT CONFUSE TYPE A WITH HYPOKALEMIA (-/+)
Type B: symmetrical inverted T waves
Pericarditis
inflammation of the pericardium
Sharp CP during respiration
Pericarditis Cardiac Tamponade/Constrictive
Constrictive: scarring
Cardiac Tamponade: fluid build up which compresses the heart.
Beck’s Triad for CT: 1.Hypotension 2. Muffle Heart Sounds 3. Jugular Vein distended
Pulse Paradox for CT: > 10mmHg drop during inspiration
CT need to do pericardiocentesis
Pericarditis ECG
Sinus tachycardia at rest**
PR depression**
Electric Alternans**
Low Voltage** (QRS limb < 5mm | QRS in precordial < 10 mm)
Spodick Sign: V1 downwards TP segment
Widespread STE** ½ weeks > T wave flattening 3 weeks> T wave inversion beyond 3 week > Normal ECG
what are non-specific ST changes?
when there is no clinical data to correlate with ECG changes
Secondary ST change
due to ventricular depolarization BBB, WPW, PVCs, LVH
Primary ST changes:
ischemia, drugs, electrolytes
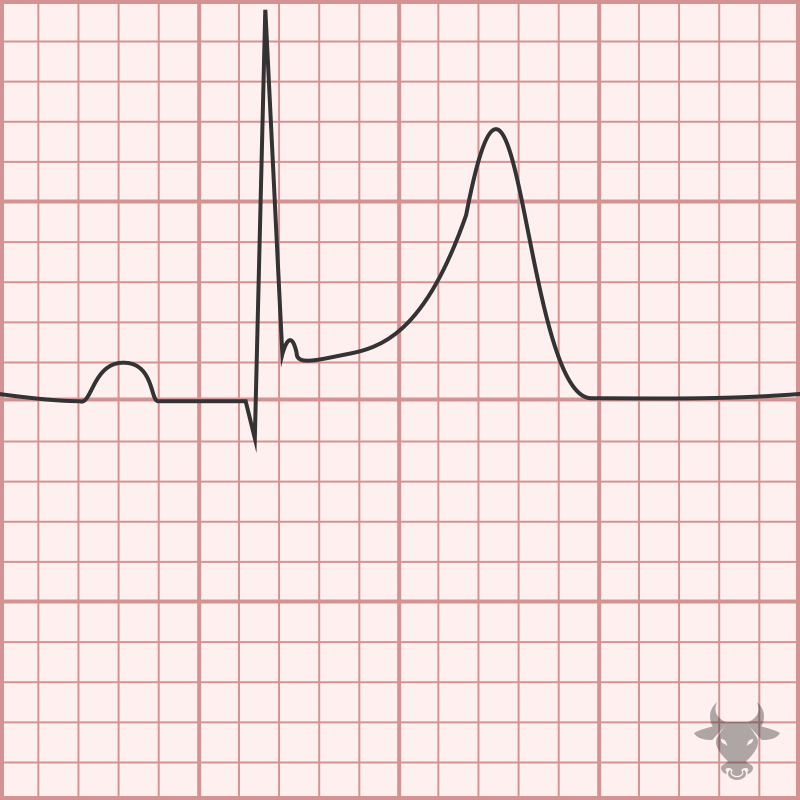
Normal variant of ST changes
Early repolarization, symmetrical T wave (usually in young pts)
J point notching may be seen
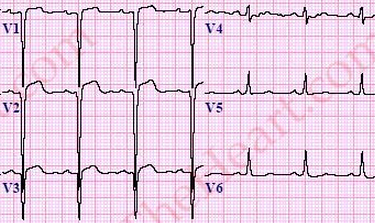
Persistent coving ST elevation after a ACUTE MI (after a couple of weeks)
Ventricular Aneurysm
What can help alleviate MI
CCB, Nitroglycerin
early STD in aVL could indicate
impending inferior MI
Occlusion MI
isolated STE/STD in a single lead with prominent hyperacute T waves
RVMI
RVMI leads to reduce preload which can lead to hypotension
STE III > II**
STE V1 and STD V2**
STE V1 > V2
Posterior MI
Tall R waves in V1 to V3 and Horizontal STD in V1 to V3
Posterior Lead only need 0.5 mm STE to confirm (usually lower voltage)
If a person has RVMI what do you not give them?
Nitroglycerin or vasodilators as it decreases venous return and lead to dangerously low hypotension which can lead to shock.
Pitfalls of WCT
reliance on II
AF with rapid ventricular response can turn into rate related BBB (confused with VT) do not want to give lidocaine
Why do we not give lidocaine to AF?
increases conduction through AVN = increase AF
WTC 3 diagnosis
VT
SVT with aberrancy(due to BBB)
SVT aberrancy due to WPW
What is given for SVT?
What is given orally to prevent reoccurrence
adeosine
CCB, BB, Digitalis
VT criteria (7)
eRAD | all inferior lead pointed down | Upright V1 (99% specific)
or RAD with V1 negative (90%)
If V1 positive: Mariott signs (L>R) / STeeple sign/ Fireman Hat
All leads down or up Concordance
Josephson sign; Notch of S wave
Brugada sign: onset of QRS S > 100ms
Capture or fusion beats
Difference between RBBB and VT V1
L> R in VT
R>L in RBBB
Other prominent VT signs outside ECG
patient age > 35 years
Previous MI
Structural Heart Diease
Family history of SCA
SVT with aberrancy criteria:
Previous ECG shows BBB or WPW
Pt history has terminated with adenosine or VM
Triphasic RSR’
Pt is young
Really wide WTC
> 200 msec thick toxicity or metabolic
AVOID SODIUMC HANNEL BLOCKERS GIVE BICARBS OR CALCIUM
most common cause of hyperkalemia
renal failure
Normal Hyperkalemia AND Abnormal
3.5-5 mmol/l
>5.5 Peak T wave
>6.5 PRI prolongs, P goes.
>7 Bizarre QRS sinus wave
>9 VF, Cardiac Arrest. PEA
Hypokalemia
decrease in potassium, increases hyperexcitability which can lead to re-entrant arrhythmias
Usually caused by diuretics
Biphasic T waves (-/+) / STD / U waves
Normal Calcium and Magenisum
2.2 - 2.7 mmol/L
0.65 - 1.05 mmol/L
Hypercalcemia
Shortening of QT
Osborne waves (J wave; common in hypothermia)
Hypocalcemia
QT prolongations > 450 ms can lead to TDP
Hypomagnesium
often occurs with hypokalemia.
QT prolongation
Hypermageniusm
similar to hyperkalemia
uncommon due to kidneys eliminate Mg alot.
Thus cause: renal failure
Digoxin Toxicity
hypokalemia adds to the effect
Scooped STD
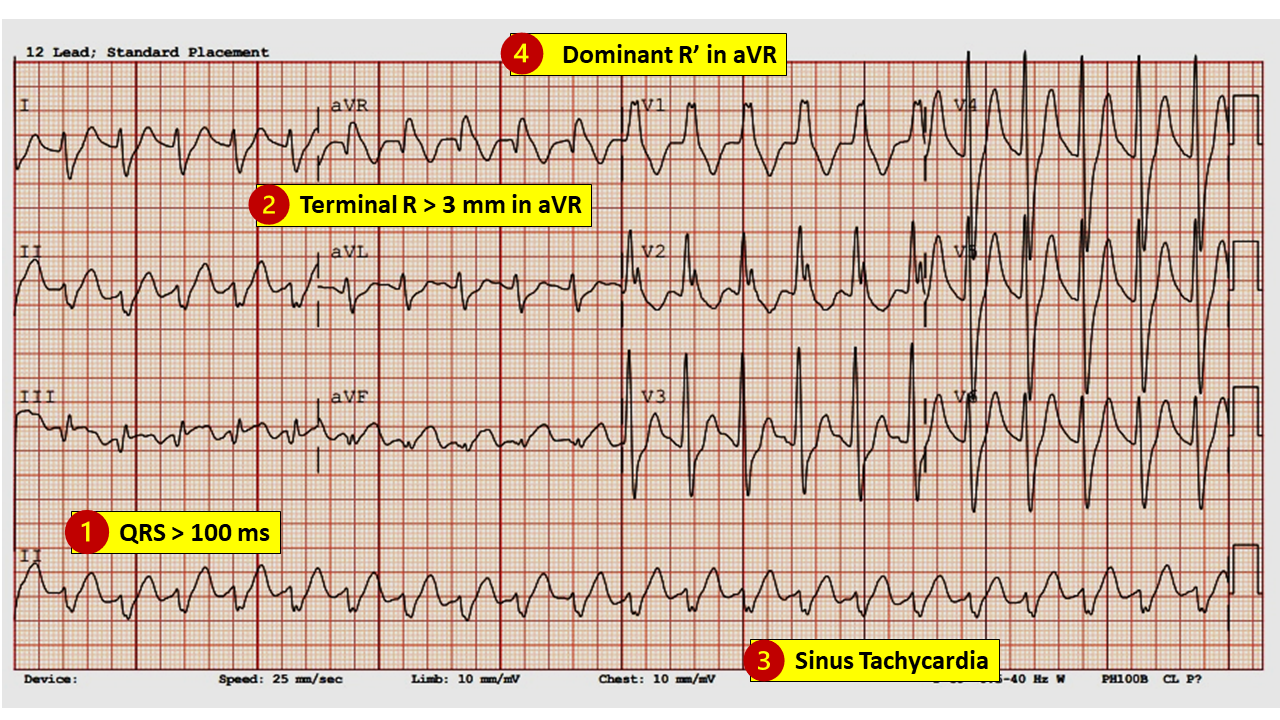
Tricyclic Overdose ECG
R’ in avR
R > 3mm avR
Sinus tachycardia
WIDE WIDE QRS
sodium channel blockade****
Toxic Drug Effects: CAUSE LONG QT
Anti-arrhythmias I
Amiodarone
Phenothiazines
AAI: increase QT, blocks SA node and cause AV blocks
Amiodarone: slows conductions everywhere
Phenothiazines: widens QRS
AVNRT criteria
micro-circuit
short RP < 70 ms**
140-240 bpm
Pseudo R’ (retrograde P in V1)**
Pseudo S (rounded) in I and inferior leads; retrograde P waves)
AVRT
macro-circuit involving accessory pathways triggered by premature beats.
ECG: 200-300 bpm
Retrograde p waves in inferior leads
RP > 70ms***
Antidromic AVRT
Fat QRS Antegrade AP retrograde AVN
often confused with VT but VT < 180
Treatment: Vagal Man or amiodarone / Procainamide
Unstable: Cardioversion
Orthodromic AVRT
most common
antegrade AVN, retrograde AP
Thin QRS
often confused with junctional tachycardia
Treatment: Vagal Man. / Adenosine / CCB
unstable: cardioversion
WPW
Involves the Bundle of Kent ***
PRI < 120ms
Delta wave
QRS prolongations
ST-T discordance
Type A: V1 positive
Type B: V1 negative
some pt have concealed pathways where retrograde only AP conductions so no feature in sinus rhythm,
Long-Ganong Syndrome
short PRI no dealt wave
Bundle of James
Short RP (after QRS)
retrograde through fast pathway (retrograde P)
AVNRT
Orthodromic AVRT
junctional tachycardia with inverted P after QRS
Long RP (before QRS)
retrograde through slow pathway (Antegrade P)
Sinus tachycardia
Antidromic AVRT
Atrial Tachycardia
Junctional tachycardia with inverted P before QRS
Atrial Tachycardia
originate within the atrai outside SA and AVN node
Long RP
inverted P waves in inferior leads
Narrow complex above > 160 bpm treats as
SVT
Atrial Flutter
re-entry circuit around the TV
AF 1:1 300 bpm
AF 2:1 150 bpm (always be sus of A flutt at 150 bpm exact)
Counterclockwise inverted Flutter waves most common
What can help unmask flutter waves
adenosine
IV adenosine no change in rate:
VT or inadequate dose
adenosine causes gradual slowing:
sinus tachycardia
Atrial tachycardia
Junctional Tachycardia
adenosine causes termination:
AVRT or AVNRT
adenosine causes persistent atrial tachycardia with intermittent AV block:
atrial flutter
Adenosine works on
slowing conduction at the AVN
Sgarbossa Criteria
Concordance STE > 1mm in positive QRS
Concordance STD > 1mm in v1 to V3
Discordant STE > 5mm or STE 25% of S wave in negatvie QRS
Once determine LBBB cannot have
LVH
Once determine RBBB cannot have
RVH
Once determine RVH cannot have
LPFB
If determine LVH can still have
LAFB
Old lateral MI can cause
LAD
Old inferior MI can mimic
LAFB
Regular Atrial Fibrillation can mean
CHB with underlying AF.
Once determine WPW cannot have
LAFB
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
dagger Q waves in lateral leads
LVH with strain may be present
Diastolic DSYFUNCTION
seen in young men/athletes
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVD)
Autosomal dominant causes fat tissues to take over RV wall lead to ventricular arrhythmias and SCA.
Epsilon wave****
T wave inversion w/o RBBB
Prolong S upstroke and Localized QRS widening V1toV3
Fontan Leads for ARVD
RA: Manubrium
LA: Xiphoid
LL: V4
Intracardial Hemorrhage
Giant T wave inversion & QT prolongation