MIcroeconmics
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cp. 5,7,11,12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
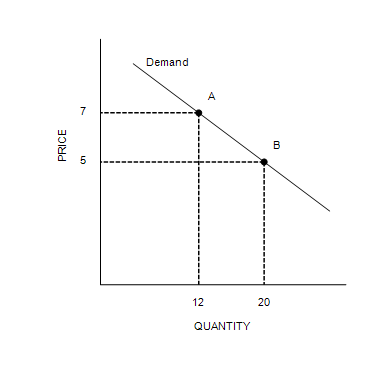
Between point A and point B, price elasticity of demand is equal to
1.5.
A good will have a more inelastic demand, the
broader the definition of the market.
Demand is said to be inelastic if
the quantity demanded changes only slightly when the price of the good changes
Demand is said to be price elastic if
buyers respond substantially to changes in the price of the good.
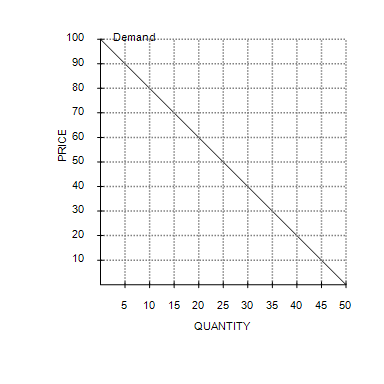
Using the midpoint method, between prices of $20 and $30, price elasticity of demand is about
0.33.
For a good that is a luxury, demand
tends to be elastic.
Goods with many close substitutes tend to have
more elastic demands.
Using the midpoint method, if the price falls from $200 to $150, the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand is
(Dollars per unit) | Quantity Demanded (Units) |
250 | 0 |
200 | 30 |
150 | 70 |
100 | 110 |
50 | 150 |
0 | 190 |
2.8
Income (Dollars) | Quantity of Good X Purchased | Quantity of Good Y Purchased |
30,000 | 2 | 20 |
40,000 | 6 | 10 |
Using the midpoint method, the income elasticity of demand for good Y is
−2.33, and good Y is an inferior good.
The demand for grape-flavored Hubba Bubba bubble gum is likely
elastic because there are many close substitutes for grape-flavored Hubba Bubba.
For a particular good, a 2 percent increase in price causes a 12 percent decrease in quantity demanded. Which of the following statements is most likely applicable to this good?
The good is a luxury.
For which of the following goods is the income elasticity of demand likely highest?
Diamonds
If a 15% increase in price for a good results in a 20 percent decrease in quantity demanded, the price elasticity of demand is
1.33
If marijuana were legalized, it is likely that there would be an increase in the demand for marijuana. If demand for marijuana is inelastic and the supply of marijuana is perfectly elastic, this will result in
the same price and higher total revenue from marijuana sales.
If the demand for donuts is elastic, then a decrease in the price of donuts will
increase total revenue of donut sellers.
If the price of walnuts rises, many people would switch from consuming walnuts to consuming pecans. But if the price of salt rises, people would have difficulty purchasing something to use in its place. These examples illustrate the importance of
the availability of close substitutes in determining the price elasticity of demand.
Income elasticity of demand measures how
the quantity demanded changes as consumer income changes.
Jerome says that he will spend exactly $25 each month on new apps for his mobile device, regardless of the price of apps. Jerome's demand for apps is
unit elastic
Last year, Tess bought five handbags when her income was $54,000. This year, her income is $60,000, and she purchased seven handbags. Holding other factors constant and using the midpoint method, it follows that Tess's income elasticity of demand is about
3.17, and Tess regards handbags as normal goods.
Studies indicate that the price elasticity of demand for cigarettes is about 0.4. A government policy aimed at reducing smoking changed the price of a pack of cigarettes from $2 to $6. According to the midpoint method, the government policy should have reduced smoking by
40 percent.
A key determinant of the price elasticity of supply is the
time horizon.
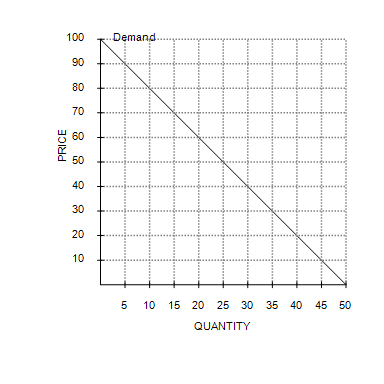
At a price of $70 per unit, sellers' total revenue equals
$1,050.
For which pairs of goods is the cross-price elasticity most likely to be positive?
Pens and pencils
If the cross-price elasticity of two goods is negative, then the two goods are
complements.
If the price elasticity of supply is 1.5, and a price increase led to a 1.8 percent increase in quantity supplied, then the price increase is about
1.20 percent.
If the price of walnuts rises, many people would switch from consuming walnuts to consuming pecans. But if the price of salt rises, people would have difficulty purchasing something to use in its place. These examples illustrate the importance of
the availability of close substitutes in determining the price elasticity of demand.
The supply of aged cheddar cheese is inelastic, and the supply of bread is elastic. Both goods are considered to be normal goods by a majority of consumers. Suppose that a large income tax increase decreases the demand for both goods by 10 percent.
decrease in both the aged cheddar cheese and bread markets
| Supply Curve B | Supply Curve C | ||||
Price | $1.00 | $2.00 | $1.00 | $3.00 | $2.00 | $5.00 |
Quantity Supplied | 500 | 600 | 600 | 900 | 400 | 700 |
Using the midpoint method, which of the three supply curves represents the least elastic supply?
Supply curve A
The price elasticity of supply measures how much
the quantity supplied responds to changes in the price of the good.
The supply of a good will be more elastic, the
longer the time period being considered.
Which of the following statements is valid when the market supply curve is vertical?
Market quantity supplied does not change when the price changes.
A drought in California destroys many red grapes causing the prices of both red grapes and red wine to rise. As a result, the consumer surplus in the market for red grapes
decreases, and the consumer surplus in the market for red wine decreases.
A result of welfare economics is that the equilibrium price of a product is considered to be the best price because it
maximizes the combined welfare of buyers and sellers.
All else equal, what happens to consumer surplus if the price of a good increases?
Consumer surplus decreases
Billie Jo values a stainless steel dishwasher for her new house at $500, but she succeeds in buying one for $425. Billie Jo's willingness to pay for the dishwasher is
$500
Bob purchases a book for $6, and his consumer surplus is $2. How much is Bob willing to pay for the book?
$8
Dawn's bridal boutique is having a sale on evening dresses. The increase in consumer surplus comes from the benefit of the lower prices to
both existing customers who now get lower prices on the gowns they were already planning to purchase and new customers who enter the market because of the lower prices.
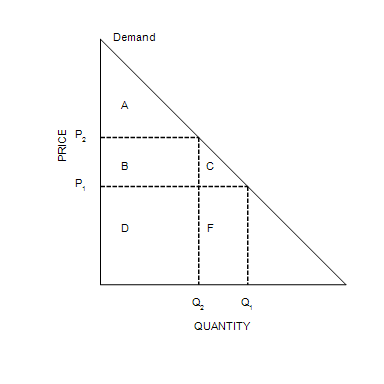
Area C represents the
consumer surplus to new consumers who enter the market when the price falls from P2to P1.
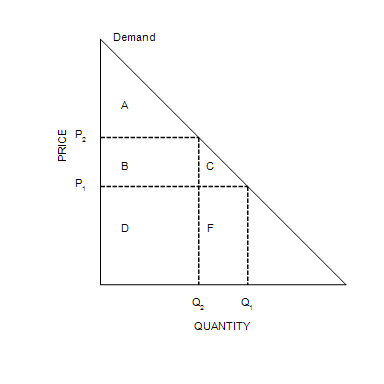
When the price is P1, consumer surplus is
A+B+C.
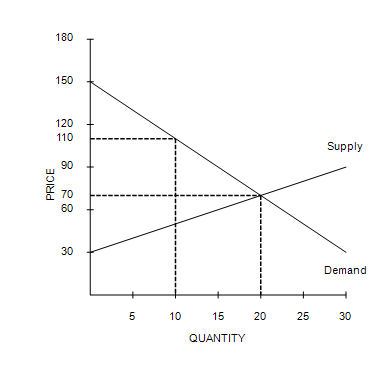
At the equilibrium price, consumer surplus is
$800.
A seller's opportunity cost measures the
value of everything she must give up to produce a good.
A supply curve can be used to measure producer surplus because it reflects
sellers' costs.
At Nick's Bakery, the cost to make a cheese danish is $1.50 per danish. As a result of selling 10 danishes, Nick experiences a producer surplus in the amount of $20. Nick must be selling his danishes for
$3.50 each.
Cost is a measure of the
seller's willingness to sell.
Justin builds fences for a living. Justin's out-of-pocket expenses (for wood, paint, etc.) plus the value that he places on his own time amount to his
cost of building fences.
Kristi and Rebecca sell lemonade on the corner for $0.50 per cup. It costs them $0.10 to make each cup. On a certain day, their producer surplus is $20. How many cups did Kristi and Rebecca sell?
50
Producer surplus is
the amount a seller is paid minus the cost of production.
Price (Dollars per unit) | Quantity Demanded (Units) | Quantity Supplied (Units) |
12.00 | 0 | 36 |
10.00 | 3 | 30 |
8.00 | 6 | 24 |
6.00 | 9 | 18 |
4.00 | 12 | 12 |
2.00 | 15 | 6 |
0.00 | 18 | 0 |
Both the demand curve and the supply curve are straight lines. At equilibrium, producer surplus is
$24.
Price (Dollars per unit) | Quantity Demanded (Units) | Quantity Supplied (Units) |
12.00 | 0 | 36 |
10.00 | 3 | 30 |
8.00 | 6 | 24 |
6.00 | 9 | 18 |
4.00 | 12 | 12 |
2.00 | 15 | 6 |
0.00 | 18 | 0 |
Both the demand curve and the supply curve are straight lines. If the price is $4 but only 6 units are bought and sold, producer surplus will be
$18.
Seller | Cost (Dollars) |
Abby | 1,600 |
Bobby | 1,300 |
Dianne | 1,100 |
Evaline | 900 |
Carlos | 800 |
If the market price is $1,000, the producer surplus in the market is
$300
A result of welfare economics is that the equilibrium price of a product is considered to be the best price because it
maximizes the combined welfare of buyers and sellers.
Maximi
A result of welfare economics is that the equilibrium price of a product is considered to be the best price because it
An example of positive analysis is studying
Efficiency in a market is achieved when
the sum of producer surplus and consumer surplus is maximized.
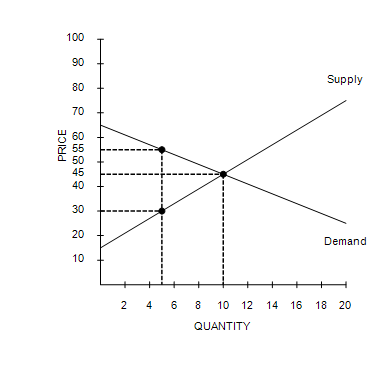
If the government imposes a price ceiling of $55 in this market, then total surplus will be
$250.00
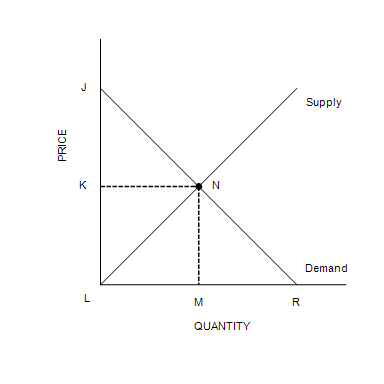
Total surplus can be measured as the area
JNL
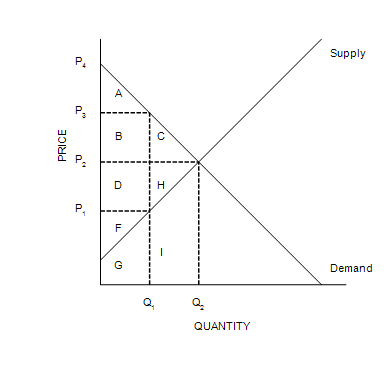
The equilibrium price is
P2.
The distinction between efficiency and equality can be described as follows:
Efficiency refers to maximizing the size of the pie; equality refers to distributing the pie fairly among members of society.
We can say that the allocation of resources is efficient if
total surplus is maximized.
We can say that the allocation of resources is efficient if
total surplus is maximized.
A city street is
a common resource when it is congested, but it is a public good when it is not congested.
A cost-benefit analysis of a highway is difficult to conduct because analysts
will have difficulty estimating the value of the highway.
A free rider is a person who
receives the benefit of a good but avoids paying for it.
A good is excludable if
people can be prevented from using it.
A television broadcast is an example of a good that is
not rival in consumption.
A textbook is a
private good and the knowledge that one gains from reading the book is a public good.
Before considering any public project, the government should
conduct a cost-benefit analysis and compare the total cost and total benefits of the project.
Brad owns 5 acres of land. Brad sells the land to a real estate developer who builds a subdivision with 10 houses. The land is an example of a good that is
both rival in consumption and excludable
| |||
|
| Yes | No |
Excludable? | Yes | A | B |
No | C | D | |
Emma's use of good x does not affect anyone else's use of good x. Neither Emma nor anyone else can be prevented from using the good. Good x is an example of the type of good that belongs in
Box D, which represents public goods.
|
| Rival in Consumption? | |
|
| Yes | No |
Excludable? | Yes | A | B |
No | C | D | |
|
|
|
|
A membership at a gym that always has space in classes and on machines is an example of the type of good represented by Box
B.
Goods that are excludable include both
private goods and club goods.
Imagine a 2,000-acre park with picnic benches, trees, and a pond. Suppose it is publicly owned, and people are invited to enjoy its beauty. When the weather is nice, it is difficult to find parking, and the trash cans overflow with food wrappers on summer afternoons. Otherwise, it is a great place. The park is a common resource because
if too many people use it, one person's use diminishes other peoples' use.
Knowledge that is patented is a
club good, whereas knowledge that is not patented is a public good.
Miguel, Maria, and Marcos all would like a place to sit while waiting at their children's bus stop. The neighborhood association is considering installing several park benches at the bus stop. Miguel values the benches at $20, Maria at $30, and Marcos at $40. The park benches and labor for installation cost $100. If Miguel, Maria, and Marcos are the only residents who value the benches, what should the neighborhood association do?
Do not install the park benches because the costs outweigh the benefits.
Pollution is a
negative externality that can be viewed as a common-resource problem.
Producers have little incentive to produce a public good because
there is a free-rider problem.
Consider the town of Springfield with only three residents, Sophia, Amber, and Cedric. The three residents are trying to determine how large, in acres, they should build the public park. The following table shows each resident's willingness to pay for each acre of the park.
Acres | Willingness to Pay (Dollars) | ||
Sophia | Amber | Cedric | |
1 | 10 | 24 | 6 |
2 | 8 | 18 | 5 |
3 | 6 | 14 | 4 |
4 | 3 | 8 | 3 |
5 | 1 | 6 | 2 |
6 | 0 | 4 | 1 |
7 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
Suppose the cost to build the park is $24 per acre. How many acres should the park be to maximize total surplus from the park in Springfield?
3 acres
The failure of markets to adequately protect the environment can be viewed either as a problem of
externalities or as a problem of common resources.
The parable called the Tragedy of the Commons applies to goods such as
clean air and clean water.
The Pennsylvania Turnpike is a tolled freeway running through the state of Pennsylvania. Motorists must pay tolls at various points along the Turnpike based on the distance they traveled on the freeway. Suppose that despite the tolls, many motorists in the urban areas use the Turnpike causing traffic to slow during peak times. What type of good would the Turnpike be classified as in this case?
Private good
The goal of requiring licenses for hunting and fishing is to
reduce the use of a common resource.
The town of Isle is on a small island connected to Big City by a single bridge. Most of the residents of Isle work in Big City. As a result, the bridge becomes very congested for two hours each day at the typical morning and evening commute times. Which of the following policies considered by the mayor of Isle would likely be most efficient in alleviating the congestion?
A variable toll for the bridge payable only by vehicles crossing the bridge during the congested commute times.
The Tragedy of the Commons results when a good is
rival in consumption and not excludable.
The Tragedy of the Commons will be evident when a growing number of sheep grazing on the town commons leads to a destruction of the grazing resource. To correct for this problem, the town could
auction off a limited number of sheep-grazing permits.
The U.S. military defends Jacob from foreign conflict. The fact that Jacob enjoys this protection does not detract from other Americans' enjoyment of it. For this reason, we say that national defense is
not rival in consumption.
What causes the Tragedy of the Commons?
Social and private incentives differ, and common resources are not excludable but are rival in consumption.
Which of the following is not a common resource?
A vegetable garden
Which of the following is not a reason why government agencies subsidize basic research?
The government wants to attract the brightest researchers away from private research firms.
Which of the following is usually true about government-provided goods?
People do not have to pay an explicit fee to enjoy these goods.
Ernie listens to National Public Radio, but does not contribute to any fundraising efforts.
Who among the following is a free rider?
Overview of US Taxation
Government revenue – increased
As percentage of total income
As economy’s income has grown
Government’s revenue from taxation has grown even more
As a nation gets richer
Government takes a larger share of income in taxes
Marginal Tax Rate
Tax rate applied to each additional dollar of income
Rises as income rises, higher-income families pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes
Taxes collected by federal government
Payroll taxes: a tax on the wages that a firm pays its workers
“Social insurance taxes” – pay for Social Security and Medicare
Social Security: income-support program for the elderly
Medicare: government health program for the elderly
Excise taxes: taxes on specific goods like gasoline, cigarettes, and alcoholic beverages
Estate taxes
Customs duties
Taxes collected by federal government pt.2
Corporate income tax: tax on profits
Corporation: business set up to have its own legal existence
Corporate profits are taxed twice
Corporate income tax when the corporation earns the profits
Individual income tax when the corporation uses its profits to pay dividends to its shareholders
axes collected by state and local governments
Sales tax
Property taxes
Individual and corporate income taxes
Sales tax
Percentage of total amount spent at retail stores
Property taxes
Percentage of estimated value of land and structures – paid by property owners
axes collected by state and local governments
Funds from the federal government
Redistributes funds from high-income states (which pay more taxes) to low-income states (which receive more benefits)
Other receipts
Fees for fishing and hunting licenses;
Tolls from roads and bridges
Fares for public buses and subways
Horizontal equity
Taxpayers with similar abilities to pay taxes should pay the same amount
similar tax payers- Determine which differences are relevant for a family’s ability to pay and which differences are not
U.S. income tax- Special provisions that alter a family’s tax based on its specific circumstances
Proportional tax
High-income and low-income taxpayers pay the same fraction of income