Flexible Structures Final
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Tufting
Sewing (stitching) of surface yarns onto a primary backing
Tufted Carpet Structure
Surface yarns (nylon, polyester, cotton), primary backing (usually woven or split film polypropylene yarns), coating (latex), and secondary backing (either spun jute or fibrillated polypropylene yarns).
Needle Gauge
Number of needles per unit width
Stitches per minute
the rate of reciprocal up and down motions by the needle bar (it is also equal to the speed of the needle bar in revolutions per minute, rpm)
Stitches per inch
spacing of the needle bar stitches along the machine (or vertical) direction of the fabric
Pile height
the distance of the loops below the primary fabric
Tufting elements for loop pile
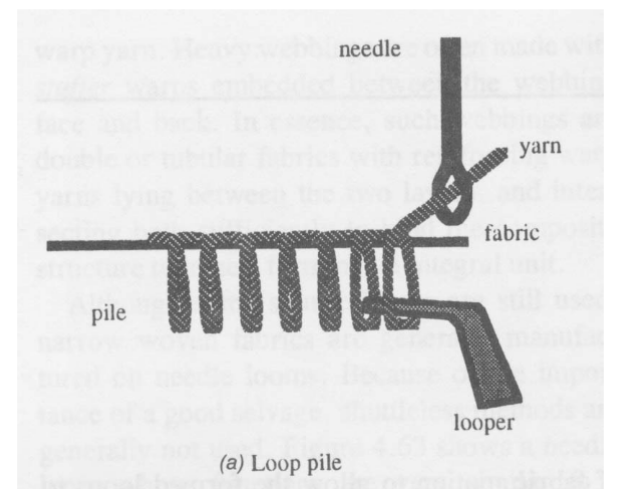
Various Surface Elements
By using different types of loopers, knives and yarn feed control, the following effects can occur:
Level loops
Multi Level Loops
Level cut loops
Multi Level cut and uncut loops
Level cut and uncut loops
Tufting Elements for cut pile
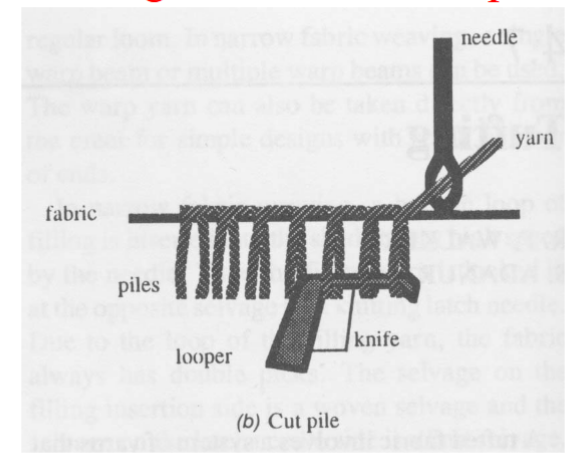
How to build a backing
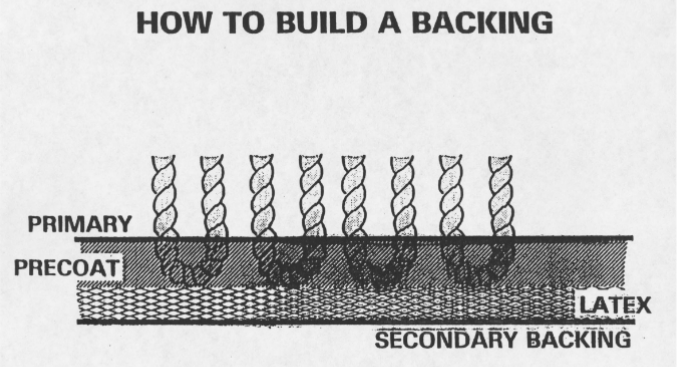
Twist Level
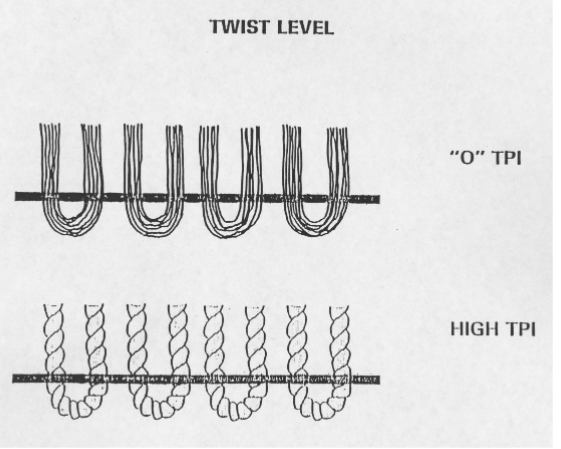
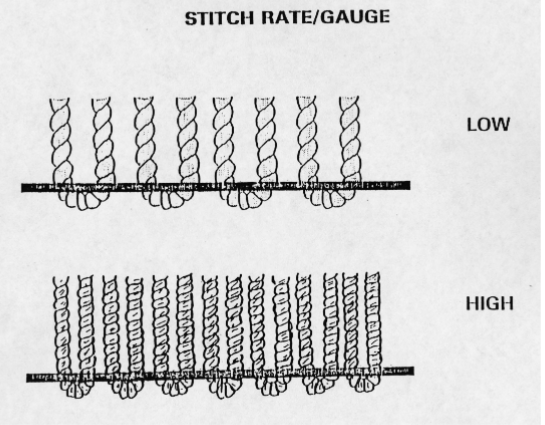
Stitch rate/gauge
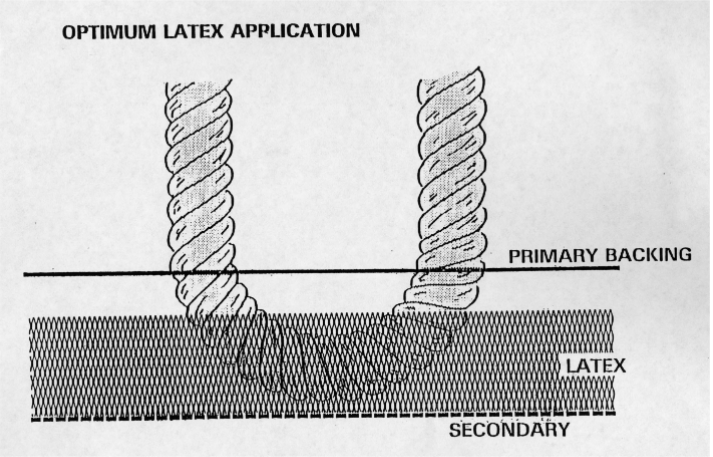
Optimum Latex application
Saxony Carpet
Cut-pile carpet
Highly twisted yarn
Evenly sheared
Medium length pile yarns
Plush Carpet
Cut-pile carpet
Pile yarns are slightly twisted, dense and very evenly sheared
Has the look of a solid, flat velvet surface
Shag Carpet
Loosely tufted carpet construction
Cut pile of 1-5 inches
Greater than normal spacing between tufts
Markets for Carpet
Homes (consumer)
Business institutions
Indoor
Outdoor
Factors for Carpet Selection
Location and traffic pattern
Frequency and kind of cleaning
Flammability
Nature of the environment
Static control
Typical Carpet Styles
Primary Backing
Jute (8-10 oz/sy)
Split film woven polypropylene (3-4 oz)
Polypropylene film sheet
Cotton duck
The secondary backing is added to provide…
Increased thickness (resilience, hand, insulation)
Dimensional stability
Improvement in locking tufts
Resistance to fraying
Skid resistance
The secondary backing fabric must…
Be dimensionally stable
Stick to the adhesive which binds it to the carpet
Resist environmental degradation
Tufted Fabric Control
Secondary Backing (type, composition construction)
Primary backing (type, composition construction)
Surface fiber (material, characteristics i.e: type, length, denier)
Yarn
Fabric
Coloration
Finish (shearing, brushing, final inspection)
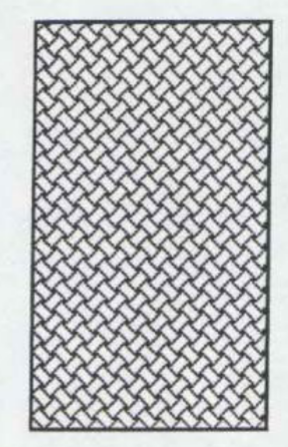
Braiding
Simplest form of fabric formation: diagonal intersection of yarns
Braiding Industrial Applications
Electrical wires and cables
Harnesses
Hoses and belts
Surgical sutures
Composite reinforcements
Reinforcement structure of sporting goods
Braiding Manufacturing
Geometry directly related to the machine that forms the fabric
2D Brading
Circular Braiding (Maypole and rotary)
3D Braiding
Common 2D Braiding Patterns
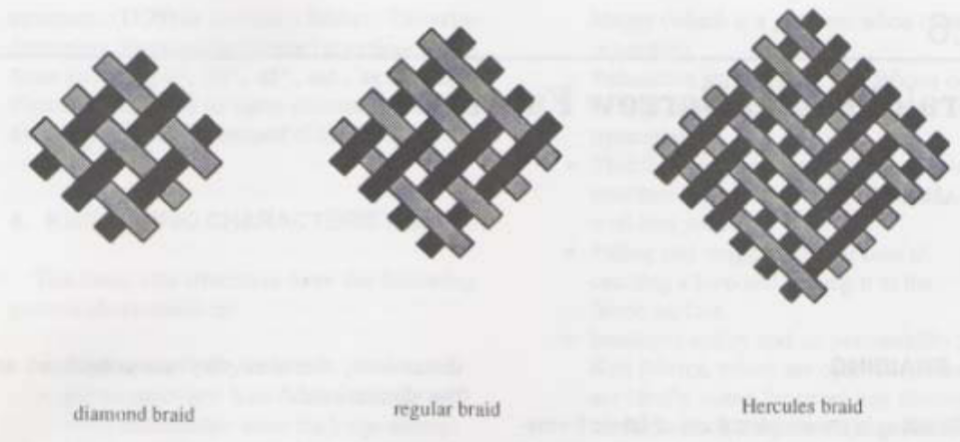
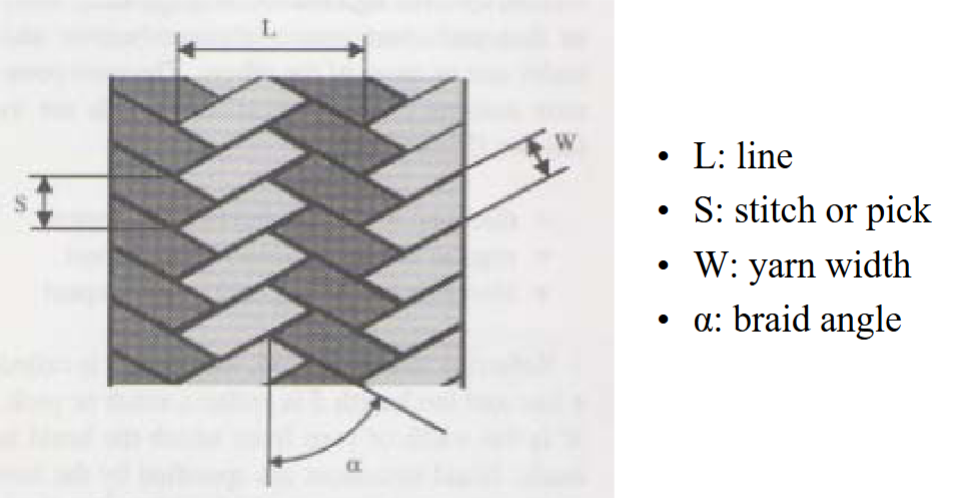
Braiding Fabric Parameters
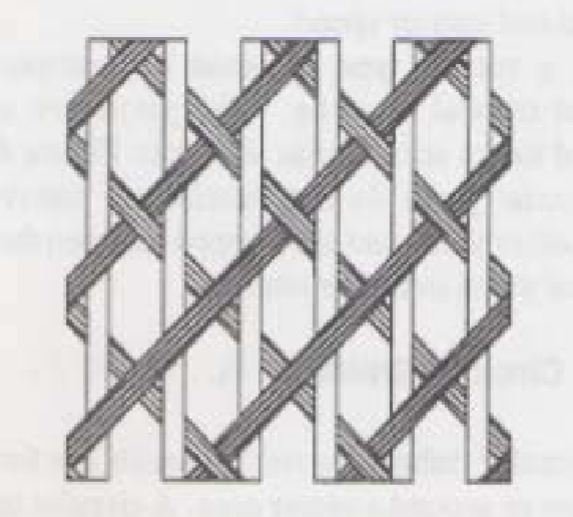
Triaxial Braid
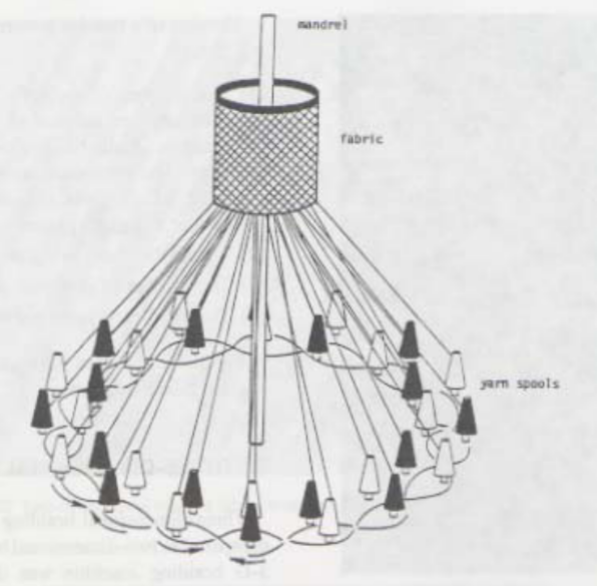
Schematic of Maypole Braiding
Size of Braid is governed by…
The number of carriers
Tubular braids: even number of carriers
Flat braids: odd number of carriers
Diameter of the yarns
Number of yarn ends per carrier
Number of yarns per unit length
Narrow Fabrics
Less than 12 inches (30 cm) in width
Woven selvage
Examples are Ribbons, Tapes, and Webbings
Narrow Fabrics Manufacturing
Several sets of warp yarns may be beamed to make several narrow fabrics, side-by-side on the same loom
A full width thermoplastic fabric can be cut into strips; edges are sealed, forming ribbons
Elastic webbing or tape is made by using bare or wrapped rubber warp yarn
Heavy webbings are made with stuffer warps
Single warp beam or multiple beams
Warp yarn can be taken from the creel directly
Needle inserts a loop of filling yarn into the shed at a high speed
Essential Fiber Properties for Architecture and Construction
Synthetic Fibers
Good strength
Hydrophobicity
Rot and fungi resistant
UV resistant
Temperature resistant
Biological resistance
Weather resistant
Advantages of Fibers in Construction
Weight
1/30th of the conventional weight of bricks and steel
Large, obstruction-free spans
Shorter erection time of the fabric envelope
Mechanical damage due to wear is restricted to a small area by the fabric structure
Damage can be easily repaired
Resistance to Earthquakes
Freedom to design various shapes and appearances
Film Membrane Structure
Transparent polymers in sheet form without coating or lamination
Clear vinyl, polyester or polyethylene
Less expensive and durable
Mesh Membrane Structure
Porous fabrics that are lightly coated with vinyl
Knitted meshes
High density polyethylene, polypropylene or acrylic yarns
Used as shelters from wind and sun
Not as much rain protection
Fabric Structures
The most widely used membrane structures
Coated or laminated to improve strength and environmental resistance
Coated Fabrics
“Envelope” of large building constructions
Airports, stadiums, sports halls
Schematic of a Laminate

Typical requirements for fabrics in construction
Resistance to deformation and extension under tension
Waterproof
Impermeable to air and wind
Resistant to abrasion and mechanical damage
Resistance to sunlight and acid rain
Base Fibers
Made of synthetic fibers
Carrier layer
Provides the necessary strength to the structure
High tenacity polyester
Fiberglass
Nylon
Continuous filament yarns
Inherent strength
Elongation resistance
Low yarn twist to carry higher tensile loads
Hydrophobic materials
Base Fabrics Manufacturing
Woven (plain, low-harness twill)
Warp tension not to exceed 9 N/tex during weaving
Rapier, projectile, air-jet and water-jet
Width up to 5m
Knit (warp-knit)
Nonwoven stitch bonded
Heat-setting usually not required
Coating and Laminating
Provides waterproofness
Protects base fabric from sunlight and weathering degradation
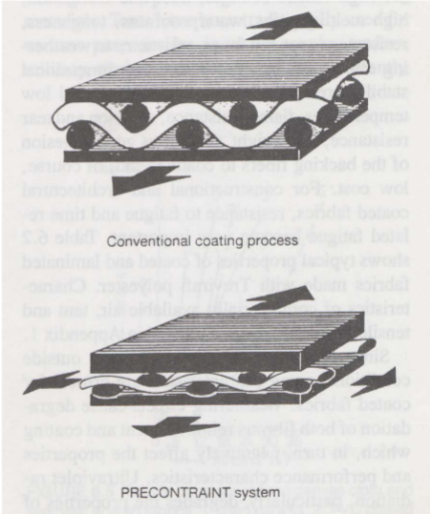
Polyester Fabrics
Usually coated or laminated with PVC films
Precontraint process used to improve dimensional stability
Fiberglass Fabrics
Usually coated with PTFE for durability
PTFE coated fiberglass is the only material that meets the US model building codes definition of non-combustible materials
Coated vs. Laminated

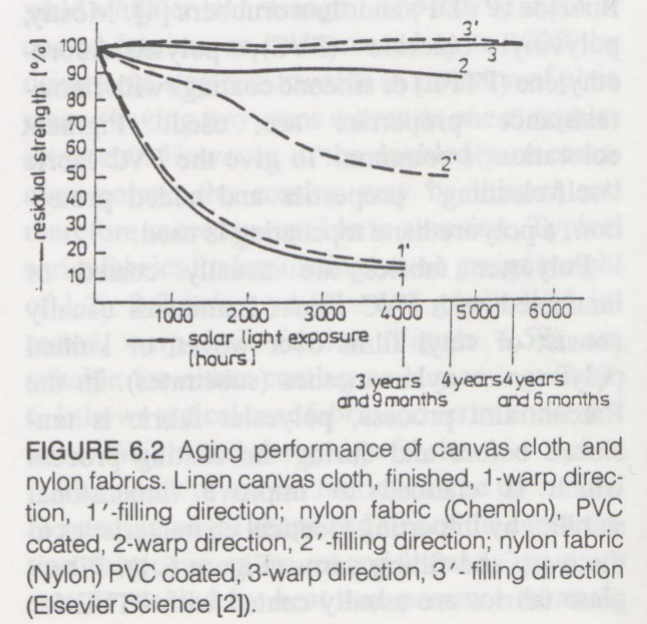
Aging of Fabrics
Weather effects and Residual strength
Application of Coated Fabrics in Building Structures
Membrane structures
Tents
Clear-span structures
Air structures
Tensile structures
Most widely used structures
PVC coated polyester
PTFE coated woven fiberglass
Silicone coated fiberglass
Tents
Probably the first constructions
Used by nomadic people, traders, military, explorers and campers
New tents for building construction, businesses, exhibits, leisure and recreation
Typical materials for tent walls include polyesters, nylon and vinyls

Pole Tents
Fabric is draped or hung
Mass produced

Tension tent
Fall between tents and tensile structures
Provides clear span
Does not require ropes or cords
Mass produced
Clear-Span Structures
Provides clear space beneath the fabric
Free of poles and other supporting elements
Fabric is pulled taut through channels in the frame’s ribs
More permanent than tents and less permanent than air or tensile structures
Can accommodate doors, flooring, insulation and HVAC
PVC coated polyester
Tension Structures
Metal bars, tensioning cables, wooden or metal frameworks
Fabric carries most of the load
Curvilinear structures
Fabric is highly tensioned
Schematic of Tension Structures
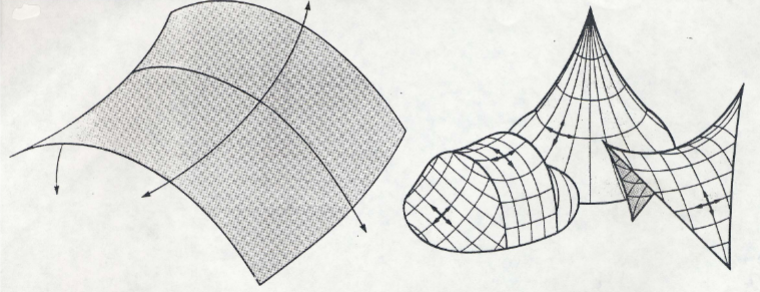
Basic building block shapes
Hyperbolic paraboloid
Hyperboloid
Fabric is double curved
Curvatures opposing each other from a single intersecting point
Crossed arc appears parabolic in cross section and as an “X” from above
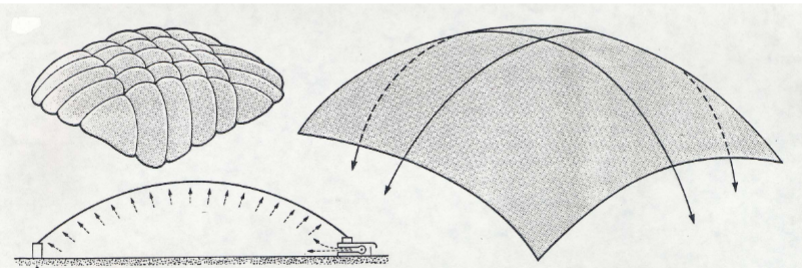
Air Structures
Air Supported System
Air pressure inside the envelope
Provides tensioning
Maintains required configuration and stability
Main components
Envelope (fabric)
Inflation system (fans)
Anchorage systems (cables and foundation)
Doors and access equipment
Pressure 0.3% above the ambient pressure
PVC coated polyester is the most used
Pressurized air-supported structure
History of Air Pressurized Structures
Collapse of some large-scale stadium domes in the early 80s
Well-built air structures are stable and strong
Modular buildings
Can be designed for nearly any shape
Surfaces are curved
Air Inflated Ribs (Air Beams)
Pressurized air-inflated support tubes
Wide diameter (42 inches)
Low pressure (4-10 psi)
Narrow diameter (4-18 inches)
High pressure (30-100 psi)
Mostly for lightweight, easy to transport military structures
Polyester and nylon

Safety tarpaulins for cold weather construction
Waterproof. flame retardant tarpaulins
Cold weather construction
Usually polyester fabrics (6-8 ounces)
Designing with Coated Fabrics
Three types of stresses
Stresses due to applied load tension in the fabric
Weight of suspended fabric
Stresses induced by natural forces die to wind, rain and snow
Textiles as Roofing Materials
Single-ply and multi-ply materials
Traditional built-up roofing (BUR)
Alternating plies of felts, fabrics and mats are bonded together with asphalt or coal tar
Single ply roofing
Introduced in the 1960s in the US
Used mostly in commercial applications
Single Ply Roofing
Made of single layer, watertight, weatherable membrane
Sealed at the seams and edges
Three types of membranes
Elastomers and thermosets (rubber)
Thermoplastics
Modified bitumens
Elastomer Membranes
EDPM (ethylene propylene diene monomer): most commonly used single ply elastomer
Neoprene (chloroprene rubber)
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE)
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE)
Polyisobutylene (PIB)
Properties Required in Roof Materials
Toughness, non-wicking, delamination resistance, chemical resistance, UV resistance, flame resistance and fungus resistance
Textiles for Acoustic and Heat Insulation
Two types of noises and buildings
Airborne noise
Impact noise
Three acoustical properties
To improve audibility
Preserve the natural quality of sound
Prevent the transmission of undesired sound
Reverberation Time
Time it takes a sound to die away in a budling
Absorbent materials to reduce the time
Carpet
Textile wall coverings
Curtains
Factors affecting sound absorption
Cut pile is better than a loop pile
In cut pile construction, pile height and density increase absorption
In loop pile, pile height is more important than density
Acoustic performance is independent of the pile fiber type
Filtration
Process of separation (separation of one material from another)
Purpose is to improve the purity of the filtered material and recover solid particles
Why textiles are suitable?
• Complicated structure
• Considerable thickness
• 3D network of fibers
• Small pockets of void volume
• “tortuous” path around textile fibers
• High filtration efficiency (25%-99.9%)
• Reasonable filter life before plugging
• Woven and nonwoven fabrics
Principles of Filtration
Main objective of the filter medium:
Maximize the possibility of collision
Subsequent retention of the suspended particles in the fluid
Minimize the energy lost
Fabric Structure
• Porosity: air volume/total volume
• The amount and distribution of air space influences the efficiency of filtration
• Air permeability: capacity of a porous medium to transmit fluids
• As the porosity increases, the pressure drop decreases
• Pressure drop should be minimized
Process of Separation
• Particle filtration
• Microfiltration
• Ultrafiltration
• Nanofiltration
• Reverse osmosis (hyperfiltration)
Filtration Equipment
• Filters for Dry Filtration
• Filters for Liquid Filtration
• Drum, disk, plate, frame, belt, vessel, ...filters
Liquid Filter Bags
• petroleum derivatives
• chemicals
• cutting oil
• cleaning fluid
• paints
• pharmaceuticals
• food processing
• beverages
• cosmetics
• semiconductors
Rotary Drum Filters
For slurry filtration
Large drum (20 ft in diameter, 20 ft long)
Vacuum type (rotary drum vacuum filters)
Drum rotates continuously and slowly
Lower part is dipped in the slurry
Vacuum is applied inside the drum to suck the fluid leaving a layer of solid on the outside of the fabric
As the drum rotates, solid is lifted and separated by the fabric by knife
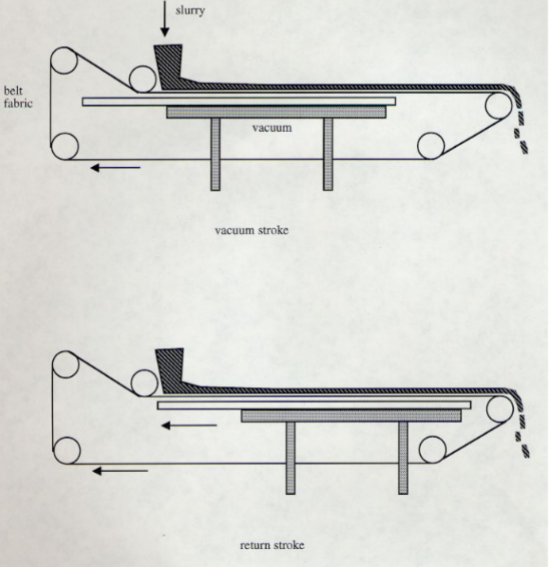
Belt Filter
Suction tray supports a rotating filter cloth
Continuous cycle of vacuum stroke/return stroke
Bag Filters
• Used for dust removal in industrial atmosphere
• Dust can be captured on the internal or external surface of the bag
• Large numbers of woven or nonwoven fabric tubes or bags used
• Suction created by a fan pulls the dusty air through the bags, collecting the dust on the fabric surface
• Filtration efficiency: 99.9% for fine dust collection
• Collected dust must be removed from the fabric surface periodically for efficient filtration
• Dust is collected in a container below the bags and removed periodically
Textiles in Dry Filtration
• mining, chemical, iron and steel industry
• cement, lime, clay, kaolin and ceramic works
• utilities
• feed, grain and food industry
• woodworking and furniture industry
• paper related industry
• textile plants
Polyester in Filtration
Advantages
Strength
Relatively high temperature resistance
low cost
Disadvantages
Low resistance to alkalis, acids and steams
Nonwoven Fabrics in Filtration
Filtration of gases
Needle punched fabrics
Good dimensional stability
Excellent particle retention
Freedom from plugging
Geosynthetics
Geo refers to earth
Synthetics is manmade materials
Manufacturing: Polymer and Fiber Engineering
Application: Civil Engineering
Heavy construction
Building construction
Hydrogeology
Environmental engineering
Soil, rock and ground related activities
Geosynthetic Functions
Separation of soils
Reinforcing poor soils
Soil filtration
Water drainage
Leak proof barrier for preventing liquid movement
Advantages of Geosynthetics
Performance (no deterioration of material or excessive leakage)
Economics (lower initial costs and long life)
Geotextiles
Largest group of geosynthetics
Traditional textile structures
Tremendous growth last 40 years
Biodegradation is not a problem
Flexible, porous fabric structures
Woven, nonwoven, warp knit
80 specific applications for geotextiles
Geogrids
• Small but rapidly growing segment of geosynthetics
• not textile-like structures
• plastics formed into a very open, gridlike configuration with large apertures
• at least 25 application areas
• two functions (reinforcement and seperation)
Geonets
• Manufactured by continuous extrusion of polymeric ribs at acute angles to one another
• large apertures in a netlike configuration
• function: drainage (to convey fluids)
Geomembranes
• Second largest group of geosynthetics
• Impervious thin sheets of rubber or plastic materials
• Used for linings and covers of liquid or solid storage facilities
• Primary function: liquid or solid barrier
• At least 30 individual applications
Geocomposites
Combination of the other geostructures
Major functions include separation, reinforcement, filtration, drainage, and moisture barrier
Geosynthetic Clay Liners (GCL)
• Newest member of the family
• Rolls of thin layers of clay sandwiched between two geotextiles or bonded to a geomembrane
• Needle punched, stitched or adhesive bonded
• Used as primary or secondary liners or beneath a geomembrane
Geo-others
• Threaded soil masses
• Polymeric anchors
• Encapsulated soil cells
• Any of the five major functions of geosynthetics
Designing with Geotextiles
Design by cost and availability
Design by specification
Using standard tables
Designed by function
Factor of safety (FS)
Design by Function
FS = Allowable property/required property
Allowable property (value based on a lab test that models the actual situation)
Required property (value based on design method that models the actual situation)
Geotextile Properties and Test Methods
• Physical Properties
• Mechanical Properties
• Hydraulic Properties
• Endurance Properties
• Degradation Properties
Application areas of medical textiles
Protective medical apparel
Implants
Blood filters
Surgical dressings
Biomaterials
Materials used in contact with tissue, blood, cells, protein and any other living substance