Module 9
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
STR- Short tandem repeats
The allele is based on the length of the DNA segment, with different alleles having different lengths because they have different numbers of copies of a short, repeated DNA sequence.
Polymorphic- important bc unlikely that two ppl will have same profile
VNTR
Variable Number of Tandem Repeats
Gel electrophoresis
Put samples in wells of gel
Run electrical current through sample (DNA is negatively charged)
Separates DNA based on SIZE
Small pieces move faster than big pieces

Microsatellite regions
Polymerase Chain Reaction
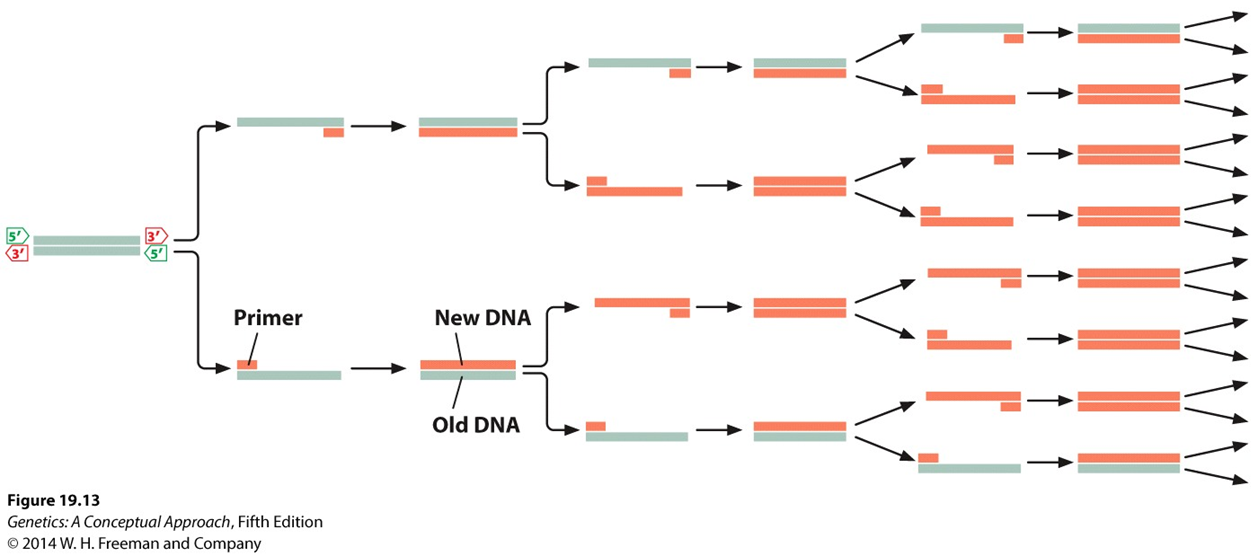
Denature DNA by heating to 95oC
Strands separate
Each strand is template for replication
Primers anneal to identify target that will be identified
Taq polymerase adds nucleotides to 3’ end of primer
Repeat many times
Who won nobel prize for PCR?
Kary Mullis
PCR Limitations
•Must know something about sequence surrounding gene of interest in order to use PCR to clone a gene
•PCR reactions are easily contaminated from other DNA in the lab
•Taq polymerase does not proofread and correct errors (error rate about 1 in 20,000 bp)
•Fragments amplified by PCR are relatively small (2000 bp standard, modified reactions up to 50,000 bp)
CODIS- Combined DNA Index System
Database funded by FBI
Uses 20 polymorphic regions
Loci assort independently- product rule applies
13 mil profiles from offenders and 3 mil from arrestees
845,000 from crime scenes
415,000 hits
Ethical Issues
Partial Matches and familial DNA searching
The Innocence Project
•There have been ~350 people who were falsely convicted released from prison and ~149 alternative perpetrators identified
SNP- Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
•a specific site in the genome where the DNA base varies in at least 1% of the population.
SNPS near each other are haplotype
TagSNPS= few SNPS used to identify a haplotype
SNPs in association studies
Can be correlated with genetic disorders
Quicker to identify DNA sequences between individuals than sequencing whole genomes
Ecogenetics
Study of genetic variation that affects responses to environmental chemicals
Risk of exposure to a chemical depends on the genetics involved in:
Transport of chemical
Metabolism of chemical
Excretion of chemical
Sensitivity to pesticides example
Parathion breaks down into toxic chemical paraoxan
Ppl with RR genotype detoxify 10x faster than those with QQ
Different populations have different QQ frequencies
Drug Sensitivities and Genetics
Individuals break down drugs at different rates
-Can lead to toxic (even fatal) complications
Eg. Suxamethonium
Muscle relaxant, short-acting anesthetic
• Most people take minutes to recover from small dose
• Autosomal recessive condition- takes HOURS to recover from small dose
• Can cause paralysis of respiratory system and death
Breast Cancer and Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen mimics the shape of estrogen, but, unlike estrogen does not stimulate the cells to divide
-helps with breast cancer
CYP2D6 gene metabolizes it
women with poor metabolism higher risk of cancer resurgence
Warfarin
Anti-coagulant
Greater than 10-fold inter-individual variability in the dose required to attain a therapeutic response
Required dose also varies depending on individual’s diet and is not the same for each person
What 2 genes influence effective Warfarin dose?
CYP2C9 (warfarin metabolic enzyme)
VKORC1 (Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex 1)
DTC Testing
The lab extracts and amplifies your DNA
Samples are placed on a gene chip that has 500,000 SNP probes
Your DNA binds to complementary probes
Computer identifies which SNPs are present in you and correlates your SNPs to those that are used for ancestry analysis.
DTC Testing differences from medical testing
SNPs used in DTC testing are limited and do not do as thorough a test as the medical testing conducted by genetic counselors and physicians.
Genomics ethical questions
How do you control/regulate the spread of use of your genetic information?
Is the information going to make life simpler or more complex?
Who has access to your genetic information?
Genetic counseling
Helping people understand and adapt to genetic disease
• Analyzing family and medical histories
• Education
• Risk assessment
• Counseling to help people reach decisions
• Psychological support
Genetic counselors responsibilities
• Obtaining medical history
• Assessing risk and assist in determining diagnosis
• Providing education about the disorder
• Reviewing options available to patient
• Facilitating genetic testing
• Assist in getting services covered by health insurance
• Providing referrals to support groups, medical and social service agencies
Non directive counseling
The genetic counselor shares his/her expertise, knowledge and experiences
But the patient and the patient’s family members are responsible for making the decision that they feel is best for their situation
Prenatal Genetic Counseling
Positive results on screening tests
High risk pregnancies due to age (>35)
Anomalies seen on ultrasound
Those interested in diagnostic testing
Family history of genetic disorder
Individuals with fertility problems or repeat pregnancy loss
Prenatal exposures
Screening vs diagnostic meaning
Screening is estimate for risk
Diagnostic is a specific diagnosis
Screening vs Diagnostic tests in pregnancy
Screening
1st tri screening (ultrasound and protein levels)
Maternal serum screening (levels of 4 proteins)
Cell-free DNA screening (baby’s DNA in mother’s blood)
Ultrasound- morphological appearance
Diagnostic
CVS
Amniocentesis
Karyotype and Microarray analysis
Prenatal microarray is now offered to anyone who undergoes a diagnostic procedure
Informed consent is crucial
• Consanguinity
• VUS (variant of unknown significance)
Pediatric Genetic Counseling used for children and adults with
Children with a family history of genetic disorders to rule out or diagnose suspected syndromes
Children with Developmental or Intellectual Delay
Babies with abnormal newborn screening tests.
Children with teratogenic exposures
Children with dysmorphic (atypical) features
NICU consultations
PICU consultations
Known diagnoses
Failure to thrive
Autism
Cancer Genetic Counseling
Family history of cancer
Been diagnosed with cancer at a young age
Been diagnosed with multiple cancers
Individuals who need more information to make decisions regarding their medical care
A known family cancer syndrome or mutation
Genetic Counseling Career Opportunities
Clinical Genetic Counselor
Laboratory Counselor
Public Health Counselor
Health Educator
Public Policy Consultant
University Faculty Member
Private Healthcare Company Employee
Science Researcher
How to Become a Genetic Counselor
Bachelor's degree
Shadowing a genetic counselor
Master’s degree in Genetic Counseling from an ABGC accredited program
Board certification