ELSEVIER: LABORATORY CALCULATIONS | Quizlet
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
How many liters are in 4 dL?
a. 400
b. 40
c. 0.4
d. 0.04
c. Each liter contains 10 dL, so multiply 4 dL x
1 L/10 dL (or 0.1, which is equivalent) to cancel
out the deciliter units.
How many liters are in 3 mL?
a. 0.003
b. 0.000003
c. 0.0000003
d. 0.000000003
b. Each liter contains 100,000 mL, so multiply 3 uL x 1 L/100,000 uL (or 0.000001, which is equivalent) to cancel out the microliter units.
How many micrograms are in 10 mg?
a. 100
b. 1000
c. 10000
d. 100000
c. Each gram contains 1000 mg, so multiply 10 mg
x 1 g/1000 mg to get the number of grams. Then
multiply the number of grams by the number of
micrograms in each gram (106
) to get the number
of micrograms present.
How many grams are in 0.85 kg?
a. 8.5
b. 85
c. 850
d. 8500
c. Each kilogram contains 1000 g, so multiply
0.85 kg by 1 x 103 g/1 kg to get the number of
grams.
25" C is equivalent to how many degrees Fahrenheit?
a. 31.7
b. 45.9
c. 77
d. 102.6
c. Using the equation to convert degrees Celsius to
degrees Fahrenheit:
F= 9/5 C + 32
F= 9/5 25 + 32
F= 9/5 C + 32
F= 45 + 32
F1⁄477
80" F is equivalent to how many Kelvin?
a. 285.4
b. 299.7
c. 353.0
d. 359.4
b. First convert degrees Fahrenheit to degrees
Celsius:
C= 5/9 (F - 32)
C= 5/9 (80 - 32)
C= 5/9 (48)
C= 26.7
Then convert the degrees Celsius to Kelvin:
K= C + 273
K= 26.7 + 273
K= 299.7
How would you prepare a 1=5 dilution of a urine
sample?
a. 1 part urine + 3 parts diluent
b. 1 part urine + 4 parts diluent
c. 1 part urine + 5 parts diluent
d. 1 part urine + 6 parts diluent
b. A 1/5 dilution is equivalent to 1 part of urine in a
total of 5 parts. The remaining 4 parts are the diluent, so to prepare a 1/5 dilution of a urine sample,
use 1 part urine and 4 parts diluent.
A 50-g/L solution was diluted 1:5. This diluted sam-
ple was then diluted 1:10. What is the concentration
of the final solution?
a. 0.8 g/L
b. 1 g/L
c. 2.9 g/L
d. 3.3 g/L
b. 1 g/L
How much diluent is needed to prepare 300 mL of
a 0.2-M working solution from a 0.8-M stock
solution?
a. 75 mL
b. 225 mL
c. 900 mL
d. 1200 mL
b. When making a dilution that changes concentrations, use the following formula (where 1 represents the stock solution and 2 represents the
working solution)
What is the molarity of a solution containing 2 mol
of sodium in 400 mL of water?
a. 0.005 M
b. 0.5 M
c. 5 M
d. 50 M
c. Molarity is the number of moles per liter of solution. In this problem, milliliters are given as units
so convert this to L (1000 mL in 1 L)
How many moles of glucose are in 300 mL of a 2-M
glucose solution?
a. 0.6
b. 6
c. 60
d. 600
a. Multiply molarity (which is converted from M to mol/L) by volume to solve for moles.
How many grams of NaCl are required to make
0.50 L of a 1.5-M NaCl solution? (MW of
NaCl1⁄458.5 g/mol)
a. 4
b. 19.5
c. 44
d. 175.5
c. Multiply the volume of the solution by the molarity (written as mol/L) by molecular weight (g/mol)
to solve for grams
What volume of diluent is in a 4-M solution contain-
ing 125.6 g of KCl (MW1⁄474.5 g/mol)?
a. 0.42 L
b. 2.37 L
c. 6.74 L
d. 421 L
a. Knowing that 4 M equals 4 mol/L, solve for volume by multiplying the weight of the sample
by the inverse of the molarity by the inverse
of molecular weight (to isolate liters in the
numerator)
What is the normality of a 2-L solution of 54.2 g
H2SO4 (MW1⁄498.0 g)?
a. 0.28 N
b. 0.56 N
c. 0.91 N
d. 1.11 N
b. 0.56 N
How many grams of NaCl (MW1⁄458.5 g/mol) are in
a 0.67-osmol/kg solution that was made from 3.0 kg
of water?
a. 39.4
b. 59.1
c. 102.2
d. 236.4
b. First determine the amount of osmoles in the 3-kg solution by setting up a proportion
In the calculation of themean,what does "n" represent?
a. The sum of the values
b. The number of values in the set
c. The average of the values
d. The middle number of the set
b. The number of values in the set
What is the mode a reflection of in a data set?
a. The average of the individual values in the data set
b. The most frequent number in the data set
c. The average of the lowest and highest numbers in
the data set
d. The number in the middle of the date set
b. The most frequent number in the data set
Which of the following statistics is equivalent to the
square root of the variance?
a. Coefficient of variation
b. Standard deviation
c. Sensitivity
d. Specificity
b. Standard deviation
19-21
Cholesterol Results for 10 Patients
180, 200, 150, 170,
150, 165, 205
150, 168, 145
19. Using the data in Box 11-1, what is the mean of the
cholesterol results?
a. 150
b. 168
c. 187
d. 189
b. 168
19-21
Cholesterol Results for 10 Patients
180, 200, 150, 170,
150, 165, 205
150, 168, 145
20. Using the data in Box 11-1, what is the mode of cholesterol results?
a. 150
b. 165
c. 168
d. 187
a. 150
19-21
Cholesterol Results for 10 Patients
180, 200, 150, 170,
150, 165, 205
150, 168, 145
Using the data in Box 11-1, what is the standard
deviation of the cholesterol results?
a. 13.8
b. 15.1
c. 21.2
d. 26.1
c. 21.2
What is the midrange of the following data set: 10,
4, 6, 7, 12, 9, 14?
a. 7
b. 8.8
c. 9
d. 9.5
c. 9
Which of the following is correct when rounding
2.25 to one decimal place?
a. 2.2
b. 2.3
a. 2.2
What is the sum of the following figures:
0.125 + 3.45 + 32.981?
a. 36.556
b. 36.55
c. 36.56
d. 36.6
c. 36.56
Which of the following represents the product of
(4 x 103)(6 x 102)?
a. 10 x 105
b. 10 x 106
c. 24 x 105
d. 24 x 106
c. 24 x 105
The closeness of a test value to the actual value describes which of the following?
a. Accuracy
b. Precision
c. Reproducibility
d. Reliability
a. Accuracy
Which of the Westgard rules is violated in the control
data below? (Figure 11-3)
a. 22s
b. R4s
c. 41S
d. 10x
c. 41S
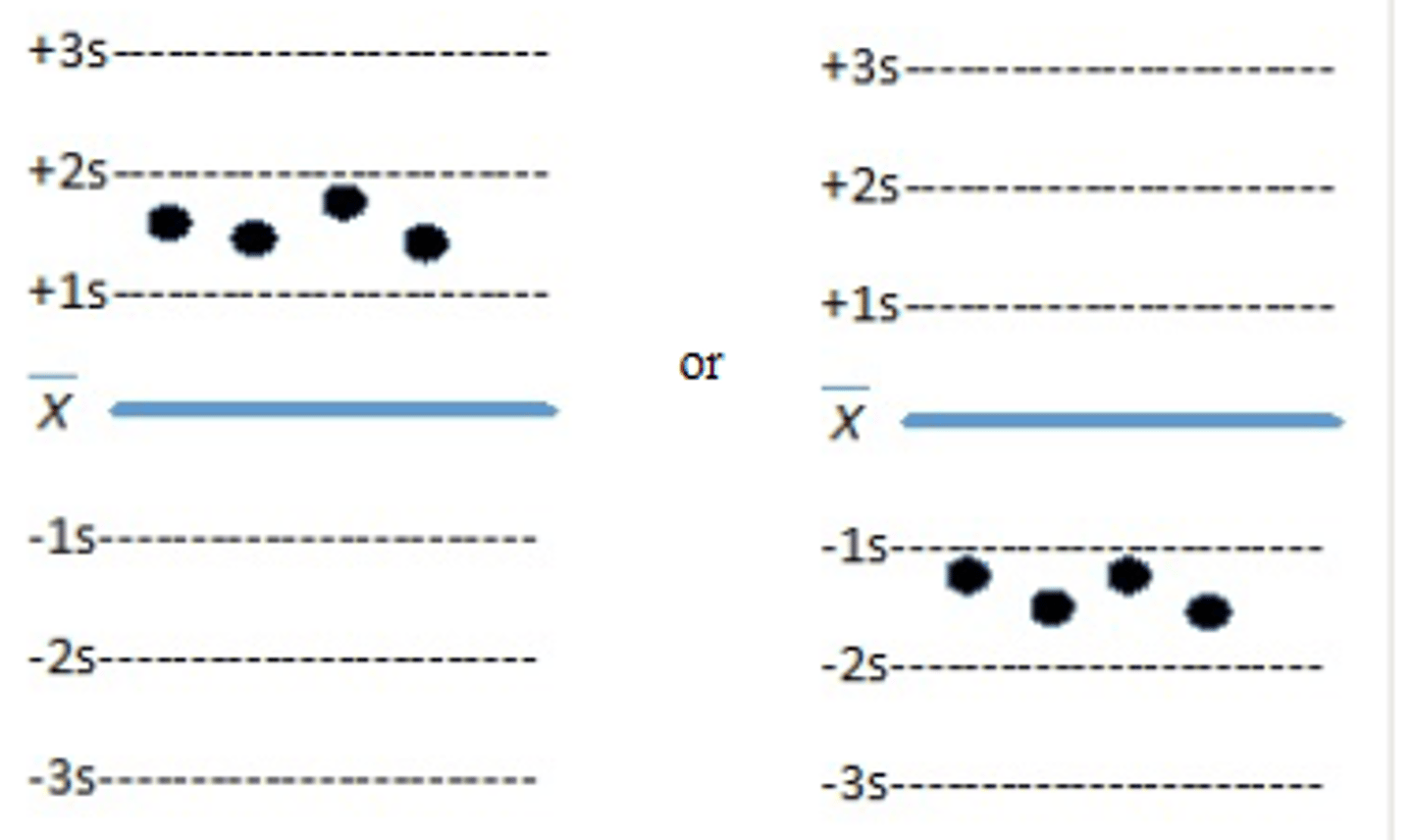
Which of the following Westgard rules is indicative
of random error?
a. 13S
b. 22s
c. 41s
d. 10x
a. 13S
Which of the following pairs of concepts are correctly matched?
a. Sensitivity: prevent false negatives :: specificity:
prevent false positives
b. Sensitivity: prevent false positives :: specificity:
prevent false negatives
c. Sensitivity: precision :: specificity: accuracy
d. Sensitivity: coefficient of variation :: specificity:
standard deviation
a. Sensitivity: prevent false negatives :: specificity:
Which of the following equations represents the clinical sensitivity of a test?
a. TP/TP + FN x 100%
b. TN/TN + FP x 100%
c. TP/TP + FP x 100%
d. TP/TP + FP x 100%
a. TP/TP + FN x 100%