M2 Lesson 3 - Isomerism: Fischer Structure and Haworth Structure
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Structural or constitutional isomers
share the same chemical formulas, but their atoms are arranged differently.
Skeletal isomerism (chain isomerism)
structural isomers in which components of the skeleton are arranged in a different order. This is most commonly seen when the skeleton or backbone consists of a carbon chain
Position isomerism (regioisomerism)
constitutional isomers in which a functional group or substituent changes position on a parent structure.
Functional group isomerism
structural isomers with the same molecular formula, but with atoms connected differently so dissimilar functional groups are formed.
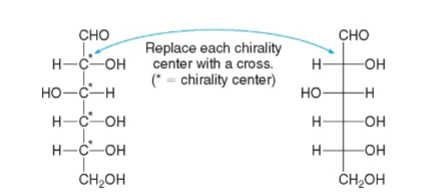
chirality centers
All carbohydrates have 1 or more
D
is used when the –OH group is drawn on the right side of the carbon chain
L
is used when the –OH group is drawn on the left side of the carbon chain
glucose
as four chirality centers and is drawn as
farthest
The configuration of the chirality center _____ from the carbonyl group determines whether a monosaccharide is D or L.
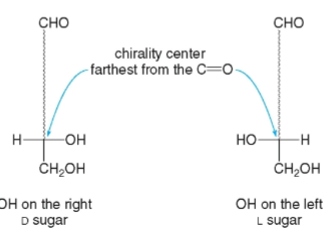
D-sugars
All naturally occurring sugars are
hemiacetal
When an aldehyde reacts with an alcohol, a ______ is formed
anomer
The C atom that is part of the hemiacetal is a new chirality center, called the _____ carbon.
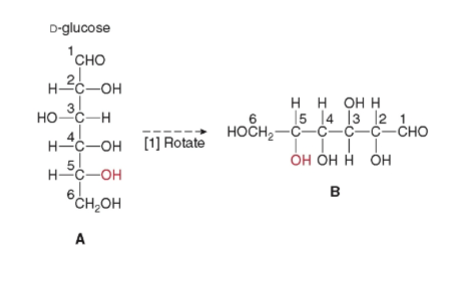
90degree
The first step in cyclization is to rotate glucose
six-membered ring
after turning to 90 degrees next, the chain must be twisted around, forming
a ______-
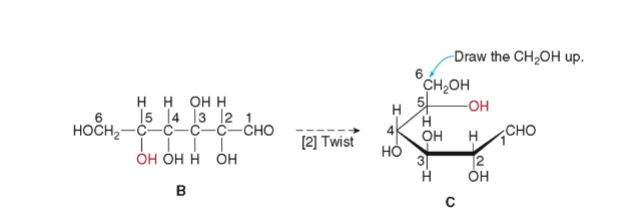
Haworth projections
As the reaction occurs, there are two cyclic forms of D-glucose, an a anomer and a b anomer.
•These rings are called _________.