Viruses and Viroids
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Virion
Metabolically inert (inactive), extracellular virus particle, not considered living organism
what happens when a virion enters a host
viral nucleic acids become active and viral multiplication results THEREFORE VIRUSES ARE ALIVE WHEN MULTIPLY IN A HOST
Obligatory intracellular parasites
require living host cells in order to multiply
What can viruses do nor not do
DNA or RNA, surrounded by protein coat (capsid), no ribosomes, no plasma membrane, no binary fission, can pass through bacteriological filters (WAYYY SMALLER THAN BACTERIA)
What do viruses lack?
enzymes for protein synthesis for ATP generation thus they take over metabolic machinery of a host cell
Viruses may be
an agent of disease, agent of heredity (permanent genetic change which may be harmful, have no effect, or provide beneficial effects
what are we all infected with?
Herpes virus, over 90% of U.S. population has one or both of HSV-1 and HSV 2
ever had chicken pox?
still have varicella-ZosterVirus
What is the Tobacco Mosaic virus
Adolf Mayer demonstrated TMV could be transmitted form plant to plant,
who is dimitri iwanowski
the man who attempted to filter out the infectious agent in TMV plants, found that sap from infected plants was filtered through a porcelain filter, filtered sap was still infectious
first disease caused by a filterable agent
Yellow fever
Host range
spectrum of host cells the virus can infect
why can viruses only able to infect specific types
match up with specific host species, and only sometimes cross host species barrier thus expanding host range
- human specific
- animal specific
bacteriophage (phage)
viruses that infect bacteria
phages are a major component of the human virome why is this important?
enemy of my enemy, phage therapy uses phages to treat bacterial infections
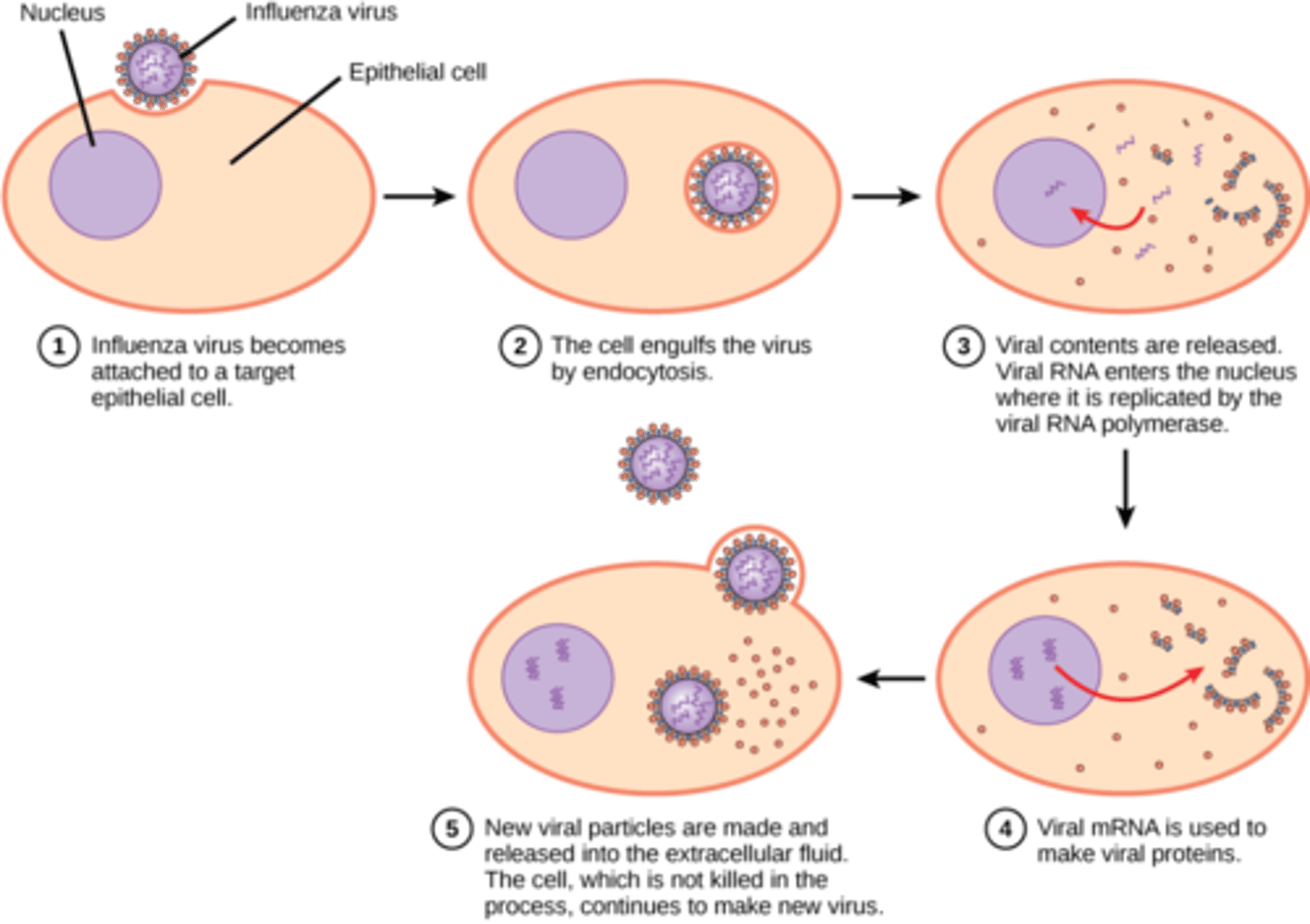
steps to viral infection
Influenza virus becomes attached to a target epithelial cell
The cell engulfs the virus by endocytosis
Viral contents are released, Viral RNA enters the nucleus where it is replicated by the viral RNA polymerase
Viral mRNA is used to make viral proteins
New Viral particles are made and released into the extracellular fluid the cell, which is not killed in the process, continues to make new virus
characteristics of living organisms
- Responsiveness
- Order
- Growth
- Metabolism
- Energy transformation
- Reproduction
- Made of cells
Viruses components
2 components: capsid and genetic material
why are viruses not living
cannot carry out life processes (metabolism, reproduction) without a host
Cells components
genetic material and the other "stuff" that lets them make proteins
What is a virion
complete fully developed infectious viral particle composed of nucleic acid and surrounded by a protein coat
RNA
single- stranded, instead of thymine they have uracil
DNA
double stranded, instead of uracil they have thymine
Viruses can either be DNA or RNA but
NEVER BOTH, they can have
ssRNA( single-stranded)
dsRNA (double-stranded)
ssDNA (single-stranded)
dsDNA (double-stranded)
Which type of virus infect every type of organism
viruses with ALL types of nucleic acids eg Retroviruses which has only been found in animals
retroviruses have rna and insert into the host genome (ssRNA)
3 shapes of viruses
helical, polyhedral, complex
what is viral capsid made up of
capsomeres
functions of capsids
Protection from environment
Facilitate interaction with host cell
Assist in movement between cells in multicellular organisms
Facilitate vector-mediated transmission between organisms
enveloped virus
membrane derived from portions of host cell membranes
purpose of envelope
Helps them attach to host cells
May help them avoid immune system
The membranous envelope sensitive to desiccation, heat, and detergents = easier to kill than non-enveloped viruses
EX: herpesviruses, Hepatitis D, Retroviruses (HIV)
nonenveloped helical virus
capsid is resistant to disinfectants and solvents
Norovirus: high resistance and can remain infective for several months in environment
which is more resistant to disinfectants non-enveloped or enveloped
non-enveloped
viral classification
Not very standardized
Often named for host or appearance or disease
Usually grouped by structure, chemical composition, and genetic similarities
Virus families end in -viridae
Viral genera usually end in -virus
what is HPC
human papilloma (warts) virus
what is HIV
human immunodeficiency virus
ranavirus
Virus that infects fish, amphibians, reptiles (Rana is latin for frog; it was first discovered in a frog)
zoonosis
an infectious disease transmitted between species from animals to humans (or vice versa)
antigenic shift
animal pathogens undergoes genetic change in an intermediate host and can infect humans
how to quantify viruses
plaque assay
what is plaque assay
Virus Determine number of infectious units per volume of fluid
Mix dilution of virus with enough bacterial cells that a lawn of cells form
Count zones of lysis clear zones caused by virus bursting or lysing cells) = plaque
Assume each plaque originated from 1 virus
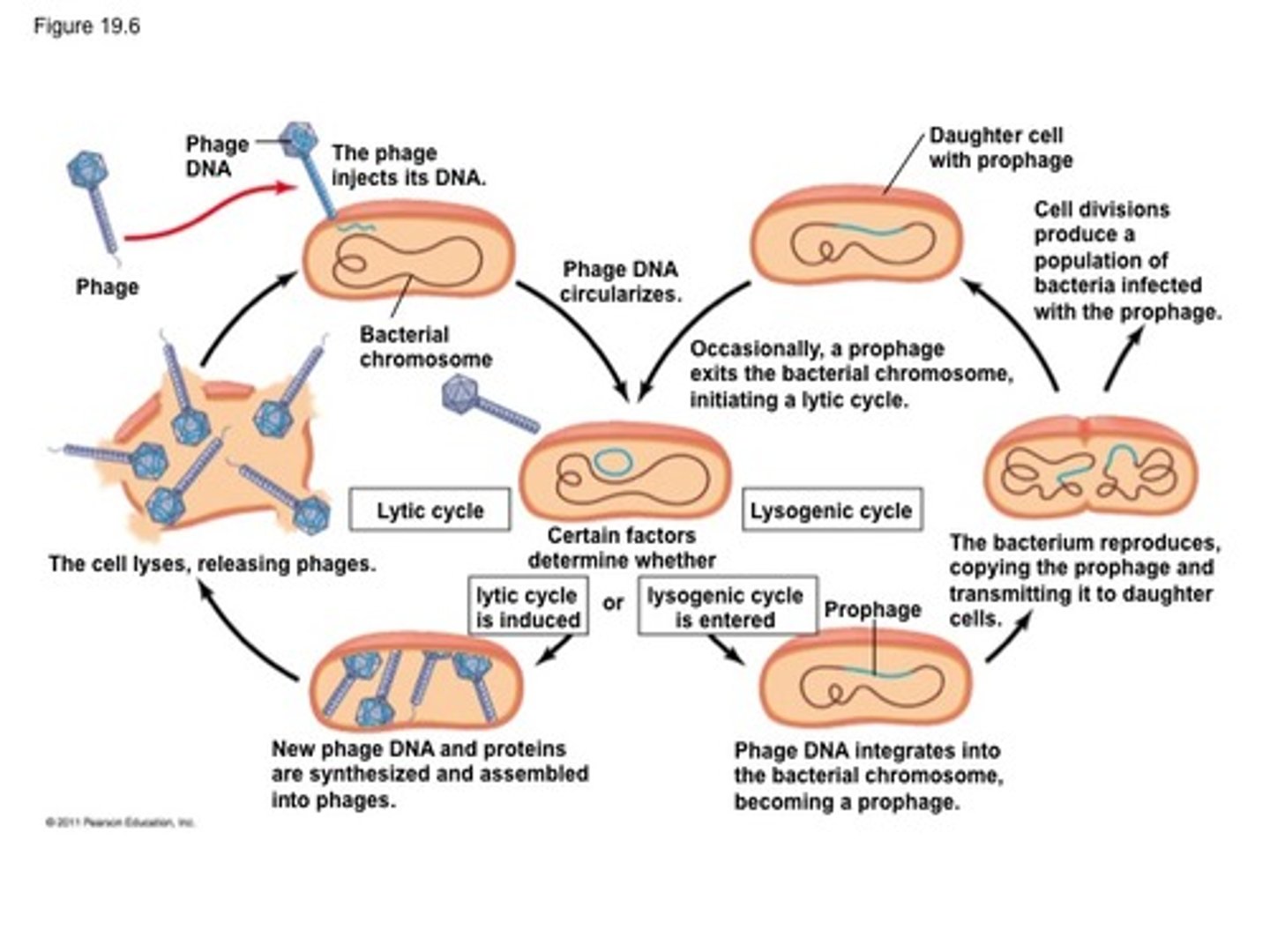
lytic cycle of bacteriophage
Phage attaches to host cell and injects DNA
Phage DNA circularizes and enters lytic cycle or lysogenic cycle
New phage DNA and proteins are synthesized and assembled into virions
Cell lyses, releasing phage virions
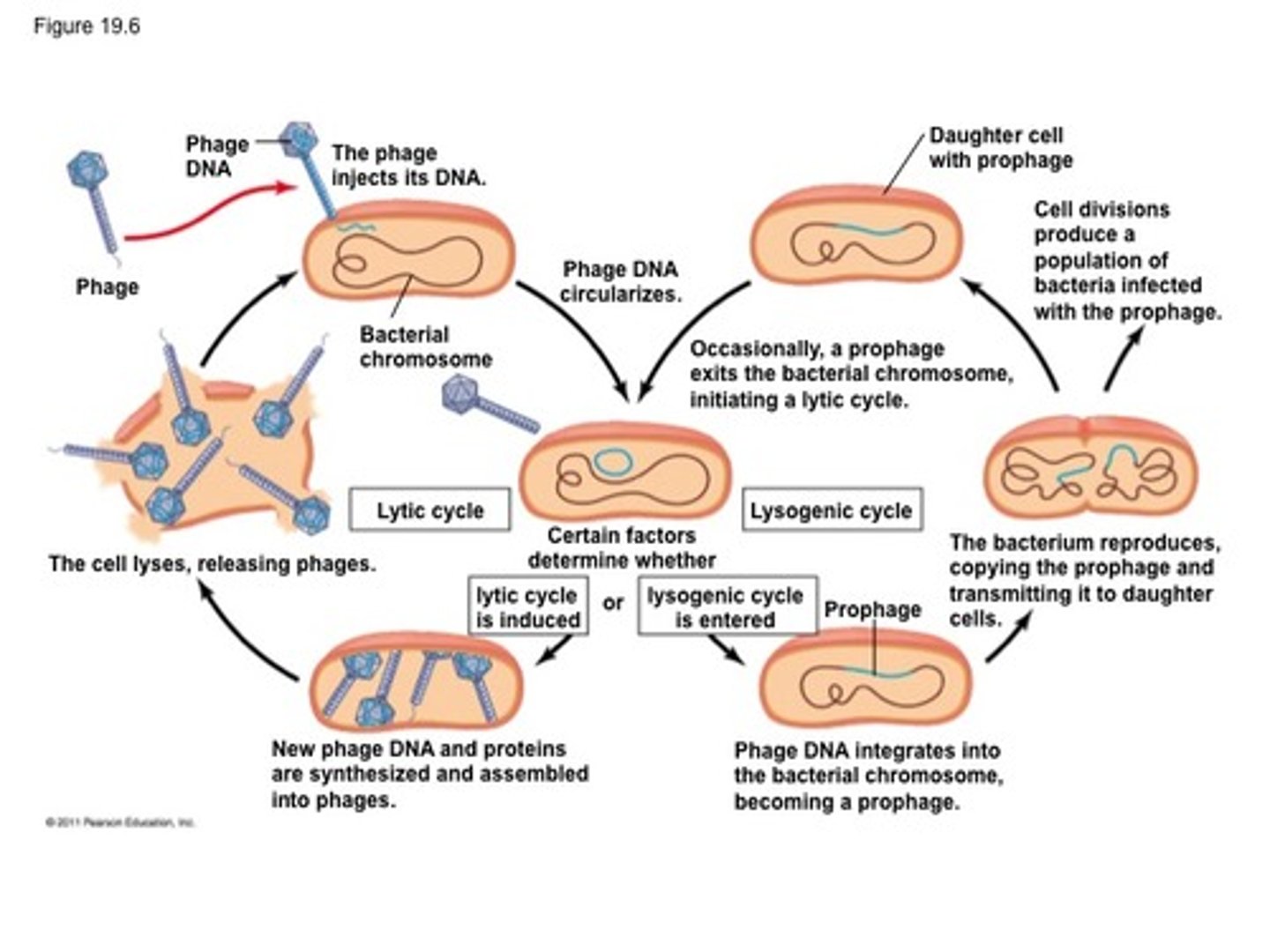
lysogenic cycle of bacteriophage
Phage attaches to host cell and injects DNA
Phage DNA circularizes and enters lytic cycle or lysogenic cycle
Phage DNA integrates within the bacterial chromosome by recombination becoming a prophage
Cell undergoes binary fission
what does lytic cycle end with
lysis
what does lysogenic cycle end with
host cell remains alive, lysogenic cells immune to reinfection by same phage
phage conversion
cells ma have new properties (produce a toxin)
transformation
Some viruses can cause our cells to become cancerous (HPV)
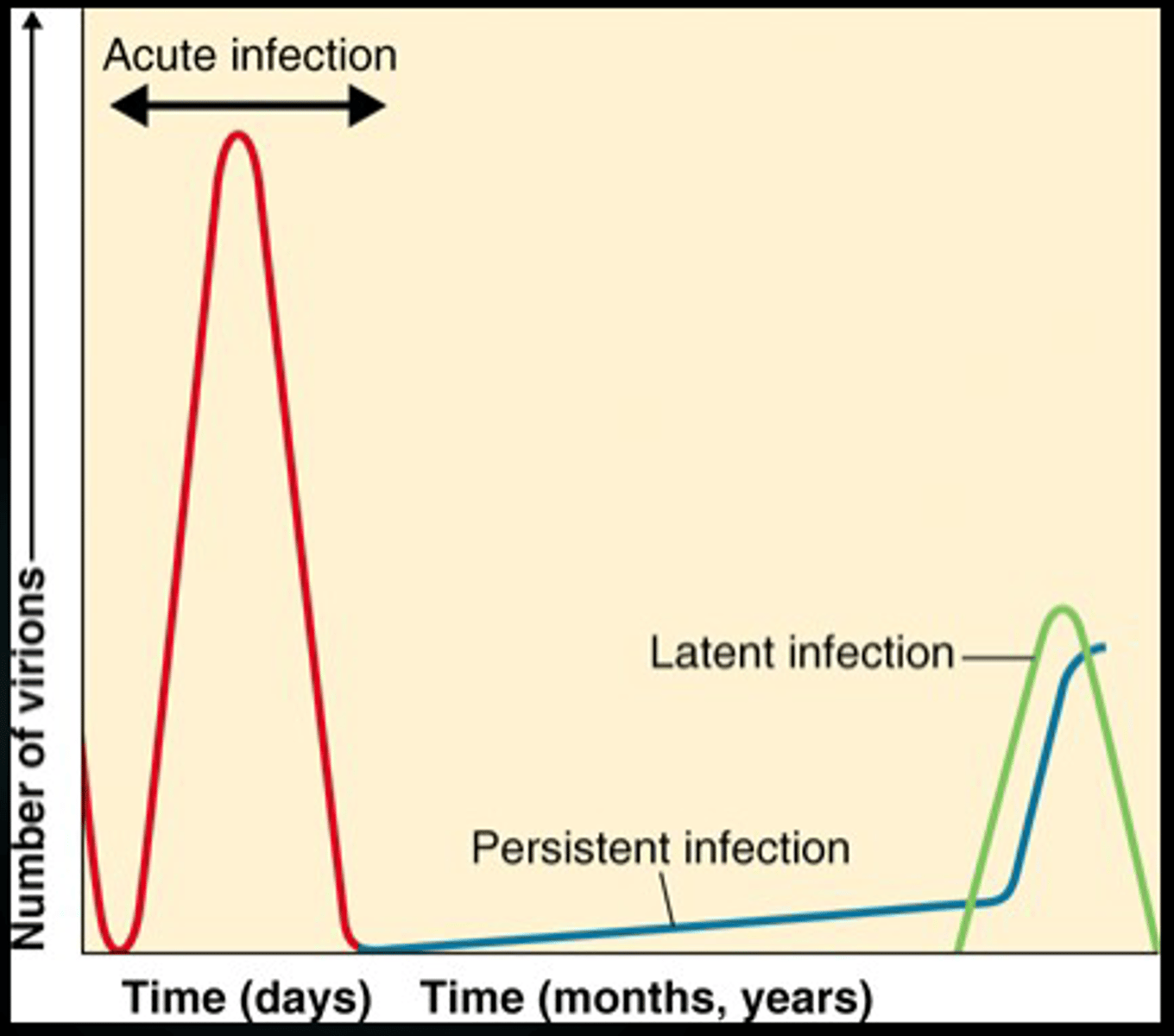
lysis
Multiplication if virus causes cell death and release of virus (Influenza)
persistent
slow release of virus without cell death (rare form of encephalitis)
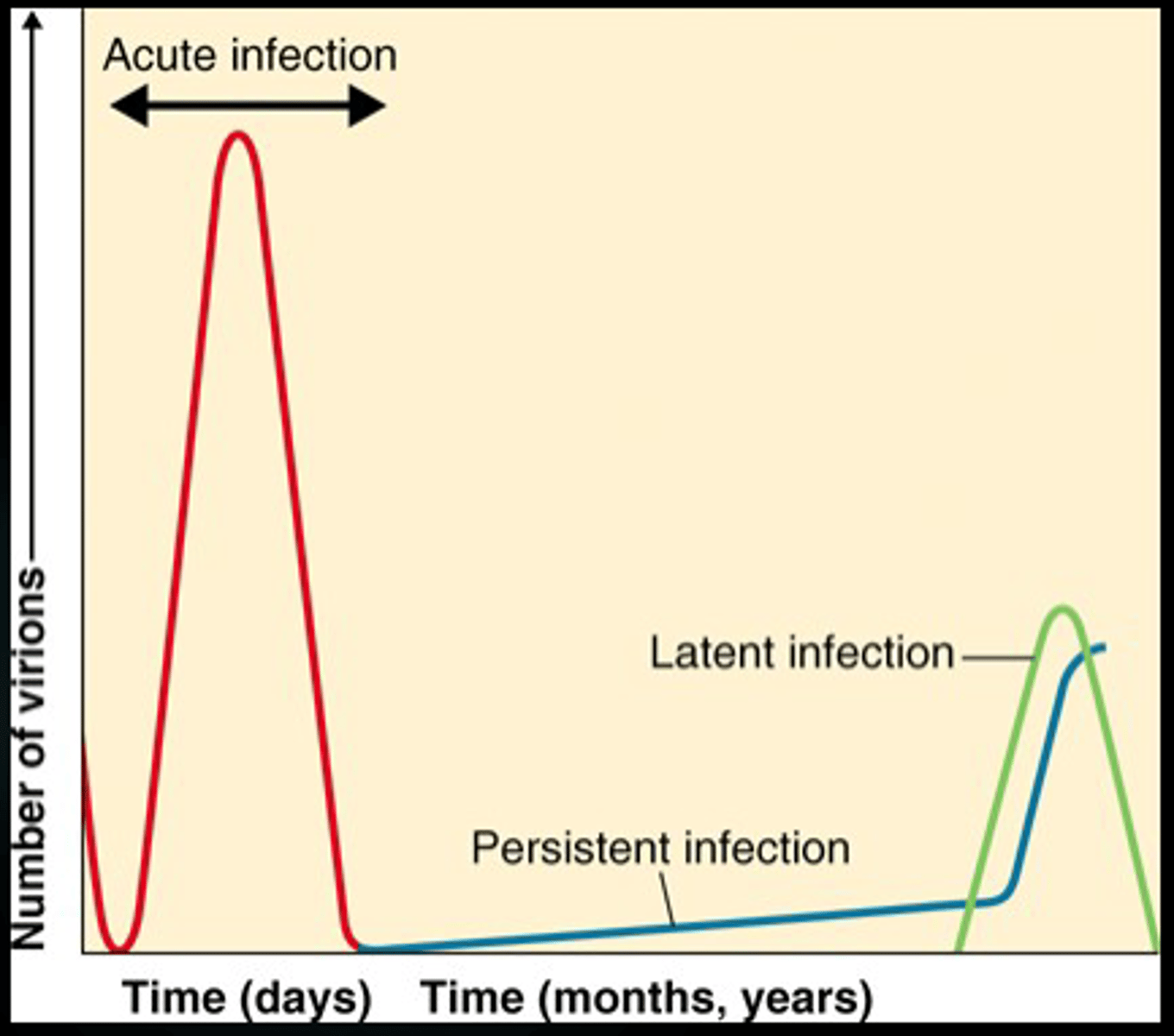
latent
Virus lays dormant until activated by a stimulus (herpesvirus that causes chickenpox)
tumor viruses
Virus makes proteins that interfere with cell functions that would normally prevent excessive growth
Example: HPV
Group of more than 200 related viruses
40+ spread through sexual contact
Low risk: non cancerous
High risk: cancerous ( about 12 types)
low risk
most high-risk infections are
asymptomatic and go away within 1-2 years. Some can persist for many years through - cancer risk higher
plant disease and viroid's how to infect plants?
remember plant cells have cell wall therefore protection
- viruses must enter through wounds or be assisted by plant parasites
plant viroids
short pieces of naked RNA, replicated continuously by host range RNA polymerase
RNA does not code for any proteins through
may cause disease by gene silencing
prion
infectious agent consisting of a self replicating protein, with no detectable nucleic acid (mad cow disease)
Diseases caused by conversion of normal host glycoprotein called Prpc (located on chromosome 20) into infectious form called PrPsc
chronic wastings disease
Affects deer, elk, and moose (not a huge % of population)
Caused by prions
Transmission can occur through direct contact and environmental
So far no evidence that it can be transmitted to humans but CDC recommends not consuming meat from infected animal