adbio cardiovascular
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Cardiovascular system
-organ system that distributes blood to all parts ofthe body
-Major function - transportation, using blood as the transport vehicle
This system ___,__,___ hormones and other substances vital for body homeostasis to and form cells
carries oxygen, nutrients, cell wastes
The force to move blood around the body is provided by the ___.
The force to move blood around the body is provided by the pumping heart and blood pressure
size and weight of human heart
The human heart is approximately the size of a fist, and weighs less than a pound
It is enclosed within the __, the medial cavity of the thorax, and flanked on each side by the lungs
inferior mediastinum
apex is directed towards where
The pointed apex is directed toward the left hip
apex rests where
rests at about the fifth intercostal space
the broad aspect or base is directed towards where
points toward the right shoulder
the base lies where
lies beneath the second rib
pericardium
The heart is enclosed by a double-walled sac called the
fibrous pericardium
-The superficial loosely fitted part is called the fibrous pericardium
-Protects and anchors the heart
two-layer serous pericardium
Deep to the fibrous pericardium is the slippery,
parietal layer
-lines the interior of the fibrous pericardium
-attaches to the large arteries leaving the heart and then makes a U-turn and continues inferiorly over the heart surface as the visceral layer, or epicardium
serous pericardial membranes
-produces A slippery lubricating fluid
-which allows the heart to beat easily in a relative frictionless environment
pericarditis
-Inflammation of the pericardium often results in a decrease in the serous fluid
-The cause the pericardial layers to stick, forming painful adhesions that interfere with heart movements
1. outer epicardium 2. myocardium 3. endocardium
The heart walls are composed of three layers:
myocardium
consists of thick bundles of the cardiac muscle twisted into ringlike arrangements
This is the layer of the heart that actually contracts.
Reinforced by dense, fibrous connective tissue ("heart skeleton")
endocardium
is a thin, glistening sheet of endothelium that lines the heart chambers
Continuous with the linings of the blood vessels leaving and entering the heart
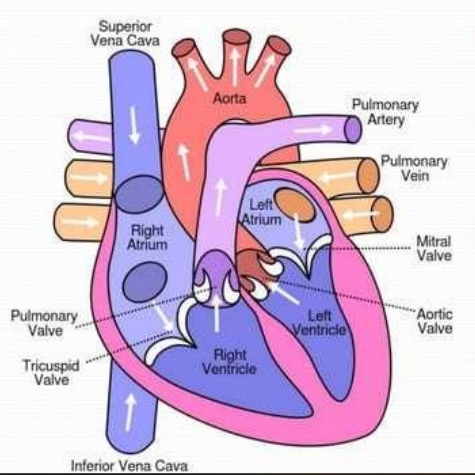
2 atria - receiving chambers 2 ventricles - filling chambers
The heart has four hollow chambers:
2 atria
receiving chambers
2 ventricles
filling chambers
blood flow
Blood flows into the atria under low pressure from the veins, and continues into the ventricles
ventricles
thickwalled discharging chambers
They are the pumps of the heart
When they contract, blood is propelled out of the heart and into circulation
right venrticle
forms most of the heart's anterior surface
left venrticle
forms the apеx
septum
divides the heart
interventricular septum
divides the heart longitudinally
interatrial septum
based on the chambers it separates
first process
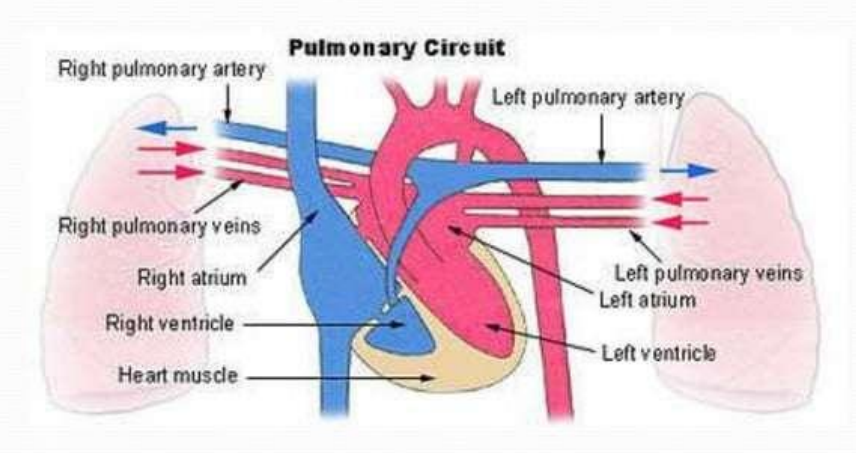
The heart functions as a double pump
The right side works as the pulmonary circuit pump .
Receives relatively oxygen-poor blood from the veins of the body through the large superior and inferior vena Superior cavae
seconf process
The blood then pumps out through the pulmonary trunk which splits into the left and right pulmonary arteries
The pulmonary arteries carry blood to the lungs, where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is unloaded
pulmonary circulation (3rd prcoess)
Oxygen-rich blood drains from the lungs and is returned to the left side of the heart through the four pulmonary veins
Its only function is to carry blood to the lungs for gas exchange and then return it to the heart
pulmonary circuit
fourth process
Blood returned to the left side of the heart is pumped out of the heart into the aorta
The systemic arteries branch from the aorta to supply the body tissues with blood
process starts again
Oxygen-poor blood circulates from the tissues back to the right atrium via the systemic veins, which empty their blood into either the superior or inferior vena cava
systemic circulation
This second circuit, from the left side of the heart through the body tissues and back to the right side of the heart
It supplies oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to all body organs
left ventricle
is the systemic pump that pumps blood over a much longer pathway through the body,
its walls are thicker than those of the right ventricle It is a more powerful pump
The heart also has four valves:
2 that separate the atria from the ventricles
2 that separate the ventricles from their arteries
All of these valves prevent back flow
The atrioventricular (AV) valves
between the atria and ventricles
On the left
bicuspid or mitral valve
On the right
tricuspid valve
chordae tendineae
valves are anchored by
hangs limply
When the heart is relaxed and blood is passively filling its chambers, the AV-valve flaps hangs ___ into the ventricles
the intraventricular pressure rises
As the ventricles contract, they press on the blood in their chamber,
The semilunar valves
guard the bases of the large arteries leaving the ventricular chambers
on the right
pulmonary valve
On the left
aortic valve
When the ventricles are contracting
these valves are forced open and flattened against the arterial walls
When the ventricles are relaxed
the blood flows back towards the heart
The coronary arteries
branch from the base of the aorta and encircle the heart in the coronary sulcus (AV groove) at the junction of the atria and ventricles
coronary sulcus (AV groove)
The coronary arteries branch from the base of the aorta and encircle the heart in the ___ at the junction of the atria and ventricles
compressed
The coronary arteries and their major branches are ___ when the ventricles are contracting and fill when the heart is relaxed
angina pectoris
When the heart beats rapidly the myocardium can received an inadequate amount of blood
This can result in crushing chest pain
myocardial infarction
"heart attack
If angina is prolonged, oxygen-deprived heart cells may die forming an infarct
heart pumps
the body's 6 quart supply of blood through the blood vessels over 1000 times per day
600o quarts of blood
heart pumps about __ in a single day
spontaneously and independently
Cardiac muscles cells can and do contract __, and __
even if all nervous connections are severed These contractions occur in a regular and continuous way
Atrial cells
60 bpm
Ventricular cells
20-40 bpm
Autonomic nervous system
brakes and accelerator Acts to decrease or increase heart rate
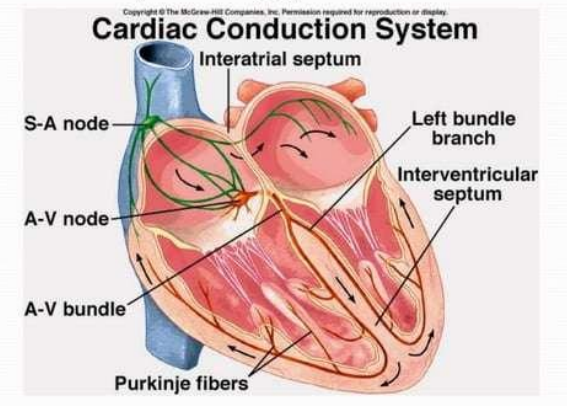
Intrinsic conduction system (nodal system)
Composed of specialized tissue that is a cross between muscle and nervous tissue
Causes heart muscle depolarization from the atria to the ventricles
Enforces contraction rate ~ 75bpm
Two systems act to regulate heart activity:
Autonomic nervous system
Intrinsic conduction system (nodal system)
septum
Intrinsic Conduction System
The sinoatrial (SA) node is a crescent shaped node in the right atrium
The atrioventricular (AV) node is at the junction of the atria and ventricles
The atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of His)
Branch bundles in the interventricular septum
Purkinje fibers which spread with the muscle of the ventricle walls
The sinoatrial (SA) node
crescent shaped node in the right atrium
The atrioventricular (AV) node
is at the junction of the atria and ventricles
Purkinje fibers
which spread with the muscle of the ventricle walls
SA node
has the highest rate of depolarization in the whole system
It starts each heartbeat and sets the pace for the whole heart and is therefore called the pacemaker
The impulse travels from the SA node through the atria to the AV node, causing the atria to contract
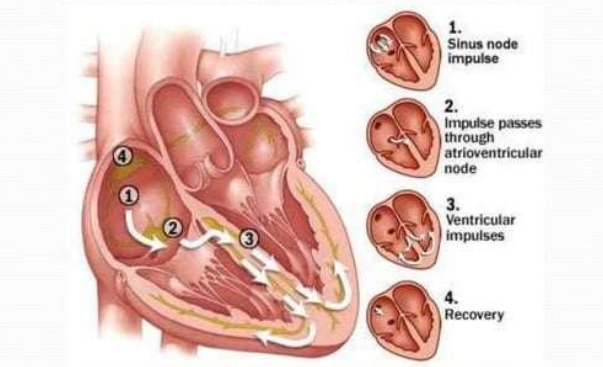
AV node
the impulse is delayed to give the atria time to finish contracting
It then passes rapidly through the AV bundle, the bundle branches, and the Purkinje fibers, causing a "wringing" contraction of the ventricles that begins at the apex and moves toward the atria
This contraction effectively ejects blood superiorly into the large arteries leaving the heart
Tachycardia
is a rapid heart rate (> 100 bpm)
but prolonged tachycardia may progress to fibrillation
Bradycardia
is a slow heart rate (< 60 bpm)
Fibrillation
is a rapid, uncoordinated shuddering of the heart muscle
makes the heart totally useless as a pump and is a major cause of death from heart attacks in adults
pacemaker
is a small device, about the size of a half dollar piece, placed under the skin near the heart to help control the heartbeat.
is implanted as part of what's often referred to as "cardiac resynchronization therapy."
Systole
heart contraction
atria contract simultaneously
diastole
relaxation
contraction of the ventricles begins
cardiac cycles
refers to the events of one complete heartbeat, during which both atria and ventricles contract and then relax
average beats per minute
75 times per minute
o.8 seconds
average length of a cardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle occurs in three major steps:
1. mid-to-late diastole
2. ventricular systole
3. early diastole
Mid-to-late diastole
The heart is in complete relaxation Pressure in the heart is low
Blood is flowing passively into and through the atria and into the ventricles from pulmonary and systemic hovemetric
Vent ontrastmw circulations A
The semilunar valves are closed
The AV valves are open
Then the atria contract and force the blood into the ventricles
Ventricular systole
The pressure within the ventricles increases rapidly, closing the AV valves
When the intraventricular pressure is higher than the pressure in the large arteries leaving the heart, the semilunar valves are forced open, and blood rushes out of the ventricles
The atria are relaxed, and again are filling with blood
Early diastole
At the end of systole, the ventricles relax, the semilunar valves snap shut, and for a moment the ventricles are completely closed chambers
During early diastole, the intraventricular pressure drops
When it drops below the pressure in the atria, the AV valves are forced open. And the ventricles again begin to refill rapidly with blood
heart sounds
When using a stethoscope, the heart beat usually has two distinct sounds - "lup" and "dup"
These are caused by the closing of the two sets of valves
"lup"
AV sounds
"dup"
semilunar valves
blood vessels
create a closed transport system, or vascular system
Higher, changing blood pressure
Thicker walls The middle section (tunica media) is especially thick
Strong and stretchy
capillaries
minute blood vessels that connect arterioles and venules
Form capillary beds
veins
Lower, constant blood pressure
Thinner walls Blood often flows against gravity
Have valves
blood vessels
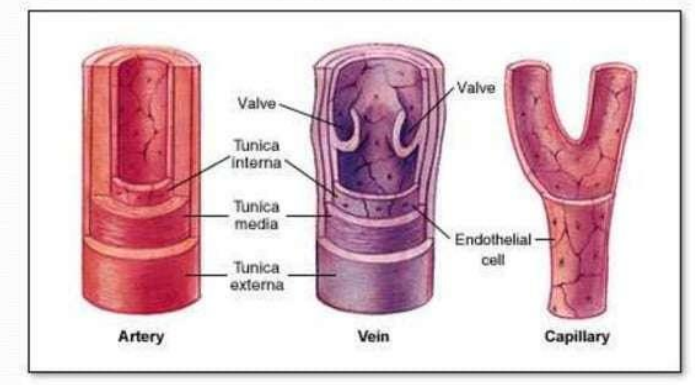
structure of blood vessel
tunica externa
tunica media
tunica interna
elastic arteries
largest arteries in the body with large diameter
consists more of elastic lamellae
aorta, pulmonary trunk, branches of aorta
muscular arteries
tunica media contains more smooth muscles and less elastic fibers
capable of greater vasoconstriction and vasolidation for blood flow
femoral arteries, axilary arteries
arterioles