2.6 Macroeconomic objectives and policies
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Main macroeconomic objectives
High economic growth: strong, sustained, sustainable. 2.5% in the UK.
Low unemployment: full employment. Unemployment rate at 3%.
Low and stable rate of inflation: 2% target
Balance of payments equilibrium: on current account
Other macroeconomic objectives
balanced government budget
Protection of the environment
Greater income equality: fair + balanced
2 types of demand side policies
Fiscal
Increase government spending and decrease taxation in order to increase AD.
Monetary
Decrease interest rate,changes to money supply and exchange rate(by the central bank) in order to increase AD.
Reasons for the need of expansionary fiscal policies(↑ AD) on macro objectives - link to multiplier effect
Boost growth
Reduce unemployment
Increase inflation
Redistribute income
Reasons for the need of contractionary fiscal policies (↓ AD)
Reduce inflation
Reduce budget deficit(less borrowing from bank)/ national debt
Redistribute income
Reduce current account deficit
Expansionary fiscal policy examples
↓ Income tax: chain of reasoning from 2.2AD
↓ Corporation tax: cut regressive taxes e.g. VAT → ↑ income for poor more than rich who have higher MPC.
↑ Government spending: on healthcare, education
Automatic stabilisers
Fiscal policy tools that influence GDP + counter fluctuations in the economic cycle.
Progressive income tax
IN A BOOM: ↑ incomes, workers pay higher tax, ↑ tax rate, C ↓, growth ↓.
Welfare benefits
IN A BOOM: unemployment benefits ↓, gov. spending ↓, growth ↓.
Problems with expansionary fiscal policies
Demand pull inflation: exceeds target.
Current account deficit: economic growth→higher income→more spending on imports.
Worsening of government finances: budget deficit rises, policies needed to be funded which come out of government budget. May need taxes to rise to fund it.
Time lags: AD won’t increase straight away. Policies take time to implement e.g. infrastructure being built may take years.
Crowding out effect: increased gov. spending on public sector drives down private sector spending- too much reliance on gov. spending.
Evaluation of expansionary fiscal policies
Size of output gap: if AD is closer to full employment, demand pull inflation will increase more than real GDP. (use graph to show)
Size of multiplier: the bigger the multiplier, the bigger the increase in AD. A bigger multiplier means less of a need for policies.
State of gov. budget: If there is budget deficit/ large national debt, gov. can’t finance policies.
Self-correcting in recession: classical view- economy will correct itself, eventually wages will fall, economy will return to full employment on its own.
Reasons for expansionary monetary policy(↑ AD)
Increase inflation
Increase growth
Reduce unemployment
Reasons for contractionary monetary policy(↓ AD)
Reduces inflation
Prevent excessive borrowing + growth in house price
Reduce current account deficit
Expansionary monetary policy examples:
↓ credit card interest rates(consumer borrowing): MPS ↓, ↑ consumption
↓ mortgage rates: ↑ consumption
↓ rates on business loans: ↑ investment
weaker exchange rate: low interest rates, less incentive to save, savings move out of country(hot money outflows), increasing supply of currency which depreciates it, ↑ net exports
Cons of monetary policy
Tradeoff of macroeconomic objectives: demand pull inflation+current account deficit as a result of economic growth.
Negative impact on savers: Rate of return on savings decreases + if inflation rate is higher than nominal interest rate, real return on savings may be negative.
Time lag: takes time for interest rate to be cut + boost AD.
Evaluation for effectiveness of monetary policy
Size of output gap: If close to full employment, there will be a smaller ↑ in output and larger demand pull inflation.
Consumer+business confidence: lower confidence means less likely to borrow + consume/ invest even if interest rate falls.
Banks willingness to lend: cutting interest rate is pointless in banks aren’t willing to lend
Size of interest rate cut
Supply side policies
Policies designed to increase the productive capacity of the economy, shifting LRAS to the right.
Interventionist policies: Government intervenes to boost LRAS in the economy.
Market based: Increasing competition + free market efficiency.
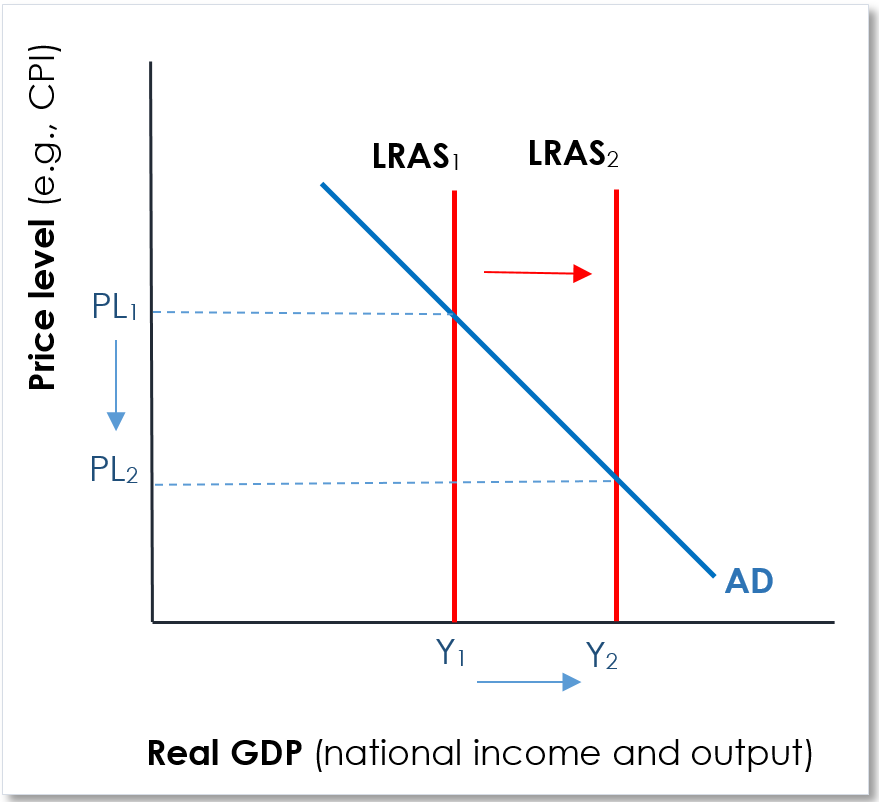
Reasons for supply side policies(↑ AS)
Reduced inflation
Boosts growth
Reduces unemployment
Reduced current account deficit
Interventionist policies
Gov. spending on education/ training: improve quality of labour
Gov. spending on infrastructure: can reduce cost of production(transport), improve productivity(healthcare)
Subsidies to firms to promote investment: investing in R&D-improves productivity(↓ LRAC), increases quality of capital
Market-based policies
Tax reform
Lower income tax: incentivises inactive population to enter labour force + active population to work harder to earn more disposable income→quantity of labour increases
Lower corporation tax: more retained profits→use for investment→quality of capital increases
Labour market reform
Reduce benefits: increased incentive to work→quantity of labour ↑
Reduce minimum wages: reduces cost of production→boost productive efficiency
Competition policy: boost competition→LRAC of production decreases→productive efficiency ↑.
Privatisation
Deregulation
Trade liberalisation
Cons/ evaluation of supply side policies
No guarantee of success: opportunity cost
Time lag + cost: Policies like infrastructure may take years to finish + increase LRAS, policies are costly
Size of output gap: if economy is in recession, supply side policies are useless in boosting growth
2 types of budget deficit.
Structural: budget deficit at full employment- not earning enough tax revenue to fully cover gov. spending.
Cyclical: budget deficit in a recession- gov. spending on benefits rises.
Pros + cons of budget deficit
PROS
Higher growth, lower unemployment: increase AD.
More spending on education, infrastructure, healthcare: boost living standards
Reduction in income inequality: less regressive taxes, benefits for low income workers.
CONS
Deterioration of gov. finances: ↑ gov. spending leads to more national debt- lower credit rating, impact future pop. as debt must be paid back-opportunity cost as spending can go towards something else.
Macroeconomic objectives conflict: Inflation increases + current account deficit worsens- rise in incomes means more spending on imports + higher demand pull inflation as AD rises
Evaluation of budget deficit
State of gov. finances: if gov. has a lot of national debt, budget deficit will worsen it.
Stage of economic cycle: in recession, budget deficit will increase AD, close negative output gap.
Automatic stabilisers: if these are strong, there is less of a need for ↑ gov. spending.
Policies to reduce inflation
Contractionary fiscal/ monetary policy: reduce AD + therefore demand pull inflation
Supply side policies: increase AS + therefore decrease cost push inflation
Policies to reduce current account deficit
Contractionary monetary policy: lower inflation→more internationally competitive (cheaper) exports→exports increase→current account increases
Supply side policy: lower LR cost of production→boost export competitiveness →current account increases
Policies to reduce income inequality
Expansionary fiscal: ↑ gov. spending on benefits
Expansionary fiscal: ↓ regressive taxation
Macroeconomic tradeoffs
Expansionary fiscal + monetary policy(+vice versa)
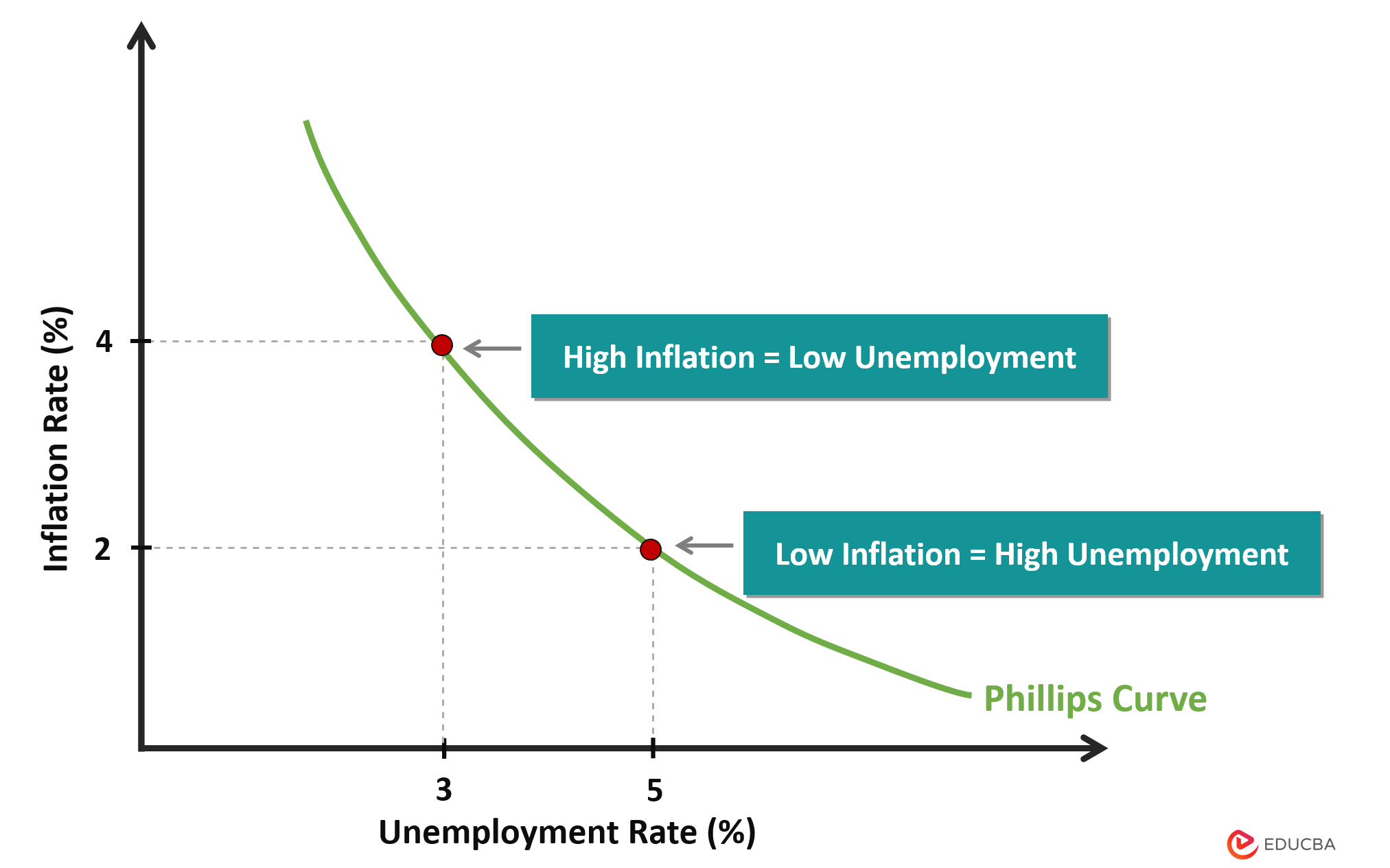
-phillips curve
+growth ↑, unemployment ↓, income inequality ↓
-inflation ↑, CA position, gov. finances, environment ↓
EVALUATION
Size of output gap: smaller output gap→higher inflation+lower growth.
Policy used: different tradeoff based on different policy used.
Supply side policies
+growth ↑ ,unemployment ↓, inflation ↓, CA position improves
EVALUATION
Size of output gap: if output gap is large(recession), supply side policies are useless in meeting objectives.
Gov. finances: interventionist policies may damage gov. budget.