DNA Genetics Vocabulary
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
DNA
a molecule containing genetic information that codes for traits
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides together

Chromatin
Long, thin structure composed of DNA wound around histone proteins
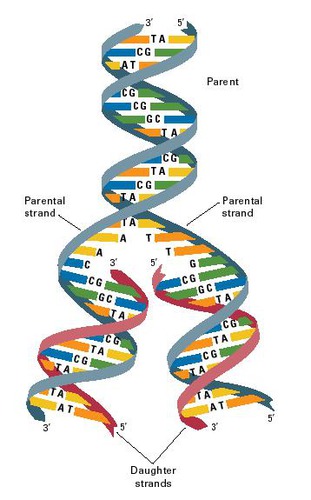
Replication
Copying process by which a cell duplicates its DNA
Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the double helix of DNA and separates the DNA strands in preparation for DNA replication.
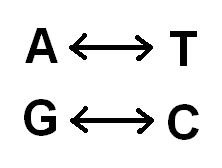
Base Pairing
principle that bonds in DNA can form only between adenine (A) and thymine (T) and between guanine (G) and cytosine (C)
mRNA (messenger RNA)
molecule that is a complimentary copy of DNA and carries instructions for assembling amino acids into proteins
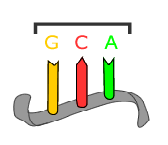
Codon
A three-nucleotide sequence of mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal. ex. GCA
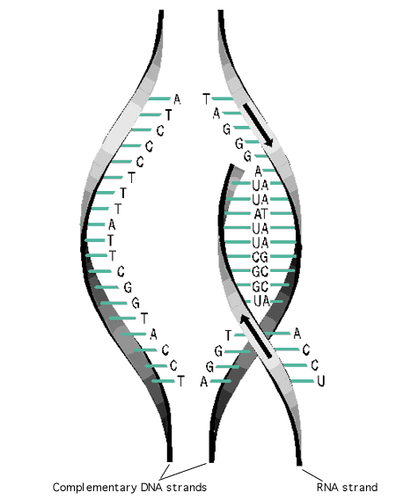
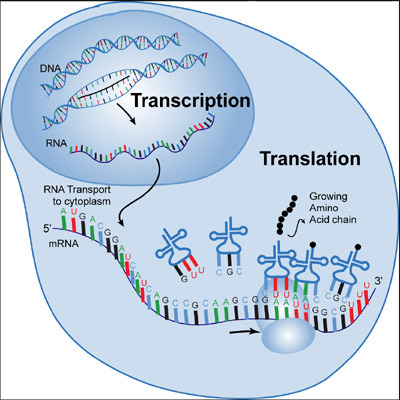
Transcription
the process in which a DNA sequence of a gene is copied into mRNA
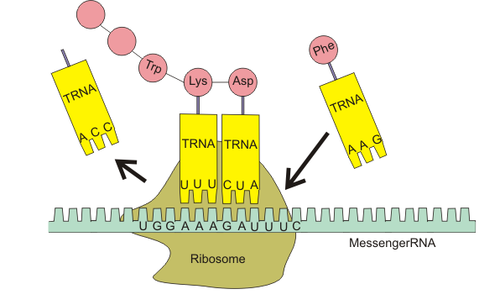
Translation
the process where genetic information coded in mRNA directs the ordered assembly of Amino Acids into a specific protein at a ribosome
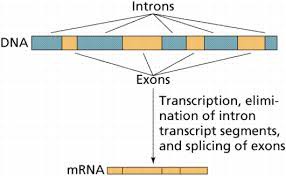
Intron
Non-coding nucleotides in DNA that are not important for the amino acid making process, and stay in the nucleus
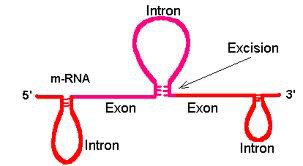
Exon
Coding sequences for specific protein products that leave the nucleus
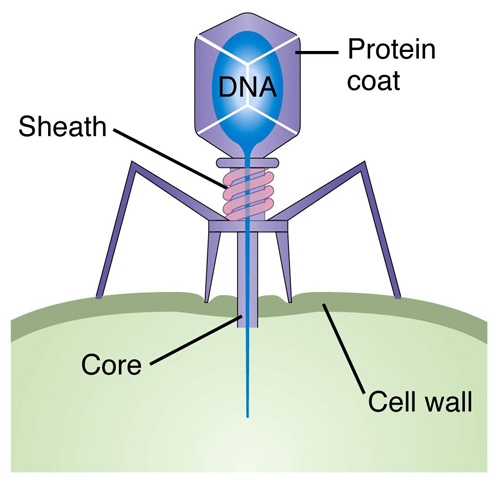
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria and used in transformation experiments.
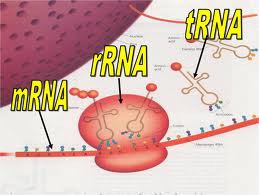
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
Molecules that together with proteins make up ribosomes
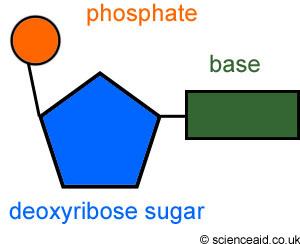
Nucleotide
A building block of DNA and RNA, consisting of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group
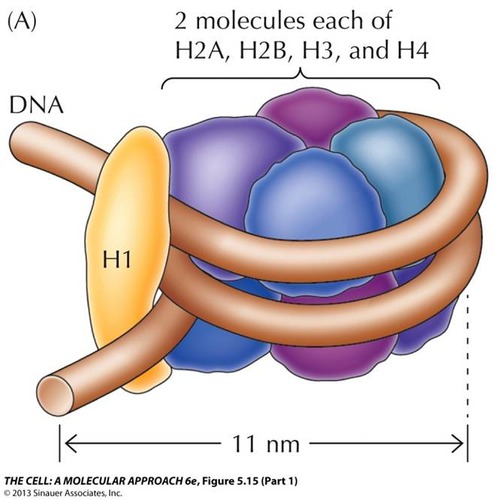
Histone
The protein that DNA winds around to stay organized in chromatin
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
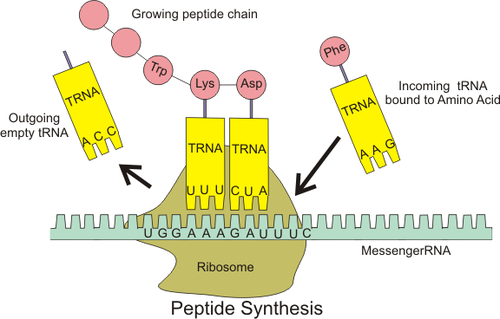
tRNA (transfer RNA)
Carries amino acids to the ribosome and matches them to the coded mRNA message; has an anticodon.
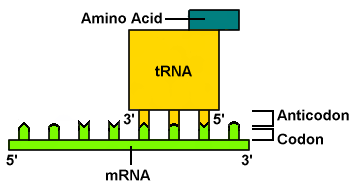
Anticodon
three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to a mRNA codon
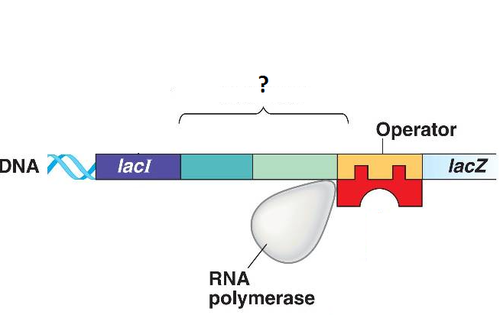
Promoter
A specific nucleotide sequence in DNA that binds RNA polymerase and indicates where to start transcribing RNA.
Hershey and Chase
These scientists radioactively marked DNA and Protein to determine which molecule carried the genetic code.
Griffith's transformation
Experiment in which proof of a molecule that carried genetic information was shown for the first time.
Watson and Crick
Build the first model of the structure DNA and determined how it encoded genetic information.
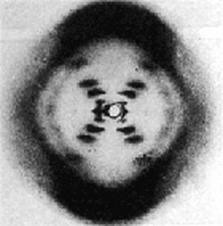
Rosalin Franklin
Took X-ray crystallography photos of DNA