NPTE FINAL QUIZLET REVIEW WITH SH*T I CANNOT REMEMBER AND NEED TO MEMORIZE FOR THE LIFE OF ME
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Phase II of cardiac rehab requires what intensity level in METs?
4-9 METs
They need to be at 4-5 to d/c from Phase I
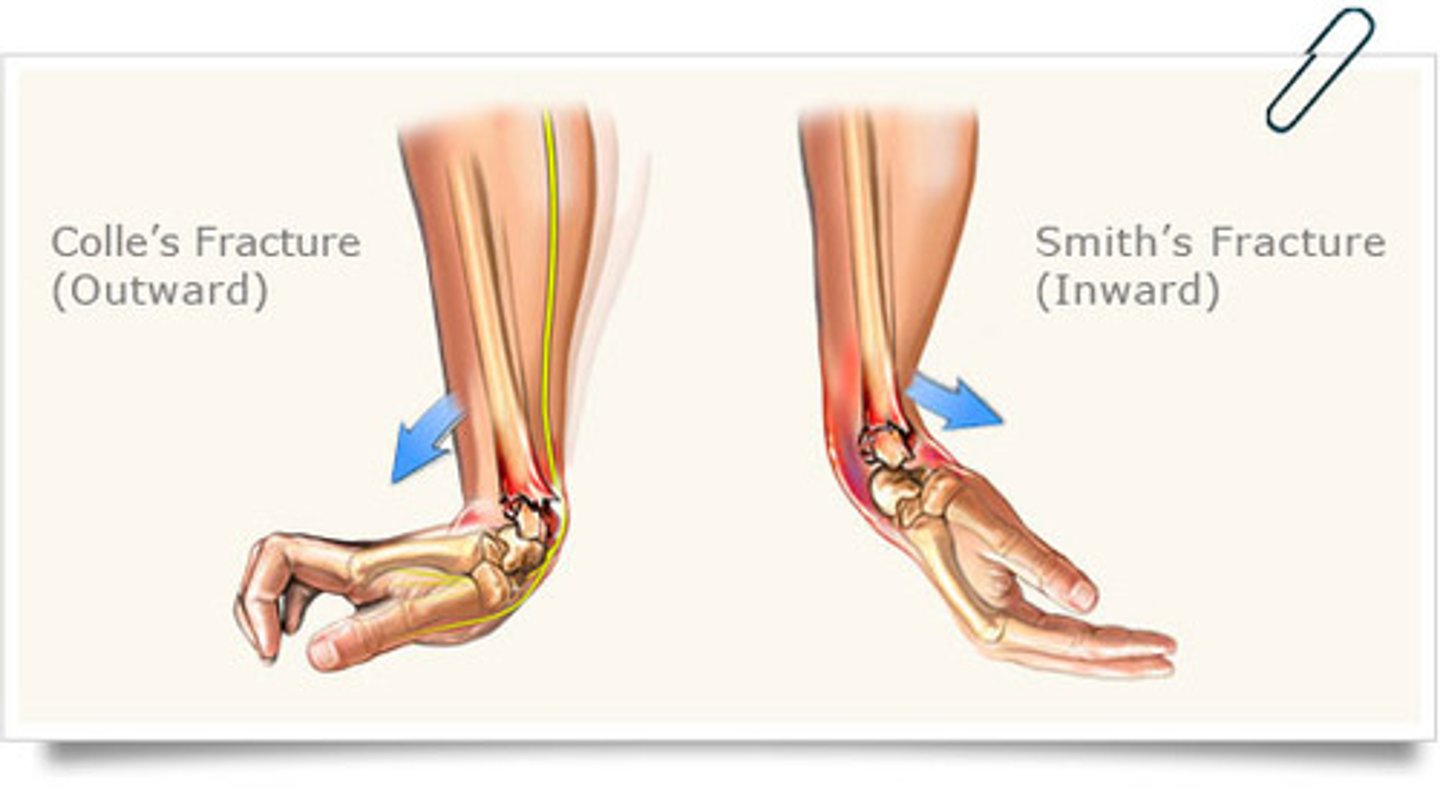
Wrist Fractures from FOOSH
Smith's Fracture: radius dislocates in volar direction (garden spade deformity)
Colle's Fracture: radius dislocations in dorsal direction (dinner fork deformity)
Painful Arc
45/60-120 deg = GH
70-120 deg = supraspinatus tendinitis
170-180 deg= AC joint dysfunction

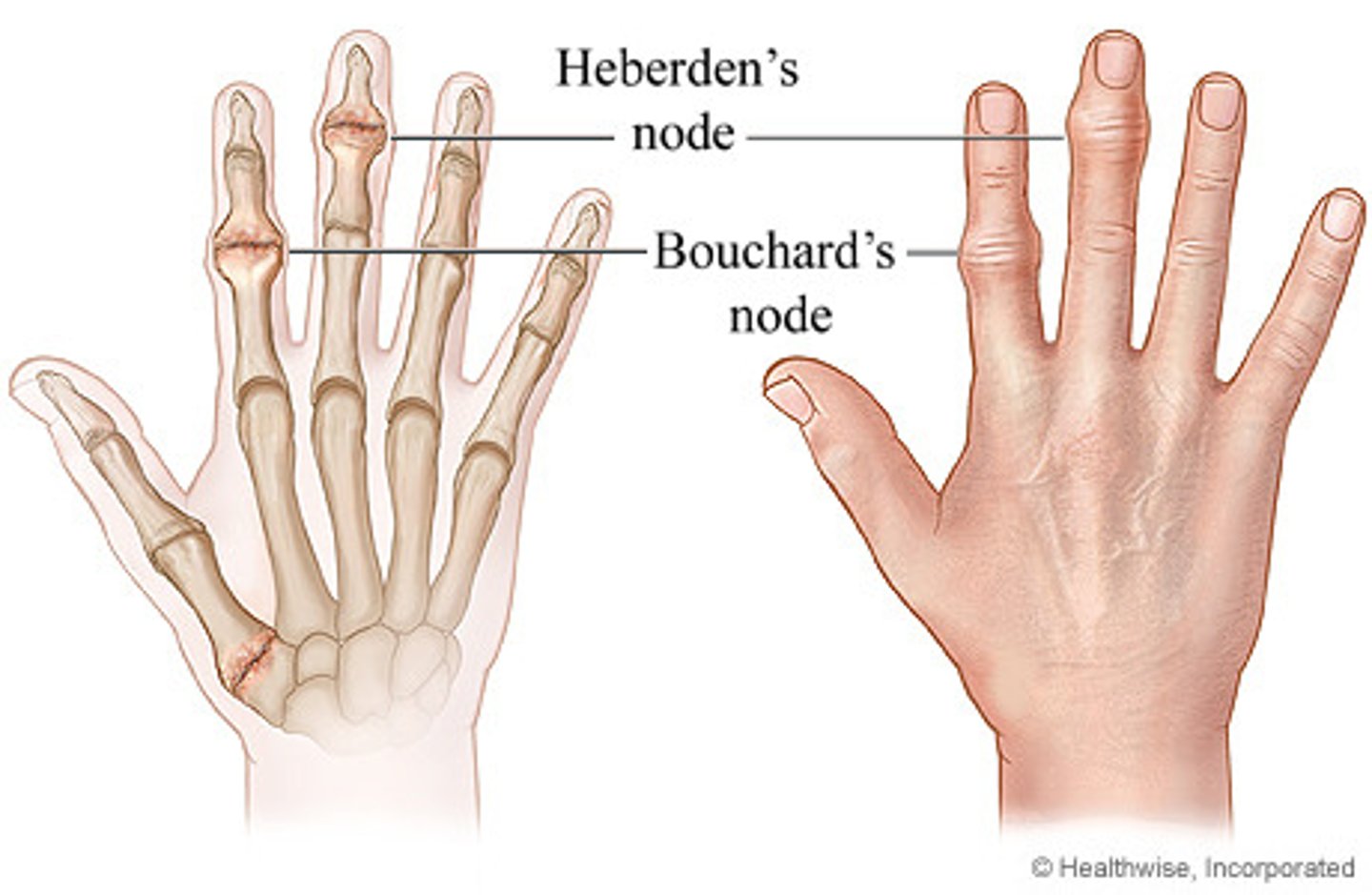
OA Nodules
Herbeden's (DIP) and Bouchard's (PIP)
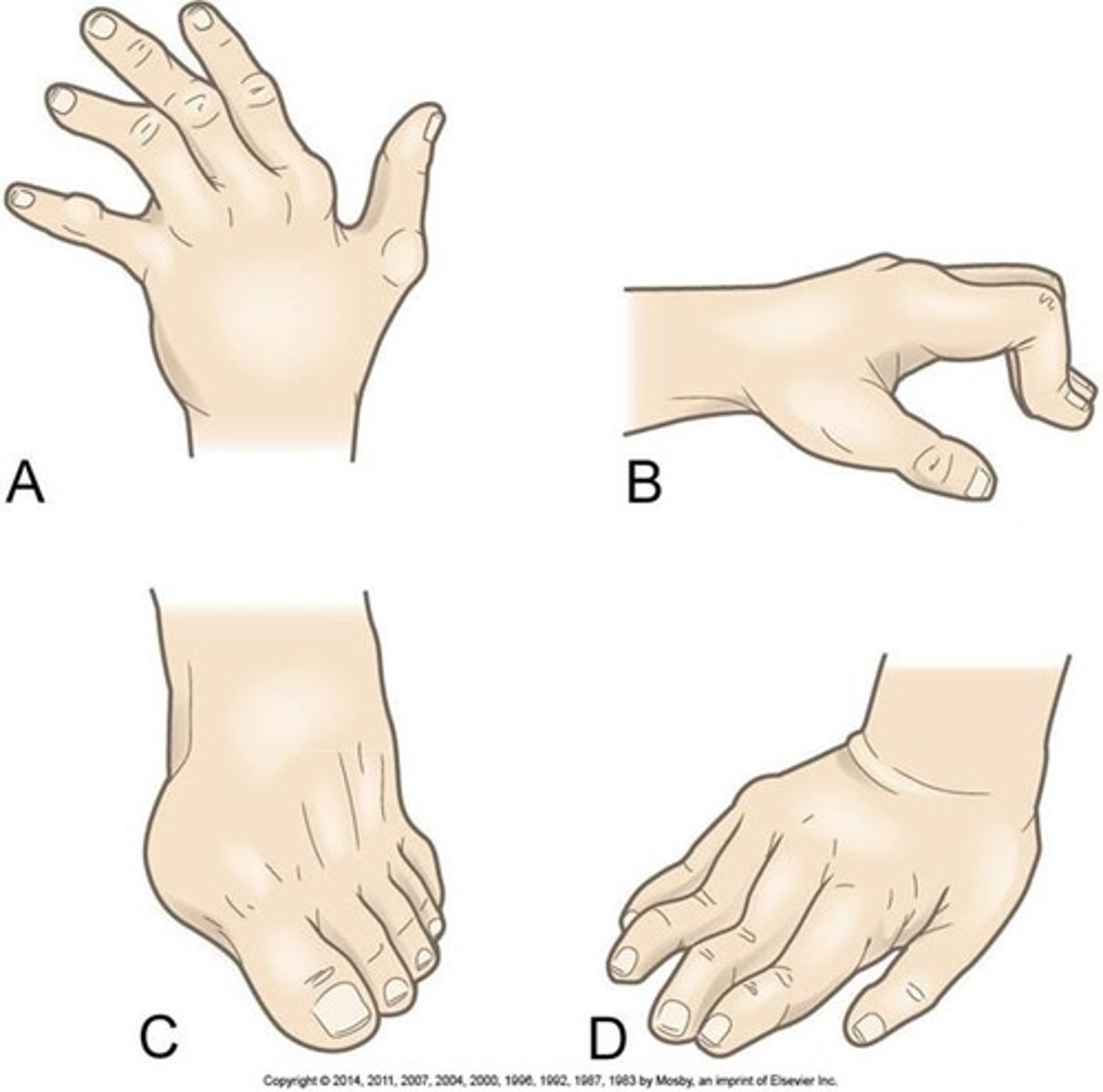
RA Deformities
Ulnar drift
Boutonniere's deformity
Hallux valgus and bunion
swan neck deformity
Hammer Toes
Rheumatoid nodules
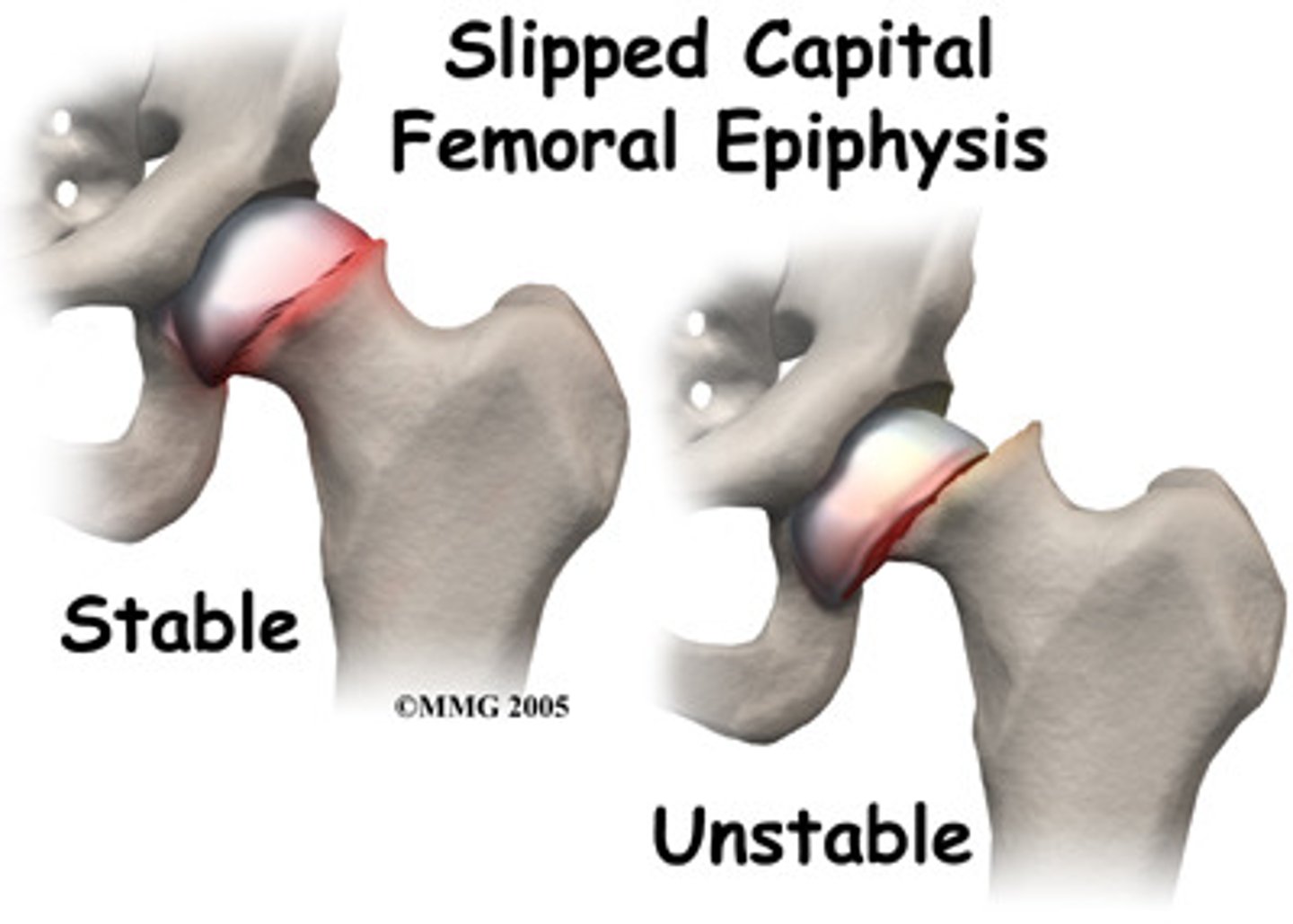
SCFE has what ROM limitations
Flex, ABD and IR
LCP has what ROM limitations
Ext, ABD, and IR
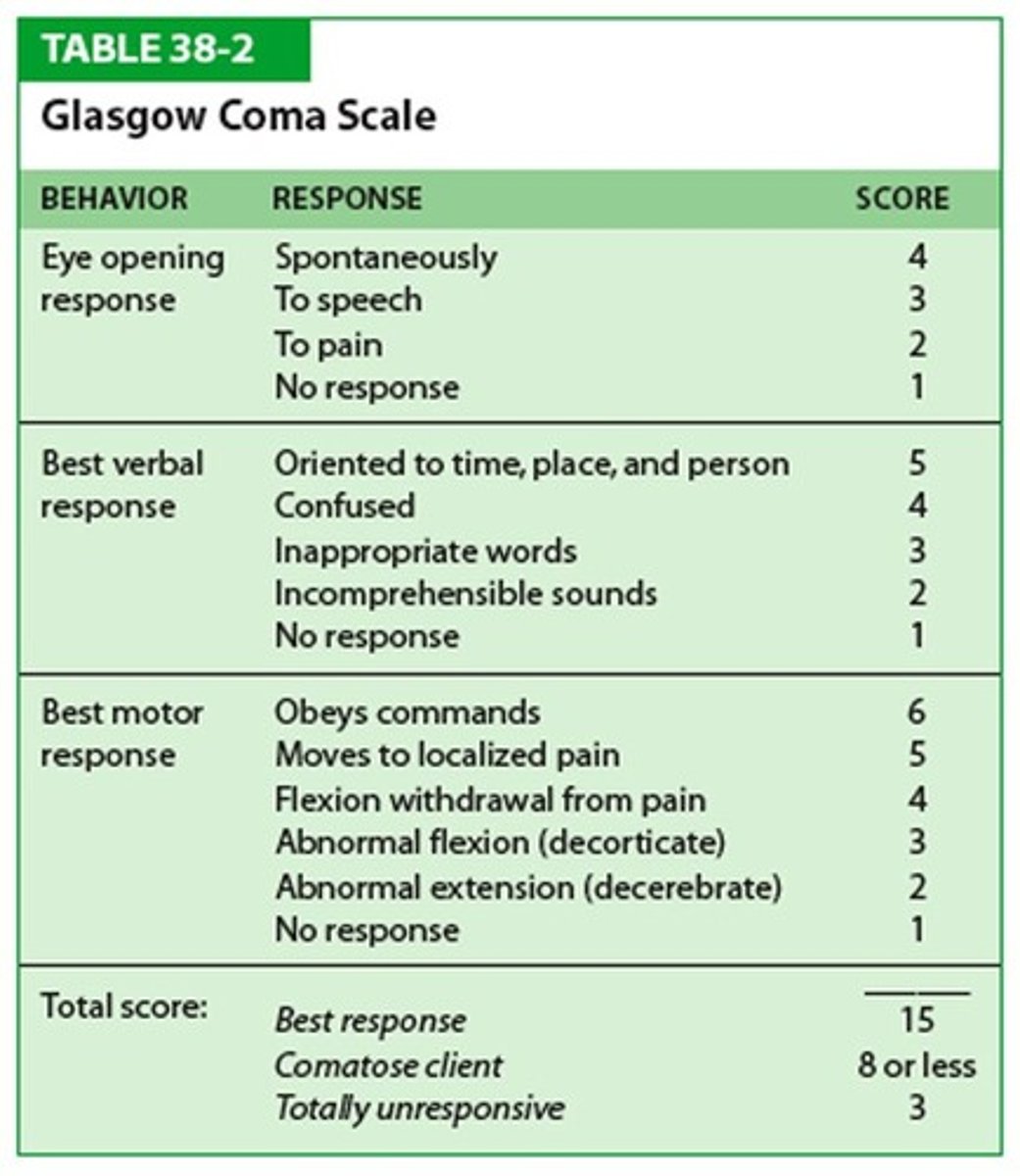
GCS
Eye Opening
4-Spontaneous
3-To sound
2-Pain
1-Never
Motor Response
6-Obeys commands
5-Localizes to pain
4-Normal flexion withdrawal
3-Abnormal flexion
2-Extension
1-None
Verbal Response
5-Oriented
4-Confused conversation
3-Inappropriate words
2-Incomprehensible sounds
1-None
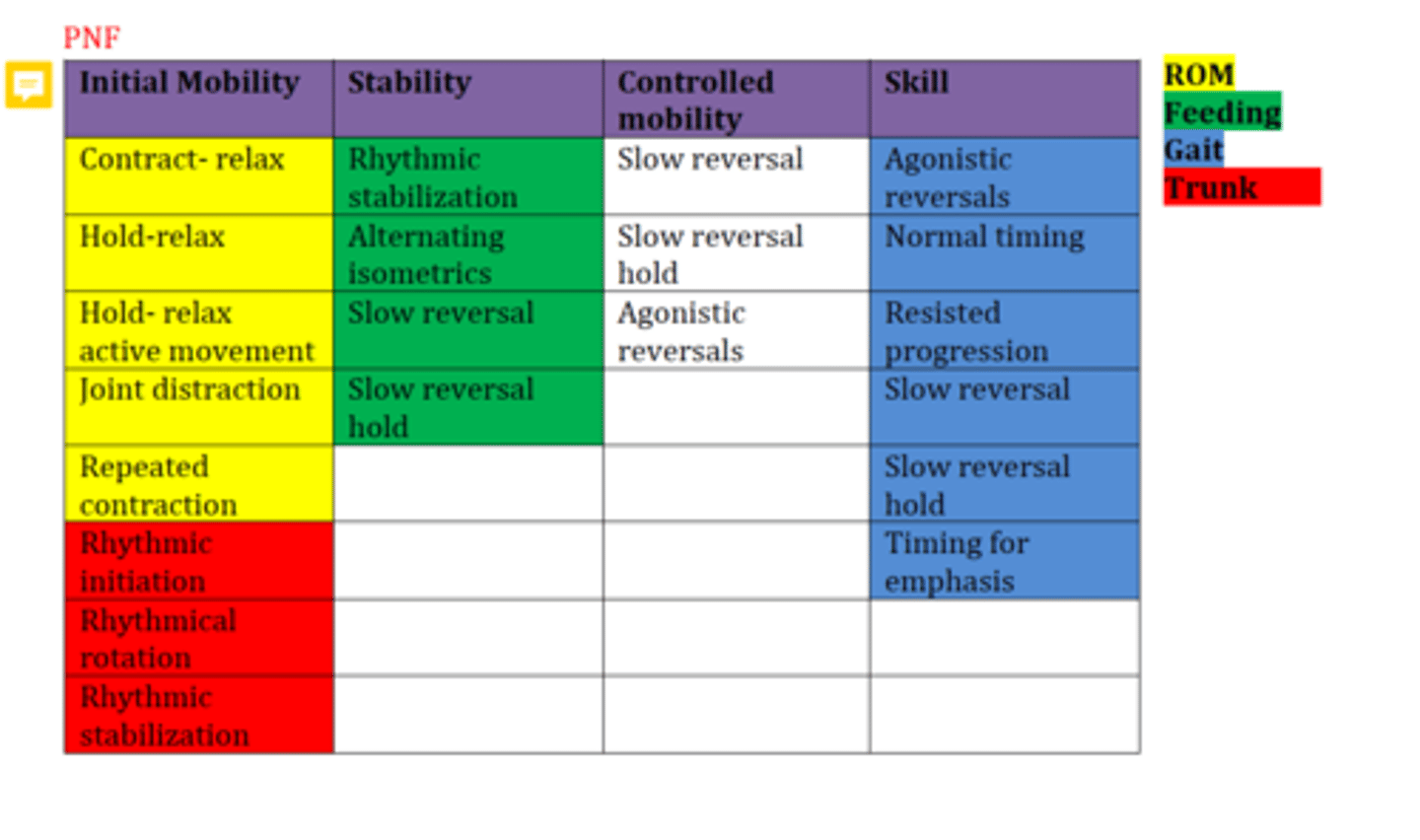
PNF for Gait
LE D1 Flexion bc flexion, ADD and ER are needed most for gait?

PNF Techniques for Mobility:
Contract-Relax
Hold-Relax
Hold-Relax Active Movement
Joint distraction
Repeated contractions (initiate movement patterns)
Rhythmic Initiation (RI)
Rhythmic Stabilization
Rhythmical Rotation (hypertonia)
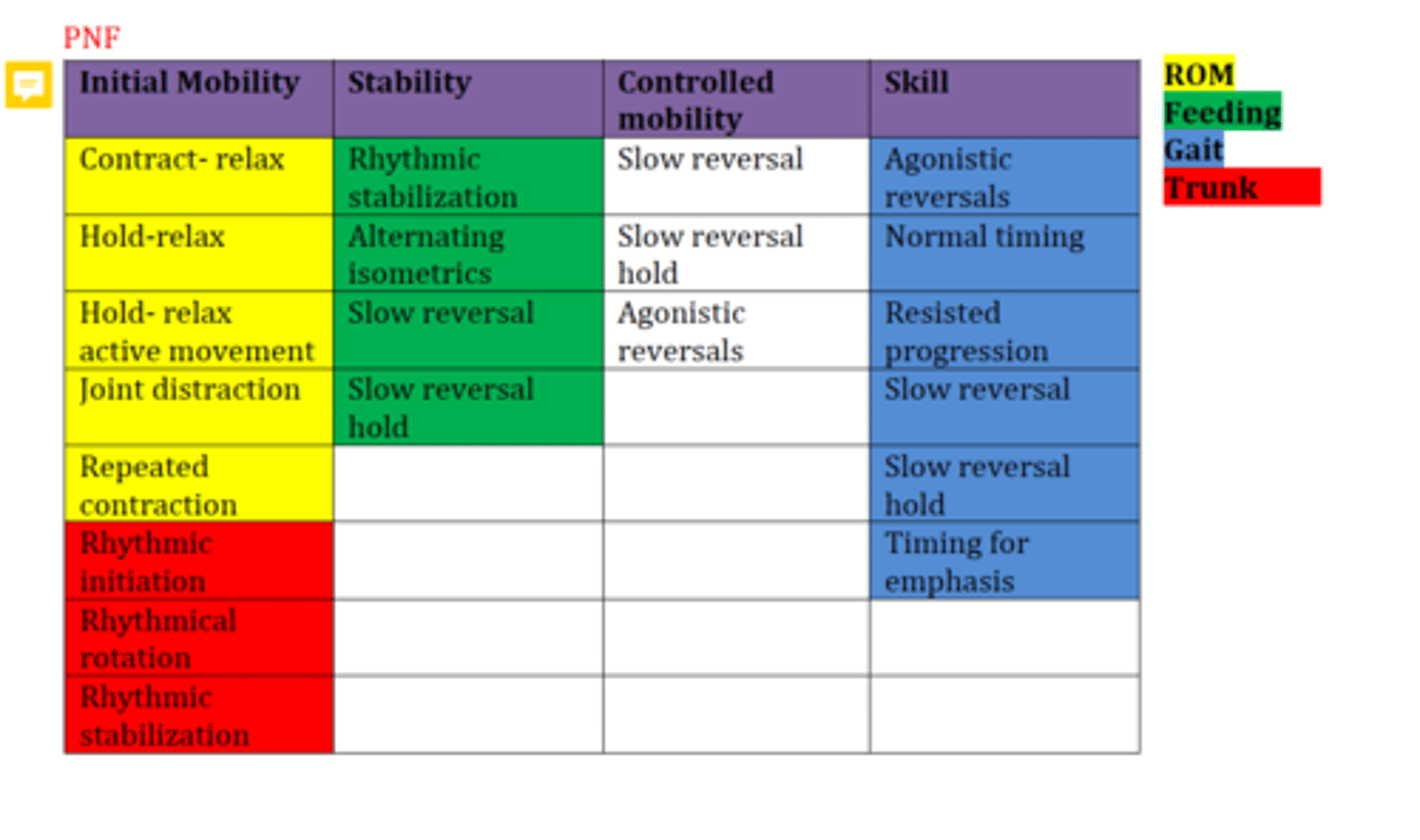
PNF techniques for stability
Alternating Isometrics
Rhythmic Stabilization
Slow reversals
Slow reversal holds
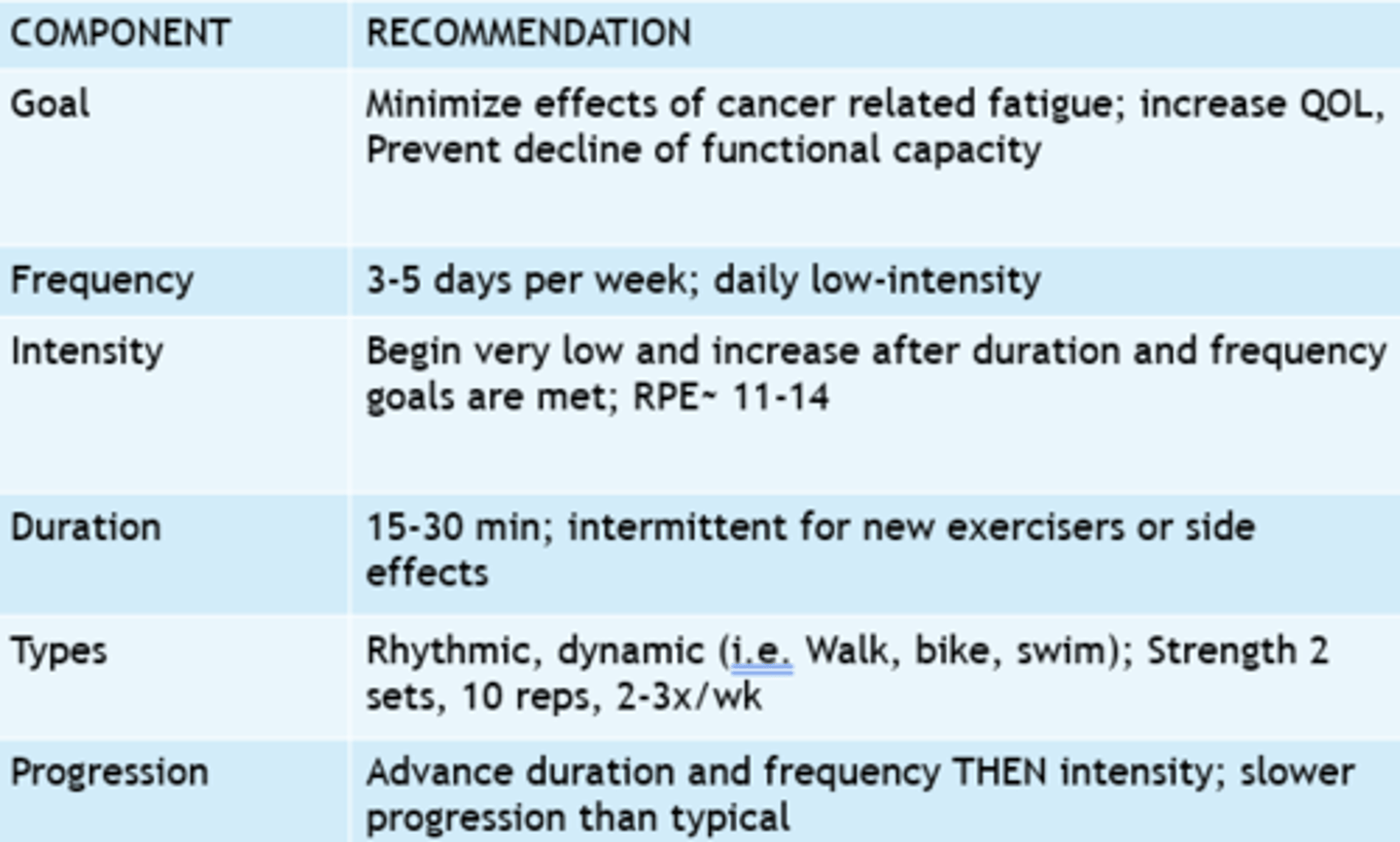
FITT for pt with cancer
Strength
F: 2-3x/week
I: 8-15 reps < 70% 1RM (maintaining strength)
T: n/a
T: light weights, resistance bands, bodyweight
Aerobic Capacity
F: 3-4x/week
I: 40-59% VO2max but up to 60-80% VO2 max
T: 30-60 min
T: walking, biking, aquatics
Contraindications for Exercising pt with Cancer
-Day of chemo or within 24hrs after
-Severe reaction to radiation
-Severe nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea in last 24-36 hrs
-Unusual fatigue
-Platelets <20,000 can only do ADLs and AROM
-Caution at 20,000-50,000
Caution when pt platelet levels are low, at risk of bone fractures, ecchymosis, anemia, and possible spontaneous bleeding
Contraindications to Exercise a Pregnant Patient
-Preeclampsia
-Restrictive Lung Disease
-Severe anemia
-Incompetent cervix
-placenta previa
-vaginal bleeding
-rupture of membranes
-hemodynamic signs of heart disease
Obesity Classifications (BMI kg/m)
Overweight= 25-29.9
Obese= > or equal to 30
Morbidly obese= > or equal to 40
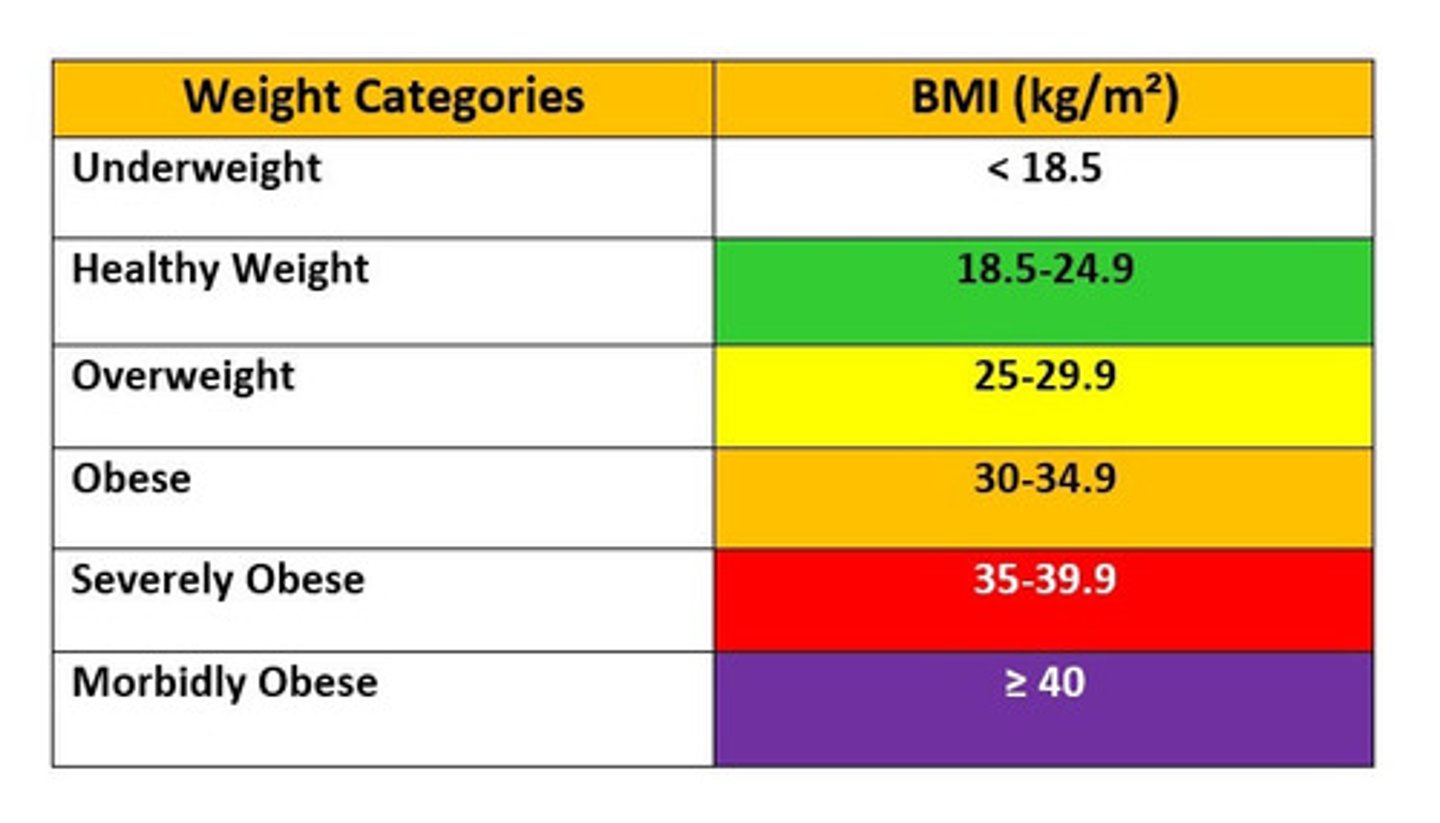
Obesity is
BMI of 30 or higher
Exercise Rx for Obese patients (FITT)
F= 5-7 days/week (more is better to maximize expenditure)
I= 40-60% and work up to 70%
T= 30/45 - 60 mins
T= aerobic + resistance, aquatics3
FITT for resistance training: Muscular strength and hypertrophy (muscle gains)
F= 2-4x/week
I= 70-90% 1RM for 2-3 sets of 8-12 reps
T= 2-3 min rest between sets
T= weights, resistance bands
FITT for resistance training: Muscular Endurance
F= 2-4x/week
I= 50-70% 1RM for <2 sets of 15-20 reps
T= less rest btw sets
T= bands and weights
FITT for resistance training: Muscular Power
F= 2-4x/week
I= 30-70% 1RM with fast velocity for 3-5 sets of 3-6 reps
T= 3-5 min rest btw
T= multi-joint, total body exercises, olympic lifts
Strength training sequencing
Large muscle groups and multi-joint muscles first along with more complex or higher intensity and finish with smaller group muscles
Aquatics: Ways to use water to assist in motion for weaker patients
-Go horizontal to water or go up toward surface away from the body
-use a floatie (+ go horizontal or toward surface)
-move slower
Aquatics: Ways to use water to increase strength in patients
-Increase speed
-Use turbulent water
-Movements toward the body or away from the surface
-Add a floatie (+ move toward body or away from surface)
-Add paddle/increase surface area of the extremity or limb=
Contraindications to Aquatic therapy
-Bowel or bladder incontinence
-Severe kidney disease (ESRD)
-Severe Epilespy
-Severe cardiac or respiratory dysfunction (severe CHF or severe COPD with very low vital capacity)
-Unstable blood pressure
-Peripheral vascular disease
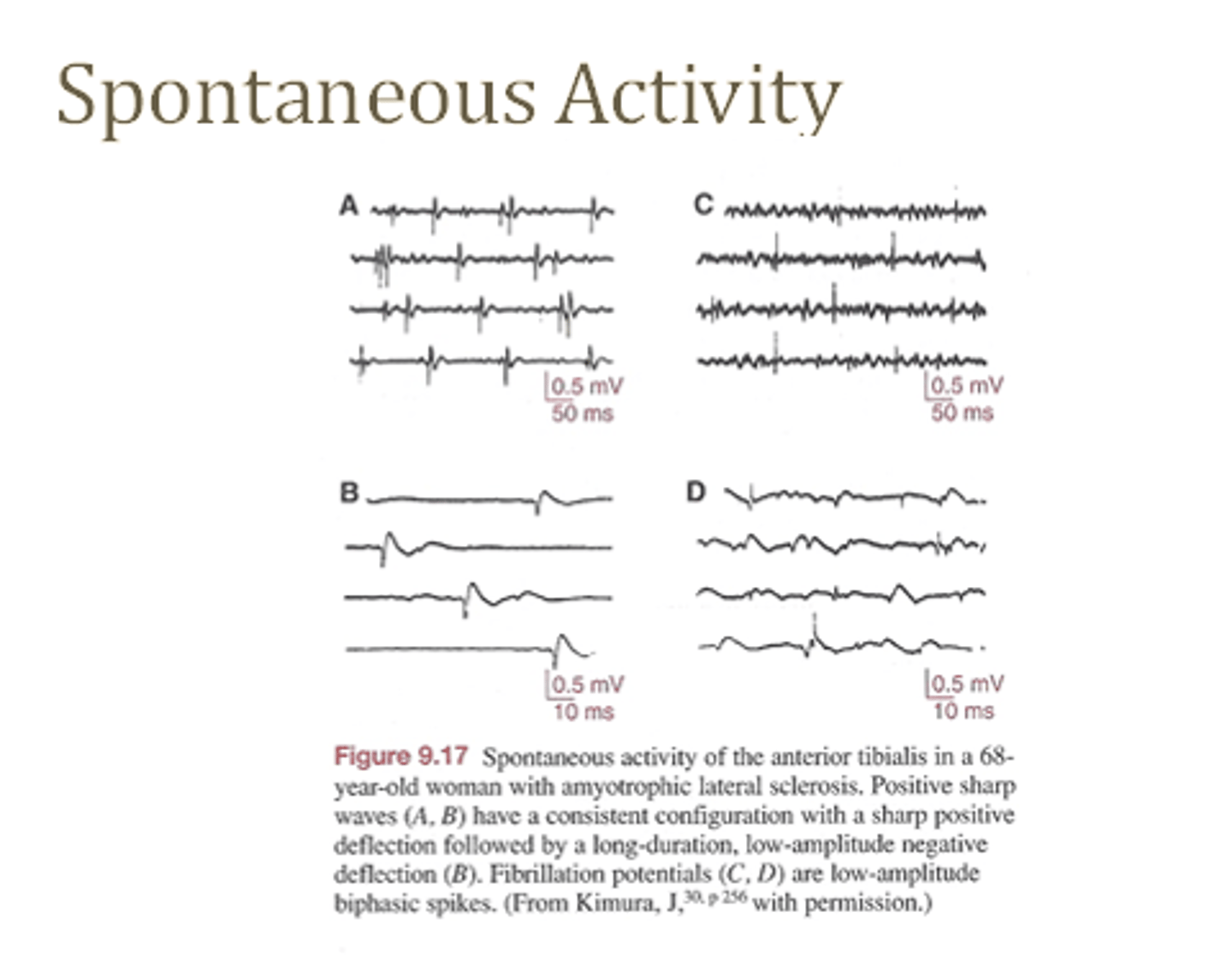
EMG (electromyography)
-used to examine electrical activity of a muscle
Findings on EMG
-Silence= normal resting muscle (nothing should be on the EMG)
-Burst Action potential when needle is inserted= insertional activity (increased in acute denervated mm or decreased in chronic neuropathies/myopathies
-Fibrillation, positive sharp wave potentials and fasciculations while a muscle is at rest is all hallmark signs of denervated or diseased muscle'
-Polyphasic potentials (rapid firing of motor units with multiple phases are suggestive of reinnervation and collateral sprouting
-Decreased MUPs in lower motor neuron injury
-Myopathic potentials: small amplitude and rapidly spatially summate on minimal activation indicates myopathy

EMG Spontaneous activity
See photo for examples
(in general is pathological)
Burns (5 types)
Epidermal
-only epidermis
-pink or red, dry, no blister
-min edema
-tenderness
-no scarring, 3-7 days
Superficial Partial Thickness
-epidermis and up to dermis
-pink or red
-blanches with quick refill
-blister and weeping
-mild edema
-painful to touch
-min scar (7-21 days)
Deep Partial Thickness
-epidermis and dermis
-nerve endings, hair follicles and sweat glands affected
-blanches but slow refill
-sensitive to pressure but not to LT or soft PP
-possible excessive scarring
Full Thickness
-white, charred
-no blanching
-little pain
-most likely get keloid scarring
-grafts maybe needed
Subdermal
-often due to electrical burns
-Requires skin graft or possible amputation
TSA ROM restrictions
Phase 1/into 2
-NO elevation above 120 deg and ER >30 deg when arm is by side
-NO active IR for 6 weeks
-NO GH ext past neutral up to 6 weeks
rTSA ROM restrictions
For up to 12 weeks
-NO GH ext or IR past neutral
-NO ER >20 deg
-elevation allowed up to 90-120 deg in scap plane
-NO combined Ext+IR+ADD (reaching back for bra strap)
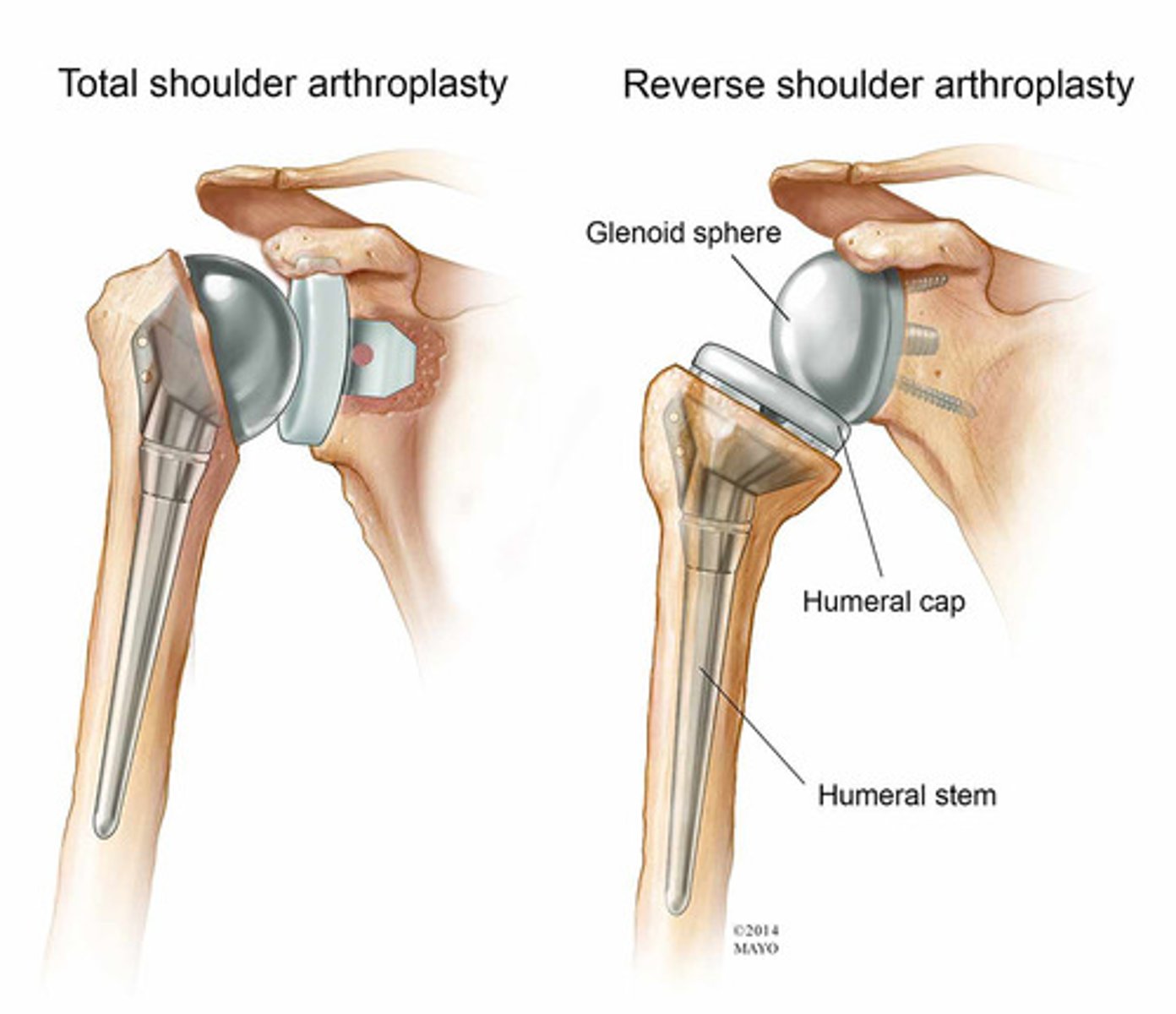
SLAP Repair ROM restrictions
Phase 1 (first 6 weeks)
-NO elevation past 60 deg for 2 wks
-NO elevation past 90 deg for 3-4 weeks
-Weeks 3-4 ER up to 30 deg and IR 60 deg
-No active elbow flexion for 6 weeks and no resistive until 8 weeks
-No ABD with ER of GH
Wrist Flexor Tendon Repair ROM restrictions
Phase 1
-Immobilize in 10-45 deg wrist flexion and 40-70 deg MCP flexion with IP joints in full extension
-DO TENDON gliding to prevent adhesions
Extensor Tendon Repair ROM restrictions
Phase 1
-immobilize in extension
-EARLY controlled active motion is good
ACL Repair ROM restrictions
Phase 1
-NO knee flexion past 60 deg (mini squats) in CKC
-No knees over toes
-No OKC (LAQ or SAQ) with resistance at ankle from 30-45 deg flexion to full extension
Achilles Tendon Repair Restrictions
WB
-Full WB not until weeks 4-6 in CAM boot
-Full WB in normal shoes with heel lift at 6-8 weeks
-Wean heel lift by 10 weeks post-op
ROM
-no DF >10 deg until 8 weeks
-stretch in sitting first on rocker board and progress to BL standing and no UL until 12 weeks
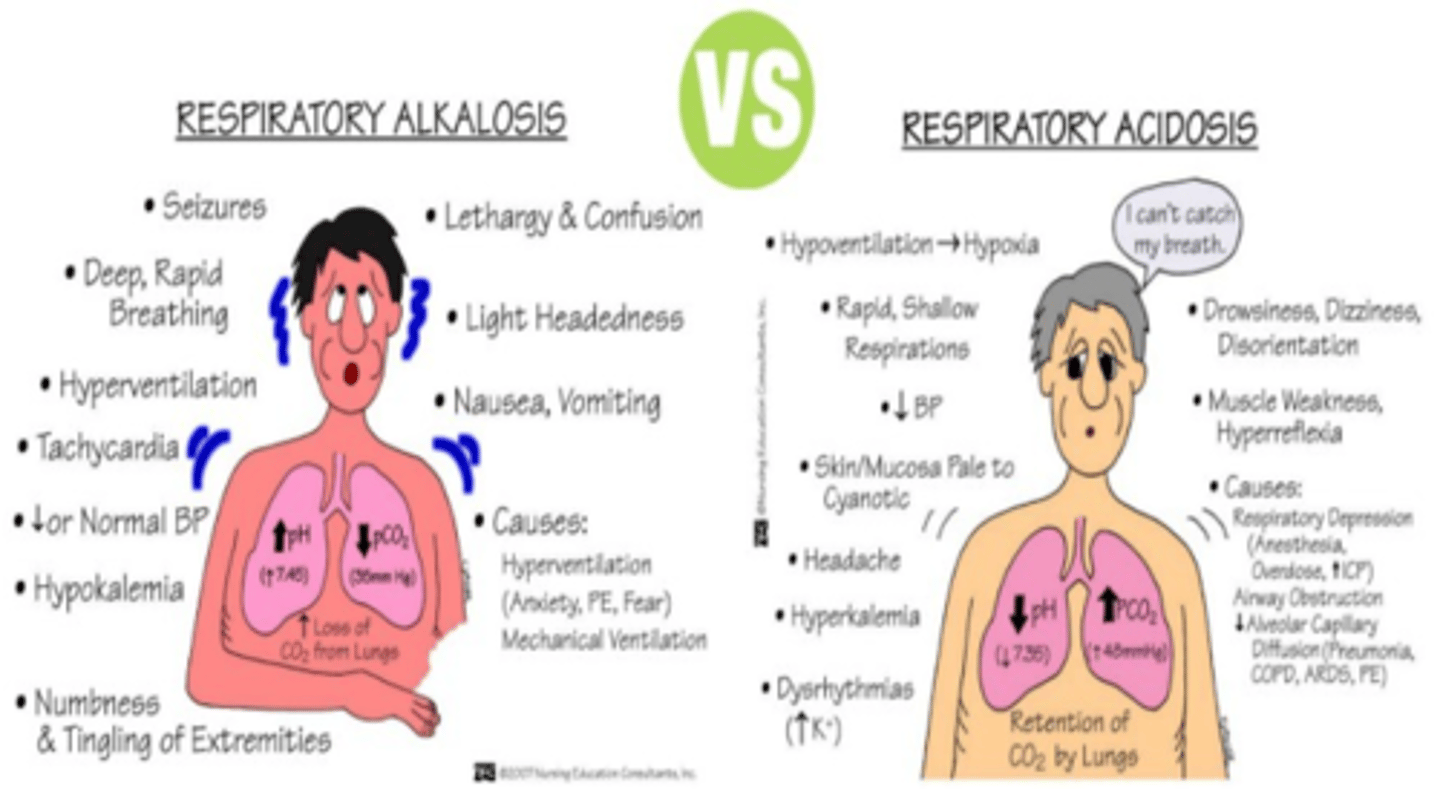
Respiratory Alkalosis vs Acidosis
Acidosis: CARBS
-Confusion
-Agitation
-Restlessness
-Blurred Vision
-Seizures
Seen in pt with COPD and those that are hypoventilating
Alkalosis: NO CARDS
-Numbness/tingling
-Orthostatic hypotension
-Confusion
-Anxiety
-Rapid Breathing (hyperventilation)
-Dizziness
-Seizures
Seen in pt with CHF or PE, hyperventilating
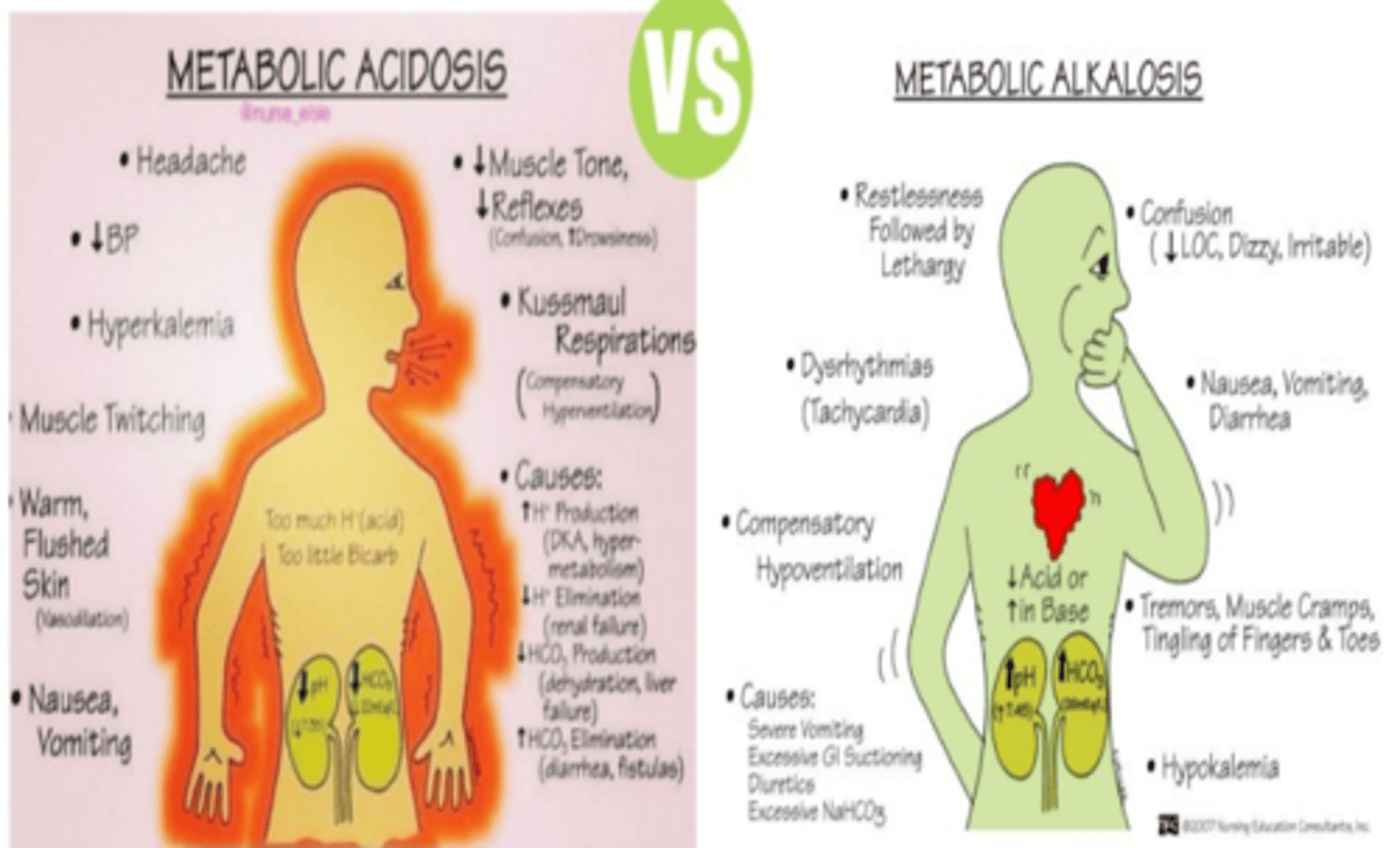
Metabolic Acidosis vs Alkalosis
Acidosis: SHAMED
-Stupor (unconsciousness)
-Hyperkalemia
-Arrthymias
-Muscle twitching
-Emesis
-Decreased CO
Alkalosis: Quad T
-Tetany
-Tachycardia
-Tremors
-Tingling
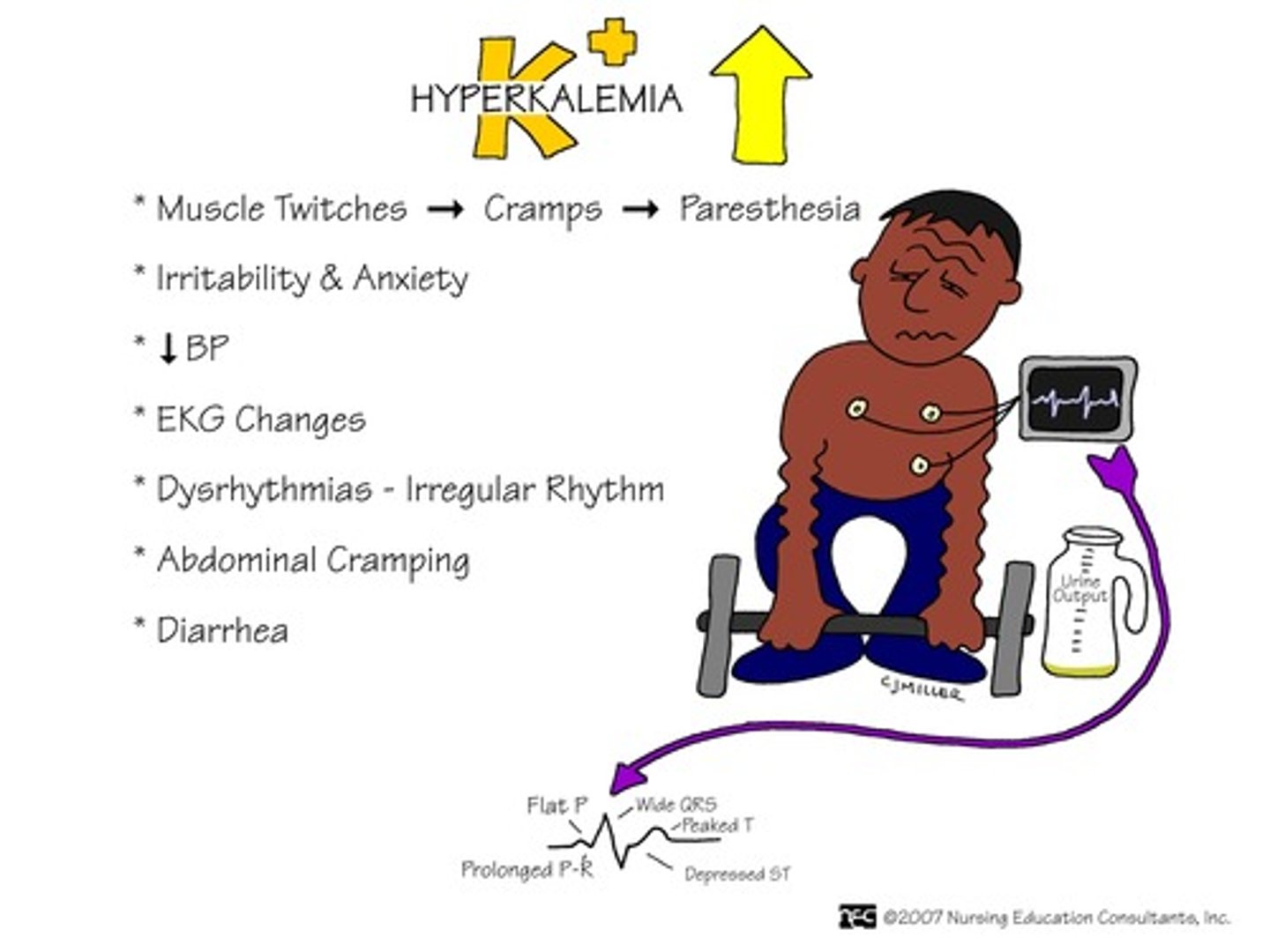
Hyperkalemia
Associated with Diff Dx:
-Addison's Disease
Associated with Medication use:
-Digitalis (Used in pt with CHF)
-Spirnolactone with ACE inhibitors (HTN and CHF)
-Angiotensin II blocker (ARBs) - CHF and HTN
ECG changes:
-Flat P-waves, wide QRS, Peaked T waves bc decrease rate and force of heart contraction
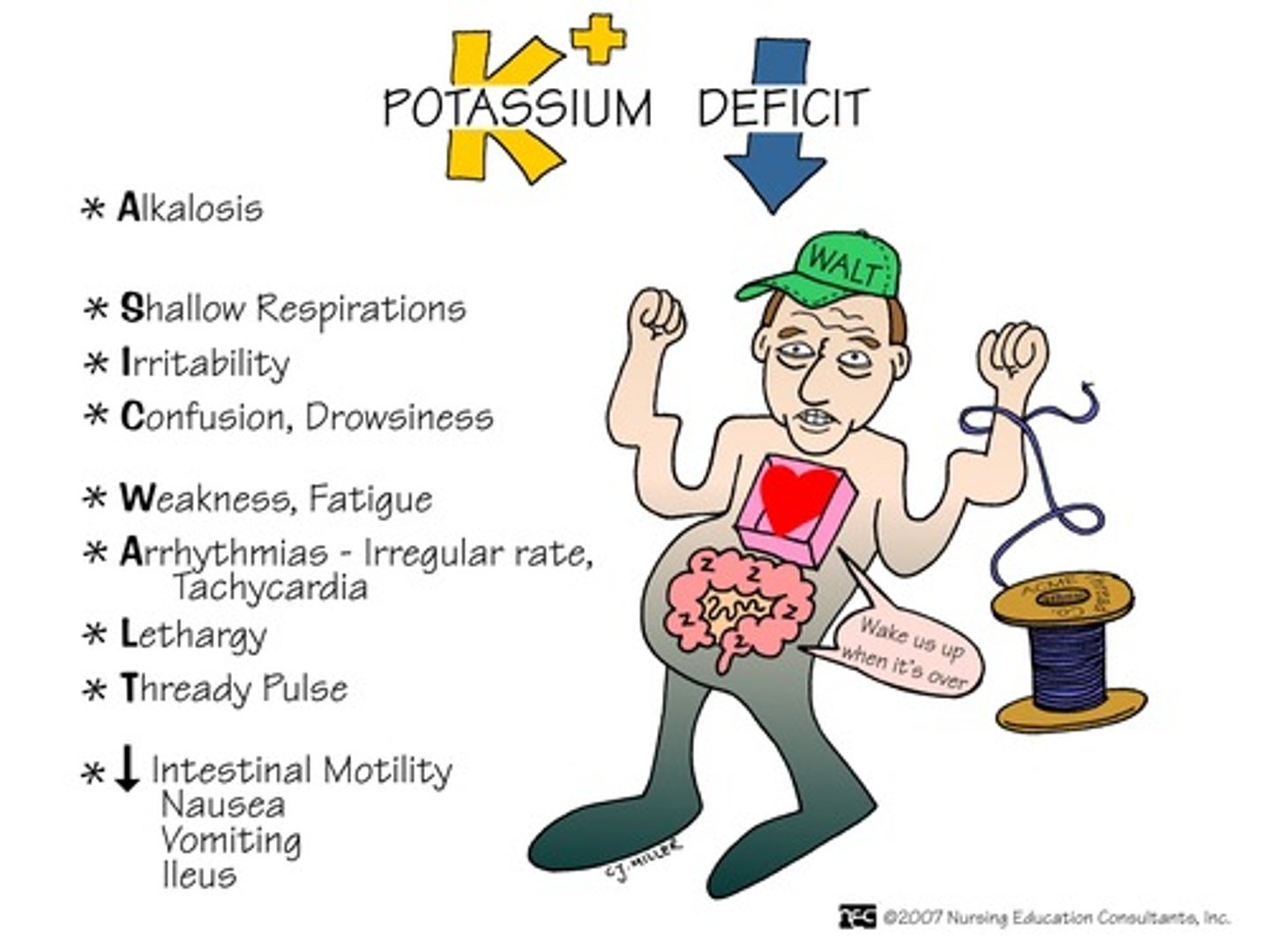
Hypokalemia
Associated with Diff Dx:
-Cushing's
Associated with Medication use:
-Lasix, Thiazides, Digitalis - CHF, HTN,
ECG changes:
-Flat or inverted T waves
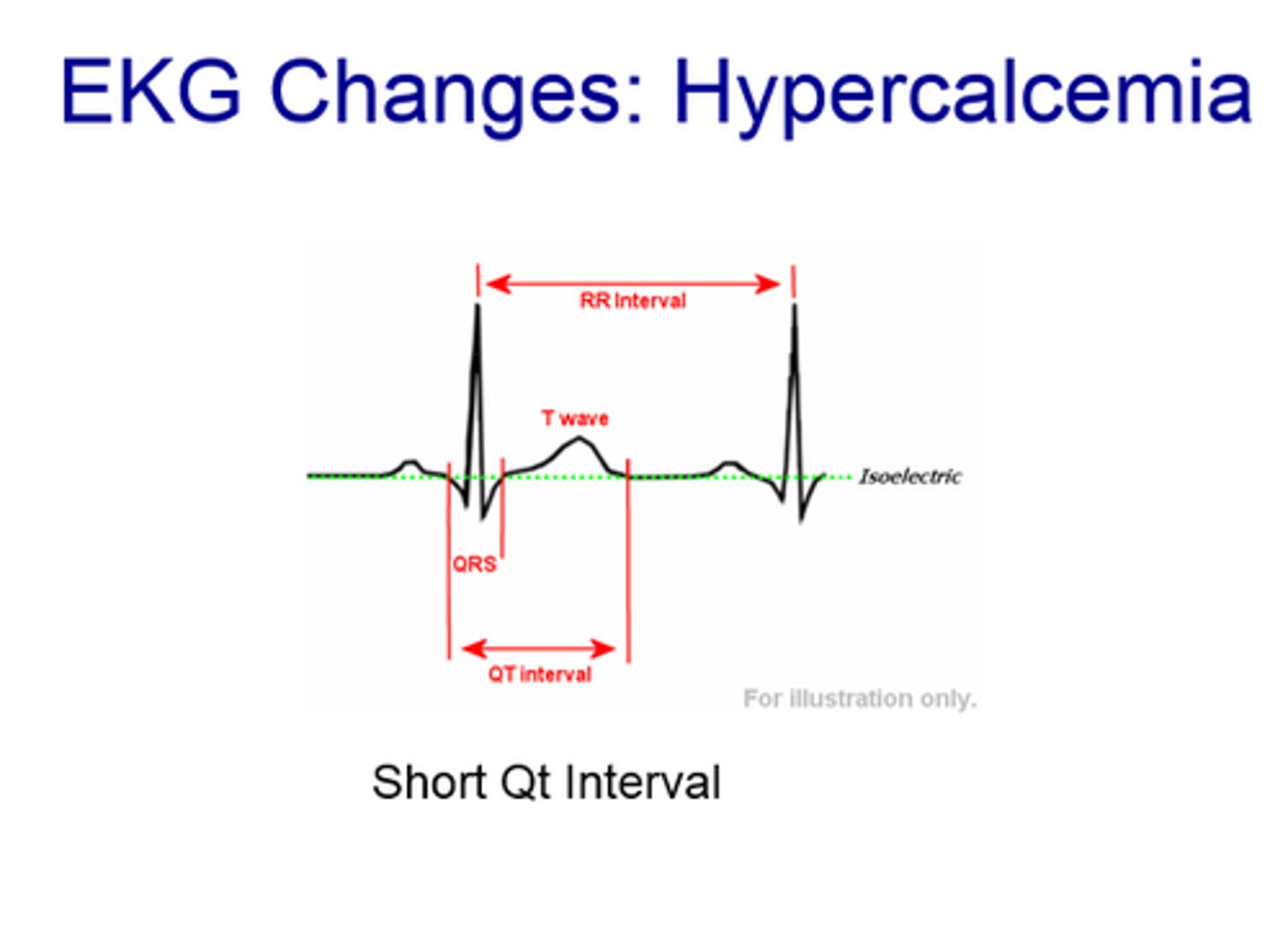
Hypercalemia
ECG Changes
-wide QRS and short QT
-increased heart actions
Hypocalemia
ECG Changes
-prolonged QTR